Microsoft Fabric Integration Pathways for ISVs
Microsoft Fabric offers three distinct pathways for Independent Software Vendors (ISVs) to seamlessly integrate with Fabric. For an ISV starting on this journey, we want to walk through various resources we have available under each of these pathways.
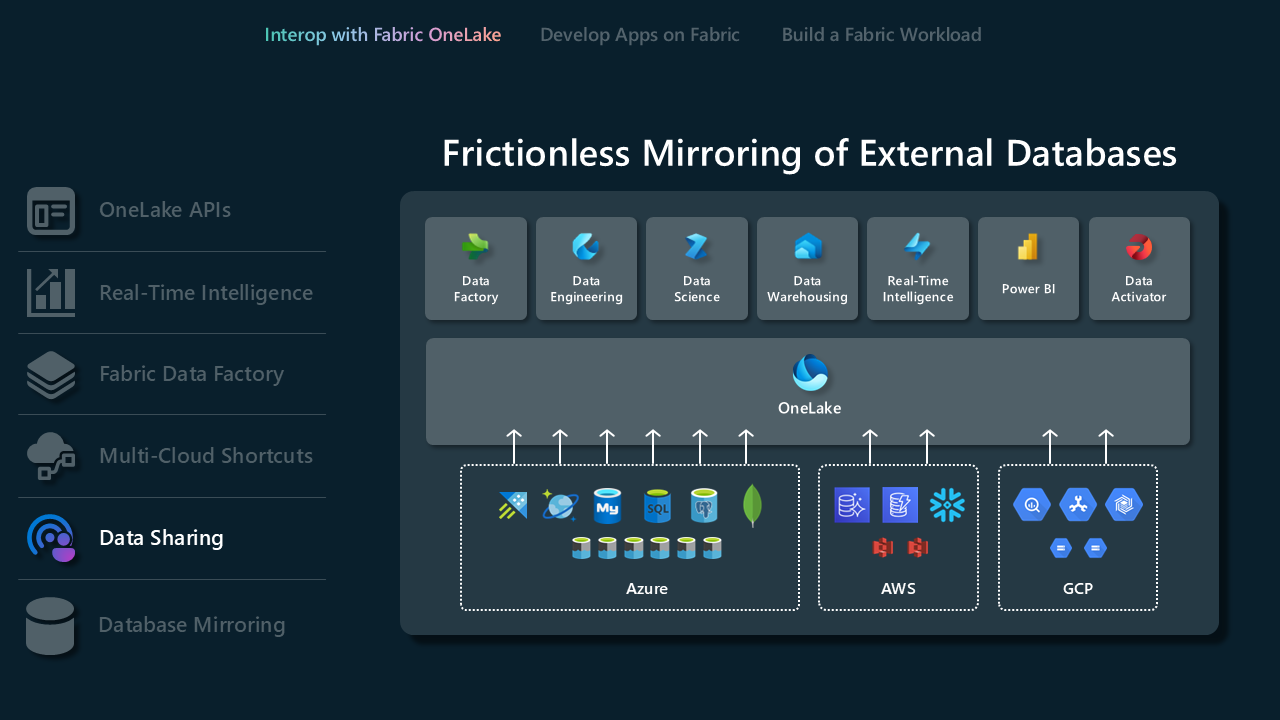
Interop with Fabric OneLake
The primary focus with Interop model is on enabling ISVs to integrate their solutions with the OneLake Foundation. To Interop with Microsoft Fabric, we provide integration using a multitude of connectors in Data Factory and in Real-Time Intelligence, REST APIs for OneLake, shortcuts in OneLake, data sharing across Fabric tenants, and database mirroring.

The following sections describe some of the ways you can get started with this model.
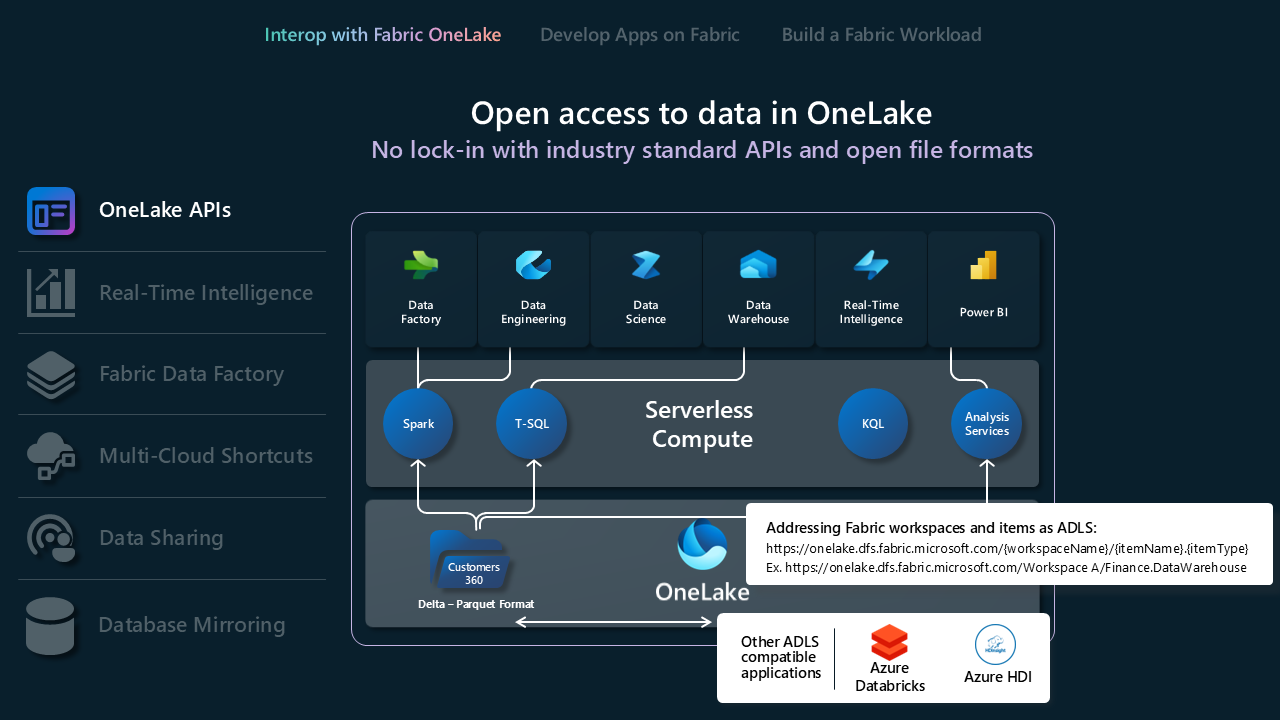
OneLake APIs
- OneLake supports existing Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS) Gen2 APIs and SDKs for direct interaction, allowing developers to read, write, and manage their data in OneLake. Learn more about ADLS Gen2 REST APIs and how to connect to OneLake.
- Since not all functionality in ADLS Gen2 maps directly to OneLake, OneLake also enforces a set folder structure to support Fabric workspaces and items. For a full list of different behaviors between OneLake and ADLS Gen2 when calling these APIs, see OneLake API parity.
- If you're using Databricks and want to connect to Microsoft Fabric, Databricks works with ADLS Gen2 APIs. Integrate OneLake with Azure Databricks.
- To take full advantage of what the Delta Lake storage format can do for you, review and understand the format, table optimization, and V-Order. Delta Lake table optimization and V-Order.
- Once the data is in OneLake, explore locally using OneLake File Explorer. OneLake file explorer seamlessly integrates OneLake with Windows File Explorer. This application automatically syncs all OneLake items that you have access to in Windows File Explorer. You can also use any other tool compatible with ADLS Gen2 like Azure Storage Explorer.
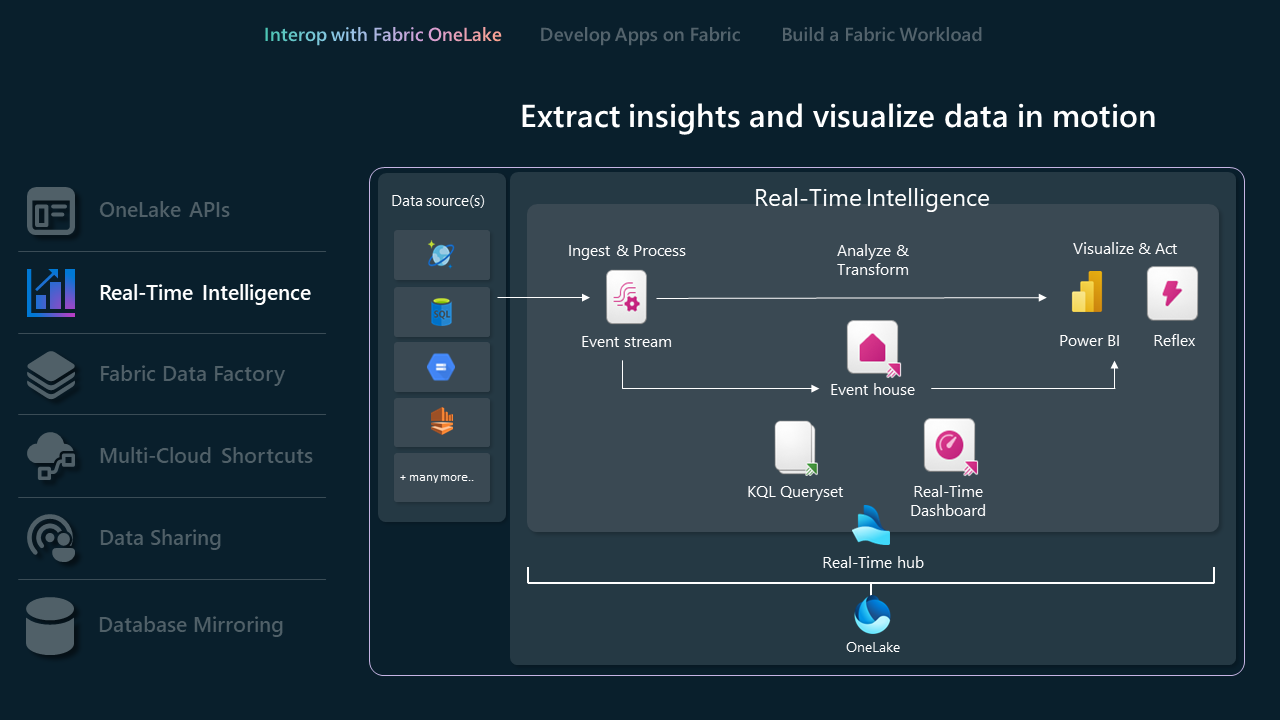
Real-Time Intelligence APIs
Real-Time Intelligence streamlines data analysis and visualization, offering a centralized solution for immediate insights and actions on data in motion within an organization. It efficiently manages large volumes of data through robust querying, transformation, and storage capabilities.
- Eventhouses are specifically designed for streaming data, compatible with Real-Time hub, and ideal for time-based events. Data is automatically indexed and partitioned based on ingestion time, giving you incredibly fast and complex analytic querying capabilities on high-granularity data that can be accessed in OneLake for use across Fabric's suite of experiences. Eventhouses support existing Eventhouse APIs and SDKs for direct interaction, allowing developers to read, write, and manage their data in Eventhouses. Learn more about REST API.
- Eventstreams enable you to bring real-time events from various sources and route them to various destinations, such as OneLake, KQL databases in eventhouses, and Fabric Activator. Learn more about eventstreams and eventstreams API.
- If you're using Databricks or Jupyter Notebooks, you can utilize the Kusto Python Client Library to work with KQL databases in Fabric. Learn more about Kusto Python SDK.
- You can utilize the existing Microsoft Logic Apps, Azure Data Factory, or Microsoft Power Automate connectors to interact with your Eventhouses or KQL Databases.
- Database shortcuts in Real-Time Intelligence are embedded references within an eventhouse to a source database. The source database can either be a KQL Database in Real-Time Intelligence or an Azure Data Explorer database. Shortcuts can be used for in place sharing of data within the same tenant or across tenants. Learn more about managing database shortcuts using the API.
Data Factory in Fabric
- Data Pipelines boast an extensive set of connectors, enabling ISVs to effortlessly connect to a myriad of data stores. Whether you're interfacing traditional databases or modern cloud-based solutions, our connectors ensure a smooth integration process. Connector overview.
- With our supported Dataflow Gen2 connectors, ISVs can harness the power of Fabric Data Factory to manage complex data workflows. This feature is especially beneficial for ISVs looking to streamline data processing and transformation tasks. Dataflow Gen2 connectors in Microsoft Fabric.
- For a full list of capabilities supported by Data Factory in Fabric checkout this Data Factory in Fabric Blog.
Multicloud shortcuts
Shortcuts in Microsoft OneLake allow you to unify your data across domains, clouds, and accounts by creating a single virtual data lake for your entire enterprise. All Fabric experiences and analytical engines can directly point to your existing data sources such as OneLake in different tenant, Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS) Gen2, Amazon S3 storage accounts, Google Cloud Storage(GCS), S3 Compatible data sources and Dataverse through a unified namespace. OneLake presents ISVs with a transformative data access solution, seamlessly bridging integration across diverse domains and cloud platforms.
- Learn more about OneLake shortcuts
- Learn more about OneLake one logical copy
- Learn more about KQL database shortcuts
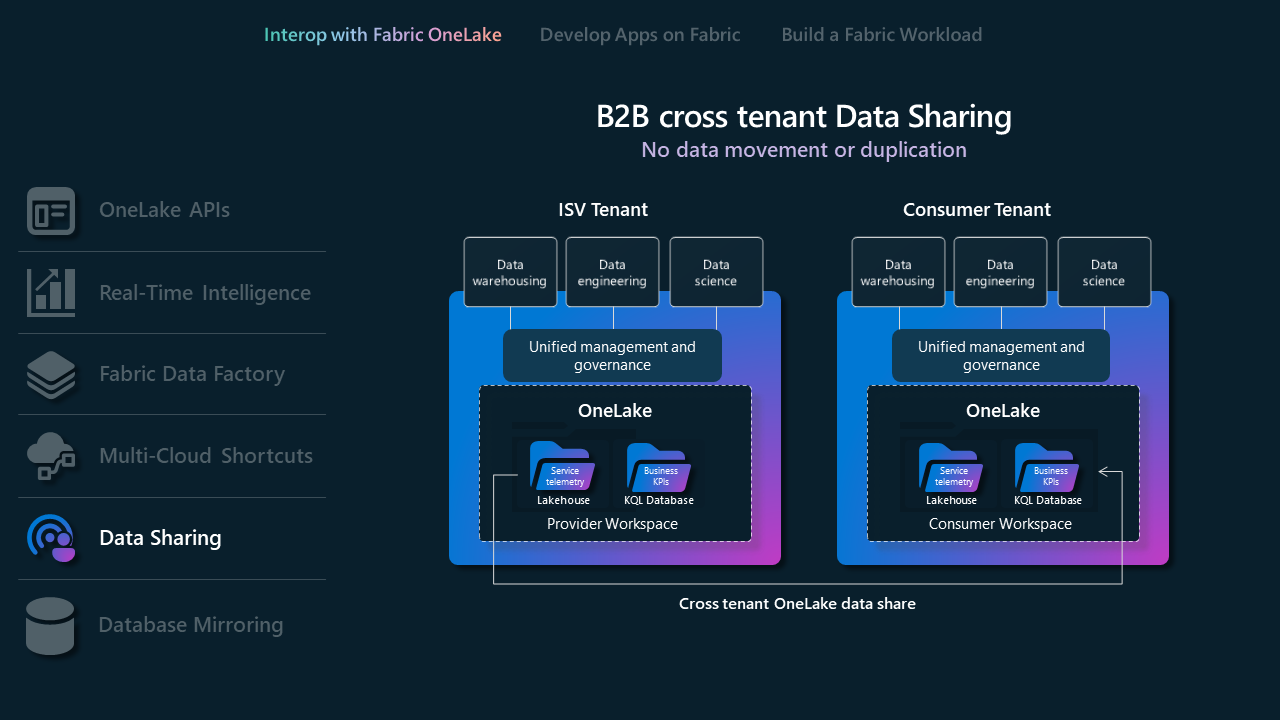
Data sharing
Data Sharing allows Fabric users to share data across different Fabric tenants without duplicating it. This feature enhances collaboration by enabling data to be shared "in-place" from OneLake storage locations. The data is shared as read-only, accessible through various Fabric computation engines, including SQL, Spark, KQL, and semantic models. To use this feature, Fabric admins must enable it in both the sharing and receiving tenants. The process includes selecting data within the OneLake data hub or workspace, configuring sharing settings, and sending an invitation to the intended recipient.
Database mirroring
Mirroring provides a modern way of accessing and ingesting data continuously and seamlessly from external databases or data warehouse into the data warehousing experience in Microsoft Fabric. Mirroring is all in near real-time giving users immediate access to changes in the source. Learn more about mirroring and the supported databases.
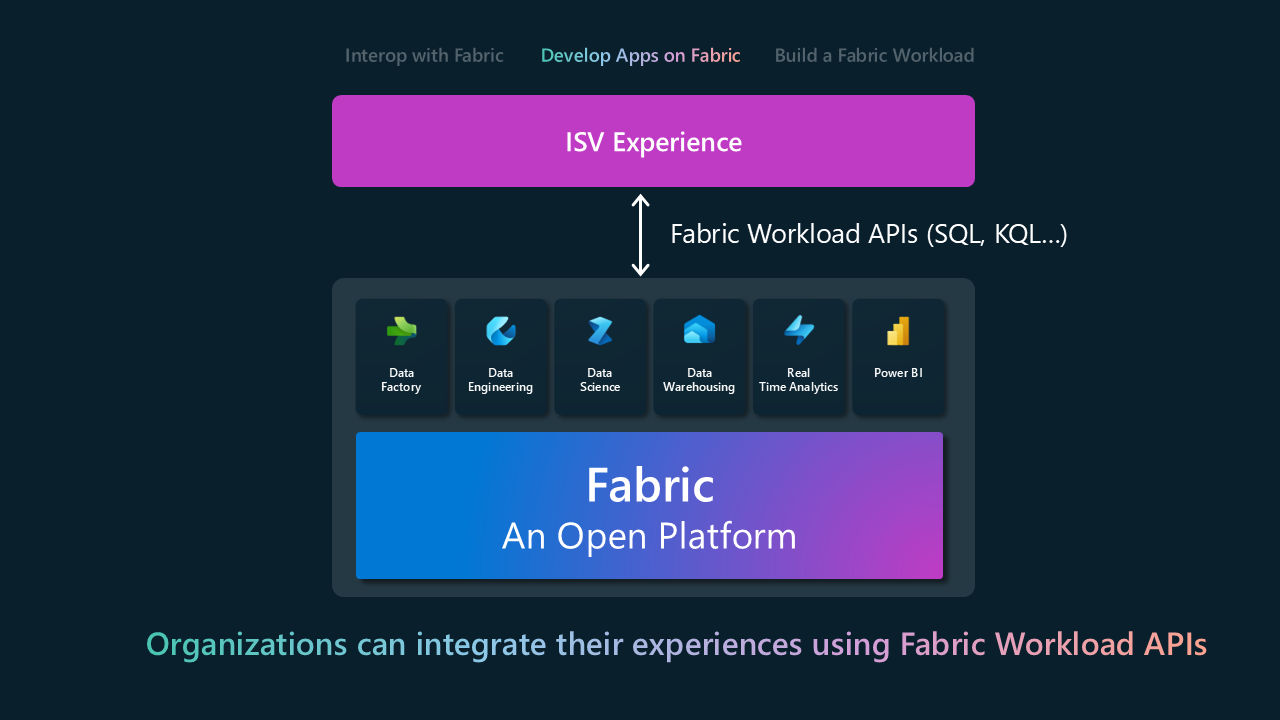
Develop on Fabric
With the Develop on Fabric model ISVs can build their products and services on top of Fabric or seamlessly embed Fabric's functionalities within their existing applications. It's a transition from basic integration to actively applying the capabilities Fabric offers. The main integration surface area is via REST APIs for various Fabric experiences. The following table shows a subset of REST APIs grouped by the Fabric experience. For a complete list, see the Fabric REST API documentation.
| Fabric Experience | API |
|---|---|
| Data Warehouse | - Warehouse - Mirrored Warehouse |
| Data Engineering | - Lakehouse - Spark - Spark Job Definition - Tables - Jobs |
| Data Factory | - DataPipeline |
| Real-Time Intelligence | - Eventhouse - KQL Database - KQL Queryset - Eventstream |
| Data Science | - Notebook - ML Experiment - ML Model |
| OneLake | - Shortcut - ADLS Gen2 APIs |
| Power BI | - Report - Dashboard - Semantic Model |
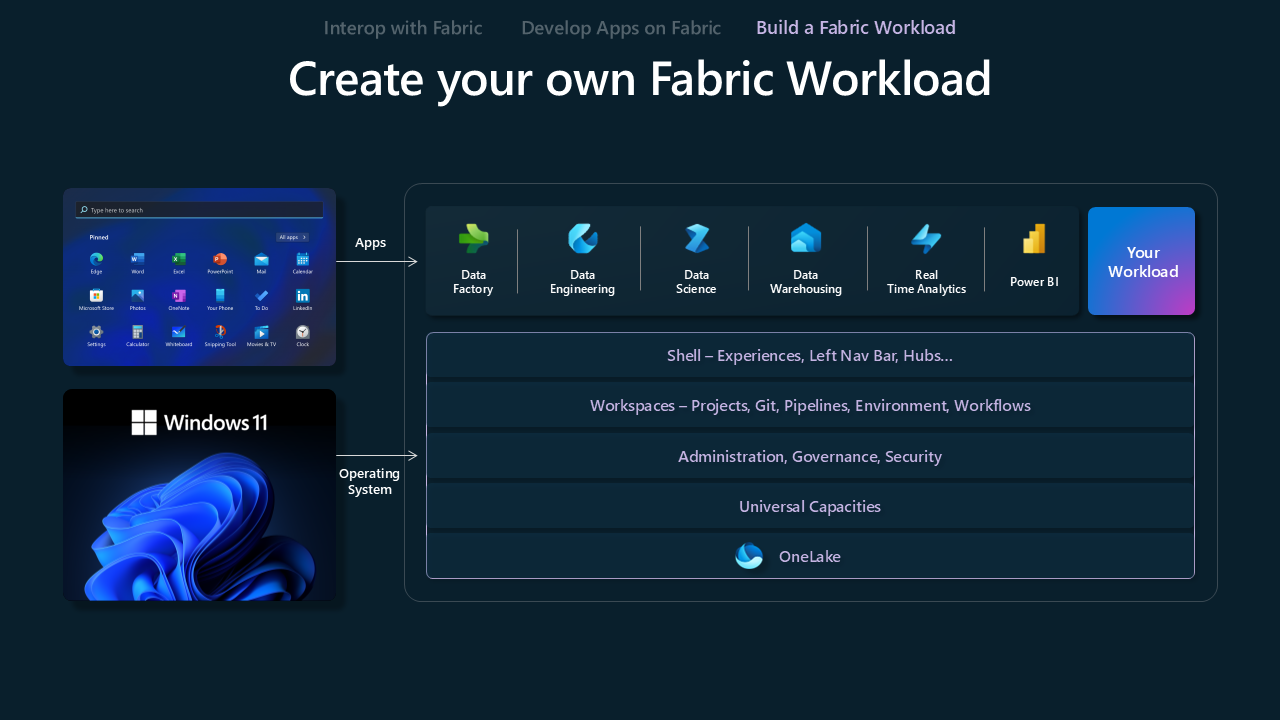
Build a Fabric workload
Build a Fabric workload model is designed to empower ISVs to create custom experiences on the Fabric platform. It provides ISVs with the necessary tools and capabilities to align their offerings with the Fabric ecosystem, optimizing the combination of their unique value propositions with Fabric's extensive capabilities.
The Microsoft Fabric Workload Development Kit offers a comprehensive toolkit for developers to integrate applications into the Microsoft Fabric hub. This integration allows for the addition of new capabilities directly within the Fabric workspace, enhancing the analytics journey for users. It provides developers and ISVs with a new avenue to reach customers, delivering both familiar and new experiences, and leveraging existing data applications. Fabric admins gain the ability to manage access to the workload hub, enabling it for the entire tenant or assigning it with specific scope to control access within the organization.