Mapping a custom domain with a special character to an Azure Website
This article has been moved to its new home here: https://benperk.github.io/waws/2014/2014-10-mapping-a-custom-domain-with-a-special-character-to-an-azure-website.html
Azure Web Apps have not always supported the mapping of custom domain names with special characters in them, but it looks like it does now. I was able to map a custom domain with a special character to my Standard mode Azure Web App.
To successfully configure an Azure Web App custom domain with a special character, I performed the following:
- Modified my DNS entry so that both AWVERIFY and WWW host names point to my Azure Website
- Used the Azure Management Portal to bind the domain name with the special character
- What about named domains with special characters?
Add or Modify CNAMEs via your DNS provider console
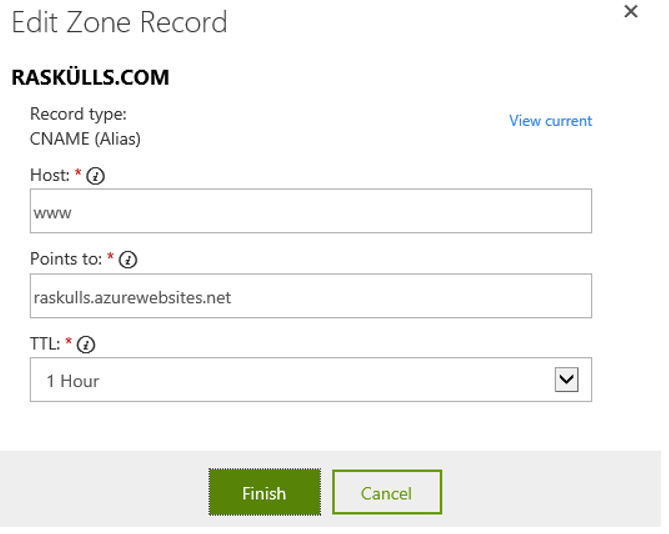
As shown in Figure 1 and 2, add a CNAME for both AWVERIFY and WWW. The AWVERIFY CNAME is what the Azure Website logic uses to validate that you do actually own the domain name.
Figure 1, add CNAME where HOST = WWW for special character custom domain
Figure 2, add CNAME where HOST = awverify for the custom domain with special character
Bind the custom domain name with special characters
If you try to use the current Azure Management Console you might receive a message stating ‘Enter a value in the format: mysitename.com’, similar to that shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3, using special character for custom domain name Azure Websites error
However, in the new version of the Azure Portal, I was able to bind the custom domain with the special character to my Azure Web App. To do this, access the newest version of the Azure Management Portal and select Browse -> Web Apps -> Select the web site you want to bind the custom domain to -> Scroll down and select the ‘Domains and SSL’ box, as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4, how to bind a special character custom domain to an Azure Website
Once the blade opens as shown in Figure 5, enter your custom domain and press the Save button at the top of the blade.
Figure 5, adding a custom domain with special character to an Azure Website
Once these 2 activities have been completed, you will be able to enter the domain with the special character in it and the request is responded to from your Azure Web App.
What about a naked domain?
Naked domains are domain names that do not have WWW in front of them, for example, https://raskülls.com. I wrote an article about how to map a naked domain which does not have special characters here. To configure a naked domain with special characters, you again must use the new Azure Portal, Azure PowerShell commands work as well.
To configure a naked domain, perform the following 2 actions:
- Add an A Record to your DNS provider
- Bind the naked domain to your Azure Website
NOTE: It is expected that you have already added the AWVERIFY CNAME for your Azure Website as shown previously via Figure 2.
Add an A Record
As shown in Figure 5 previously, click on the ‘the IP address to use when you configure an A Record’ and write down or copy the IP address. Or you can get the IP address from the previous version of the Azure Management Console via the CONFIGURATION link -> Manage Domain link, as illustrated by Figure 6.
Figure 6, get the IP address for an A Record to use with custom domain containing special characters
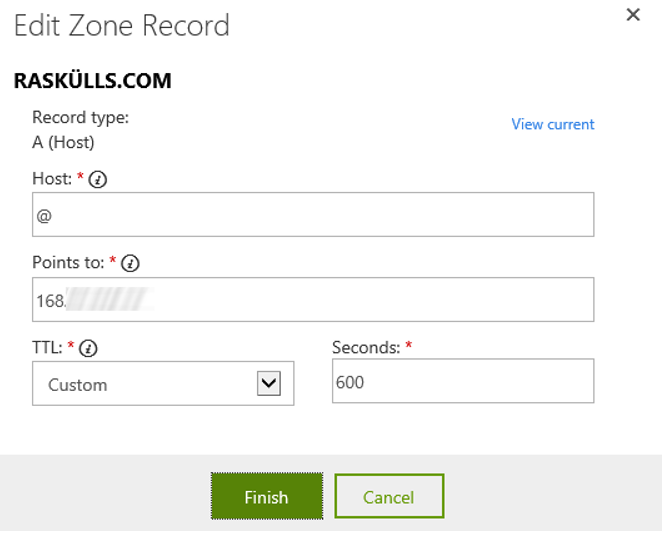
Once you have the IP address, modify or add an A Record via your DNS providers’ management console. Figure 7 shows how this might look.
Figure 7, an A Record for an Azure Website custom domain with special characters
Once this is added, it may take up to 48 hours to propagate. You can use a tool like NSLOOKUP or DIGWEBINTERFACE to check if the change is available.
Bind the naked domain with special character to you Azure Website
Navigate to the Domain and SSL page and enter the naked domain into the Domain names section as shown in Figure 8. Once the DNS is valid, your naked custom domain with special characters will work as expected.
Figure 8, naked custom domain with special characters on Azure Websites
See the list of articles below for information about that and how to map other types of custom domains to your Azure Web App.
- Mapping a subdomain to an Azure Web App, here
- Mapping a naked domain to an Azure Web App, here
- Mapping a custom domain to a Traffic Manager domain, here
- Mapping a custom domain that includes a special character, here
- Mapping a wildcard domain to an Azure Web App, here
Comments
- Anonymous
October 20, 2014
Thank you man! This is the only guide that really works with Umlaut domains on the web that I could find. Well done and really appreciated. S. Vogel