Indicizzazione dinamica con HLSL 5.1
L'esempio D3D12DynamicIndexing illustra alcune delle nuove funzionalità HLSL disponibili in Shader Model 5.1, in particolare l'indicizzazione dinamica e le matrici non associate, per eseguire il rendering della stessa mesh più volte, ogni volta che viene eseguito il rendering con un materiale selezionato in modo dinamico. Con l'indicizzazione dinamica, gli shader possono ora indicizzare in una matrice senza conoscere il valore dell'indice in fase di compilazione. In combinazione con array non limitati, questo aggiunge un altro livello di indirezione e flessibilità per gli autori di shader e le pipeline artistiche.
- Configurare l' pixel shader
- Configurare la firma principale
- Creare le trame
- Caricare i dati della trama
- Caricare la trama diffusa
- Creare un sampler
- modificare dinamicamente l'indice del parametro radice
- Esegui l'esempio
- argomenti correlati
Configurare il pixel shader
Esaminiamo innanzitutto lo shader stesso, che per questo esempio è un pixel shader.
Texture2D g_txDiffuse : register(t0);
Texture2D g_txMats[] : register(t1);
SamplerState g_sampler : register(s0);
struct PSSceneIn
{
float4 pos : SV_Position;
float2 tex : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct MaterialConstants
{
uint matIndex; // Dynamically set index for looking up from g_txMats[].
};
ConstantBuffer<MaterialConstants> materialConstants : register(b0, space0);
float4 PSSceneMain(PSSceneIn input) : SV_Target
{
float3 diffuse = g_txDiffuse.Sample(g_sampler, input.tex).rgb;
float3 mat = g_txMats[materialConstants.matIndex].Sample(g_sampler, input.tex).rgb;
return float4(diffuse * mat, 1.0f);
}
La funzionalità di matrice illimitata è illustrata dalla matrice g_txMats[] dato che non specifica una dimensione della matrice. L'indicizzazione dinamica viene usata per indicizzare g_txMats[] con matIndex, definita come costante di radice. Lo shader non conosce le dimensioni o la matrice o il valore dell'indice in fase di compilazione. Entrambi gli attributi sono definiti nella signature di radice dell'oggetto stato della pipeline utilizzato con lo shader.
Per sfruttare le funzionalità di indicizzazione dinamica in HLSL, è necessario compilare lo shader con SM 5.1. Inoltre, per usare matrici non associate, è necessario usare anche il flag /enable_unbounded_descriptor_tables . Le opzioni della riga di comando seguenti vengono usate per compilare questo shader con lo strumento Effect-Compiler (FXC):
fxc /Zi /E"PSSceneMain" /Od /Fo"dynamic_indexing_pixel.cso" /ps"_5_1" /nologo /enable_unbounded_descriptor_tables
Impostare la firma principale
Ora, esaminiamo la definizione della firma della radice, in particolare come si definisce la dimensione dell'array illimitato e si collega una costante radice a matIndex. Per il pixel shader, definiamo tre elementi: una tabella del descrittore per le unità srv (texture2D), una tabella del descrittore per i campionatori e una singola costante radice. La tabella dei descrittori per gli SRV contiene CityMaterialCount + 1 voci.
CityMaterialCount è una costante che definisce la lunghezza di g_txMats[] e + 1 è per g_txDiffuse. La tabella dei descrittori per i campionatori contiene una sola voce e definiamo solo una costante radice a 32 bit tramite InitAsConstants(...), nel metodo LoadAssets.
// Create the root signature.
{
CD3DX12_DESCRIPTOR_RANGE ranges[3];
ranges[0].Init(D3D12_DESCRIPTOR_RANGE_TYPE_SRV, 1 + CityMaterialCount, 0); // Diffuse texture + array of materials.
ranges[1].Init(D3D12_DESCRIPTOR_RANGE_TYPE_SAMPLER, 1, 0);
ranges[2].Init(D3D12_DESCRIPTOR_RANGE_TYPE_CBV, 1, 0);
CD3DX12_ROOT_PARAMETER rootParameters[4];
rootParameters[0].InitAsDescriptorTable(1, &ranges[0], D3D12_SHADER_VISIBILITY_PIXEL);
rootParameters[1].InitAsDescriptorTable(1, &ranges[1], D3D12_SHADER_VISIBILITY_PIXEL);
rootParameters[2].InitAsDescriptorTable(1, &ranges[2], D3D12_SHADER_VISIBILITY_VERTEX);
rootParameters[3].InitAsConstants(1, 0, 0, D3D12_SHADER_VISIBILITY_PIXEL);
CD3DX12_ROOT_SIGNATURE_DESC rootSignatureDesc;
rootSignatureDesc.Init(_countof(rootParameters), rootParameters, 0, nullptr, D3D12_ROOT_SIGNATURE_FLAG_ALLOW_INPUT_ASSEMBLER_INPUT_LAYOUT);
ComPtr<ID3DBlob> signature;
ComPtr<ID3DBlob> error;
ThrowIfFailed(D3D12SerializeRootSignature(&rootSignatureDesc, D3D_ROOT_SIGNATURE_VERSION_1, &signature, &error));
ThrowIfFailed(m_device->CreateRootSignature(0, signature->GetBufferPointer(), signature->GetBufferSize(), IID_PPV_ARGS(&m_rootSignature)));
}
Creare le trame
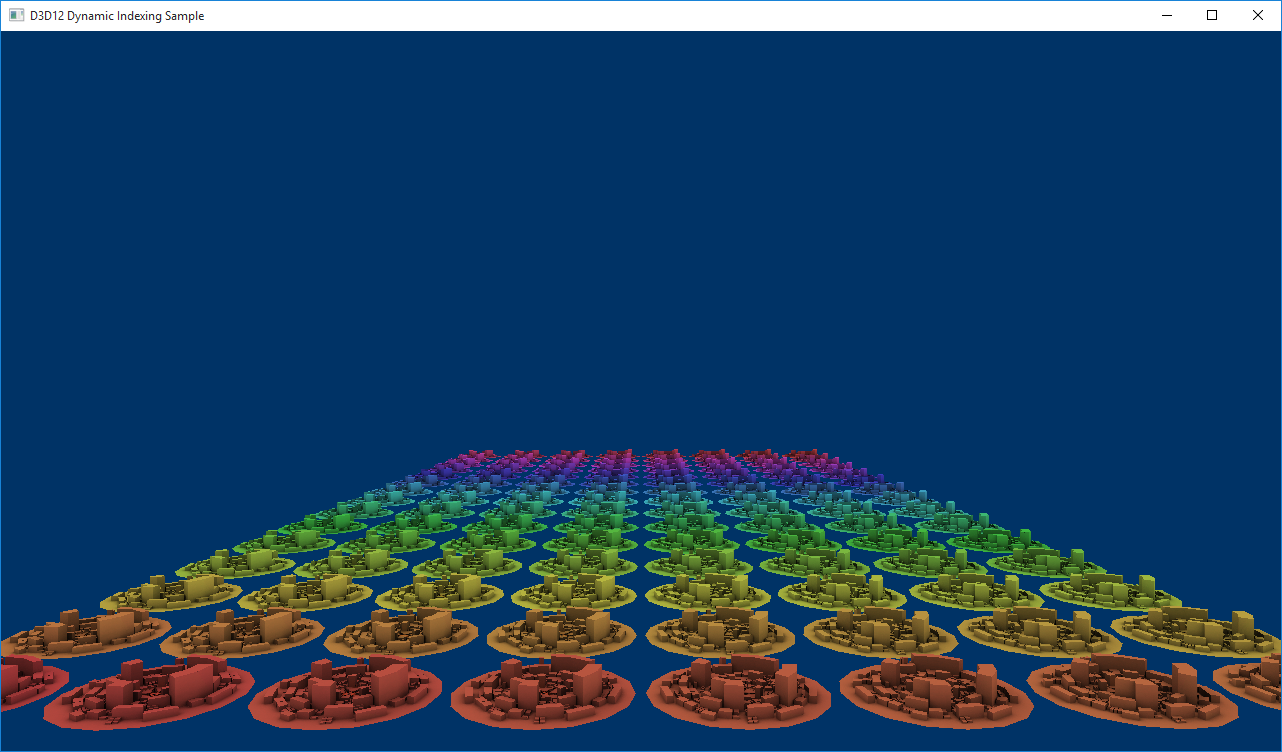
I contenuti di g_txMats[] sono texture generate in modo procedurale create in LoadAssets. Ogni città sottoposta a rendering nella scena condivide la stessa trama diffusa, ma ognuna ha anche una trama generata in modo procedurale. La matrice di trame si estende sullo spettro arcobaleno per visualizzare facilmente la tecnica di indicizzazione.
// Create the textures and sampler.
{
// Procedurally generate an array of textures to use as city materials.
{
// All of these materials use the same texture desc.
D3D12_RESOURCE_DESC textureDesc = {};
textureDesc.MipLevels = 1;
textureDesc.Format = DXGI_FORMAT_R8G8B8A8_UNORM;
textureDesc.Width = CityMaterialTextureWidth;
textureDesc.Height = CityMaterialTextureHeight;
textureDesc.Flags = D3D12_RESOURCE_FLAG_NONE;
textureDesc.DepthOrArraySize = 1;
textureDesc.SampleDesc.Count = 1;
textureDesc.SampleDesc.Quality = 0;
textureDesc.Dimension = D3D12_RESOURCE_DIMENSION_TEXTURE2D;
// The textures evenly span the color rainbow so that each city gets
// a different material.
float materialGradStep = (1.0f / static_cast<float>(CityMaterialCount));
// Generate texture data.
vector<vector<unsigned char>> cityTextureData;
cityTextureData.resize(CityMaterialCount);
for (int i = 0; i < CityMaterialCount; ++i)
{
CD3DX12_HEAP_PROPERTIES heapProps(D3D12_HEAP_TYPE_DEFAULT);
ThrowIfFailed(m_device->CreateCommittedResource(
&heapProps,
D3D12_HEAP_FLAG_NONE,
&textureDesc,
D3D12_RESOURCE_STATE_COPY_DEST,
nullptr,
IID_PPV_ARGS(&m_cityMaterialTextures[i])));
// Fill the texture.
float t = i * materialGradStep;
cityTextureData[i].resize(CityMaterialTextureWidth * CityMaterialTextureHeight * CityMaterialTextureChannelCount);
for (int x = 0; x < CityMaterialTextureWidth; ++x)
{
for (int y = 0; y < CityMaterialTextureHeight; ++y)
{
// Compute the appropriate index into the buffer based on the x/y coordinates.
int pixelIndex = (y * CityMaterialTextureChannelCount * CityMaterialTextureWidth) + (x * CityMaterialTextureChannelCount);
// Determine this row's position along the rainbow gradient.
float tPrime = t + ((static_cast<float>(y) / static_cast<float>(CityMaterialTextureHeight)) * materialGradStep);
// Compute the RGB value for this position along the rainbow
// and pack the pixel value.
XMVECTOR hsl = XMVectorSet(tPrime, 0.5f, 0.5f, 1.0f);
XMVECTOR rgb = XMColorHSLToRGB(hsl);
cityTextureData[i][pixelIndex + 0] = static_cast<unsigned char>((255 * XMVectorGetX(rgb)));
cityTextureData[i][pixelIndex + 1] = static_cast<unsigned char>((255 * XMVectorGetY(rgb)));
cityTextureData[i][pixelIndex + 2] = static_cast<unsigned char>((255 * XMVectorGetZ(rgb)));
cityTextureData[i][pixelIndex + 3] = 255;
}
}
}
}
| Flusso di chiamata | Parametri |
|---|---|
| D3D12_RESOURCE_DESC |
D3D12_RESOURCE_FLAGS [D3D12_RESOURCE_DIMENSION](/windows/desktop/api/d3d12/ne-d3d12-d3d12_resource_dimension) |
| CreateCommittedResource |
D3D12_HEAP_TYPE [D3D12_HEAP_FLAG](/windows/desktop/api/d3d12/ne-d3d12-d3d12_heap_flags) CD3DX12_RESOURCE_DESC [D3D12_RESOURCE_STATES](/windows/desktop/api/d3d12/ne-d3d12-d3d12_resource_states) |
| XMVECTOR |
[XMColorHSLToRGB](/windows/desktop/api/directxmath/nf-directxmath-xmcolorhsltorgb) |
Caricare i dati della trama
I dati delle texture vengono caricati nella GPU tramite un heap di caricamento e per ciascuno vengono creati e archiviati in un heap del descrittore SRV.
// Upload texture data to the default heap resources.
{
const UINT subresourceCount = textureDesc.DepthOrArraySize * textureDesc.MipLevels;
const UINT64 uploadBufferStep = GetRequiredIntermediateSize(m_cityMaterialTextures[0].Get(), 0, subresourceCount); // All of our textures are the same size in this case.
const UINT64 uploadBufferSize = uploadBufferStep * CityMaterialCount;
CD3DX12_HEAP_PROPERTIES uploadHeap(D3D12_HEAP_TYPE_UPLOAD);
auto uploadDesc = CD3DX12_RESOURCE_DESC::Buffer(uploadBufferSize);
ThrowIfFailed(m_device->CreateCommittedResource(
&uploadHeap,
D3D12_HEAP_FLAG_NONE,
&uploadDesc,
D3D12_RESOURCE_STATE_GENERIC_READ,
nullptr,
IID_PPV_ARGS(&materialsUploadHeap)));
for (int i = 0; i < CityMaterialCount; ++i)
{
// Copy data to the intermediate upload heap and then schedule
// a copy from the upload heap to the appropriate texture.
D3D12_SUBRESOURCE_DATA textureData = {};
textureData.pData = &cityTextureData[i][0];
textureData.RowPitch = static_cast<LONG_PTR>((CityMaterialTextureChannelCount * textureDesc.Width));
textureData.SlicePitch = textureData.RowPitch * textureDesc.Height;
UpdateSubresources(m_commandList.Get(), m_cityMaterialTextures[i].Get(), materialsUploadHeap.Get(), i * uploadBufferStep, 0, subresourceCount, &textureData);
auto barrier = CD3DX12_RESOURCE_BARRIER::Transition(m_cityMaterialTextures[i].Get(), D3D12_RESOURCE_STATE_COPY_DEST, D3D12_RESOURCE_STATE_PIXEL_SHADER_RESOURCE);
m_commandList->ResourceBarrier(1, &barrier);
}
}
| Flusso di chiamata | Parametri |
|---|---|
| GetRequiredIntermediateSize | |
| CreateCommittedResource | |
| D3D12_SUBRESOURCE_DATA | |
| UpdateSubresources | |
| ResourceBarrier |
Caricare la trama diffusa
La trama diffusa, g_txDiffuse, viene caricata in modo simile e ottiene anche il proprio SRV, ma i dati della trama sono già definiti in occcity.bin.
// Load the occcity diffuse texture with baked-in ambient lighting.
// This texture will be blended with a texture from the materials
// array in the pixel shader.
{
D3D12_RESOURCE_DESC textureDesc = {};
textureDesc.MipLevels = SampleAssets::Textures[0].MipLevels;
textureDesc.Format = SampleAssets::Textures[0].Format;
textureDesc.Width = SampleAssets::Textures[0].Width;
textureDesc.Height = SampleAssets::Textures[0].Height;
textureDesc.Flags = D3D12_RESOURCE_FLAG_NONE;
textureDesc.DepthOrArraySize = 1;
textureDesc.SampleDesc.Count = 1;
textureDesc.SampleDesc.Quality = 0;
textureDesc.Dimension = D3D12_RESOURCE_DIMENSION_TEXTURE2D;
CD3DX12_HEAP_PROPERTIES heapProps(D3D12_HEAP_TYPE_DEFAULT);
ThrowIfFailed(m_device->CreateCommittedResource(
&heapProps,
D3D12_HEAP_FLAG_NONE,
&textureDesc,
D3D12_RESOURCE_STATE_COPY_DEST,
nullptr,
IID_PPV_ARGS(&m_cityDiffuseTexture)));
const UINT subresourceCount = textureDesc.DepthOrArraySize * textureDesc.MipLevels;
const UINT64 uploadBufferSize = GetRequiredIntermediateSize(m_cityDiffuseTexture.Get(), 0, subresourceCount);
CD3DX12_HEAP_PROPERTIES uploadHeap(D3D12_HEAP_TYPE_UPLOAD);
auto uploadDesc = CD3DX12_RESOURCE_DESC::Buffer(uploadBufferSize);
ThrowIfFailed(m_device->CreateCommittedResource(
&uploadHeap,
D3D12_HEAP_FLAG_NONE,
&uploadDesc,
D3D12_RESOURCE_STATE_GENERIC_READ,
nullptr,
IID_PPV_ARGS(&textureUploadHeap)));
// Copy data to the intermediate upload heap and then schedule
// a copy from the upload heap to the diffuse texture.
D3D12_SUBRESOURCE_DATA textureData = {};
textureData.pData = pMeshData + SampleAssets::Textures[0].Data[0].Offset;
textureData.RowPitch = SampleAssets::Textures[0].Data[0].Pitch;
textureData.SlicePitch = SampleAssets::Textures[0].Data[0].Size;
UpdateSubresources(m_commandList.Get(), m_cityDiffuseTexture.Get(), textureUploadHeap.Get(), 0, 0, subresourceCount, &textureData);
auto barrier = CD3DX12_RESOURCE_BARRIER::Transition(m_cityDiffuseTexture.Get(), D3D12_RESOURCE_STATE_COPY_DEST, D3D12_RESOURCE_STATE_PIXEL_SHADER_RESOURCE);
m_commandList->ResourceBarrier(1, &barrier);
}
| Flusso di chiamata | Parametri |
|---|---|
| D3D12_RESOURCE_DESC | |
| CreateCommittedResource | |
| GetRequiredIntermediateSize | |
| CreateCommittedResource | |
| D3D12_SUBRESOURCE_DATA | |
| ResourceBarrier |
Creare un campionatore
Infine, per LoadAssetsviene creato un singolo campionatore per campionare dalla texture diffusa o dall'array di texture.
// Describe and create a sampler.
D3D12_SAMPLER_DESC samplerDesc = {};
samplerDesc.Filter = D3D12_FILTER_MIN_MAG_MIP_LINEAR;
samplerDesc.AddressU = D3D12_TEXTURE_ADDRESS_MODE_WRAP;
samplerDesc.AddressV = D3D12_TEXTURE_ADDRESS_MODE_WRAP;
samplerDesc.AddressW = D3D12_TEXTURE_ADDRESS_MODE_WRAP;
samplerDesc.MinLOD = 0;
samplerDesc.MaxLOD = D3D12_FLOAT32_MAX;
samplerDesc.MipLODBias = 0.0f;
samplerDesc.MaxAnisotropy = 1;
samplerDesc.ComparisonFunc = D3D12_COMPARISON_FUNC_ALWAYS;
m_device->CreateSampler(&samplerDesc, m_samplerHeap->GetCPUDescriptorHandleForHeapStart());
// Create SRV for the city's diffuse texture.
CD3DX12_CPU_DESCRIPTOR_HANDLE srvHandle(m_cbvSrvHeap->GetCPUDescriptorHandleForHeapStart(), 0, m_cbvSrvDescriptorSize);
D3D12_SHADER_RESOURCE_VIEW_DESC diffuseSrvDesc = {};
diffuseSrvDesc.Shader4ComponentMapping = D3D12_DEFAULT_SHADER_4_COMPONENT_MAPPING;
diffuseSrvDesc.Format = SampleAssets::Textures->Format;
diffuseSrvDesc.ViewDimension = D3D12_SRV_DIMENSION_TEXTURE2D;
diffuseSrvDesc.Texture2D.MipLevels = 1;
m_device->CreateShaderResourceView(m_cityDiffuseTexture.Get(), &diffuseSrvDesc, srvHandle);
srvHandle.Offset(m_cbvSrvDescriptorSize);
// Create SRVs for each city material.
for (int i = 0; i < CityMaterialCount; ++i)
{
D3D12_SHADER_RESOURCE_VIEW_DESC materialSrvDesc = {};
materialSrvDesc.Shader4ComponentMapping = D3D12_DEFAULT_SHADER_4_COMPONENT_MAPPING;
materialSrvDesc.Format = DXGI_FORMAT_R8G8B8A8_UNORM;
materialSrvDesc.ViewDimension = D3D12_SRV_DIMENSION_TEXTURE2D;
materialSrvDesc.Texture2D.MipLevels = 1;
m_device->CreateShaderResourceView(m_cityMaterialTextures[i].Get(), &materialSrvDesc, srvHandle);
srvHandle.Offset(m_cbvSrvDescriptorSize);
}
| Flusso di chiamata | Parametri |
|---|---|
| D3D12_SAMPLER_DESC |
D3D12_FLOAT32_MAX ( Costanti) D3D12_COMPARISON_FUNC |
| CreateSampler | |
| CD3DX12_CPU_DESCRIPTOR_HANDLE | GetCPUDescriptorHandleForHeapStart |
| D3D12_SHADER_RESOURCE_VIEW_DESC | |
| CreateShaderResourceView | |
| D3D12_SHADER_RESOURCE_VIEW_DESC | |
| CreateShaderResourceView |
Modificare dinamicamente l'indice dei parametri radice
Se si dovesse eseguire il rendering della scena ora, tutte le città apparirebbero uguali, perché non è stato impostato il valore della costante radice, matIndex. Ogni pixel shader viene indicizzato nello slot 0 di g_txMats e la scena sarà simile alla seguente:

Il valore della costante radice viene impostato in FrameResource::PopulateCommandLists. Nello schema doppio per in cui viene registrato un comando di disegno per ogni città, si registra una chiamata a SetGraphicsRoot32BitConstants specificando l'indice del parametro radice rispetto alla root signature, in questo caso 3, il valore dell'indice dinamico e un offset, in questo caso 0. Poiché la lunghezza di g_txMats è uguale al numero di città di cui viene eseguito il rendering, il valore dell'indice viene impostato in modo incrementale per ogni città.
for (UINT i = 0; i < m_cityRowCount; i++)
{
for (UINT j = 0; j < m_cityColumnCount; j++)
{
pCommandList->SetPipelineState(pPso);
// Set the city's root constant for dynamically indexing into the material array.
pCommandList->SetGraphicsRoot32BitConstant(3, (i * m_cityColumnCount) + j, 0);
// Set this city's CBV table and move to the next descriptor.
pCommandList->SetGraphicsRootDescriptorTable(2, cbvSrvHandle);
cbvSrvHandle.Offset(cbvSrvDescriptorSize);
pCommandList->DrawIndexedInstanced(numIndices, 1, 0, 0, 0);
}
}
| Flusso di chiamata | Parametri |
|---|---|
| SetPipelineState | |
| SetGraphicsRoot32BitConstant | |
| SetGraphicsRootDescriptorTable | |
| DrawIndexedInstanced |
Eseguire l'esempio
Ora, quando renderizziamo la scena, ogni città avrà un valore diverso per matIndex e quindi cercherà una texture diversa da g_txMats[] facendo apparire la scena in questo modo: