Dane punktów klastrowania w zestawie Sdk systemu Android
Podczas wizualizacji wielu punktów danych na mapie punkty danych mogą się nakładać na siebie. Nakładanie się może spowodować, że mapa może stać się nieczytelna i trudna do użycia. Dane punktu klastrowania to proces łączenia danych punktów, które znajdują się blisko siebie i przedstawiania ich na mapie jako pojedynczego klastrowanego punktu danych. Gdy użytkownik powiększa mapę, klastry dzielą się na poszczególne punkty danych. Podczas pracy z dużą liczbą punktów danych użyj procesów klastrowania, aby poprawić środowisko użytkownika.
Uwaga
Wycofanie zestawu SDK systemu Android w usłudze Azure Maps
Zestaw SDK natywny usługi Azure Maps dla systemu Android jest teraz przestarzały i zostanie wycofany w dniu 3/31/25. Aby uniknąć przerw w działaniu usługi, przeprowadź migrację do zestawu Web SDK usługi Azure Maps przez 3/31/25. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Przewodnik migracji zestawu SDK systemu Android usługi Azure Maps.
Wymagania wstępne
Pamiętaj, aby wykonać kroki opisane w przewodniku Szybki start: tworzenie dokumentu aplikacji dla systemu Android. Bloki kodu w tym artykule można wstawić do programu obsługi zdarzeń map onReady .
Włączanie klastrowania w źródle danych
Włącz klastrowanie w DataSource klasie, ustawiając cluster opcję na true. Ustaw clusterRadius pozycję , aby wybrać punkty w pobliżu i połączyć je w klaster. Wartość jest wyrażona clusterRadius w pikselach. Użyj clusterMaxZoom polecenia , aby określić poziom powiększenia, na którym ma być wyłączona logika klastrowania. Oto przykład włączania klastrowania w źródle danych.
//Create a data source and enable clustering.
DataSource source = new DataSource(
//Tell the data source to cluster point data.
cluster(true),
//The radius in pixels to cluster points together.
clusterRadius(45),
//The maximum zoom level in which clustering occurs.
//If you zoom in more than this, all points are rendered as symbols.
clusterMaxZoom(15)
);
//Create a data source and enable clustering.
val source = DataSource(
//Tell the data source to cluster point data.
cluster(true),
//The radius in pixels to cluster points together.
clusterRadius(45),
//The maximum zoom level in which clustering occurs.
//If you zoom in more than this, all points are rendered as symbols.
clusterMaxZoom(15)
)
Uwaga
Klastrowanie działa tylko z funkcjami Point . Jeśli źródło danych zawiera funkcje innych typów geometrii, takich jak LineString lub Polygon, wystąpi błąd.
Napiwek
Jeśli dwa punkty danych są blisko siebie na ziemi, możliwe, że klaster nigdy się nie rozbije, niezależnie od tego, jak blisko użytkownika powiększa się. Aby rozwiązać ten problem, możesz ustawić clusterMaxZoom opcję wyłączenia logiki klastrowania i po prostu wyświetlić wszystko.
Klasa DataSource udostępnia również następujące metody związane z klastrowaniem.
| Metoda | Typ zwracany | opis |
|---|---|---|
getClusterChildren(Feature clusterFeature) |
FeatureCollection |
Pobiera elementy podrzędne danego klastra na następnym poziomie powiększenia. Te elementy podrzędne mogą być kombinacją kształtów i podciągów. Subclusters stają się funkcjami z właściwościami zgodnymi z właściwościami ClusteredProperties. |
getClusterExpansionZoom(Feature clusterFeature) |
int |
Oblicza poziom powiększenia, na którym klaster zaczyna się rozszerzać lub rozbijać. |
getClusterLeaves(Feature clusterFeature, long limit, long offset) |
FeatureCollection |
Pobiera wszystkie punkty w klastrze. Ustaw wartość , limit aby zwrócić podzbiór punktów, i użyj elementu offset , aby przestronicować punkty. |
Wyświetlanie klastrów przy użyciu warstwy bąbelkowej
Warstwa bąbelkowa to doskonały sposób renderowania punktów klastrowanych. Użyj wyrażeń, aby skalować promień i zmieniać kolor na podstawie liczby punktów w klastrze. Jeśli klastry są wyświetlane przy użyciu warstwy bąbelkowej, należy użyć oddzielnej warstwy do renderowania nieklastrowanych punktów danych.
Aby wyświetlić rozmiar klastra w górnej części bąbelka, użyj warstwy symboli z tekstem i nie używaj ikony.
Poniższy kod wyświetla punkty klastrowane przy użyciu warstwy bąbelkowej i liczbę punktów w każdym klastrze przy użyciu warstwy symboli. Druga warstwa symboli służy do wyświetlania poszczególnych punktów, które nie należą do klastra.
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
DataSource source = new DataSource(
//Tell the data source to cluster point data.
cluster(true),
//The radius in pixels to cluster points together.
clusterRadius(45),
//The maximum zoom level in which clustering occurs.
//If you zoom in more than this, all points are rendered as symbols.
clusterMaxZoom(15)
);
//Import the geojson data and add it to the data source.
map.importDataFromUrl("https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/feed/v1.0/summary/all_week.geojson");
//Add data source to the map.
map.sources.add(source);
//Create a bubble layer for rendering clustered data points.
map.layers.add(new BubbleLayer(source,
//Scale the size of the clustered bubble based on the number of points in the cluster.
bubbleRadius(
step(
get("point_count"),
20, //Default of 20 pixel radius.
stop(100, 30), //If point_count >= 100, radius is 30 pixels.
stop(750, 40) //If point_count >= 750, radius is 40 pixels.
)
),
//Change the color of the cluster based on the value on the point_cluster property of the cluster.
bubbleColor(
step(
toNumber(get("point_count")),
color(Color.GREEN), //Default to lime green.
stop(100, color(Color.YELLOW)), //If the point_count >= 100, color is yellow.
stop(750, color(Color.RED)) //If the point_count >= 100, color is red.
)
),
bubbleStrokeWidth(0f),
//Only rendered data points which have a point_count property, which clusters do.
BubbleLayerOptions.filter(has("point_count"))
));
//Create a symbol layer to render the count of locations in a cluster.
map.layers.add(new SymbolLayer(source,
iconImage("none"), //Hide the icon image.
textField(get("point_count")), //Display the point count as text.
textOffset(new Float[]{ 0f, 0.4f }),
//Allow clustered points in this layer.
SymbolLayerOptions.filter(has("point_count"))
));
//Create a layer to render the individual locations.
map.layers.add(new SymbolLayer(source,
//Filter out clustered points from this layer.
SymbolLayerOptions.filter(not(has("point_count")))
));
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
val source = DataSource(
//Tell the data source to cluster point data.
cluster(true),
//The radius in pixels to cluster points together.
clusterRadius(45),
//The maximum zoom level in which clustering occurs.
//If you zoom in more than this, all points are rendered as symbols.
clusterMaxZoom(15)
)
//Import the geojson data and add it to the data source.
map.importDataFromUrl("https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/feed/v1.0/summary/all_week.geojson")
//Add data source to the map.
map.sources.add(source)
//Create a bubble layer for rendering clustered data points.
map.layers.add(
BubbleLayer(
source,
//Scale the size of the clustered bubble based on the number of points in the cluster.
bubbleRadius(
step(
get("point_count"),
20, //Default of 20 pixel radius.
stop(100, 30), //If point_count >= 100, radius is 30 pixels.
stop(750, 40) //If point_count >= 750, radius is 40 pixels.
)
),
//Change the color of the cluster based on the value on the point_cluster property of the cluster.
bubbleColor(
step(
toNumber(get("point_count")),
color(Color.GREEN), //Default to lime green.
stop(100, color(Color.YELLOW)), //If the point_count >= 100, color is yellow.
stop(750, color(Color.RED)) //If the point_count >= 100, color is red.
)
),
bubbleStrokeWidth(0f),
//Only rendered data points which have a point_count property, which clusters do.
BubbleLayerOptions.filter(has("point_count"))
)
)
//Create a symbol layer to render the count of locations in a cluster.
map.layers.add(
SymbolLayer(
source,
iconImage("none"), //Hide the icon image.
textField(get("point_count")), //Display the point count as text.
textOffset(arrayOf(0f, 0.4f)),
//Allow clustered points in this layer.
SymbolLayerOptions.filter(has("point_count"))
)
)
//Create a layer to render the individual locations.
map.layers.add(
SymbolLayer(
source,
//Filter out clustered points from this layer.
SymbolLayerOptions.filter(not(has("point_count")))
)
)
Na poniższej ilustracji przedstawiono powyższe funkcje punktów klastrowanych w warstwie bąbelkowej, skalowane i kolorowe na podstawie liczby punktów w klastrze. Punkty nieklastrowane są renderowane przy użyciu warstwy symboli.
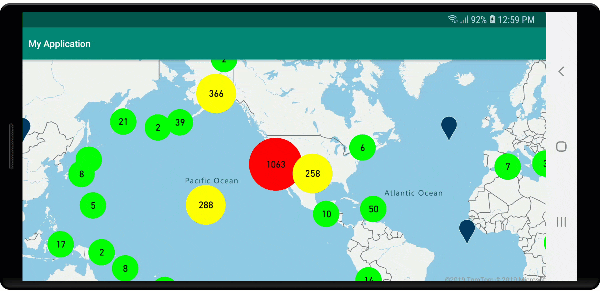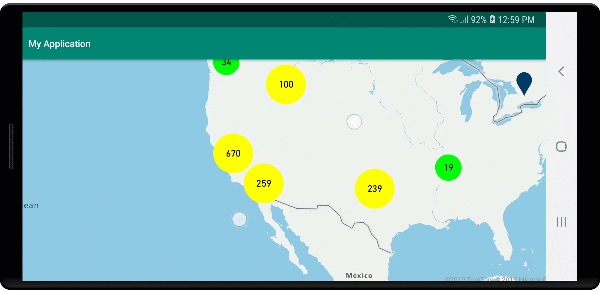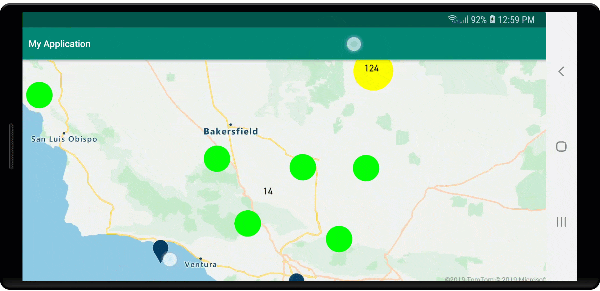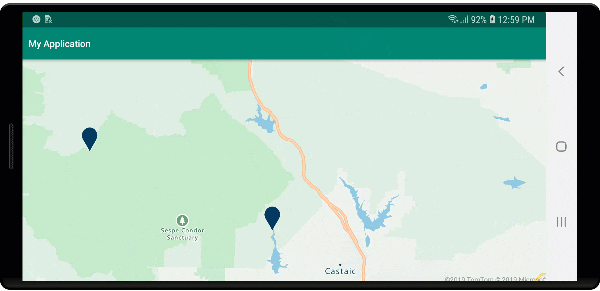
Wyświetlanie klastrów przy użyciu warstwy symboli
Podczas wizualizacji punktów danych warstwa symboli automatycznie ukrywa symbole nakładające się na siebie w celu zapewnienia czytelnego interfejsu użytkownika. To domyślne zachowanie może być niepożądane, jeśli chcesz pokazać gęstość punktów danych na mapie. Można jednak zmienić te ustawienia. Aby wyświetlić wszystkie symbole, ustaw iconAllowOverlap opcję warstwy symboli na true.
Użyj klastrowania, aby pokazać gęstość punktów danych przy zachowaniu czystego interfejsu użytkownika. W poniższym przykładzie pokazano, jak dodać niestandardowe symbole i reprezentować klastry i poszczególne punkty danych przy użyciu warstwy symboli.
//Load all the custom image icons into the map resources.
map.images.add("earthquake_icon", R.drawable.earthquake_icon);
map.images.add("warning_triangle_icon", R.drawable.warning_triangle_icon);
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
DataSource source = new DataSource(
//Tell the data source to cluster point data.
cluster(true)
);
//Import the geojson data and add it to the data source.
map.importDataFromUrl("https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/feed/v1.0/summary/all_week.geojson");
//Add data source to the map.
map.sources.add(source);
//Create a symbol layer to render the clusters.
map.layers.add(new SymbolLayer(source,
iconImage("warning_triangle_icon"),
textField(get("point_count")),
textOffset(new Float[]{ 0f, -0.4f }),
//Allow clustered points in this layer.
filter(has("point_count"))
));
//Create a layer to render the individual locations.
map.layers.add(new SymbolLayer(source,
iconImage("earthquake_icon"),
//Filter out clustered points from this layer.
filter(not(has("point_count")))
));
//Load all the custom image icons into the map resources.
map.images.add("earthquake_icon", R.drawable.earthquake_icon)
map.images.add("warning_triangle_icon", R.drawable.warning_triangle_icon)
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
val source = DataSource(
//Tell the data source to cluster point data.
cluster(true)
)
//Import the geojson data and add it to the data source.
map.importDataFromUrl("https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/feed/v1.0/summary/all_week.geojson")
//Add data source to the map.
map.sources.add(source)
//Create a symbol layer to render the clusters.
map.layers.add(
SymbolLayer(
source,
iconImage("warning_triangle_icon"),
textField(get("point_count")),
textOffset(arrayOf(0f, -0.4f)),
//Allow clustered points in this layer.
filter(has("point_count"))
)
)
//Create a layer to render the individual locations.
map.layers.add(
SymbolLayer(
source,
iconImage("earthquake_icon"),
//Filter out clustered points from this layer.
filter(not(has("point_count")))
)
)
W tym przykładzie poniższy obraz jest ładowany do folderu drawable aplikacji.
| earthquake_icon.png | warning_triangle_icon.png |
Na poniższej ilustracji przedstawiono powyższe funkcje klastrowanych i nieklastrowanych punktów renderowania kodu przy użyciu ikon niestandardowych.
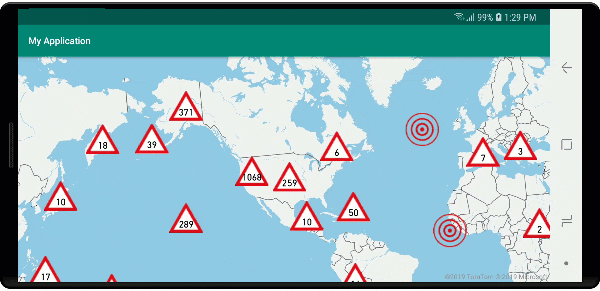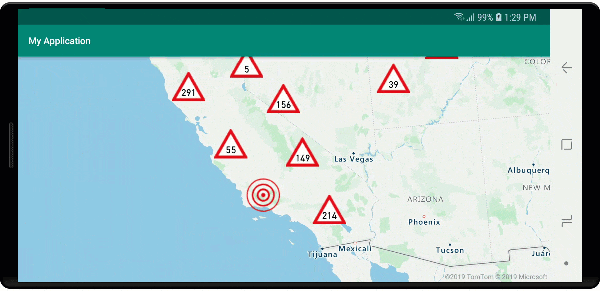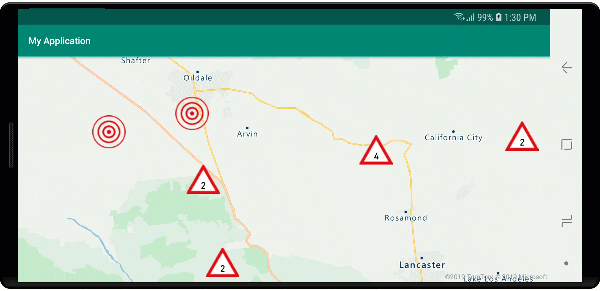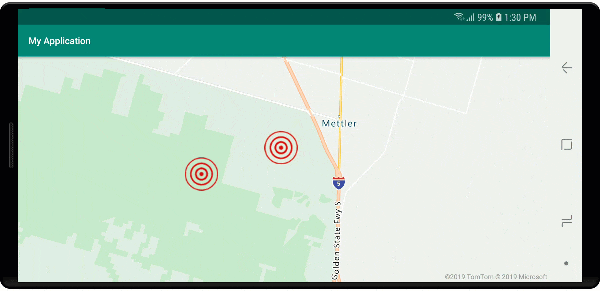
Klastrowanie i warstwa map cieplnych
Mapy cieplne to doskonały sposób wyświetlania gęstości danych na mapie. Ta metoda wizualizacji może obsługiwać dużą liczbę punktów danych samodzielnie. Jeśli punkty danych są klastrowane, a rozmiar klastra jest używany jako waga mapy cieplnej, mapa cieplna może obsłużyć jeszcze więcej danych. Aby osiągnąć tę opcję, ustaw heatmapWeight opcję warstwy mapy cieplnej na get("point_count")wartość . Gdy promień klastra jest mały, mapa cieplna wygląda niemal identycznie z mapą cieplną przy użyciu nieklastrowanych punktów danych, ale działa lepiej. Jednak mniejszy promień klastra daje dokładniejszą mapę cieplną, ale z mniejszą wydajnością.
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
DataSource source = new DataSource(
//Tell the data source to cluster point data.
cluster(true),
//The radius in pixels to cluster points together.
clusterRadius(10)
);
//Import the geojson data and add it to the data source.
map.importDataFromUrl("https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/feed/v1.0/summary/all_week.geojson");
//Add data source to the map.
map.sources.add(source);
//Create a heat map and add it to the map.
map.layers.add(new HeatMapLayer(source,
//Set the weight to the point_count property of the data points.
heatmapWeight(get("point_count")),
//Optionally adjust the radius of each heat point.
heatmapRadius(20f)
), "labels");
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
val source = DataSource(
//Tell the data source to cluster point data.
cluster(true),
//The radius in pixels to cluster points together.
clusterRadius(10)
)
//Import the geojson data and add it to the data source.
map.importDataFromUrl("https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/feed/v1.0/summary/all_week.geojson")
//Add data source to the map.
map.sources.add(source)
//Create a heat map and add it to the map.
map.layers.add(
HeatMapLayer(
source,
//Set the weight to the point_count property of the data points.
heatmapWeight(get("point_count")),
//Optionally adjust the radius of each heat point.
heatmapRadius(20f)
), "labels"
)
Na poniższej ilustracji przedstawiono powyższy kod przedstawiający mapę cieplną zoptymalizowaną przy użyciu funkcji punktów klastrowanych oraz liczbę klastrów jako wagę na mapie cieplnej.
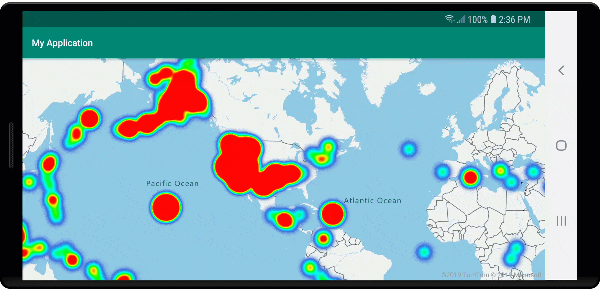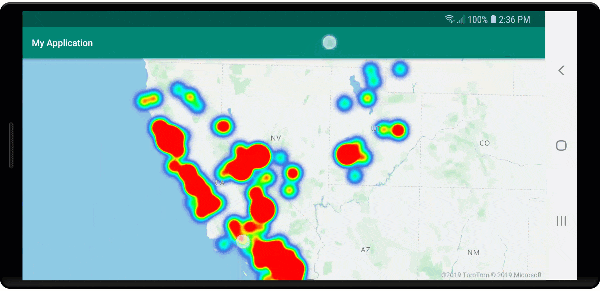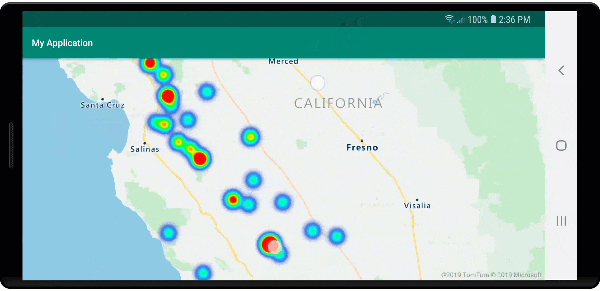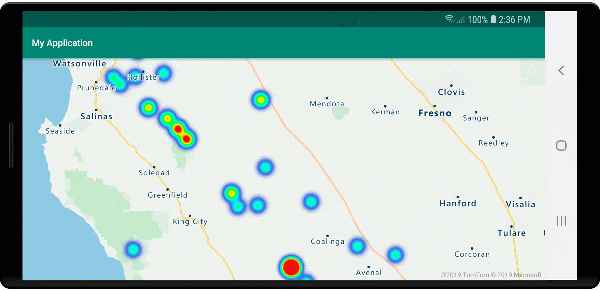
Zdarzenia myszy w punktach danych klastrowanych
Gdy zdarzenia myszy występują w warstwie zawierającej klastrowane punkty danych, punkt danych klastrowanych powróci do zdarzenia jako obiekt funkcji punktu GeoJSON. Ta funkcja punktu ma następujące właściwości:
| Nazwa właściwości | Typ | Opis |
|---|---|---|
cluster |
boolean | Wskazuje, czy funkcja reprezentuje klaster. |
point_count |
Liczba | Liczba punktów, które zawiera klaster. |
point_count |
Liczba | Liczba punktów, które zawiera klaster. |
point_count_abbreviated |
string | Ciąg, który skraca wartość, point_count jeśli jest długa. (na przykład 4000 staje się 4K) |
W tym przykładzie jest pobierana warstwa bąbelkowa, która renderuje punkty klastra i dodaje zdarzenie kliknięcia. Po wyzwoleniu zdarzenia kliknięcia kod oblicza i powiększa mapę do następnego poziomu powiększenia, na którym klaster się rozpada. Ta funkcja jest implementowana przy użyciu getClusterExpansionZoom metody DataSource klasy i cluster_id właściwości klikniętego punktu danych klastrowanego.
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
DataSource source = new DataSource(
//Tell the data source to cluster point data.
cluster(true),
//The radius in pixels to cluster points together.
clusterRadius(45),
//The maximum zoom level in which clustering occurs.
//If you zoom in more than this, all points are rendered as symbols.
clusterMaxZoom(15)
);
//Import the geojson data and add it to the data source.
source.importDataFromUrl("https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/feed/v1.0/summary/all_week.geojson");
//Add data source to the map.
map.sources.add(source);
//Create a bubble layer for rendering clustered data points.
BubbleLayer clusterBubbleLayer = new BubbleLayer(source,
//Scale the size of the clustered bubble based on the number of points in the cluster.
bubbleRadius(
step(
get("point_count"),
20f, //Default of 20 pixel radius.
stop(100, 30), //If point_count >= 100, radius is 30 pixels.
stop(750, 40) //If point_count >= 750, radius is 40 pixels.
)
),
//Change the color of the cluster based on the value on the point_cluster property of the cluster.
bubbleColor(
step(
get("point_count"),
color(Color.GREEN), //Default to green.
stop(100, color(Color.YELLOW)), //If the point_count >= 100, color is yellow.
stop(750, color(Color.RED)) //If the point_count >= 100, color is red.
)
),
bubbleStrokeWidth(0f),
//Only rendered data points which have a point_count property, which clusters do.
BubbleLayerOptions.filter(has("point_count"))
);
//Add the clusterBubbleLayer and two additional layers to the map.
map.layers.add(clusterBubbleLayer);
//Create a symbol layer to render the count of locations in a cluster.
map.layers.add(new SymbolLayer(source,
//Hide the icon image.
iconImage("none"),
//Display the 'point_count_abbreviated' property value.
textField(get("point_count_abbreviated")),
//Offset the text position so that it's centered nicely.
textOffset(new Float[] { 0f, 0.4f }),
//Only rendered data points which have a point_count property, which clusters do.
SymbolLayerOptions.filter(has("point_count"))
));
//Create a layer to render the individual locations.
map.layers.add(new SymbolLayer(source,
//Filter out clustered points from this layer.
SymbolLayerOptions.filter(not(has("point_count")))
));
//Add a click event to the cluster layer so we can zoom in when a user clicks a cluster.
map.events.add((OnFeatureClick) (features) -> {
if(features.size() > 0) {
//Get the clustered point from the event.
Feature cluster = features.get(0);
//Get the cluster expansion zoom level. This is the zoom level at which the cluster starts to break apart.
int expansionZoom = source.getClusterExpansionZoom(cluster);
//Update the map camera to be centered over the cluster.
map.setCamera(
//Center the map over the cluster points location.
center((Point)cluster.geometry()),
//Zoom to the clusters expansion zoom level.
zoom(expansionZoom),
//Animate the movement of the camera to the new position.
animationType(AnimationType.EASE),
animationDuration(200)
);
}
//Return true indicating if event should be consumed and not passed further to other listeners registered afterwards, false otherwise.
return true;
}, clusterBubbleLayer);
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
val source = DataSource( //Tell the data source to cluster point data.
//The radius in pixels to cluster points together.
cluster(true),
//The maximum zoom level in which clustering occurs.
clusterRadius(45),
//If you zoom in more than this, all points are rendered as symbols.
clusterMaxZoom(15)
)
//Import the geojson data and add it to the data source.
source.importDataFromUrl("https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/feed/v1.0/summary/all_week.geojson")
//Add data source to the map.
map.sources.add(source)
//Create a bubble layer for rendering clustered data points.
val clusterBubbleLayer = BubbleLayer(
source,
//Scale the size of the clustered bubble based on the number of points in the cluster.
bubbleRadius(
step(
get("point_count"),
20f, //Default of 20 pixel radius.
stop(100, 30), //If point_count >= 100, radius is 30 pixels.
stop(750, 40) //If point_count >= 750, radius is 40 pixels.
)
),
//Change the color of the cluster based on the value on the point_cluster property of the cluster.
bubbleColor(
step(
get("point_count"),
color(Color.GREEN), //Default to green.
stop(
100,
color(Color.YELLOW)
), //If the point_count >= 100, color is yellow.
stop(750, color(Color.RED)) //If the point_count >= 100, color is red.
)
),
bubbleStrokeWidth(0f),
//Only rendered data points which have a point_count property, which clusters do.
BubbleLayerOptions.filter(has("point_count"))
)
//Add the clusterBubbleLayer and two additional layers to the map.
map.layers.add(clusterBubbleLayer)
//Create a symbol layer to render the count of locations in a cluster.
map.layers.add(
SymbolLayer(
source,
//Hide the icon image.
iconImage("none"),
//Display the 'point_count_abbreviated' property value.
textField(get("point_count_abbreviated")),
//Offset the text position so that it's centered nicely.
textOffset(
arrayOf(
0f,
0.4f
)
),
//Only rendered data points which have a point_count property, which clusters do.
SymbolLayerOptions.filter(has("point_count"))
)
)
//Create a layer to render the individual locations.
map.layers.add(
SymbolLayer(
source,
//Filter out clustered points from this layer.
SymbolLayerOptions.filter(not(has("point_count")))
)
)
//Add a click event to the cluster layer so we can zoom in when a user clicks a cluster.
map.events.add(OnFeatureClick { features: List<Feature?>? ->
if (features.size() > 0) {
//Get the clustered point from the event.
val cluster: Feature = features.get(0)
//Get the cluster expansion zoom level. This is the zoom level at which the cluster starts to break apart.
val expansionZoom: Int = source.getClusterExpansionZoom(cluster)
//Update the map camera to be centered over the cluster.
map.setCamera(
//Center the map over the cluster points location.
center(cluster.geometry() as Point?),
//Zoom to the clusters expansion zoom level.
zoom(expansionZoom),
//Animate the movement of the camera to the new position.
animationType(AnimationType.EASE),
animationDuration(200)
)
}
true
}, clusterBubbleLayer)
Na poniższej ilustracji przedstawiono powyższy kod wyświetlający punkty klastrowane na mapie, które po wybraniu powiększają następny poziom powiększenia, który klaster zaczyna się rozpadać i rozwijać.
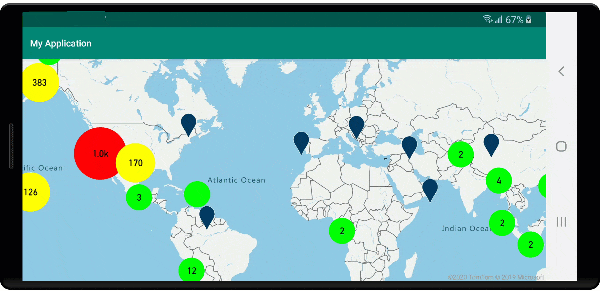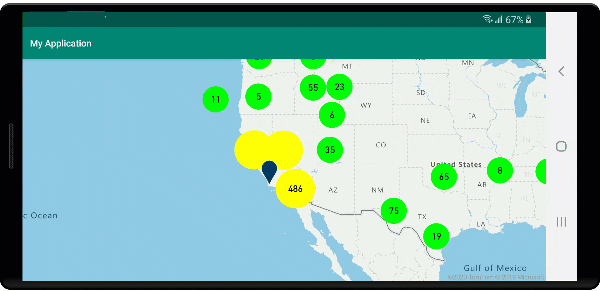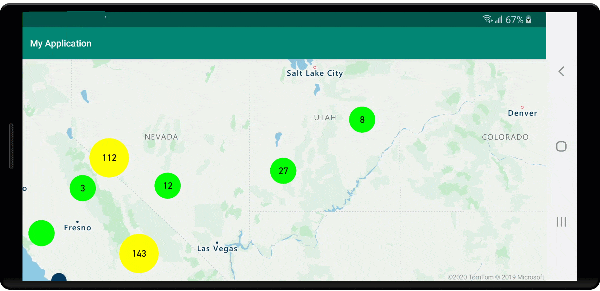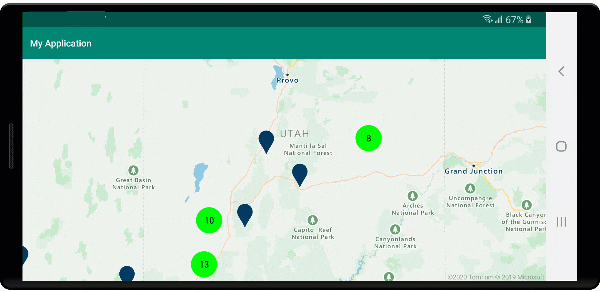
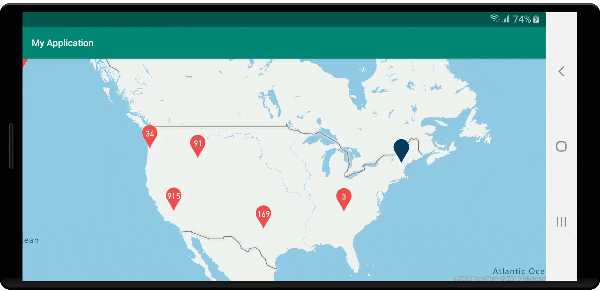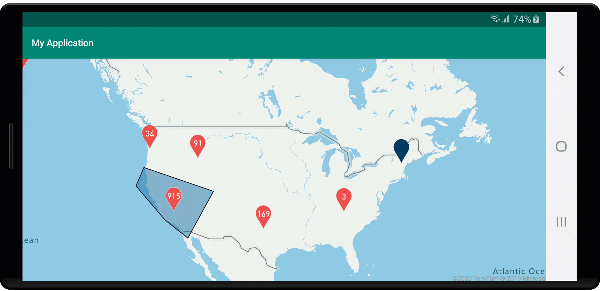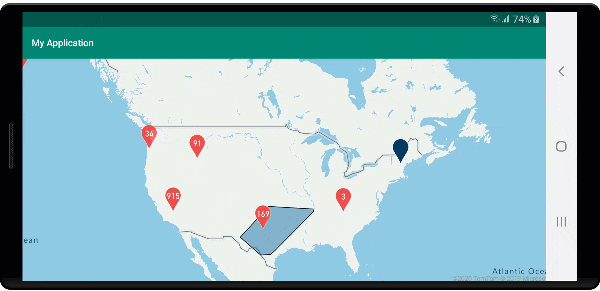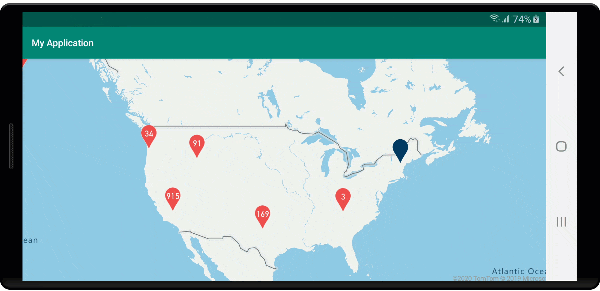
Wyświetlanie obszaru klastra
Dane punktów reprezentowane przez klaster są rozłożone na obszar. W tym przykładzie po umieszczeniu wskaźnika myszy nad klastrem występują dwa główne zachowania. Najpierw poszczególne punkty danych zawarte w klastrze będą używane do obliczania wypukłego kadłuba. Następnie kadłub wypukły jest wyświetlany na mapie, aby wyświetlić obszar. Kadłub wypukły jest wielokątem, który owija zestaw punktów, takich jak elastyczne pasmo, i można go obliczyć przy użyciu atlas.math.getConvexHull metody . Wszystkie punkty zawarte w klastrze można pobrać ze źródła danych przy użyciu getClusterLeaves metody .
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
DataSource source = new DataSource(
//Tell the data source to cluster point data.
cluster(true)
);
//Import the geojson data and add it to the data source.
source.importDataFromUrl("https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/feed/v1.0/summary/all_week.geojson");
//Add data source to the map.
map.sources.add(source);
//Create a data source for the convex hull polygon. Since this will be updated frequently it is more efficient to separate this into its own data source.
DataSource polygonDataSource = new DataSource();
//Add data source to the map.
map.sources.add(polygonDataSource);
//Add a polygon layer and a line layer to display the convex hull.
map.layers.add(new PolygonLayer(polygonDataSource));
map.layers.add(new LineLayer(polygonDataSource));
//Create a symbol layer to render the clusters.
SymbolLayer clusterLayer = new SymbolLayer(source,
iconImage("marker-red"),
textField(get("point_count_abbreviated")),
textOffset(new Float[] { 0f, -1.2f }),
textColor(Color.WHITE),
textSize(14f),
//Only rendered data points which have a point_count property, which clusters do.
SymbolLayerOptions.filter(has("point_count"))
);
map.layers.add(clusterLayer);
//Create a layer to render the individual locations.
map.layers.add(new SymbolLayer(source,
//Filter out clustered points from this layer.
SymbolLayerOptions.filter(not(has("point_count")))
));
//Add a click event to the layer so we can calculate the convex hull of all the points within a cluster.
map.events.add((OnFeatureClick) (features) -> {
if(features.size() > 0) {
//Get the clustered point from the event.
Feature cluster = features.get(0);
//Get all points in the cluster. Set the offset to 0 and the max long value to return all points.
FeatureCollection leaves = source.getClusterLeaves(cluster, Long.MAX_VALUE, 0);
//Get the point features from the feature collection.
List<Feature> childFeatures = leaves.features();
//When only two points in a cluster. Render a line.
if(childFeatures.size() == 2){
//Extract the geometry points from the child features.
List<Point> points = new ArrayList();
childFeatures.forEach(f -> {
points.add((Point)f.geometry());
});
//Create a line from the points.
polygonDataSource.setShapes(LineString.fromLngLats(points));
} else {
Polygon hullPolygon = MapMath.getConvexHull(leaves);
//Overwrite all data in the polygon data source with the newly calculated convex hull polygon.
polygonDataSource.setShapes(hullPolygon);
}
}
//Return true indicating if event should be consumed and not passed further to other listeners registered afterwards, false otherwise.
return true;
}, clusterLayer);
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
val source = DataSource(
//Tell the data source to cluster point data.
cluster(true)
)
//Import the geojson data and add it to the data source.
source.importDataFromUrl("https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/feed/v1.0/summary/all_week.geojson")
//Add data source to the map.
map.sources.add(source)
//Create a data source for the convex hull polygon. Since this will be updated frequently it is more efficient to separate this into its own data source.
val polygonDataSource = DataSource()
//Add data source to the map.
map.sources.add(polygonDataSource)
//Add a polygon layer and a line layer to display the convex hull.
map.layers.add(PolygonLayer(polygonDataSource))
map.layers.add(LineLayer(polygonDataSource))
//Create a symbol layer to render the clusters.
val clusterLayer = SymbolLayer(
source,
iconImage("marker-red"),
textField(get("point_count_abbreviated")),
textOffset(arrayOf(0f, -1.2f)),
textColor(Color.WHITE),
textSize(14f),
//Only rendered data points which have a point_count property, which clusters do.
SymbolLayerOptions.filter(has("point_count"))
)
map.layers.add(clusterLayer)
//Create a layer to render the individual locations.
map.layers.add(
SymbolLayer(
source,
//Filter out clustered points from this layer.
SymbolLayerOptions.filter(not(has("point_count")))
)
)
//Add a click event to the layer so we can calculate the convex hull of all the points within a cluster.
map.events.add(OnFeatureClick { features: List<Feature?>? ->
if (features.size() > 0) {
//Get the clustered point from the event.
val cluster: Feature = features.get(0)
//Get all points in the cluster. Set the offset to 0 and the max long value to return all points.
val leaves: FeatureCollection = source.getClusterLeaves(cluster, Long.MAX_VALUE, 0)
//Get the point features from the feature collection.
val childFeatures = leaves.features()
//When only two points in a cluster. Render a line.
if (childFeatures!!.size == 2) {
//Extract the geometry points from the child features.
val points: MutableList<Point?> = ArrayList()
childFeatures!!.forEach(Consumer { f: Feature ->
points.add(
f.geometry() as Point?
)
})
//Create a line from the points.
polygonDataSource.setShapes(LineString.fromLngLats(points))
} else {
val hullPolygon: Polygon = MapMath.getConvexHull(leaves)
//Overwrite all data in the polygon data source with the newly calculated convex hull polygon.
polygonDataSource.setShapes(hullPolygon)
}
}
true
}, clusterLayer)
Na poniższej ilustracji przedstawiono powyższy kod przedstawiający obszar wszystkich punktów w obrębie klikniętego klastra.
Agregowanie danych w klastrach
Często klastry są reprezentowane przy użyciu symbolu z liczbą punktów znajdujących się w klastrze. Jednak czasami pożądane jest dostosowanie stylu klastrów przy użyciu większej liczby metryk. Za pomocą właściwości klastra można tworzyć właściwości niestandardowe i równe obliczeniu na podstawie właściwości w każdym punkcie z klastrem. Właściwości klastra można zdefiniować w clusterProperties opcji DataSource.
Poniższy kod oblicza liczbę na podstawie właściwości typu jednostki każdego punktu danych w klastrze. Gdy użytkownik wybierze klaster, zostanie wyświetlone okno podręczne z dodatkowymi informacjami o klastrze.
//An array of all entity type property names in features of the data set.
String[] entityTypes = new String[] { "Gas Station", "Grocery Store", "Restaurant", "School" };
//Create a popup and add it to the map.
Popup popup = new Popup();
map.popups.add(popup);
//Close the popup initially.
popup.close();
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
source = new DataSource(
//Tell the data source to cluster point data.
cluster(true),
//The radius in pixels to cluster points together.
clusterRadius(50),
//Calculate counts for each entity type in a cluster as custom aggregate properties.
clusterProperties(new ClusterProperty[]{
new ClusterProperty("Gas Station", sum(accumulated(), get("Gas Station")), switchCase(eq(get("EntityType"), literal("Gas Station")), literal(1), literal(0))),
new ClusterProperty("Grocery Store", sum(accumulated(), get("Grocery Store")), switchCase(eq(get("EntityType"), literal("Grocery Store")), literal(1), literal(0))),
new ClusterProperty("Restaurant", sum(accumulated(), get("Restaurant")), switchCase(eq(get("EntityType"), literal("Restaurant")), literal(1), literal(0))),
new ClusterProperty("School", sum(accumulated(), get("School")), switchCase(eq(get("EntityType"), literal("School")), literal(1), literal(0)))
})
);
//Import the geojson data and add it to the data source.
source.importDataFromUrl("https://samples.azuremaps.com/data/geojson/SamplePoiDataSet.json");
//Add data source to the map.
map.sources.add(source);
//Create a bubble layer for rendering clustered data points.
BubbleLayer clusterBubbleLayer = new BubbleLayer(source,
bubbleRadius(20f),
bubbleColor("purple"),
bubbleStrokeWidth(0f),
//Only rendered data points which have a point_count property, which clusters do.
BubbleLayerOptions.filter(has("point_count"))
);
//Add the clusterBubbleLayer and two additional layers to the map.
map.layers.add(clusterBubbleLayer);
//Create a symbol layer to render the count of locations in a cluster.
map.layers.add(new SymbolLayer(source,
//Hide the icon image.
iconImage("none"),
//Display the 'point_count_abbreviated' property value.
textField(get("point_count_abbreviated")),
textColor(Color.WHITE),
textOffset(new Float[] { 0f, 0.4f }),
//Only rendered data points which have a point_count property, which clusters do.
SymbolLayerOptions.filter(has("point_count"))
));
//Create a layer to render the individual locations.
map.layers.add(new SymbolLayer(source,
//Filter out clustered points from this layer.
SymbolLayerOptions.filter(not(has("point_count")))
));
//Add a click event to the cluster layer and display the aggregate details of the cluster.
map.events.add((OnFeatureClick) (features) -> {
if(features.size() > 0) {
//Get the clustered point from the event.
Feature cluster = features.get(0);
//Create a number formatter that removes decimal places.
NumberFormat nf = DecimalFormat.getInstance();
nf.setMaximumFractionDigits(0);
//Create the popup's content.
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("Cluster size: ");
sb.append(nf.format(cluster.getNumberProperty("point_count")));
sb.append(" entities\n");
for(int i = 0; i < entityTypes.length; i++) {
sb.append("\n");
//Get the entity type name.
sb.append(entityTypes[i]);
sb.append(": ");
//Get the aggregated entity type count from the properties of the cluster by name.
sb.append(nf.format(cluster.getNumberProperty(entityTypes[i])));
}
//Retrieve the custom layout for the popup.
View customView = LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.popup_text, null);
//Access the text view within the custom view and set the text to the title property of the feature.
TextView tv = customView.findViewById(R.id.message);
tv.setText(sb.toString());
//Get the position of the cluster.
Position pos = MapMath.getPosition((Point)cluster.geometry());
//Set the options on the popup.
popup.setOptions(
//Set the popups position.
position(pos),
//Set the anchor point of the popup content.
anchor(AnchorType.BOTTOM),
//Set the content of the popup.
content(customView)
);
//Open the popup.
popup.open();
}
//Return a boolean indicating if event should be consumed or continue bubble up.
return true;
}, clusterBubbleLayer);
//An array of all entity type property names in features of the data set.
val entityTypes = arrayOf("Gas Station", "Grocery Store", "Restaurant", "School")
//Create a popup and add it to the map.
val popup = Popup()
map.popups.add(popup)
//Close the popup initially.
popup.close()
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
val source = DataSource(
//Tell the data source to cluster point data.
cluster(true),
//The radius in pixels to cluster points together.
clusterRadius(50),
//Calculate counts for each entity type in a cluster as custom aggregate properties.
clusterProperties(
arrayOf<ClusterProperty>(
ClusterProperty("Gas Station", sum(accumulated(), get("Gas Station")), switchCase(eq(get("EntityType"), literal("Gas Station")), literal(1), literal(0))),
ClusterProperty("Grocery Store", sum(accumulated(), get("Grocery Store")), switchCase(eq(get("EntityType"), literal("Grocery Store")), literal(1), literal(0))),
ClusterProperty("Restaurant", sum(accumulated(), get("Restaurant")), switchCase(eq(get("EntityType"), literal("Restaurant")), literal(1), literal(0))),
ClusterProperty("School", sum(accumulated(), get("School")), switchCase(eq(get("EntityType"), literal("School")), literal(1), literal(0)))
)
)
)
//Import the geojson data and add it to the data source.
source.importDataFromUrl("https://samples.azuremaps.com/data/geojson/SamplePoiDataSet.json")
//Add data source to the map.
map.sources.add(source)
//Create a bubble layer for rendering clustered data points.
val clusterBubbleLayer = BubbleLayer(
source,
bubbleRadius(20f),
bubbleColor("purple"),
bubbleStrokeWidth(0f),
//Only rendered data points which have a point_count property, which clusters do.
BubbleLayerOptions.filter(has("point_count"))
)
//Add the clusterBubbleLayer and two additional layers to the map.
map.layers.add(clusterBubbleLayer)
//Create a symbol layer to render the count of locations in a cluster.
map.layers.add(
SymbolLayer(
source,
//Hide the icon image.
iconImage("none"),
//Display the 'point_count_abbreviated' property value.
textField(get("point_count_abbreviated")),
textColor(Color.WHITE),
textOffset(arrayOf(0f, 0.4f)),
//Only rendered data points which have a point_count property, which clusters do.
SymbolLayerOptions.filter(has("point_count"))
)
)
//Create a layer to render the individual locations.
map.layers.add(
SymbolLayer(
source,
//Filter out clustered points from this layer.
SymbolLayerOptions.filter(not(has("point_count")))
)
)
//Add a click event to the cluster layer and display the aggregate details of the cluster.
map.events.add(OnFeatureClick { features: List<Feature> ->
if (features.size > 0) {
//Get the clustered point from the event.
val cluster = features[0]
//Create a number formatter that removes decimal places.
val nf: NumberFormat = DecimalFormat.getInstance()
nf.setMaximumFractionDigits(0)
//Create the popup's content.
val sb = StringBuilder()
sb.append("Cluster size: ")
sb.append(nf.format(cluster.getNumberProperty("point_count")))
sb.append(" entities\n")
for (i in entityTypes.indices) {
sb.append("\n")
//Get the entity type name.
sb.append(entityTypes[i])
sb.append(": ")
//Get the aggregated entity type count from the properties of the cluster by name.
sb.append(nf.format(cluster.getNumberProperty(entityTypes[i])))
}
//Retrieve the custom layout for the popup.
val customView: View = LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.popup_text, null)
//Access the text view within the custom view and set the text to the title property of the feature.
val tv: TextView = customView.findViewById(R.id.message)
tv.text = sb.toString()
//Get the position of the cluster.
val pos: Position = MapMath.getPosition(cluster.geometry() as Point?)
//Set the options on the popup.
popup.setOptions(
//Set the popups position.
position(pos),
//Set the anchor point of the popup content.
anchor(AnchorType.BOTTOM),
//Set the content of the popup.
content(customView)
)
//Open the popup.
popup.open()
}
//Return a boolean indicating if event should be consumed or continue bubble up.
true
} as OnFeatureClick, clusterBubbleLayer)
Wyskakujące okienko postępuje zgodnie z instrukcjami opisanymi w wyświetlonym dokumencie podręcznym .
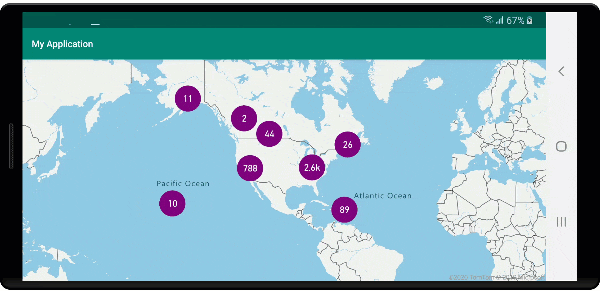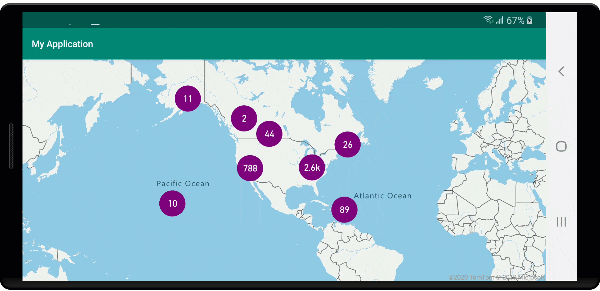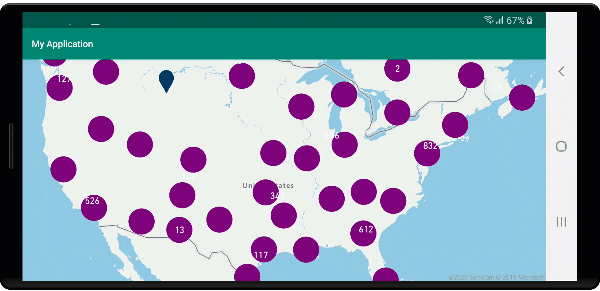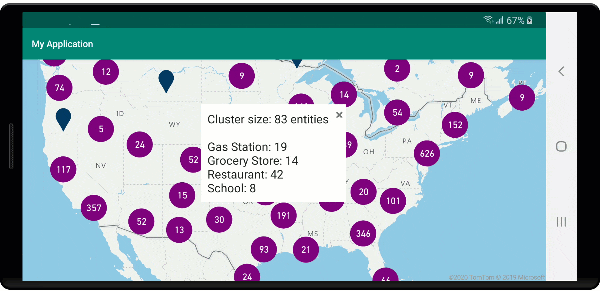
Na poniższej ilustracji przedstawiono powyższy kod przedstawiający wyskakujące okienko z zagregowanymi liczbami każdego typu wartości jednostki dla wszystkich punktów w klikniętym punkcie klastrowanym.
Następne kroki
Aby dodać więcej danych do mapy: