A から B までのルートを表示する
この記事では、ルート要求を実行し、マップにルートを表示する方法について説明します。
これには 2 つ方法があります。 最初の方法は、TypeScript REST SDK @azure-rest/maps-route を使用して Get Route Directions API に対してクエリを実行することです。 2 番目の方法は、Fetch API を使用して、Get Route Directions API に対して検索要求を行う方法です。 どちらの方法も、この記事内で説明します。
REST SDK を使用してルートのクエリを実行する
import * as atlas from "azure-maps-control";
import MapsRoute, { toColonDelimitedLatLonString } from "@azure-rest/maps-route";
import "azure-maps-control/dist/atlas.min.css";
const onload = () => {
// Initialize a map instance.
const map = new atlas.Map("map", {
view: "Auto",
// Add authentication details for connecting to Azure Maps.
authOptions: {
// Use Azure Active Directory authentication.
authType: "aad",
clientId: "<Your Azure Maps Client Id>",
aadAppId: "<Your Azure Active Directory Client Id>",
aadTenant: "<Your Azure Active Directory Tenant Id>"
}
});
map.events.add("load", async () => {
// Use the access token from the map and create an object that implements the TokenCredential interface.
const credential = {
getToken: () => {
return {
token: map.authentication.getToken()
};
}
};
// Create a Route client.
const client = MapsRoute(credential, "<Your Azure Maps Client Id>");
// Create a data source and add it to the map.
const dataSource = new atlas.source.DataSource();
map.sources.add(dataSource);
// Create the GeoJSON objects which represent the start and end points of the route.
const startPoint = new atlas.data.Feature(new atlas.data.Point([-122.130137, 47.644702]), {
title: "Redmond",
icon: "pin-blue"
});
const endPoint = new atlas.data.Feature(new atlas.data.Point([-122.3352, 47.61397]), {
title: "Seattle",
icon: "pin-round-blue"
});
// Add the data to the data source.
dataSource.add([startPoint, endPoint]);
// Create a layer for rendering the route line under the road labels.
map.layers.add(
new atlas.layer.LineLayer(dataSource, null, {
strokeColor: "#2272B9",
strokeWidth: 5,
lineJoin: "round",
lineCap: "round"
}),
"labels"
);
// Create a layer for rendering the start and end points of the route as symbols.
map.layers.add(
new atlas.layer.SymbolLayer(dataSource, null, {
iconOptions: {
image: ["get", "icon"],
allowOverlap: true,
ignorePlacement: true
},
textOptions: {
textField: ["get", "title"],
offset: [0, 1.2]
},
filter: ["any", ["==", ["geometry-type"], "Point"], ["==", ["geometry-type"], "MultiPoint"]] //Only render Point or MultiPoints in this layer.
})
);
// Get the coordinates of the start and end points.
const coordinates = [
[startPoint.geometry.coordinates[1], startPoint.geometry.coordinates[0]],
[endPoint.geometry.coordinates[1], endPoint.geometry.coordinates[0]]
];
// Get the route directions between the start and end points.
const response = await client.path("/route/directions/{format}", "json").get({
queryParameters: {
query: toColonDelimitedLatLonString(coordinates)
}
});
// Get the GeoJSON feature collection of the route.
const data = getFeatures(response.body.routes);
// Add the route data to the data source.
dataSource.add(data);
// Update the map view to center over the route.
map.setCamera({
bounds: data.bbox,
padding: 40
});
});
};
/**
* Helper function to convert a route response into a GeoJSON FeatureCollection.
*/
const getFeatures = (routes) => {
const bounds = [];
const features = routes.map((route, index) => {
const multiLineCoords = route.legs.map((leg) => {
return leg.points.map((coord) => {
const position = [coord.longitude, coord.latitude];
bounds.push(position);
return position;
});
});
// Include all properties on the route object except legs.
// Legs is used to create the MultiLineString, so we only need the summaries.
// The legSummaries property replaces the legs property with just summary data.
const props = {
...route,
legSummaries: route.legs.map((leg) => leg.summary),
resultIndex: index
};
delete props.legs;
return {
type: "Feature",
geometry: {
type: "MultiLineString",
coordinates: multiLineCoords
},
properties: props
};
});
return {
type: "FeatureCollection",
features: features,
bbox: new atlas.data.BoundingBox.fromLatLngs(bounds)
};
};
document.body.onload = onload;
上記のコード例において、最初のブロックはマップ オブジェクトを構築し、Microsoft Entra ID を使用するための認証メカニズムを設定します。 手順については、「マップの作成」を参照してください。
2 つ目のコード ブロックはアクセス トークンを使用して Azure Maps に対して HTTP 要求を認証するための TokenCredential インターフェイスを実装するオブジェクトを作成します。 その後、資格情報オブジェクトを MapsRoute に渡し、クライアントのインスタンスを作成します。
3 つ目のコード ブロックでは、DataSource オブジェクトが作成され、マップに追加されます。
4 つ目のコード ブロックでは、開始と終了の points オブジェクトが作成され、それらが dataSource オブジェクトに追加されます。
線は、LineString の Feature です。 LineLayer によって、DataSource にラップされた線オブジェクトが、マップ上に線としてレンダリングされます。 4 つ目のコード ブロックでは、線レイヤーが作成され、マップに追加されます。 線レイヤーのプロパティについては、LinestringLayerOptions に関する記事をご覧ください。
シンボル レイヤーは、テキストまたはアイコンを使用して、DataSource にラップされたポイントベースのデータをレンダリングします。 テキストまたはアイコンはシンボルとしてマップにレンダリングされます。 5 つ目のコード ブロックでは、シンボル レイヤーが作成され、マップに追加されます。
6 つ目のコード ブロックは、MapsRoute クライアントの一部である Azure Maps ルーティング サービスに対してクエリを実行します。 GET 要求は、開始点と終了点の間のルートを取得するために使用されます。 その後に getFeatures() ヘルパー関数を使用して応答から GeoJSON 地物コレクションが抽出され、データソースに追加されます。 次に、応答はマップ上にルートとしてレンダリングされます。 マップへの線の追加の詳細については、「マップへの線の追加」を参照してください。
最後のコード ブロックでは、マップの setCamera プロパティを使用してマップの境界が設定されます。
ルート クエリ、データ ソース、シンボル、線レイヤー、カメラの境界が、イベント リスナー内に作成されます。 このコード構造を使用すると、マップが完全に読み込まれた後にのみ結果が確実に表示されるようになります。
Fetch API を介してルートのクエリを実行する
import * as atlas from "azure-maps-control";
import "azure-maps-control/dist/atlas.min.css";
const onload = () => {
// Initialize a map instance.
const map = new atlas.Map("map", {
view: "Auto",
// Add authentication details for connecting to Azure Maps.
authOptions: {
// Use Azure Active Directory authentication.
authType: "aad",
clientId: "<Your Azure Maps Client Id>",
aadAppId: "<Your Azure Active Directory Client Id>",
aadTenant: "<Your Azure Active Directory Tenant Id>"
}
});
map.events.add("load", async () => {
// Create a data source and add it to the map.
const dataSource = new atlas.source.DataSource();
map.sources.add(dataSource);
// Create the GeoJSON objects which represent the start and end points of the route.
const startPoint = new atlas.data.Feature(new atlas.data.Point([-122.130137, 47.644702]), {
title: "Redmond",
icon: "pin-blue"
});
const endPoint = new atlas.data.Feature(new atlas.data.Point([-122.3352, 47.61397]), {
title: "Seattle",
icon: "pin-round-blue"
});
// Add the data to the data source.
dataSource.add([startPoint, endPoint]);
// Create a layer for rendering the route line under the road labels.
map.layers.add(
new atlas.layer.LineLayer(dataSource, null, {
strokeColor: "#2272B9",
strokeWidth: 5,
lineJoin: "round",
lineCap: "round"
}),
"labels"
);
// Create a layer for rendering the start and end points of the route as symbols.
map.layers.add(
new atlas.layer.SymbolLayer(dataSource, null, {
iconOptions: {
image: ["get", "icon"],
allowOverlap: true,
ignorePlacement: true
},
textOptions: {
textField: ["get", "title"],
offset: [0, 1.2]
},
filter: ["any", ["==", ["geometry-type"], "Point"], ["==", ["geometry-type"], "MultiPoint"]] //Only render Point or MultiPoints in this layer.
})
);
// Send a request to the route API
let url = "https://atlas.microsoft.com/route/directions/json?";
url += "&api-version=1.0";
url +=
"&query=" +
startPoint.geometry.coordinates[1] +
"," +
startPoint.geometry.coordinates[0] +
":" +
endPoint.geometry.coordinates[1] +
"," +
endPoint.geometry.coordinates[0];
// Process request
fetch(url, {
headers: {
Authorization: "Bearer " + map.authentication.getToken(),
"x-ms-client-id": "<Your Azure Maps Client Id>"
}
})
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((response) => {
const bounds = [];
const route = response.routes[0];
// Create an array to store the coordinates of each turn
let routeCoordinates = [];
route.legs.forEach((leg) => {
const legCoordinates = leg.points.map((point) => {
const position = [point.longitude, point.latitude];
bounds.push(position);
return position;
});
// Add each turn coordinate to the array
routeCoordinates = routeCoordinates.concat(legCoordinates);
});
// Add route line to the dataSource
dataSource.add(new atlas.data.Feature(new atlas.data.LineString(routeCoordinates)));
// Update the map view to center over the route.
map.setCamera({
bounds: new atlas.data.BoundingBox.fromLatLngs(bounds),
padding: 40
});
});
});
};
document.body.onload = onload;
上記のコード例において、最初のコード ブロックはマップ オブジェクトを構築し、Microsoft Entra ID を使用するための認証メカニズムを設定します。 手順については、「マップの作成」を参照してください。
2 つ目のコード ブロックでは、DataSource オブジェクトが作成され、マップに追加されます。
3 つ目のコード ブロックでは、ルートの開始点と終了点が作成されます。 その後、データ ソースに追加されます。 詳細については、「マップへのピンの追加」を参照してください。
LineLayer によって、DataSource にラップされた線オブジェクトが、マップ上に線としてレンダリングされます。 4 つ目のコード ブロックでは、線レイヤーが作成され、マップに追加されます。 線レイヤーのプロパティについては、LinestringLayerOptions に関するページを参照してください。
シンボル レイヤーは、テキストまたはアイコンを使用して、DataSource にラップされたポイントベースのデータをシンボルとしてマップにレンダリングします。 5 つ目のコード ブロックでは、シンボル レイヤーが作成され、マップに追加されます。 シンボル レイヤーのプロパティについては、SymbolLayerOptions に関する記事をご覧ください。
次のコード ブロックは、Fetch API を使用して、Get Route Directions に対して検索要求を行います。 その後、応答が解析されます。 成功応答の場合は、緯度と経度の情報を使用し、それらのポイントを結んで線の配列が作成されます。 その線データがデータ ソースに追加されて、マップ上にルートがレンダリングされます。 詳細については、「マップへの線の追加」を参照してください。
最後のコード ブロックでは、マップの setCamera プロパティを使用してマップの境界が設定されます。
ルート クエリ、データ ソース、シンボル、線レイヤー、カメラの境界が、イベント リスナー内に作成されます。 この場合も、マップが完全に読み込まれた後に結果が表示されるようにします。
次の図は、2 つのコード サンプルの結果を示すスクリーンショットです。
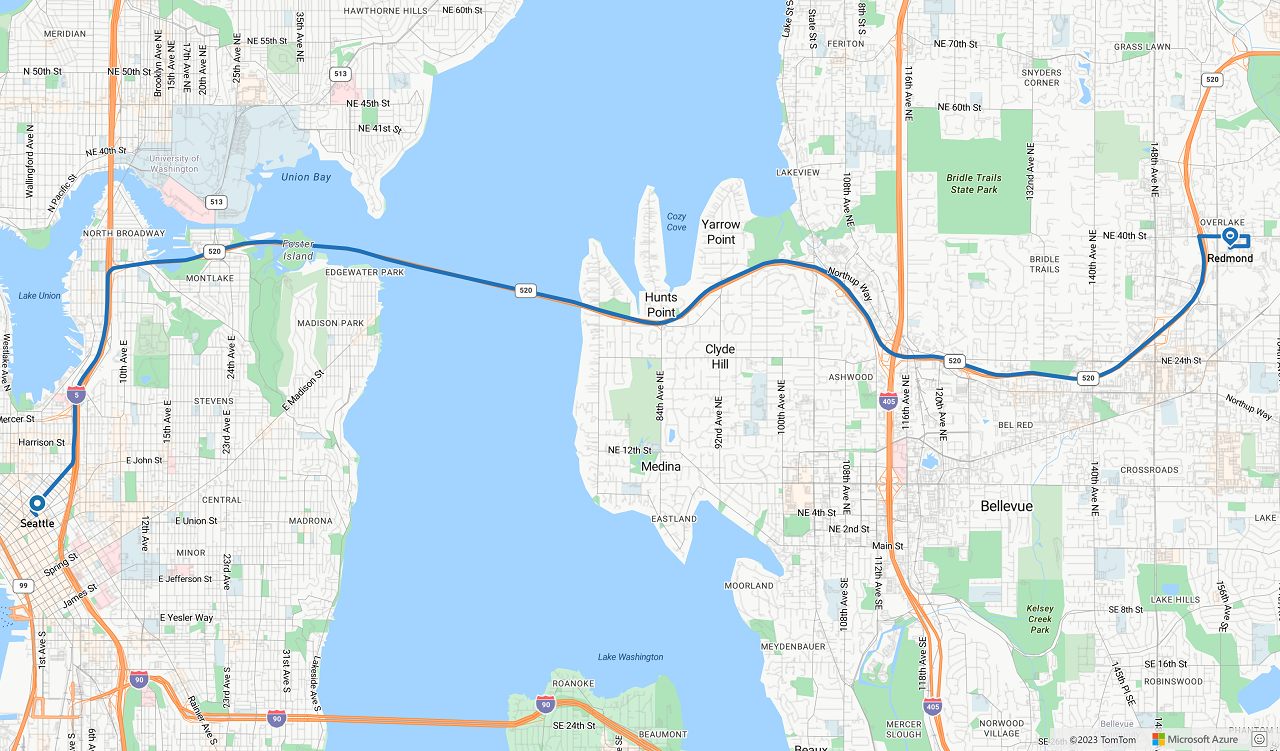
次のステップ
この記事で使われているクラスとメソッドの詳細については、次を参照してください。
完全なコードの例については、次の記事を参照してください。