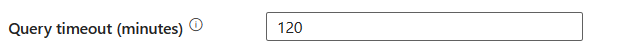Configurer une base de données SQL dans une activité de copie (préversion)
Cet article explique comment utiliser l’activité de copie dans le pipeline de données pour copier des données depuis et vers une base de données SQL.
Configuration prise en charge
Pour la configuration de chaque onglet sous activité de copie, accédez respectivement aux sections suivantes.
Généralités
Reportez-vous aux lignes directrices des paramètres généraux pour configurer l’onglet Paramètres généraux .
Source
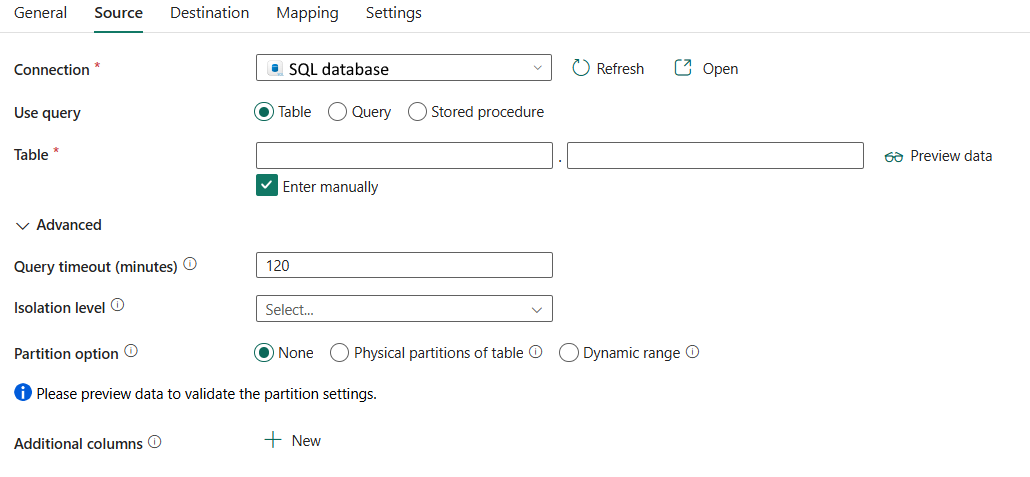
Les propriétés suivantes sont prises en charge pour la base de données SQL sous l’onglet Source d’une activité de copie.
Les propriétés suivantes sont requises :
Connexion : sélectionnez une base de données SQL existante faisant référence à l’étape décrite dans cet article.
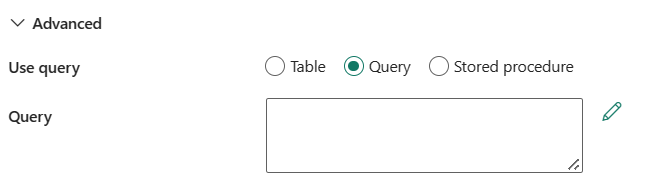
Utiliser une requête : vous pouvez choisir Table, Requête ou Procédure stockée. La liste suivante décrit la configuration de chaque paramètre :
table: spécifiez le nom de la base de données SQL à lire. Choisissez une table existante dans la liste déroulante ou sélectionnez Entrer manuellement pour entrer le schéma et le nom de la table.
requête: spécifiez la requête SQL personnalisée pour lire les données. Par exemple,
select * from MyTable. Ou sélectionnez l’icône de crayon à modifier dans l’éditeur de code.procédure stockée: sélectionnez la procédure stockée dans la liste déroulante.
Sous avancé, vous pouvez spécifier les champs suivants :
délai d’expiration de requête (minutes): spécifiez le délai d’attente pour l’exécution de la commande de requête, la valeur par défaut est de 120 minutes. Si le paramètre est défini pour cette propriété, les valeurs autorisées sont un intervalle de temps, par exemple « 02:00:00 » (120 minutes).
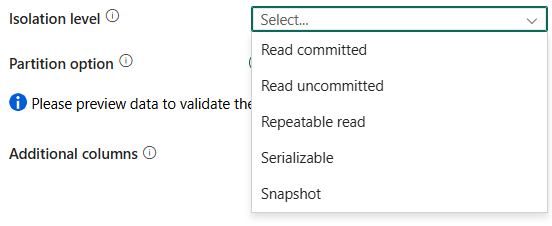
niveau d’isolation: spécifie le comportement de verrouillage des transactions pour la source SQL. Les valeurs autorisées sont les suivantes : Validée en lecture, Invalidée en lecture, Lecture renouvelable, Sérialisable, ou Instantané. Pour plus d’informations, reportez-vous à IsolationLevel Enum.
Option de partition: Spécifiez les options de partitionnement des données utilisées pour charger des données à partir de la base de données SQL. Les valeurs autorisées sont les suivantes : Aucun (valeur par défaut), partitions physiques de la tableet plage dynamique. Lorsqu’une option de partition est activée (autrement dit, pas Aucun), le degré de parallélisme pour charger simultanément des données à partir d’une base de données SQL est contrôlé par degré de parallélisme de copie dans l’onglet Paramètres de l’activité de copie.
Aucun: choisissez ce paramètre pour ne pas utiliser de partition.
partitions physiques de la table: lorsque vous utilisez une partition physique, la colonne de partition et le mécanisme sont automatiquement déterminés en fonction de votre définition de table physique.
plage dynamique: lors de l’utilisation d’une requête avec activation parallèle, le paramètre de partition de plage (
?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition) est nécessaire. Exemple de requête :SELECT * FROM <TableName> WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition.Nom de la colonne de partition : Indiquez le nom de la colonne source de type entier ou date/heure (
int,smallint,bigint,date,smalldatetime,datetime,datetime2, oudatetimeoffset) qui est utilisée par le partitionnement de plage pour la copie parallèle. S’il n’est pas spécifié, l’index ou la clé primaire de la table est détecté automatiquement et utilisé comme colonne de partition.Si vous utilisez une requête pour récupérer les données sources, intégrez le
?DfDynamicRangePartitionConditiondans la clause WHERE. Pour obtenir un exemple, consultez la section Copie parallèle à partir de la base de données SQL.limite supérieure de partition: spécifiez la valeur maximale de la colonne de partition pour le fractionnement de la plage de partitions. Cette valeur est utilisée pour décider de la progression de la partition, et non pour filtrer les lignes de la table. Toutes les lignes de la table ou du résultat de la requête sont partitionnées et copiées. Si ce n’est pas spécifié, l’activité de copie détecte automatiquement la valeur. Pour obtenir un exemple, consultez la section Copie parallèle à partir de la base de données SQL.
limite inférieure de partition: spécifiez la valeur minimale de la colonne de partition pour le fractionnement de la plage de partitions. Cette valeur est utilisée pour décider de la progression de la partition, et non pour filtrer les lignes de la table. Toutes les lignes de la table ou du résultat de la requête sont partitionnées et copiées. Si ce n’est pas spécifié, l’activité de copie détecte automatiquement la valeur. Pour obtenir un exemple, consultez la section Copie parallèle à partir de la base de données SQL.
colonnes supplémentaires: ajoutez d’autres colonnes de données pour stocker le chemin d’accès relatif ou la valeur statique des fichiers sources. L'expression est prise en charge pour ce dernier. Pour plus d’informations, accédez à Ajouter des colonnes supplémentaires pendant la copie.
Destination
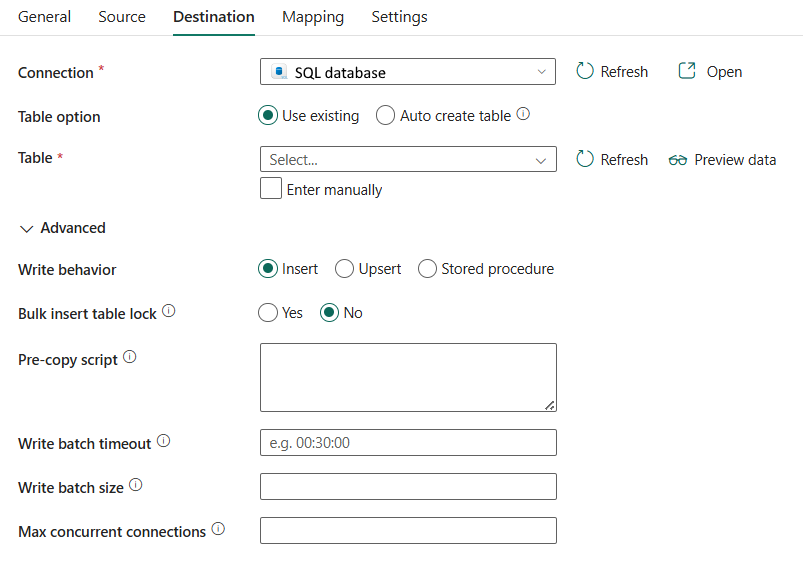
Les propriétés suivantes sont disponibles pour la base de données SQL sous l'onglet Destination d'une activité de copie.
Les propriétés suivantes sont requises :
Connexion : sélectionnez une base de données SQL existante faisant référence à l’étape décrite dans cet article.
Option Table : sélectionnez Utiliser existant ou Créer une table automatiquement.
Si vous sélectionnez Utiliser unexistant :
- Table: spécifiez le nom de la base de données SQL pour écrire des données. Choisissez une table existante dans la liste déroulante ou sélectionnez Entrer manuellement pour entrer le schéma et le nom de la table.
Si vous sélectionnez créer automatiquement une table:
- Table: elle crée automatiquement la table (si inexistante) dans le schéma source, ce qui n’est pas pris en charge lorsque la procédure stockée est utilisée comme comportement d’écriture.
Sous avancé, vous pouvez spécifier les champs suivants :
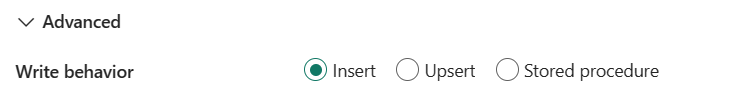
Comportement d’écriture: définit le comportement d’écriture lorsque la source est des fichiers à partir d’un magasin de données basé sur des fichiers. Vous pouvez choisir Insérer, Upsert ou Stockée.
Insérer: choisissez cette option si vos données sources ont des insertions.
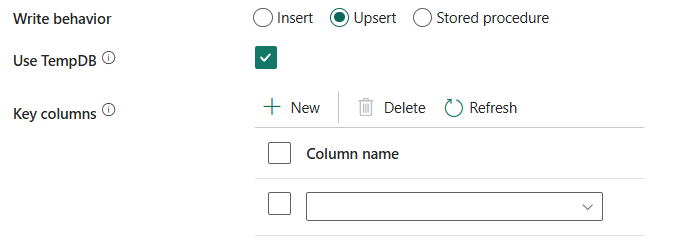
Upsert: choisissez cette option si vos données sources ont à la fois des insertions et des mises à jour.
Utiliser tempDB: spécifiez s’il faut utiliser une table temporaire globale ou une table physique comme table intermédiaire pour upsert. Par défaut, le service utilise une table temporaire globale comme table intermédiaire et cette case à cocher est cochée.
Si vous écrivez une grande quantité de données dans une base de données SQL, décochez cette case et spécifiez un nom de schéma sous lequel Data Factory créera une table intermédiaire pour charger les données en attente et procéder au nettoyage automatique une fois l'opération terminée. Vérifiez que l’utilisateur a créé une autorisation de table dans la base de données et modifiez l’autorisation sur le schéma. Si elle n'est pas spécifiée, une table temporaire globale est utilisée pour la mise en lots.Sélectionner le schéma de base de données utilisateur: lorsque l'Utiliser le TempDB n’est pas sélectionné, spécifiez un nom de schéma sous lequel Data Factory crée une table intermédiaire pour charger des données en amont et les nettoyer automatiquement une fois l’opération terminée. Vérifiez que vous disposez d'une autorisation de créer une table dans la base de données et d'une autorisation de modification du schéma.
Remarque
Vous devez disposer de l’autorisation de création et de suppression de tables. Par défaut, une table intermédiaire partage le même schéma qu’une table de destination.
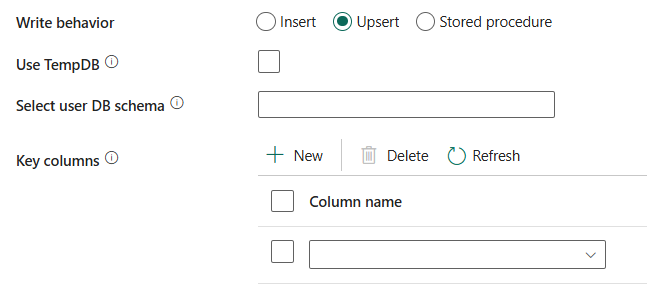
colonnes clés: choisissez la colonne utilisée pour déterminer si une ligne de la source correspond à une ligne de la destination.
nom de procédure stockée: sélectionnez la procédure stockée dans la liste déroulante.
Insérer en bloc un verrou de table : choisissez Oui ou Non. Utilisez ce paramètre pour améliorer les performances de copie pendant une opération d’insertion en bloc sur une table sans index de plusieurs clients. Pour plus d’informations, accédez à BULK INSERT (Transact-SQL)
script de pré-copie: spécifiez un script pour l’activité de copie à exécuter avant d’écrire des données dans une table de destination dans chaque exécution. Vous pouvez utiliser cette propriété pour nettoyer les données préchargées.
Délai d'attente du lot d'écriture : Temps d’attente pour que l’opération d’insertion par lot soit terminée avant d’expirer. La valeur autorisée est timespan. La valeur par défaut est « 00:30:00 » (30 minutes).
Taille de lot d’écriture : spécifiez le nombre de lignes à insérer dans la table SQL par lot. La valeur autorisée est entier (nombre de lignes). Par défaut, le service détermine dynamiquement la taille de lot appropriée en fonction de la taille de ligne.
Nombre maximal de connexions simultanées: spécifiez la limite supérieure des connexions simultanées établies au magasin de données pendant l’exécution de l’activité. Spécifiez une valeur uniquement lorsque vous souhaitez limiter les connexions simultanées.
Cartographie
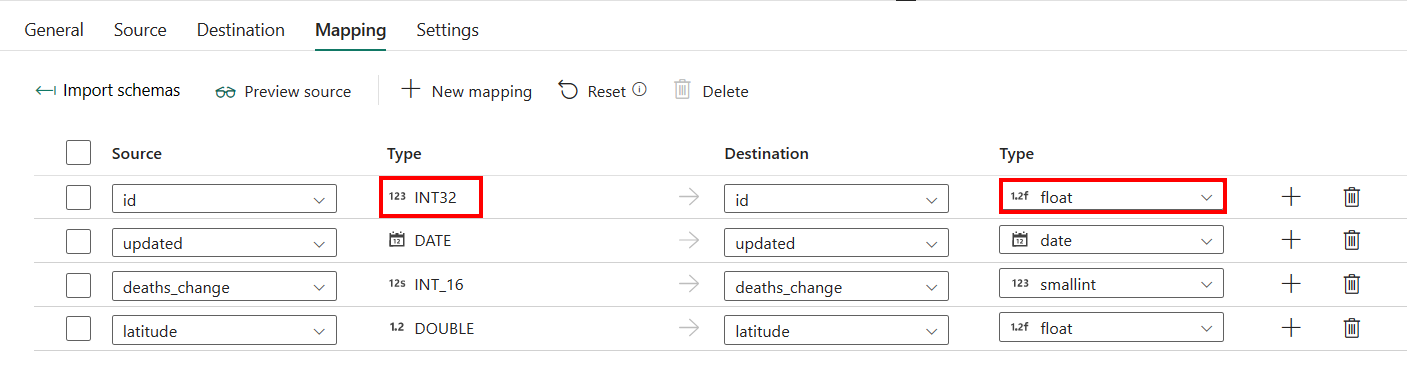
Pour la configuration de l'onglet Mappage , si vous n'utilisez pas une base de données SQL avec création automatique de table comme destination, accédez à Mappage .
Si vous appliquez une base de données SQL avec la table de création automatique en tant que destination, à l’exception de la configuration dans mappage, vous pouvez modifier le type de vos colonnes de destination. Après avoir sélectionné Importer des schémas, vous pouvez spécifier le type de colonne dans votre destination.
Par exemple, le type de ID colonne dans la source est int, et vous pouvez le modifier en type float lors du mappage à la colonne de destination.
Paramètres
Pour la configuration de l’onglet Paramètres, accédez à Configurer vos autres paramètres sous l’onglet Paramètres.
Copie parallèle à partir de la base de données SQL
Le connecteur de base de données SQL dans l’activité de copie fournit un partitionnement de données intégré pour copier des données en parallèle. Vous trouverez les options de partitionnement des données sous l’onglet Source de l’activité de copie.
Lorsque vous activez la copie partitionnée, l’activité de copie exécute des requêtes parallèles sur votre source de base de données SQL pour charger des données par partitions. Le degré parallèle est contrôlé par le Degré de parallélisme de copie dans l’onglet Paramètres de l’activité de copie. Par exemple, si vous définissez degré de parallélisme de copie sur quatre, le service génère et exécute simultanément quatre requêtes en fonction de votre option et paramètres de partition spécifiés, et chaque requête récupère une partie des données de votre base de données SQL.
Vous êtes suggéré d’activer la copie parallèle avec le partitionnement des données, en particulier lorsque vous chargez une grande quantité de données à partir de votre base de données SQL. Voici les configurations suggérées pour différents scénarios. Lors de la copie de données dans un magasin de données basé sur des fichiers, il est recommandé d’écrire dans un dossier sous la forme de plusieurs fichiers (spécifier uniquement le nom du dossier), auquel cas les performances sont meilleures que l’écriture dans un seul fichier.
| Scénario | Paramètres suggérés |
|---|---|
| Chargement complet à partir d’une table volumineuse, avec des partitions physiques. | Option de partition: partitions physiques d'une table. Pendant l’exécution, le service détecte automatiquement les partitions physiques et copie les données par partitions. Pour vérifier si votre table a, ou non, une partition physique, vous pouvez vous reporter à cette requête. |
| Charge complète à partir d’une table volumineuse, sans partitions physiques, en utilisant une colonne de type entier ou datetime pour le partitionnement des données. | Options de partition : partition dynamique par spécification de plages de valeurs. Colonne de partition (facultatif) : spécifiez la colonne utilisée pour la partition des données. S’il n’est pas spécifié, l’index ou la colonne de clé primaire est utilisé. Partition limite supérieure et partition limite inférieure (facultatif) : spécifiez si vous souhaitez déterminer la progression de la partition. Il ne s’agit pas de filtrer les lignes de la table, toutes les lignes de la table seront partitionnée et copiées. Si ce n’est pas spécifié, l’activité de copie détecte automatiquement les valeurs et peut prendre beaucoup de temps en fonction des valeurs MIN et MAX. Il est recommandé de fournir une limite supérieure et une limite inférieure. Par exemple, si votre colonne de partition « ID » a des valeurs comprises entre 1 et 100, et que vous définissez la limite inférieure sur 20 et la limite supérieure comme 80, avec une copie parallèle en tant que 4, le service récupère les données par 4 partitions - ID dans la plage <=20, [21, 50], [51, 80] et >=81, respectivement. |
| Chargez une grande quantité de données à l’aide d’une requête personnalisée, sans partitions physiques, avec un entier ou une colonne date/datetime pour le partitionnement des données. | Options de partition: une partition de plage dynamique. Requête : SELECT * FROM <TableName> WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition AND <your_additional_where_clause>.colonne de partition: spécifiez la colonne utilisée pour partitionner les données. Partition limite supérieure et partition limite inférieure (facultatif) : spécifiez si vous souhaitez déterminer la progression de la partition. Ce n’est pas pour filtrer les lignes de la table, toutes les lignes du résultat de la requête sont partitionnés et copiées. Si ce n’est pas spécifié, l’activité de copie détecte automatiquement la valeur. Par exemple, si votre colonne de partition « ID » a des valeurs comprises entre 1 et 100, et que vous définissez la limite inférieure sur 20 et la limite supérieure comme 80, avec une copie parallèle en tant que 4, le service récupère les données de 4 partitions - ID dans la plage <=20, [21, 50], [51, 80] et >=81, respectivement. Voici d’autres exemples de requêtes pour différents scénarios : • Interroger l’ensemble de la table : SELECT * FROM <TableName> WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition• Interroger une table avec une sélection de colonnes et des filtres de la clause WHERE supplémentaires : SELECT <column_list> FROM <TableName> WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition AND <your_additional_where_clause>• Interroger avec des sous-requêtes : SELECT <column_list> FROM (<your_sub_query>) AS T WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition AND <your_additional_where_clause>• Effectuer une requête avec une partition dans une sous-requête : SELECT <column_list> FROM (SELECT <your_sub_query_column_list> FROM <TableName> WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition) AS T |
Bonnes pratiques pour charger des données avec l’option de partition :
- Choisissez une colonne distincte comme colonne de partition (comme la clé primaire ou une clé unique) pour éviter l’asymétrie des données.
- Si la table a une partition intégrée, utilisez l’option de partition partitions physiques de la table pour obtenir de meilleures performances.
Exemple de requête pour vérifier la partition physique
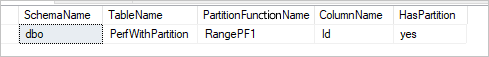
SELECT DISTINCT s.name AS SchemaName, t.name AS TableName, pf.name AS PartitionFunctionName, c.name AS ColumnName, iif(pf.name is null, 'no', 'yes') AS HasPartition
FROM sys.tables AS t
LEFT JOIN sys.objects AS o ON t.object_id = o.object_id
LEFT JOIN sys.schemas AS s ON o.schema_id = s.schema_id
LEFT JOIN sys.indexes AS i ON t.object_id = i.object_id
LEFT JOIN sys.index_columns AS ic ON ic.partition_ordinal > 0 AND ic.index_id = i.index_id AND ic.object_id = t.object_id
LEFT JOIN sys.columns AS c ON c.object_id = ic.object_id AND c.column_id = ic.column_id
LEFT JOIN sys.partition_schemes ps ON i.data_space_id = ps.data_space_id
LEFT JOIN sys.partition_functions pf ON pf.function_id = ps.function_id
WHERE s.name='[your schema]' AND t.name = '[your table name]'
Si la table a une partition physique, vous verrez « HasPartition » indiqué comme « oui » de la manière suivante.
Résumé du tableau
Les tableaux suivants contiennent plus d’informations sur l’activité de copie dans la base de données SQL.
Source
| Nom | Description | Valeur | Obligatoire | Propriété de script JSON |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Connection | Votre connexion au magasin de données source. | <votre connexion> | Oui | connection |
| Utiliser la requête | La façon de lire des données. Appliquez Table pour lire des données à partir de la table spécifiée ou appliquez Requête pour lire des données à l’aide des requêtes SQL. | • Table • Requête • Procédure stockée |
Oui | / |
| Pour Table | ||||
| nom de schéma | Nom du schéma. | < votre nom de schéma > | Non | schéma |
| nom de table | Nom de la table. | < nom de votre table > | Non | table |
| Pour Requête | ||||
| Requête | Spécifiez la requête SQL personnalisée pour lire les données. Par exemple : SELECT * FROM MyTable. |
<Requêtes SQL> | Non | sqlReaderQuery |
| Pour Procédure stockée | ||||
| Nom de la procédure stockée | Nom de la procédure stockée. | < nom de votre procédure stockée > | Non | sqlReaderStoredProcedureName |
| délai d’expiration de requête (minutes) | Le délai d’expiration de l’exécution de la commande de requête est de 120 minutes par défaut. Si le paramètre est défini pour cette propriété, les valeurs autorisées sont un intervalle de temps, par exemple « 02:00:00 » (120 minutes). | Durée | Non | queryTimeout |
| niveau d’isolation | Spécifie le comportement de verrouillage des transactions pour la source SQL. | • Lecture validée • Lecture invalidée • Lecture renouvelable • Sérialisable • Instantané |
Non | isolationLevel : • ReadCommitted • ReadUncommitted • RepeatableRead • Sérialisable • Instantané |
| Option de partition | Options de partitionnement des données utilisées pour charger des données à partir de la base de données SQL. | • Aucun • Partitions physiques de la table • Plage dynamique |
Non | partitionOption : • PhysicalPartitionsOfTable • DynamicRange |
| Pour Plage dynamique | ||||
| Nom de la colonne de partition | Nom de la colonne source dans entier ou type date/datetime (int, smallint, bigint, date, smalldatetime, datetime, datetime2ou datetimeoffset) utilisé par le partitionnement de plage pour la copie parallèle. S’il n’est pas spécifié, l’index ou la clé primaire de la table est détecté automatiquement et utilisé comme colonne de partition. Si vous utilisez une requête pour récupérer des données sources, utilisez ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition dans la clause WHERE. |
< noms de colonne de votre partition > | Non | partitionColumnName |
| Limite supérieure de partition | Valeur maximale de la colonne de partition pour le fractionnement de la plage de partition. Cette valeur est utilisée pour décider de la progression de la partition, et non pour filtrer les lignes de la table. Toutes les lignes de la table ou du résultat de la requête seront partitionnées et copiées. Si ce n’est pas spécifié, l’activité de copie détecte automatiquement la valeur. | < limite supérieure de votre partition > | Non | partitionUpperBound |
| Limite inférieure de partition | Valeur minimale de la colonne de partition pour le fractionnement de la plage de partition. Cette valeur est utilisée pour décider de la progression de la partition, et non pour filtrer les lignes de la table. Toutes les lignes de la table ou du résultat de la requête seront partitionnées et copiées. Si ce n’est pas spécifié, l’activité de copie détecte automatiquement la valeur. | < limite inférieure de votre partition > | Non | partitionLowerBound |
| Colonnes supplémentaires | Ajoutez d’autres colonnes de données pour stocker le chemin d’accès relatif ou la valeur statique des fichiers sources. L'expression est prise en charge pour ce dernier. | •Nom •Valeur |
Non | additionalColumns : • nom •valeur |
Destination
| Nom | Description | Valeur | Obligatoire | Propriété de script JSON |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Connection | Votre connexion au magasin de données de destination. | <votre connexion > | Oui | connection |
| Option de table | Votre table de données de destination. Sélectionnez parmi Utiliser existant ou Créer une table automatiquement. | • Utiliser l’existant • Créer automatiquement une table |
Oui | schéma table |
| Comportement d’écriture | Définit le comportement d’écriture lorsque la source est des fichiers à partir d’un magasin de données basé sur des fichiers. | •Insérer • Upsert • Procédure stockée |
Non | writeBehavior : • insert • upsert • sqlWriterStoredProcedureName |
| Verrou de table d’insertion en bloc | Utilisez ce paramètre pour améliorer les performances de copie pendant une opération d’insertion en bloc sur une table sans index de plusieurs clients. | Oui ou Non (valeur par défaut) | Non | sqlWriterUseTableLock : true ou false (valeur par défaut) |
| Pour Upsert | ||||
| Utiliser TempDB | Utilisation ou non d'une table temporaire globale ou d'une table physique en tant que table intermédiaire pour faire un upsert. | sélectionné (par défaut) ou non sélectionné | Non | useTempDB : true (valeur par défaut) ou false |
| colonnes clés | Choisissez la colonne utilisée pour déterminer si une ligne de la source correspond à une ligne de la destination. | < votre colonne clé> | Non | clés |
| Pour Procédure stockée | ||||
| Nom de la procédure stockée | Cette propriété est le nom de la procédure stockée qui lit les données de la table source. La dernière instruction SQL doit être une instruction SELECT dans la procédure stockée. | < nom de procédure stockée > | Non | sqlWriterStoredProcedureName |
| Script de pré-copie | Script pour l’activité de copie à exécuter avant d’écrire des données dans une table de destination dans chaque exécution. Vous pouvez utiliser cette propriété pour nettoyer les données préchargées. | <script de pré-copie> (chaîne) |
Non | preCopyScript |
| Délai d’expiration du lot d’écriture | Temps d’attente pour que l’opération d’insertion par lot soit terminée avant d’expirer. La valeur autorisée est timespan. La valeur par défaut est « 00:30:00 » (30 minutes). | intervalle de temps | Non | writeBatchTimeout |
| Écrire la taille du lot | Nombre de lignes à insérer dans la table SQL par lot. Par défaut, le service détermine dynamiquement la taille de lot appropriée en fonction de la taille de ligne. | <nombre de lignes> (entier) |
Non | writeBatchSize |
| nombre maximal de connexions simultanées | La limite supérieure de connexions simultanées établies au magasin de données pendant l’exécution de l’activité. Spécifiez une valeur uniquement lorsque vous souhaitez limiter les connexions simultanées. | <limite supérieure des connexions simultanées> (entier) |
Non | maxConcurrentConnections |