External data sharing in Microsoft Fabric
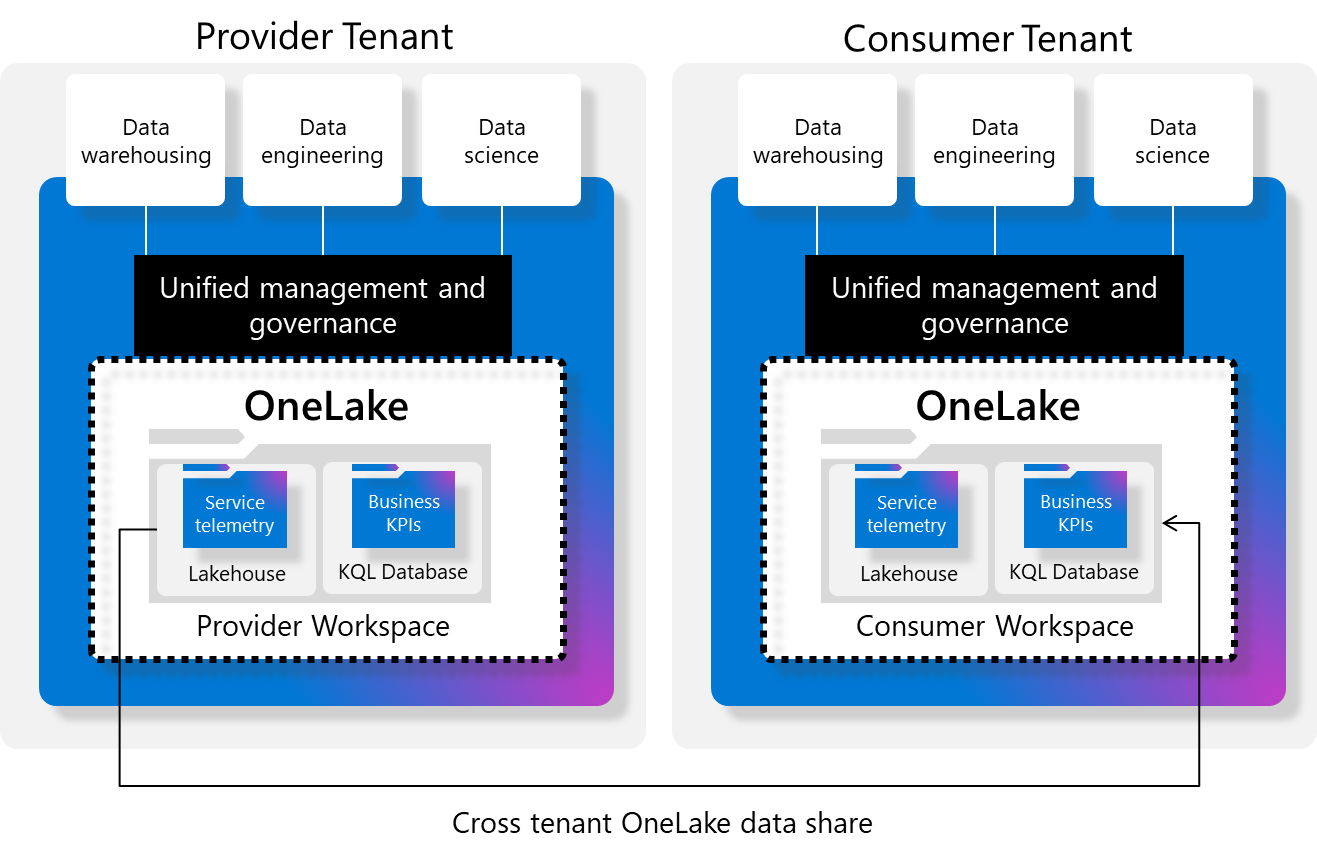
Fabric external data sharing is a feature that enables Fabric users to share data from their tenant with users in another Fabric tenant. The data is shared in-place from OneLake storage locations in the sharer's tenant, meaning that no data is actually copied to the other tenant. Rather, this cross-tenant sharing creates a OneLake shortcut in the other tenant that points back to the original data in the sharer's tenant. Data that is shared across tenant boundaries is exposed to users in the other tenant as read-only, and can be consumed by any OneLake compatible Fabric workload in that tenant.
This external data sharing feature for Fabric OneLake data isn't related to the mechanism that exists for sharing Power BI semantic models with Microsoft Entra B2B guest users.
How does external data sharing work
As a prerequisite to external data sharing, Fabric admins need to turn on external data sharing both in the sharer's tenant and in the external tenant. Enabling external data sharing includes specifying who can create and accept external data shares. For more information, see Enable external data sharing.
Users who are allowed to create external data shares can share data residing in tables or files within supported Fabric items, as long as they have the standard Fabric read and reshare permissions for the item being shared. The user creating the share invites a user from another tenant to accept the external data share. This user receives a link that they use to accept the share. Upon accepting the share, the recipient chooses a lakehouse where a shortcut to the shared data will be created.
External data share links don't work for users who are in the tenant where the external data share was created. They work only for users in external tenants. To share data from OneLake storage accounts with users in the same tenant, use OneLake shortcuts.
Note
Cross-tenant data access is enabled via a dedicated Fabric-to-Fabric authentication mechanism and does not require Entra B2B guest user access.
Supported Fabric item types
The Fabric item types that can be used in external data sharing are listed below.
Creating an external data share (provider tenant): External data shares can be created only for data residing in tables or files in lakehouses and mirrored databases.
Accepting an external data share (consuming tenant): Only lakehouses can be chosen as the location of the external data share shortcut when accepting an external data share.
Revoking external data shares
Any user in the sharing tenant who has read and reshare permissions on an externally shared item can revoke the external data share at any time using the External data shares tab on the manage permissions page. Revoking external data shares can have serious implications for the consuming tenants and should be considered carefully. For more information, see Revoking external data shares.
Security Considerations
Sharing data with users outside your home tenant has implications for data security and privacy that you should consider. It's important to understand the underlying flows of data sharing to better evaluate these implications.
Data is shared across tenants using Fabric-internal security mechanisms. The share security mechanism grants read-only access to any user within the home tenant of the user that was invited to accept the share. Data is shared “in-place”. No data is copied, and it isn't even accessed until the someone in the receiving tenant executes a Fabric workload over the shared data. Fabric evaluates and enforces Entra-ID-based roles and permissions locally, within the tenant they're defined in. This means that access control policies defined in the sharer's tenant, such as semantic model row-level security (RLS), Microsoft Purview Information Protection policies, and Purview Data Loss Prevention policies are not enforced on data that crosses organization boundaries. Rather, it is the policies defined in the consumer's tenant that are enforced on the incoming share, the same way that they're enforced on any data within that tenant.
With this understanding in mind, be aware of the following:
The sharer can't control who has access to the data in the consumer's tenant. For more information about how access control applied in the consumer tenant is enforced, see Information protection in Microsoft Fabric and Power BI: Access control.
The consumer can grant access to the data to anyone, even guest users from outside the consumer's organization.
Data might be transferred across geographic boundaries when it's accessed within the consumer's tenant.
Considerations and limitations
Shortcuts: Shortcuts contained in folders that are shared via external data sharing won't resolve in the consumer tenant.
Sharing schemas: Sharing an entire schema doesn't work: Lakehouse supports database schemas, but if you share one, it won't work.
External data shares in non-home regions: External data shares can only be accepted in a capacity that is located in the same region as the tenant. For example, if a tenant is in East US and has two capacities, one in East US and one in West US, users won't be able to accept shares in Lakehouses that use the West US capacity.