자습서: Azure Notification Hubs를 사용하여 특정 사용자에게 알림 푸시
이 자습서에서는 Azure Notification Hubs를 사용하여 특정 디바이스의 특정 앱 사용자에게 푸시 알림을 보내는 방법을 보여 줍니다. 앱 백 엔드에서 등록 지침 항목에 나와 있는 대로 ASP.NET WebAPI 백 엔드는 클라이언트를 인증하고 알림을 생성하는 데 사용됩니다.
이 자습서에서 수행하는 단계는 다음과 같습니다.
- WebAPI 프로젝트 만들기
- WebAPI 백 엔드에 클라이언트 인증
- WebAPI 백 엔드를 사용하여 알림 등록
- WebAPI 백 엔드에서 알림 보내기
- 새 WebAPI 백 엔드 게시
- iOS 앱 수정
- 애플리케이션 테스트
필수 조건
이 자습서에서는 Azure Notification Hubs를 사용하여 iOS 앱에 푸시 알림 보내기에 설명된 대로 알림 허브를 생성하고 구성했다고 가정합니다. 이 자습서는 보안 푸시(iOS) 자습서의 필수 조건이기도 합니다. Mobile Apps을 백 엔드 서비스로 사용하려는 경우 Mobile Apps 푸시 시작을 참조하세요.
WebAPI 프로젝트 만들기
다음 섹션에서는 새 ASP.NET WebAPI 백 엔드 만들기를 설명합니다. 이 프로세스에는 세 가지 주요 목적이 있습니다.
- 클라이언트 인증: 클라이언트 요청을 인증하고 사용자를 요청과 연결하는 메시지 처리기를 추가합니다.
- WebAPI 백 엔드를 사용하여 알림 등록: 클라이언트 디바이스에서 알림을 받을 수 있도록 새 등록을 처리하는 컨트롤러를 추가합니다. 인증된 사용자 이름은 태그로 등록에 자동으로 추가됩니다.
- 클라이언트로 알림 보내기: 사용자가 태그와 연결된 디바이스 및 클라이언트로 보안 푸시를 트리거할 수 있는 방법을 제공하는 컨트롤러를 추가합니다.
다음 작업을 수행하여 새 ASP.NET Core 6.0 웹 API 백 엔드를 만듭니다.
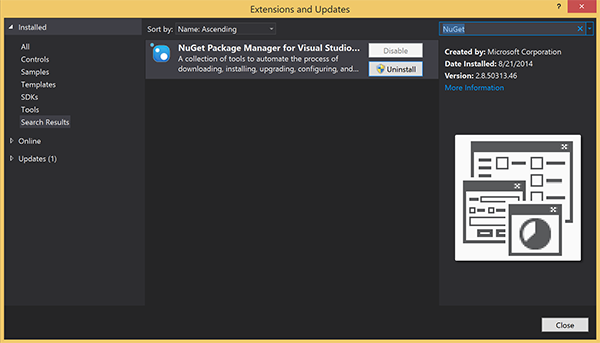
확인하려면 Visual Studio를 시작합니다. 도구 메뉴에서 확장 및 업데이트를 선택합니다. 사용하는 Visual Studio 버전에서 NuGet 패키지 관리자를 검색하고, 현재 버전이 최신 버전인지 확인합니다. 사용하는 버전이 최신 버전이 아닌 경우 해당 버전을 제거한 다음 NuGet 패키지 관리자를 다시 설치합니다.
참고 항목
웹 사이트 배포를 위해 Visual Studio Azure SDK를 설치했는지 확인합니다.
Visual Studio 또는 Visual Studio Express를 시작합니다.
서버 탐색기를 선택하고 Azure 계정에 로그인합니다. 계정에 웹 사이트 리소스를 만들려면 로그인해야 합니다.
Visual Studio의 파일 메뉴에서 새로 만들기>프로젝트를 선택합니다.
검색 상자에 Web API를 입력합니다.
ASP.NET Core 웹 API 프로젝트 템플릿을 선택하고 다음을 선택합니다.
새 프로젝트 구성 대화 상자에서 AppBackend 프로젝트 이름을 지정하고 다음을 선택합니다.
추가 정보 대화 상자에서 다음을 수행합니다.
- 프레임워크가 .Net 6.0(장기 지원)인지 확인합니다.
- 컨트롤러 사용(최소 API를 사용하려면 선택 취소) 확인란을 선택합니다.
- OpenAPI 지원 사용을 선택 취소합니다.
- 만들기를 실행합니다.
WeatherForecast 템플릿 파일 제거
- 새 AppBackend 프로젝트에서 WeatherForecast.cs 및 Controllers/WeatherForecastController.cs 예제 파일을 제거합니다.
- Properties\launchSettings.json을 엽니다.
- launchUrl 속성을 weatherforcast에서 appbackend로 변경합니다.
Microsoft Azure 웹앱 구성 창에서 구독을 선택한 다음, App Service 계획 목록에서 다음 작업 중 하나를 수행합니다.
- 이미 작성한 Azure App Service 요금제를 선택합니다.
- 새 앱 서비스 계획 만들기를 선택한 다음 새로 만듭니다.
이 자습서를 위해 데이터베이스는 필요하지 않습니다. 앱 서비스 계획을 선택한 후 확인을 선택하여 프로젝트를 만듭니다.
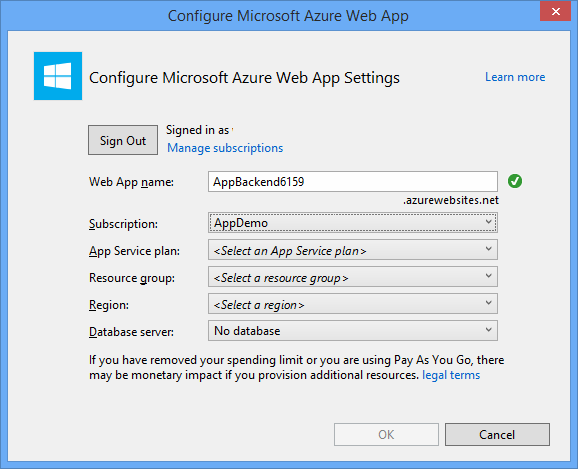
App Service 계획 구성에 사용되는 이 페이지가 보이지 않을 경우 자습서를 진행하세요. 나중에 앱을 게시할 때 구성할 수 있습니다.
WebAPI 백 엔드에 클라이언트 인증
이 섹션에서는 새 백 엔드에 대해 AuthenticationTestHandler라는 새 메시지 처리기 클래스를 만듭니다. 이 클래스는 DelegatingHandler에서 파생되며 백 엔드로 들어오는 모든 요청을 처리할 수 있도록 메시지 처리기로 추가됩니다.
솔루션 탐색기에서 AppBackend 프로젝트를 마우스 오른쪽 단추로 클릭하고 추가, 클래스를 차례로 선택합니다.
새 클래스의 이름을 AuthenticationTestHandler.cs로 지정한 다음 추가를 선택하여 클래스를 생성합니다. 이 클래스는 간단히 하기 위해 기본 인증을 사용하여 사용자를 인증합니다. 앱은 모든 인증 체계를 사용할 수 있습니다.
AuthenticationTestHandler.cs에 다음
using문을 추가합니다.using System.Net.Http; using System.Threading; using System.Security.Principal; using System.Net; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks;AuthenticationTestHandler.cs에서
AuthenticationTestHandler클래스 정의를 다음 코드로 바꿉니다.처리기는 다음 세 가지 조건이 충족될 때 요청을 인증합니다.
- 요청에 Authorization 헤더가 포함되어 있습니다.
- 요청이 기본 인증을 사용합니다.
- 사용자 이름 문자열과 암호 문자열은 동일한 문자열입니다.
그렇지 않으면 요청이 거부됩니다. 이 인증은 실제 인증 및 권한 부여 방법이 아닙니다. 이 자습서를 위한 간단한 예제일 뿐입니다.
요청 메시지가
AuthenticationTestHandler에 의해 인증되고 권한이 부여되면 HttpContext의 현재 요청에 기본 인증 사용자가 연결됩니다. HttpContext의 사용자 정보는 나중에 다른 컨트롤러(RegisterController)에서 알림 등록 요청에 태그를 추가하는 데 사용됩니다.public class AuthenticationTestHandler : DelegatingHandler { protected override Task<HttpResponseMessage> SendAsync( HttpRequestMessage request, CancellationToken cancellationToken) { var authorizationHeader = request.Headers.GetValues("Authorization").First(); if (authorizationHeader != null && authorizationHeader .StartsWith("Basic ", StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase)) { string authorizationUserAndPwdBase64 = authorizationHeader.Substring("Basic ".Length); string authorizationUserAndPwd = Encoding.Default .GetString(Convert.FromBase64String(authorizationUserAndPwdBase64)); string user = authorizationUserAndPwd.Split(':')[0]; string password = authorizationUserAndPwd.Split(':')[1]; if (VerifyUserAndPwd(user, password)) { // Attach the new principal object to the current HttpContext object HttpContext.Current.User = new GenericPrincipal(new GenericIdentity(user), new string[0]); System.Threading.Thread.CurrentPrincipal = System.Web.HttpContext.Current.User; } else return Unauthorized(); } else return Unauthorized(); return base.SendAsync(request, cancellationToken); } private bool VerifyUserAndPwd(string user, string password) { // This is not a real authentication scheme. return user == password; } private Task<HttpResponseMessage> Unauthorized() { var response = new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.Forbidden); var tsc = new TaskCompletionSource<HttpResponseMessage>(); tsc.SetResult(response); return tsc.Task; } }참고 항목
보안 정보:
AuthenticationTestHandler클래스는 진정한 의미의 인증을 제공하지 않습니다. 이 클래스는 기본 인증과 비슷한 동작을 하고 보안이 안전하지 않습니다. 프로덕션 애플리케이션 및 서비스에 보안 인증 메커니즘을 구현해야 합니다.메시지 처리기를 등록하려면 Program.cs 파일의
Register메서드 끝에 다음 코드를 추가합니다.config.MessageHandlers.Add(new AuthenticationTestHandler());변경 내용을 저장합니다.
WebAPI 백 엔드를 사용하여 알림 등록
이 섹션에서는 알림 허브에 클라이언트 라이브러리를 사용하여 알림을 위한 사용자 및 디바이스 등록 요청을 처리하는 새 컨트롤러를 WebAPI 백 엔드에 추가합니다. 이 컨트롤러는 AuthenticationTestHandler에 의해 인증되고 HttpContext에 연결된 사용자에 대한 사용자 태그를 추가합니다. 태그의 문자열 형식은 "username:<actual username>"입니다.
솔루션 탐색기에서 AppBackend 프로젝트를 마우스 오른쪽 단추로 클릭한 다음 NuGet 패키지 관리를 선택합니다.
왼쪽 창에서 온라인을 선택한 다음 검색 상자에 Microsoft.Azure.NotificationHubs를 입력합니다.
결과 목록에서 Microsoft Azure Notification Hubs를 선택한 다음 설치를 선택합니다. 설치를 완료한 다음, NuGet 패키지 관리자 창을 닫습니다.
이 작업은 Microsoft.Azure.Notification Hubs NuGet 패키지를 사용하는 Azure Notification Hubs SDK에 대한 참조를 추가합니다.
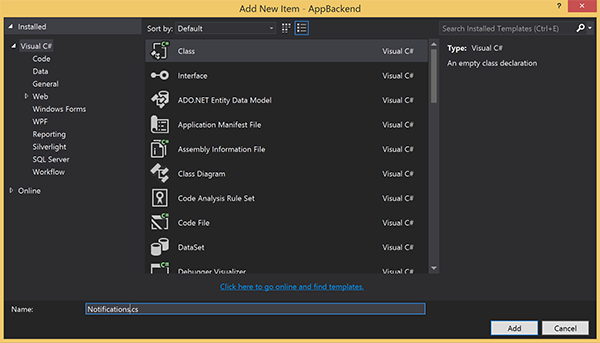
알림을 보내는 데 사용되는 알림 허브와의 연결을 나타내는 새 클래스 파일을 만듭니다. 솔루션 탐색기에서 Models 폴더를 마우스 오른쪽 단추로 클릭한 후 추가, 클래스를 차례로 선택합니다. 새 클래스 이름을 Notifications.cs로 지정한 후 추가를 선택하여 클래스를 생성합니다.
Notifications.cs에서 파일의 맨 위에
using문을 추가합니다.using Microsoft.Azure.NotificationHubs;Notifications클래스 정의를 다음 코드로 바꾸고 두 개의 자리 표시자를 알림 허브에 대한 연결 문자열(모든 권한 사용) 및 허브 이름(Azure Portal에서 제공)으로 바꿉니다.public class Notifications { public static Notifications Instance = new Notifications(); public NotificationHubClient Hub { get; set; } private Notifications() { Hub = NotificationHubClient.CreateClientFromConnectionString("<your hub's DefaultFullSharedAccessSignature>", "<hub name>"); } }Important
허브의 이름과 DefaultFullSharedAccessSignature를 입력하고 계속 진행합니다.
다음으로 RegisterController라는 새 컨트롤러를 만듭니다. 솔루션 탐색기에서 Controllers 폴더를 마우스 오른쪽 단추로 클릭한 후 추가, 컨트롤러를 차례로 선택합니다.
API 컨트롤러 - 비어 있음을 선택한 다음 추가를 선택합니다.
컨트롤러 이름 상자에서 RegisterController를 입력하여 새 클래스의 이름을 지정한 다음 추가를 선택합니다.
RegiterController.cs에 다음
using문을 추가합니다.using Microsoft.Azure.NotificationHubs; using Microsoft.Azure.NotificationHubs.Messaging; using AppBackend.Models; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Web;다음 코드를
RegisterController클래스 정의 내에 추가합니다. 이 코드에서 HttpContext에 연결된 사용자에 대한 사용자 태그를 추가합니다. 사용자는 추가한 메시지 필터AuthenticationTestHandler에 의해 인증되고 HttpContext에 연결되었습니다. 또한 선택적인 검사를 추가하여 사용자에게 요청된 태그에 등록할 수 있는 권한이 있는지 확인합니다.private NotificationHubClient hub; public RegisterController() { hub = Notifications.Instance.Hub; } public class DeviceRegistration { public string Platform { get; set; } public string Handle { get; set; } public string[] Tags { get; set; } } // POST api/register // This creates a registration id public async Task<string> Post(string handle = null) { string newRegistrationId = null; // make sure there are no existing registrations for this push handle (used for iOS and Android) if (handle != null) { var registrations = await hub.GetRegistrationsByChannelAsync(handle, 100); foreach (RegistrationDescription registration in registrations) { if (newRegistrationId == null) { newRegistrationId = registration.RegistrationId; } else { await hub.DeleteRegistrationAsync(registration); } } } if (newRegistrationId == null) newRegistrationId = await hub.CreateRegistrationIdAsync(); return newRegistrationId; } // PUT api/register/5 // This creates or updates a registration (with provided channelURI) at the specified id public async Task<HttpResponseMessage> Put(string id, DeviceRegistration deviceUpdate) { RegistrationDescription registration = null; switch (deviceUpdate.Platform) { case "mpns": registration = new MpnsRegistrationDescription(deviceUpdate.Handle); break; case "wns": registration = new WindowsRegistrationDescription(deviceUpdate.Handle); break; case "apns": registration = new AppleRegistrationDescription(deviceUpdate.Handle); break; case "fcm": registration = new FcmRegistrationDescription(deviceUpdate.Handle); break; default: throw new HttpResponseException(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest); } registration.RegistrationId = id; var username = HttpContext.Current.User.Identity.Name; // add check if user is allowed to add these tags registration.Tags = new HashSet<string>(deviceUpdate.Tags); registration.Tags.Add("username:" + username); try { await hub.CreateOrUpdateRegistrationAsync(registration); } catch (MessagingException e) { ReturnGoneIfHubResponseIsGone(e); } return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK); } // DELETE api/register/5 public async Task<HttpResponseMessage> Delete(string id) { await hub.DeleteRegistrationAsync(id); return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK); } private static void ReturnGoneIfHubResponseIsGone(MessagingException e) { var webex = e.InnerException as WebException; if (webex.Status == WebExceptionStatus.ProtocolError) { var response = (HttpWebResponse)webex.Response; if (response.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.Gone) throw new HttpRequestException(HttpStatusCode.Gone.ToString()); } }변경 내용을 저장합니다.
WebAPI 백 엔드에서 알림 보내기
이 섹션에서는 클라이언트 디바이스에서 알림을 보내기 위한 방법을 노출하는 새 컨트롤러를 추가합니다. 알림은 ASP.NET WebAPI 백 엔드에서 Azure Notification Hubs .NET 라이브러리를 사용하는 사용자 이름 태그를 기반으로 합니다.
이전 섹션에서 RegisterController를 만들었던 동일한 방식으로 NotificationsController라는 다른 새 컨트롤러를 만듭니다.
NotificationsController.cs에 다음
using문을 추가합니다.using AppBackend.Models; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Web;NotificationsController 클래스에 다음 메서드를 추가합니다.
이 코드는 PNS(Platform Notification Service)
pns매개 변수를 기반으로 알림 유형을 보냅니다.to_tag값은 메시지에서 사용자 이름 태그를 지정하는 데 사용됩니다. 이 태그는 활성 알림 허브 등록의 사용자 이름 태그와 일치해야 합니다. 알림 메시지는 POST 요청의 본문에서 가져오고 대상 PNS에 맞게 형식이 지정됩니다.알림을 수신하기 위해 지원되는 디바이스가 사용하는 PNS에 따라 다양한 형식으로 알림을 지원합니다. 예를 들어 Windows 디바이스에서 다른 PNS에서 직접 지원되지 않는 WNS로 알림을 사용할 수 있습니다. 이러한 상황에서 백 엔드는 알림을 지원하려는 디바이스의 PNS에 지원되는 알림으로 포맷해야 합니다. 그런 다음 NotificationHubClient 클래스에서 적절한 보내기 API를 사용합니다.
public async Task<HttpResponseMessage> Post(string pns, [FromBody]string message, string to_tag) { var user = HttpContext.Current.User.Identity.Name; string[] userTag = new string[2]; userTag[0] = "username:" + to_tag; userTag[1] = "from:" + user; Microsoft.Azure.NotificationHubs.NotificationOutcome outcome = null; HttpStatusCode ret = HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError; switch (pns.ToLower()) { case "wns": // Windows 8.1 / Windows Phone 8.1 var toast = @"<toast><visual><binding template=""ToastText01""><text id=""1"">" + "From " + user + ": " + message + "</text></binding></visual></toast>"; outcome = await Notifications.Instance.Hub.SendWindowsNativeNotificationAsync(toast, userTag); break; case "apns": // iOS var alert = "{\"aps\":{\"alert\":\"" + "From " + user + ": " + message + "\"}}"; outcome = await Notifications.Instance.Hub.SendAppleNativeNotificationAsync(alert, userTag); break; case "fcm": // Android var notif = "{ \"data\" : {\"message\":\"" + "From " + user + ": " + message + "\"}}"; outcome = await Notifications.Instance.Hub.SendFcmNativeNotificationAsync(notif, userTag); break; } if (outcome != null) { if (!((outcome.State == Microsoft.Azure.NotificationHubs.NotificationOutcomeState.Abandoned) || (outcome.State == Microsoft.Azure.NotificationHubs.NotificationOutcomeState.Unknown))) { ret = HttpStatusCode.OK; } } return Request.CreateResponse(ret); }애플리케이션을 실행하고 지금까지 작업의 정확성을 확인하려면 F5 키를 선택합니다. 앱은 웹 브라우저를 열고 ASP.NET 홈페이지에 표시됩니다.
새 WebAPI 백 엔드 게시
다음으로 모든 디바이스에서 액세스할 수 있도록 앱을 Azure 웹 사이트에 배포합니다.
AppBackend 프로젝트를 마우스 오른쪽 단추로 클릭한 다음 게시를 선택합니다.
Microsoft Azure App Service를 게시 대상으로 선택한 다음, \*\*[게시]를 선택합니다. App Service 만들기 창이 열립니다. 여기에서 Azure에서 ASP.NET 웹앱을 실행하는 데 필요한 모든 Azure 리소스를 만들 수 있습니다.
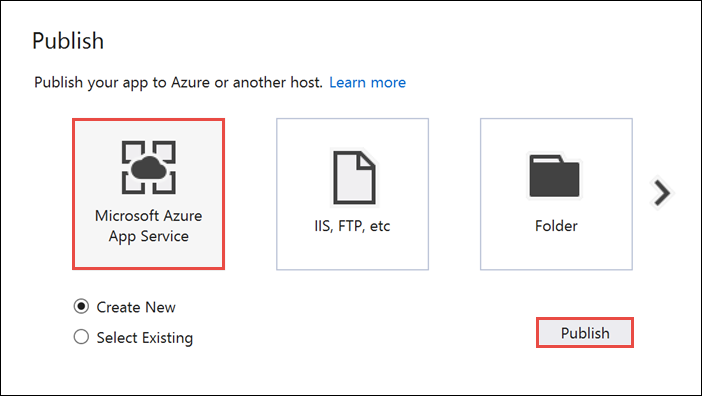
App Service 만들기 창에서 Azure 계정을 선택합니다. 유형 변경>웹앱을 선택합니다. 기본 웹앱 이름을 유지한 다음 구독, 리소스 그룹, App Service 계획을 차례로 선택합니다.
만들기를 실행합니다.
요약 섹션의 사이트 URL 속성을 메모해 둡니다. 이 URL은 자습서의 뒷부분에서 백 엔드 엔드포인트입니다.
게시를 선택합니다.
마법사를 완료한 후 Azure에 ASP.NET 웹앱을 게시한 다음 기본 브라우저에서 앱을 엽니다. 애플리케이션을 Azure App Services에서 볼 수 있습니다.
URL은 http://<app_name>.azurewebsites.net 형식으로 이전에 지정한 웹앱 이름을 사용합니다.
iOS 앱 수정
Azure Notification Hubs를 사용하여 iOS 앱에 푸시 알림 보내기 자습서에서 생성한 단일 페이지 보기 앱을 엽니다.
참고 항목
이 섹션에서는 빈 조직 이름을 사용하여 프로젝트를 구성했다고 가정합니다. 그렇지 않은 경우 모든 클래스 이름에 조직 이름을 접두어로 붙입니다.
Main.storyboard파일에서 개체 라이브러리에서 스크린샷에 표시된 구성 요소를 추가합니다.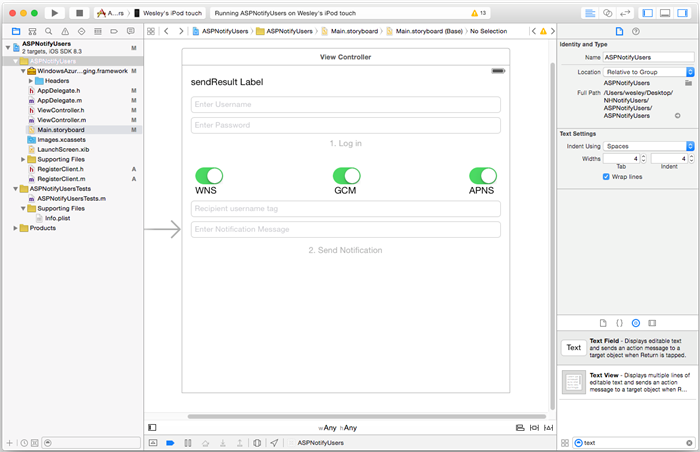
Username: 자리 표시자 텍스트가 있는 UITextField, 사용자 이름 입력, 바로 아래 결과 레이블 보내기를 지정하고 왼쪽 및 오른쪽 여백 및 보내기 결과 레이블 아래로 제한됩니다.
암호: 자리 표시자 텍스트가 있는 UITextField, 사용자 이름 입력, 바로 아래 사용자 이름 텍스트 필드 및 왼쪽 및 오른쪽 여백 및 사용자 이름 텍스트 필드 아래로 제한됩니다. 반환 키 아래 특성 검사기에서 텍스트 항목 보안옵션을 선택합니다.
로그인: 암호 텍스트 필드 바로 아래 레이블이 지정된 UIButton, Control-Content 아래 특성 검사기에서 사용 옵션의 선택을 취소합니다.
WNS: 허브에 설치된 경우 알림을 Windows 알림 서비스로 보낼 수 있는 레이블 및 스위치입니다. Windows 시작 자습서를 참조하세요.
GCM: 허브에 설치된 경우 알림을 Google 클라우드 메시징으로 보낼 수 있는 레이블 및 스위치입니다. Android 시작 자습서를 참조하세요.
APNS: Apple 플랫폼 알림 서비스로 알림을 보낼 수 있는 레이블 및 스위치입니다.
받는 사람 사용자 이름: 자리 표시자 텍스트가 있는 UITextField, 받는 사람 사용자 이름 태그, GCM 레이블 바로 아래이며 왼쪽 및 오른쪽 여백으로 제한되고 GCM 레이블 아래입니다.
일부 구성 요소는 Azure Notification Hubs를 사용하여 iOS 앱에 푸시 알림 보내기 자습서에 추가되었습니다.
보기의 구성 요소에서 Ctrl 키를 누른 채로
ViewController.h로 끌어서 이 새 아웃렛을 추가합니다.@property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextField *UsernameField; @property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextField *PasswordField; @property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextField *RecipientField; @property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UITextField *NotificationField; // Used to enable the buttons on the UI @property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UIButton *LogInButton; @property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UIButton *SendNotificationButton; // Used to enabled sending notifications across platforms @property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UISwitch *WNSSwitch; @property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UISwitch *GCMSwitch; @property (weak, nonatomic) IBOutlet UISwitch *APNSSwitch; - (IBAction)LogInAction:(id)sender;ViewController.h에서 다음#define을 import 문 뒤에 추가합니다.<Your backend endpoint>자리 표시자를 이전 섹션에서 앱 백 엔드를 배포하는 데 사용한 대상 URL로 대체합니다. 예:http://your_backend.azurewebsites.net#define BACKEND_ENDPOINT @"<Your backend endpoint>"프로젝트에서 사용자가 만든 ASP.NET 백 엔드를 사용하여
RegisterClient라는 새 Cocoa Touch 클래스를 인터페이스에 만듭니다.NSObject에서 상속하는 클래스를 만듭니다. 그런 다음, 다음 코드를RegisterClient.h에 추가합니다.@interface RegisterClient : NSObject @property (strong, nonatomic) NSString* authenticationHeader; -(void) registerWithDeviceToken:(NSData*)token tags:(NSSet*)tags andCompletion:(void(^)(NSError*))completion; -(instancetype) initWithEndpoint:(NSString*)Endpoint; @endRegisterClient.m에서@interface섹션을 업데이트합니다.@interface RegisterClient () @property (strong, nonatomic) NSURLSession* session; @property (strong, nonatomic) NSURLSession* endpoint; -(void) tryToRegisterWithDeviceToken:(NSData*)token tags:(NSSet*)tags retry:(BOOL)retry andCompletion:(void(^)(NSError*))completion; -(void) retrieveOrRequestRegistrationIdWithDeviceToken:(NSString*)token completion:(void(^)(NSString*, NSError*))completion; -(void) upsertRegistrationWithRegistrationId:(NSString*)registrationId deviceToken:(NSString*)token tags:(NSSet*)tags andCompletion:(void(^)(NSURLResponse*, NSError*))completion; @endRegisterClient.m의
@implementation섹션을 다음 코드로 바꿉니다.@implementation RegisterClient // Globals used by RegisterClient NSString *const RegistrationIdLocalStorageKey = @"RegistrationId"; -(instancetype) initWithEndpoint:(NSString*)Endpoint { self = [super init]; if (self) { NSURLSessionConfiguration* config = [NSURLSessionConfiguration defaultSessionConfiguration]; _session = [NSURLSession sessionWithConfiguration:config delegate:nil delegateQueue:nil]; _endpoint = Endpoint; } return self; } -(void) registerWithDeviceToken:(NSData*)token tags:(NSSet*)tags andCompletion:(void(^)(NSError*))completion { [self tryToRegisterWithDeviceToken:token tags:tags retry:YES andCompletion:completion]; } -(void) tryToRegisterWithDeviceToken:(NSData*)token tags:(NSSet*)tags retry:(BOOL)retry andCompletion:(void(^)(NSError*))completion { NSSet* tagsSet = tags?tags:[[NSSet alloc] init]; NSString *deviceTokenString = [[token description] stringByTrimmingCharactersInSet:[NSCharacterSet characterSetWithCharactersInString:@"<>"]]; deviceTokenString = [[deviceTokenString stringByReplacingOccurrencesOfString:@" " withString:@""] uppercaseString]; [self retrieveOrRequestRegistrationIdWithDeviceToken: deviceTokenString completion:^(NSString* registrationId, NSError *error) { NSLog(@"regId: %@", registrationId); if (error) { completion(error); return; } [self upsertRegistrationWithRegistrationId:registrationId deviceToken:deviceTokenString tags:tagsSet andCompletion:^(NSURLResponse * response, NSError *error) { if (error) { completion(error); return; } NSHTTPURLResponse* httpResponse = (NSHTTPURLResponse*)response; if (httpResponse.statusCode == 200) { completion(nil); } else if (httpResponse.statusCode == 410 && retry) { [self tryToRegisterWithDeviceToken:token tags:tags retry:NO andCompletion:completion]; } else { NSLog(@"Registration error with response status: %ld", (long)httpResponse.statusCode); completion([NSError errorWithDomain:@"Registration" code:httpResponse.statusCode userInfo:nil]); } }]; }]; } -(void) upsertRegistrationWithRegistrationId:(NSString*)registrationId deviceToken:(NSData*)token tags:(NSSet*)tags andCompletion:(void(^)(NSURLResponse*, NSError*))completion { NSDictionary* deviceRegistration = @{@"Platform" : @"apns", @"Handle": token, @"Tags": [tags allObjects]}; NSData* jsonData = [NSJSONSerialization dataWithJSONObject:deviceRegistration options:NSJSONWritingPrettyPrinted error:nil]; NSLog(@"JSON registration: %@", [[NSString alloc] initWithData:jsonData encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]); NSString* endpoint = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@/api/register/%@", _endpoint, registrationId]; NSURL* requestURL = [NSURL URLWithString:endpoint]; NSMutableURLRequest* request = [NSMutableURLRequest requestWithURL:requestURL]; [request setHTTPMethod:@"PUT"]; [request setHTTPBody:jsonData]; NSString* authorizationHeaderValue = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Basic %@", self.authenticationHeader]; [request setValue:authorizationHeaderValue forHTTPHeaderField:@"Authorization"]; [request setValue:@"application/json" forHTTPHeaderField:@"Content-Type"]; NSURLSessionDataTask* dataTask = [self.session dataTaskWithRequest:request completionHandler:^(NSData *data, NSURLResponse *response, NSError *error) { if (!error) { completion(response, error); } else { NSLog(@"Error request: %@", error); completion(nil, error); } }]; [dataTask resume]; } -(void) retrieveOrRequestRegistrationIdWithDeviceToken:(NSString*)token completion:(void(^)(NSString*, NSError*))completion { NSString* registrationId = [[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] objectForKey:RegistrationIdLocalStorageKey]; if (registrationId) { completion(registrationId, nil); return; } // request new one & save NSURL* requestURL = [NSURL URLWithString:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@/api/register?handle=%@", _endpoint, token]]; NSMutableURLRequest* request = [NSMutableURLRequest requestWithURL:requestURL]; [request setHTTPMethod:@"POST"]; NSString* authorizationHeaderValue = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Basic %@", self.authenticationHeader]; [request setValue:authorizationHeaderValue forHTTPHeaderField:@"Authorization"]; NSURLSessionDataTask* dataTask = [self.session dataTaskWithRequest:request completionHandler:^(NSData *data, NSURLResponse *response, NSError *error) { NSHTTPURLResponse* httpResponse = (NSHTTPURLResponse*) response; if (!error && httpResponse.statusCode == 200) { NSString* registrationId = [[NSString alloc] initWithData:data encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]; // remove quotes registrationId = [registrationId substringWithRange:NSMakeRange(1, [registrationId length]-2)]; [[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] setObject:registrationId forKey:RegistrationIdLocalStorageKey]; [[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] synchronize]; completion(registrationId, nil); } else { NSLog(@"Error status: %ld, request: %@", (long)httpResponse.statusCode, error); if (error) completion(nil, error); else { completion(nil, [NSError errorWithDomain:@"Registration" code:httpResponse.statusCode userInfo:nil]); } } }]; [dataTask resume]; } @end이 코드는 NSURLSession를 사용하여 앱 백 엔드에 대한 REST 호출을 수행하고 NSUserDefaults를 사용하여 알림 허브에서 반환된 registrationId를 로컬로 저장하는, 지침 문서 앱 백 엔드에서 등록에서 설명된 논리를 구현합니다.
이 클래스가 제대로 작동하려면
authorizationHeader속성을 설정해야 합니다. 이 속성은 로그인 후에ViewController클래스에 의해 설정됩니다.ViewController.h에서RegisterClient.h에 대한#import문을 추가합니다. 그런 다음 디바이스 토큰에 대한 선언 및@interface섹션에서RegisterClient인스턴스에 대한 참조를 추가합니다.#import "RegisterClient.h" @property (strong, nonatomic) NSData* deviceToken; @property (strong, nonatomic) RegisterClient* registerClient;ViewController.m에서, 프라이빗 메서드 선언을
@interface섹션에 추가합니다.@interface ViewController () <UITextFieldDelegate, NSURLConnectionDataDelegate, NSXMLParserDelegate> // create the Authorization header to perform Basic authentication with your app back-end -(void) createAndSetAuthenticationHeaderWithUsername:(NSString*)username AndPassword:(NSString*)password; @end참고 항목
다음 코드 조각은 보안 인증 체계가 아닙니다.
createAndSetAuthenticationHeaderWithUsername:AndPassword:구현을 레지스터 클라이언트 클래스(예: OAuth, Active Directory)에서 사용할 인증 토큰을 생성하는 특정 인증 메커니즘으로 대체해야 합니다.그런 다음,
ViewController.m의@implementation섹션에 디바이스 토큰 및 인증 헤더 설정을 위한 구현을 추가하는 다음 코드를 추가합니다.-(void) setDeviceToken: (NSData*) deviceToken { _deviceToken = deviceToken; self.LogInButton.enabled = YES; } -(void) createAndSetAuthenticationHeaderWithUsername:(NSString*)username AndPassword:(NSString*)password; { NSString* headerValue = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@:%@", username, password]; NSData* encodedData = [[headerValue dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding] base64EncodedDataWithOptions:NSDataBase64EncodingEndLineWithCarriageReturn]; self.registerClient.authenticationHeader = [[NSString alloc] initWithData:encodedData encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]; } -(BOOL)textFieldShouldReturn:(UITextField *)textField { [textField resignFirstResponder]; return YES; }장치 토큰 설정이 어떻게 로그인 단추를 활성화하는지에 주목하세요. 이는 로그인 작업 중에 보기 컨트롤러가 푸시 알림을 앱 백 엔드에 등록하기 때문입니다. 장치 토큰이 제대로 설정되기 전에는 로그인 작업에 액세스하지 못하게 해야 합니다. 로그인 작업이 토큰 설정 전에 발생하는 경우 푸시 등록에서 로그인을 분리할 수 있습니다.
ViewController.m에서 다음 스니펫을 사용하여 로그인 단추에 대한 작업 메소드 및 ASP.NET 백엔드를 사용하여 알림 메시지를 보내는 메서드를 구현합니다.
- (IBAction)LogInAction:(id)sender { // create authentication header and set it in register client NSString* username = self.UsernameField.text; NSString* password = self.PasswordField.text; [self createAndSetAuthenticationHeaderWithUsername:username AndPassword:password]; __weak ViewController* selfie = self; [self.registerClient registerWithDeviceToken:self.deviceToken tags:nil andCompletion:^(NSError* error) { if (!error) { dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{ selfie.SendNotificationButton.enabled = YES; [self MessageBox:@"Success" message:@"Registered successfully!"]; }); } }]; } - (void)SendNotificationASPNETBackend:(NSString*)pns UsernameTag:(NSString*)usernameTag Message:(NSString*)message { NSURLSession* session = [NSURLSession sessionWithConfiguration:[NSURLSessionConfiguration defaultSessionConfiguration] delegate:nil delegateQueue:nil]; // Pass the pns and username tag as parameters with the REST URL to the ASP.NET backend NSURL* requestURL = [NSURL URLWithString:[NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@/api/notifications?pns=%@&to_tag=%@", BACKEND_ENDPOINT, pns, usernameTag]]; NSMutableURLRequest* request = [NSMutableURLRequest requestWithURL:requestURL]; [request setHTTPMethod:@"POST"]; // Get the mock authenticationheader from the register client NSString* authorizationHeaderValue = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Basic %@", self.registerClient.authenticationHeader]; [request setValue:authorizationHeaderValue forHTTPHeaderField:@"Authorization"]; //Add the notification message body [request setValue:@"application/json;charset=utf-8" forHTTPHeaderField:@"Content-Type"]; [request setHTTPBody:[message dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]]; // Execute the send notification REST API on the ASP.NET Backend NSURLSessionDataTask* dataTask = [session dataTaskWithRequest:request completionHandler:^(NSData *data, NSURLResponse *response, NSError *error) { NSHTTPURLResponse* httpResponse = (NSHTTPURLResponse*) response; if (error || httpResponse.statusCode != 200) { NSString* status = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Error Status for %@: %d\nError: %@\n", pns, httpResponse.statusCode, error]; dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{ // Append text because all 3 PNS calls may also have information to view [self.sendResults setText:[self.sendResults.text stringByAppendingString:status]]; }); NSLog(status); } if (data != NULL) { xmlParser = [[NSXMLParser alloc] initWithData:data]; [xmlParser setDelegate:self]; [xmlParser parse]; } }]; [dataTask resume]; }알림 보내기 단추의 작업을 업데이트하여 ASP.NET 백엔드를 사용하고 스위치에서 사용하도록 설정된 모든 PNS를 보냅니다.
- (IBAction)SendNotificationMessage:(id)sender { //[self SendNotificationRESTAPI]; [self SendToEnabledPlatforms]; } -(void)SendToEnabledPlatforms { NSString* json = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"\"%@\"",self.notificationMessage.text]; [self.sendResults setText:@""]; if ([self.WNSSwitch isOn]) [self SendNotificationASPNETBackend:@"wns" UsernameTag:self.RecipientField.text Message:json]; if ([self.GCMSwitch isOn]) [self SendNotificationASPNETBackend:@"gcm" UsernameTag:self.RecipientField.text Message:json]; if ([self.APNSSwitch isOn]) [self SendNotificationASPNETBackend:@"apns" UsernameTag:self.RecipientField.text Message:json]; }ViewDidLoad함수에서 다음을 추가하여RegisterClient인스턴스를 인스턴스화하고 텍스트 필드에 대한 대리자를 설정합니다.self.UsernameField.delegate = self; self.PasswordField.delegate = self; self.RecipientField.delegate = self; self.registerClient = [[RegisterClient alloc] initWithEndpoint:BACKEND_ENDPOINT];이제
AppDelegate.m에서application:didRegisterForPushNotificationWithDeviceToken:메서드의 모든 콘텐츠를 제거하고 다음으로 바꾸어 보기 컨트롤러에 APNs에서 검색된 최신 디바이스 토큰이 포함되도록 합니다.// Add import to the top of the file #import "ViewController.h" - (void)application:(UIApplication *)application didRegisterForRemoteNotificationsWithDeviceToken:(NSData *)deviceToken { ViewController* rvc = (ViewController*) self.window.rootViewController; rvc.deviceToken = deviceToken; }마지막으로
AppDelegate.m에서 다음 메서드가 있는지 확인합니다.- (void)application:(UIApplication *)application didReceiveRemoteNotification: (NSDictionary *)userInfo { NSLog(@"%@", userInfo); [self MessageBox:@"Notification" message:[[userInfo objectForKey:@"aps"] valueForKey:@"alert"]]; }
애플리케이션 테스트
XCode에서는 실제 iOS 디바이스에서 앱을 실행합니다(푸시 알림은 시뮬레이터에서 작동하지 않음).
iOS 앱 UI에서 사용자 이름과 암호에 동일한 값을 입력합니다. 그런 다음 Log In을 클릭합니다.
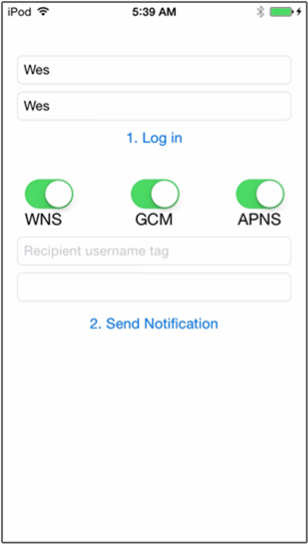
등록 성공을 알리는 팝업이 표시됩니다. 확인을 클릭합니다.
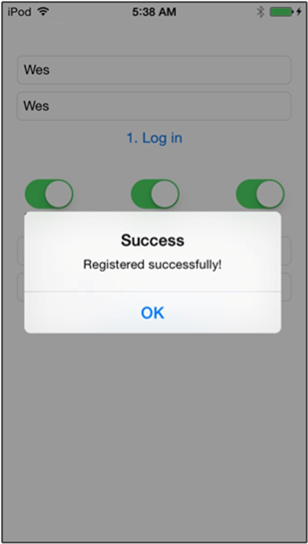
*받는 사람 사용자 이름 태그 텍스트 필드에 다른 디바이스에서 등록에 사용되는 사용자 이름 태그를 입력합니다.
알림 메시지를 입력하고 알림 보내기를 클릭합니다. 받는 사람 사용자 이름 태그로 등록된 디바이스만이 알림 메시지를 받습니다. 이러한 사용자에만 전송됩니다.
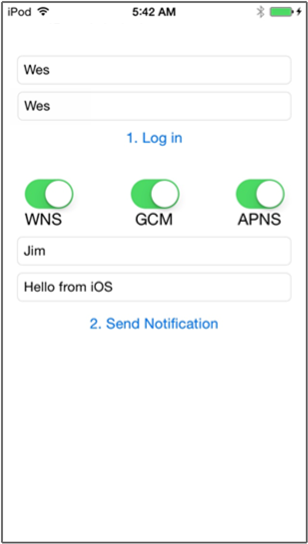
다음 단계
이 자습서에서는 등록에 태그가 연결된 특정 사용자에게 알림을 푸시하는 방법을 배웠습니다. 위치 기반 알림을 푸시하는 방법을 알아보려면 다음 자습서를 계속 진행합니다.
