Add MySQL Database CDC source to an eventstream
Note
This article contains references to the term SLAVE, a term that Microsoft no longer uses. When the term is removed from the software, we'll remove it from this article.
This article shows you how to add a MySQL Change Data Capture source to an eventstream. Currently, MySQL Database CDC is supported from the following services where the databases can be accessed publicly:
- Azure Database for MySQL
- Amazon RDS for MySQL
- Amazon Aurora MySQL
- Google Cloud SQL for MySQL (GCP).
This guide uses Azure Database for MySQL CDC as an example.
Once the MySQL Database CDC source is added to the eventstream, it captures row-level changes to the specified tables. These changes can then be processed in real-time and sent to different destinations for further analysis.
Note
This source is not supported in the following regions of your workspace capacity: West US3, Switzerland West.
Prerequisites
- Access to a workspace in the Fabric capacity license mode (or) the Trial license mode with Contributor or higher permissions.
- Access to an instance of MySQL Database, such as: a database in Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server.
- Your MySQL database must be publicly accessible and not be behind a firewall or secured in a virtual network.
- If you don't have an eventstream, create an eventstream.
Set up MySQL DB
The connector uses the Debezium MySQL connector to capture changes in your MySQL Database. You must define a MySQL user with appropriate privileges on all databases where the Messaging Connector can capture the changes from. You can directly use the admin user to connect to the database which normally has the appropriate privileges, or you can follow these steps to create a new user:
Note
The new user or admin account and the corresponding password will be used to connect to database later inside Eventstream.
At the
mysqlcommand prompt, create the MySQL user:mysql> CREATE USER 'user'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';Grant the required privileges to the user:
mysql> GRANT SELECT, SHOW DATABASES, REPLICATION SLAVE, REPLICATION CLIENT ON *.* TO 'user'@'%';Note
When a global read lock is unavailable, as in hosted options like Amazon RDS or Aurora, table-level locks are used to create the consistent snapshot. In this case, you need to grant
LOCK TABLESpermission to the user. Additionally, to supportFLUSHoperations during the snapshot, you may also need to grantRELOADorFLUSH_TABLESprivileges.Finalize the user's permissions:
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
To confirm if the user or admin has the required privileges granted, run this command and then the required privileges in step#2 should be shown:
SHOW GRANTS FOR user;
For more information about granting the required permissions to the user, see Debezium connector for MySQL: Debezium Documentation.
Enable the binlog
You must enable binary logging for MySQL replication. The binary logs record transaction updates for replication tools to propagate changes. This section uses Azure Database for MySQL CDC as an example to show the configuration steps.
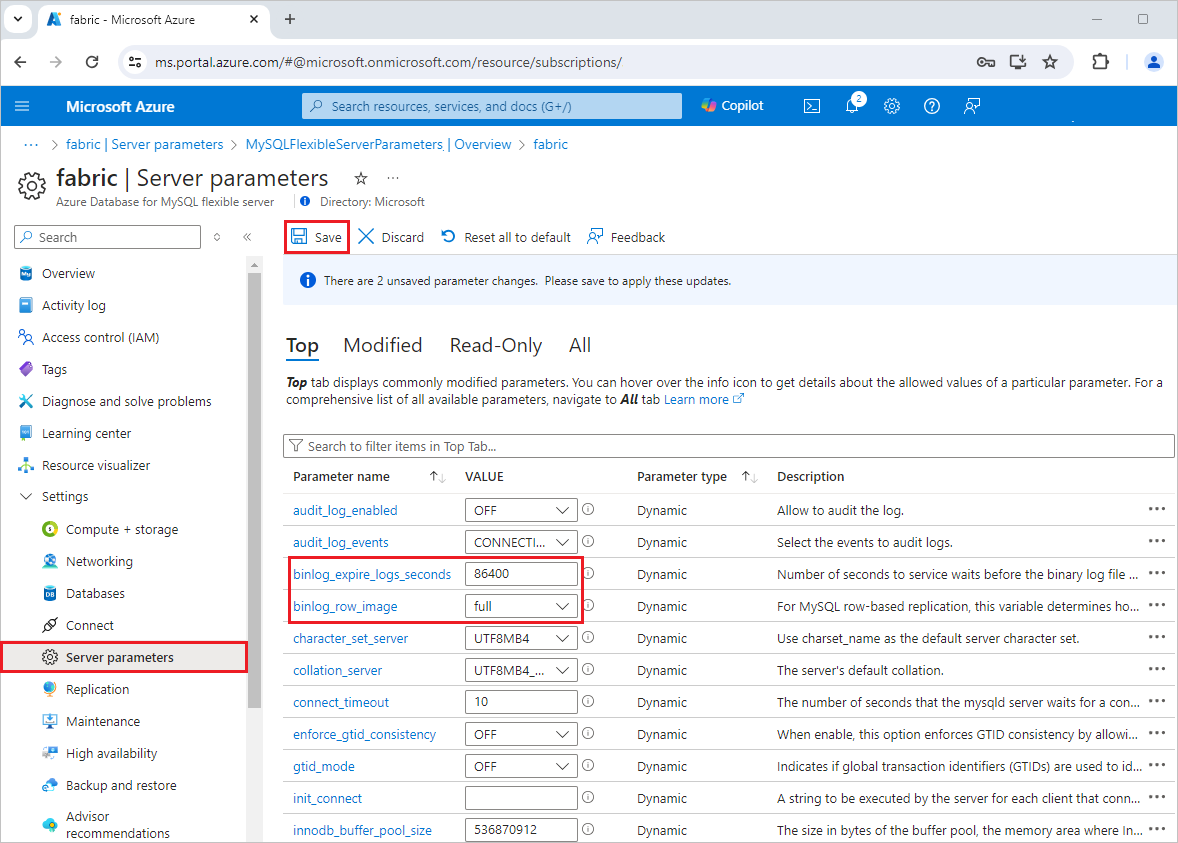
On the Azure portal page for your Azure Database for MySQL account, select Server parameters under Settings in the left navigation.
On the Server parameters page, configure the following properties, and then select Save.
For binlog_row_image, select full.
For binlog_expire_logs_seconds, set the number of seconds the service waits before the binary log file is purged. Set the value to match the needs of your environment, for example 86400.
Add MySQL DB (CDC) as a source
If you haven't added any source to your eventstream yet, select Use external source tile.
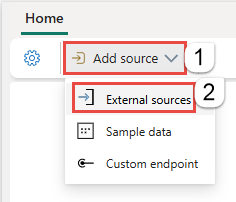
If you're adding the source to an already published eventstream, switch to Edit mode, select Add source on the ribbon, and then select External sources.
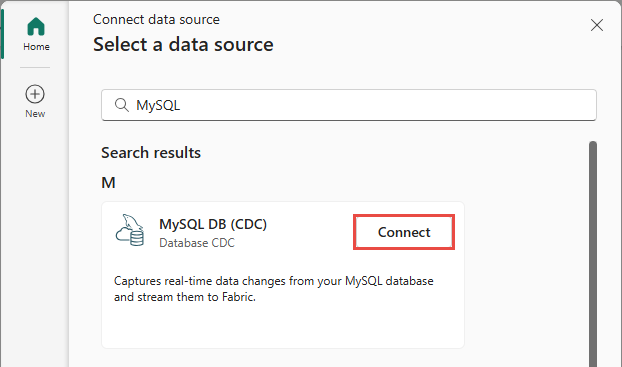
On the Select a data source page, search for and select Connect on the MySQL DB (CDC) tile.
Configure and connect to MySQL DB (CDC)
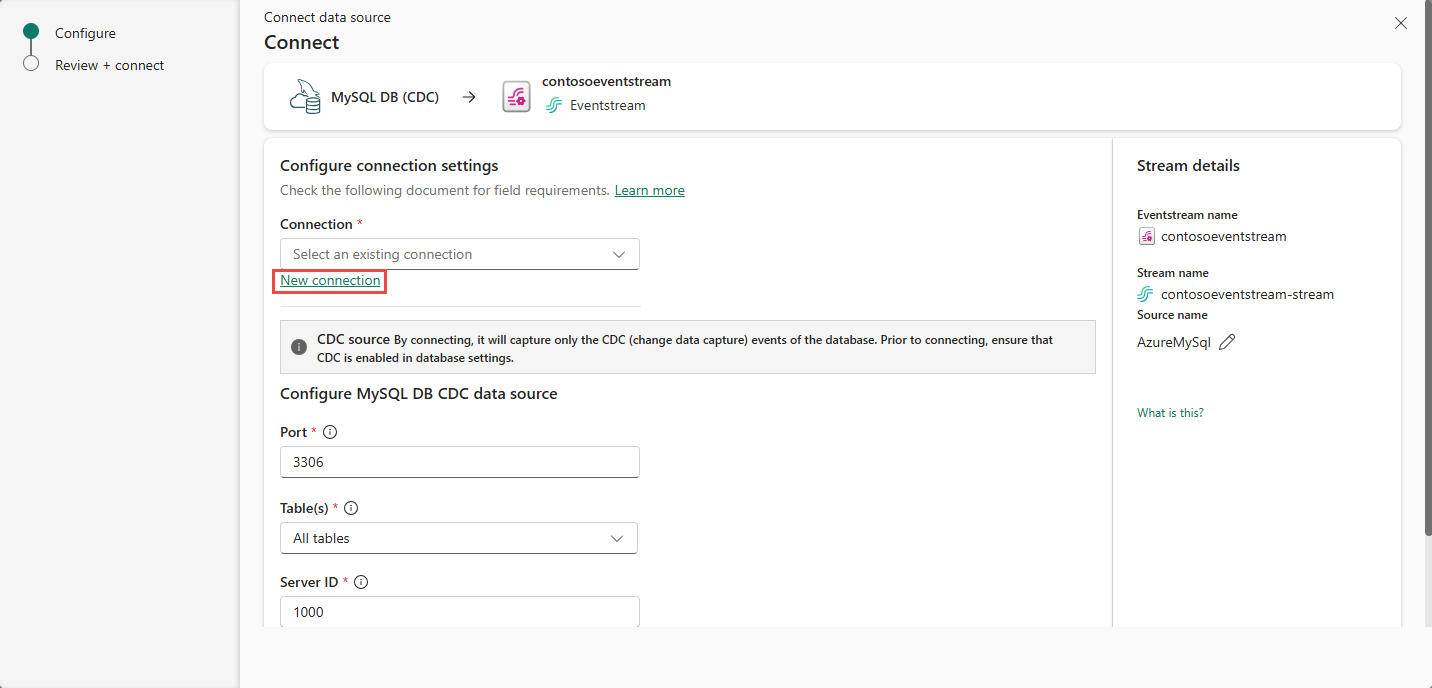
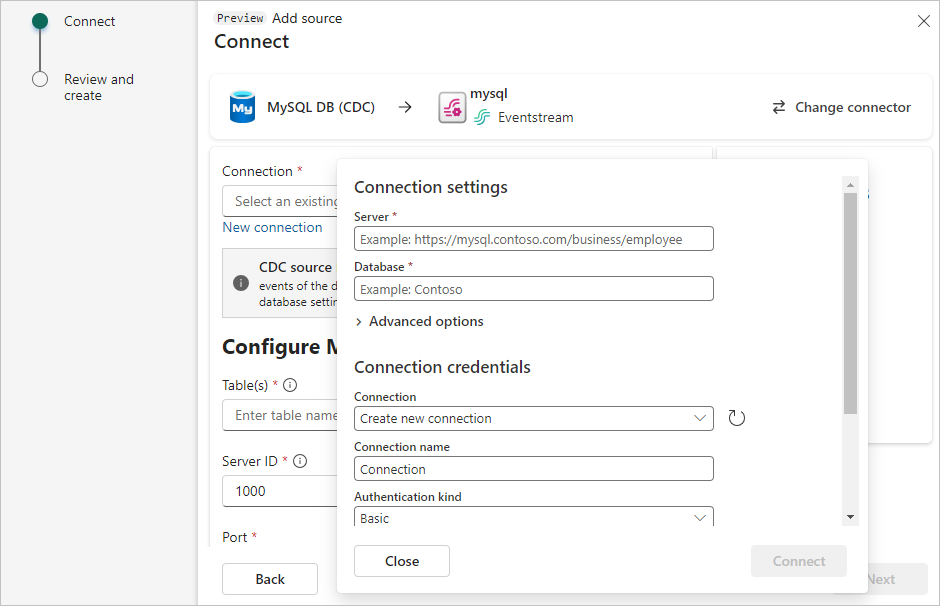
On the Connect screen, under Connection, select New connection to create a cloud connection.
Enter the following Connection settings and Connection credentials for your MySQL DB, and then select Connect.
Server: The server address of your MySQL database, for example my-mysql-server.mysql.database.azure.com.
Database: The database name, for example my_database.
Connection name: Automatically generated, or you can enter a new name for this connection.
Username and Password: Enter the credentials for your MySQL database. Make sure you enter the server admin account or the user account created with required privileges granted.
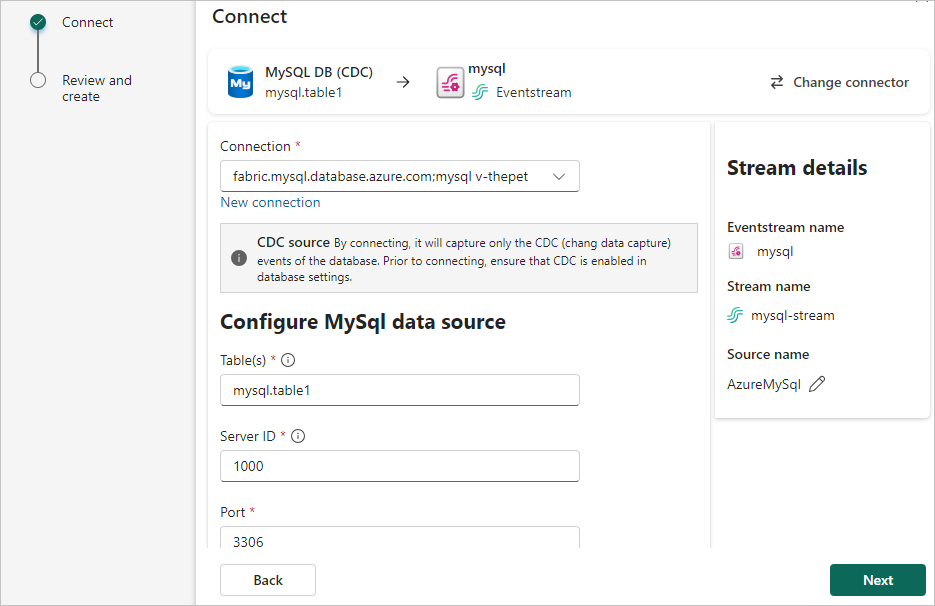
Enter the following information to configure the MySQL DB CDC data source, and then select Next.
table: Select All tables or Enter table name(s). If you select the latter, specify tables using a comma-separated list of full table identifiers (
schemaName.tableName) or valid regular expressions. For example:- Use
dbo.test.*to select all tables whose names start withdbo.test. - Use
dbo\.(test1|test2)to selectdbo.test1anddbo.test2.
You can mix both formats using commas. Up to 100 tables can be entered, with each table name (including the schema name) limited to 128 characters if using full table identifiers directly.
- Use
Server ID: Enter a unique value for each server and replication client in the MySQL cluster. The default value is 1000.
Port: The default value is 3306. If your selected cloud connection is configured in Manage connections and gateways, ensure that the port number matches the one set there. If they don't match, the port number in the cloud connection in Manage connections and gateways take precedence.
Snapshot locking mode: Select the Advanced settings to choose the Snapshot locking mode. Options are:
Minimal (default): Holds a global read lock only during the initial phase to capture schema and metadata. The rest of the snapshot uses a REPEATABLE READ transaction, allowing updates while data is being read.
Extended: Maintains a global read lock for the entire snapshot duration, blocking all writes. Use for full consistency if write blocking is acceptable.
None: Skips acquiring table locks during the snapshot. Safe only if no schema changes occur during the process.
You can also edit source name by selecting the Pencil button for Source name in the Stream details section to the right.
Note
Set a different Server ID for each reader. Every MySQL database client for reading binlog should have a unique ID, called Server ID. MySQL Server uses this ID to maintain the network connection and the binlog position. Different jobs sharing the same Server ID can result in reading from the wrong binlog position. Therefore, it's recommended to set a different Server ID for each reader.
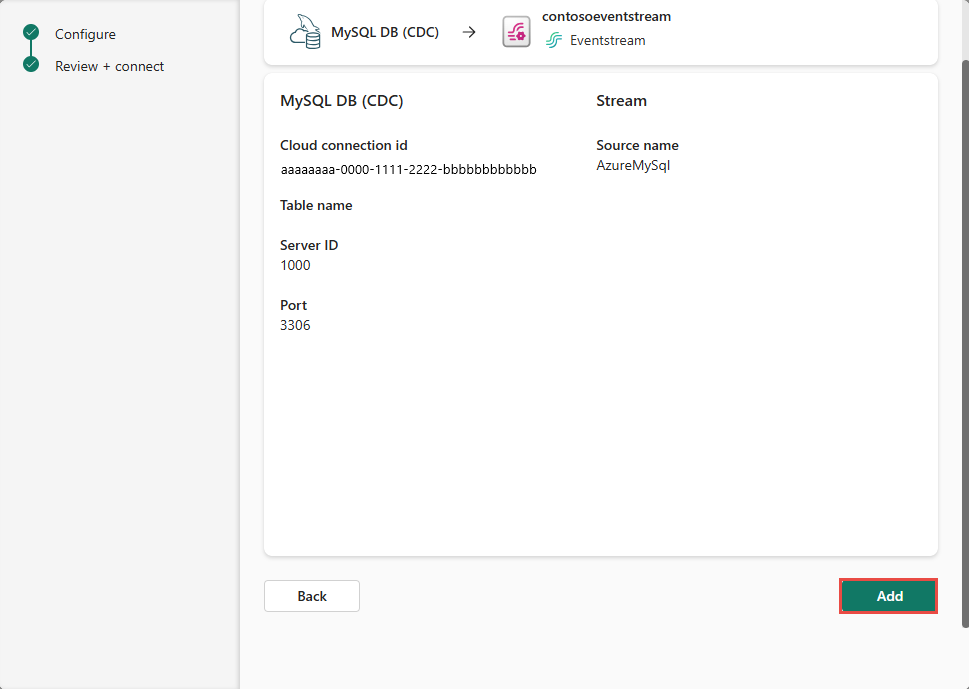
On the Review + connect page, after reviewing the summary for MySQL DB CDC source, select Add to complete the configuration.
Note
The maximum number of sources and destinations for one eventstream is 11.
View updated eventstream
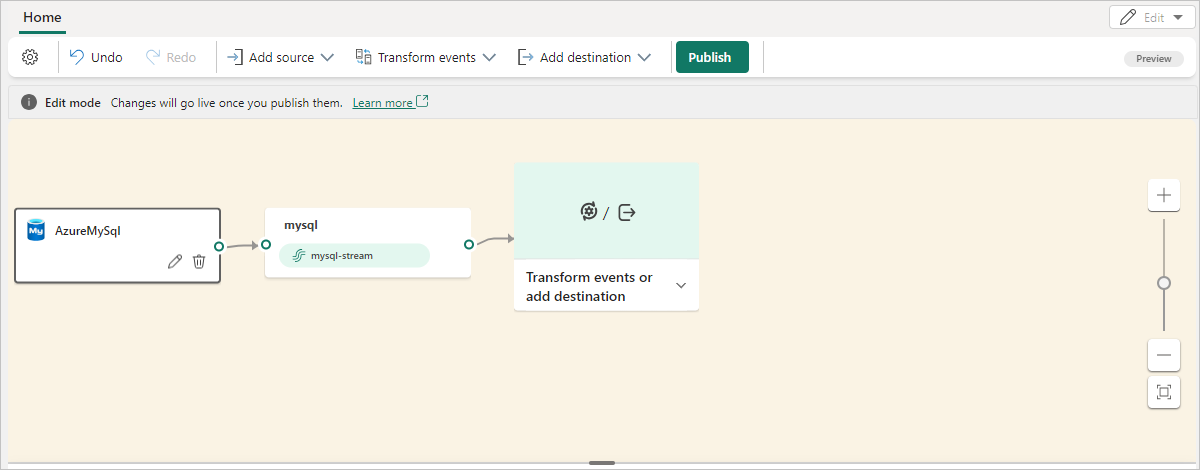
You see the MySQL DB (CDC) source added to your eventstream in Edit mode.
Select Publish to publish the changes and begin streaming MySQL DB CDC data to the eventstream.
Related content
Other connectors: