Deploy App Service in Azure Stack Hub
Important
Update Azure Stack Hub to a supported version (or deploy the latest Azure Stack Development Kit) if necessary, before deploying or updating the App Service resource provider (RP). Be sure to read the RP release notes to learn about new functionality, fixes, and any known issues that could affect your deployment.
Supported Minimum Azure Stack Hub version App Service RP version 2311 and later 24R1 Installer (release notes)
Important
Before you run the resource provider installer, you must complete the steps in Before you get started
In this article you learn how to deploy App Service in Azure Stack Hub, which gives your users the ability to create Web, API and Azure Functions applications. You need to:
- Add the App Service resource provider to your Azure Stack Hub deployment using the steps described in this article.
- After you install the App Service resource provider, you can include it in your offers and plans. Users can then subscribe to get the service and start creating apps.
Run the App Service resource provider installer
Installing the App Service resource provider takes at least an hour. The length of time needed depends on how many role instances you deploy. During the deployment, the installer runs the following tasks:
- Registers the required resource providers in the Default Provider Subscription
- Grants contributor access to the App Service Identity application
- Create Resource Group and Virtual network (if necessary)
- Create Storage accounts and containers for App Service installation artifacts, usage service, and resource hydration
- Download App Service artifacts and upload them to the App Service storage account
- Deploy the App Service
- Register the usage service
- Create DNS Entries for App Service
- Register the App Service admin and tenant resource providers
- Register Gallery Items - Web, API, Function App, App Service Plan, WordPress, DNN, Orchard, and Django applications
To deploy App Service resource provider, follow these steps:
Run appservice.exe as an admin from a computer that can access the Azure Stack Hub Admin Azure Resource Management Endpoint.
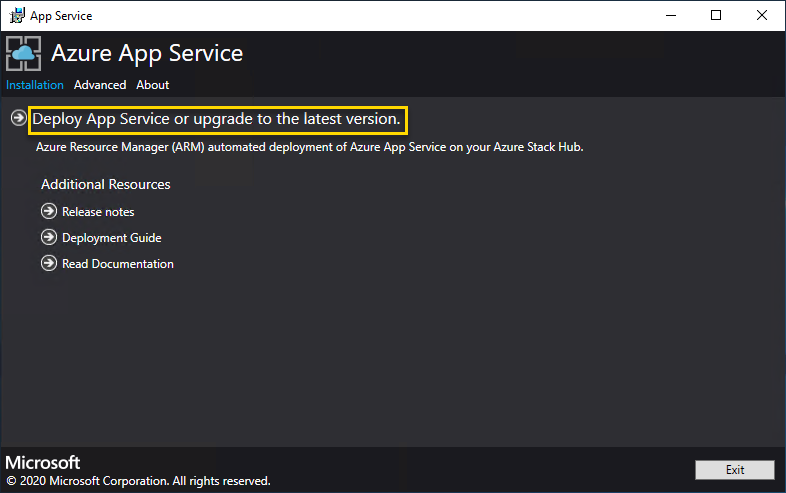
Select Deploy App Service or upgrade to the latest version.
Review and accept the Microsoft Software License Terms and then select Next.
Review and accept the third-party license terms and then select Next.
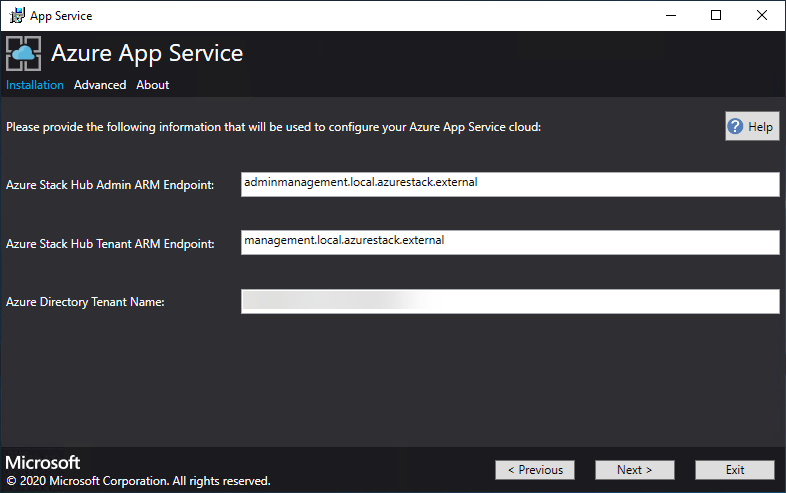
Make sure that the App Service cloud configuration information is correct. If you used the default settings during ASDK deployment, you can accept the default values. But, if you customized the options when you deployed the ASDK, or are deploying on an Azure Stack Hub integrated system, you must edit the values in this window to reflect the differences.
For example, if you use the domain suffix mycloud.com, your Azure Stack Hub Tenant Azure Resource Manager endpoint must change to management.<region>.mycloud.com. Review these settings, and then select Next to save the settings.
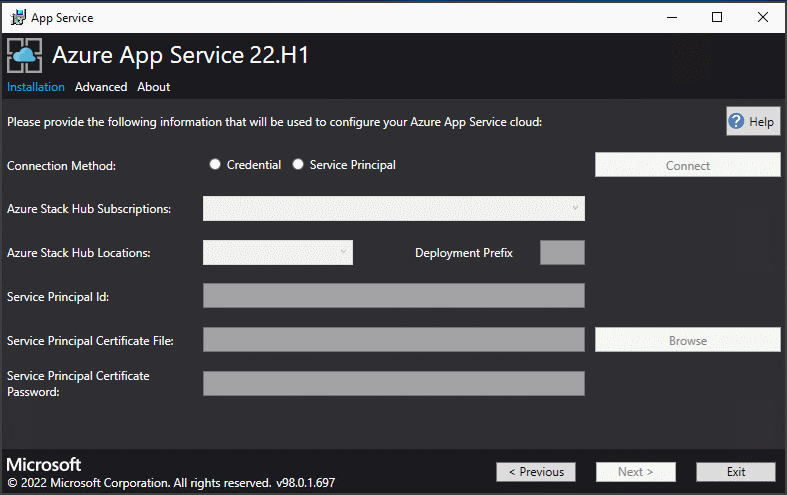
On the next App Service Installer page you will connect to your Azure Stack Hub:
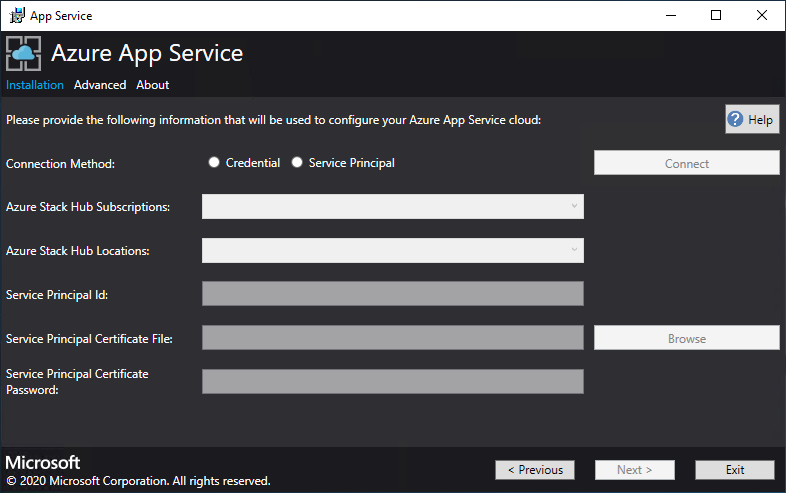
Select the connection method you wish to use - Credential or Service Principal
Credential
- If you're using Microsoft Entra ID, enter the Microsoft Entra admin account and password that you provided when you deployed Azure Stack Hub. Select Connect.
- If you're using Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS), provide your admin account. For example, cloudadmin@azurestack.local. Enter your password, and then select Connect.
Service Principal
- The service principal that you use must have Owner rights on the Default Provider Subscription
- Provide the Service Principal ID, Certificate File, and Password and select Connect.
In Azure Stack Hub Subscriptions, select the Default Provider Subscription. Azure App Service on Azure Stack Hub must be deployed in the Default Provider Subscription.
In the Azure Stack Hub Locations, select the location that corresponds to the region you're deploying to. For example, select local if you're deploying to the ASDK.
Administrators can specify a three character Deployment Prefix for the individual instances in each Virtual Machine Scale Set that are deployed. This is useful if managing multiple Azure Stack Hub instances.
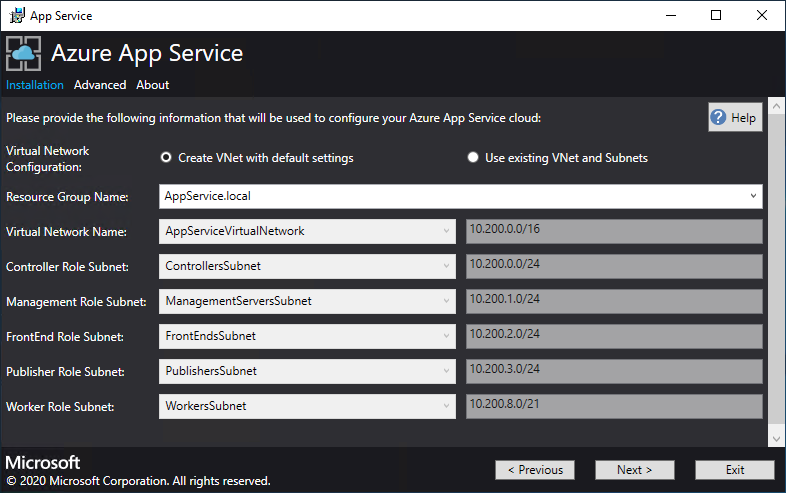
Now you can deploy into an existing virtual network that you configured using these steps, or let the App Service installer create a new virtual network and subnets. To create a VNet, follow these steps:
a. Select Create VNet with default settings, accept the defaults, and then select Next.
b. Alternatively, select Use existing VNet and Subnets. Complete the following actions:
- Select the Resource Group that contains your virtual network.
- Choose the Virtual Network name that you want to deploy to.
- Select the correct Subnet values for each of the required role subnets.
- Select Next.
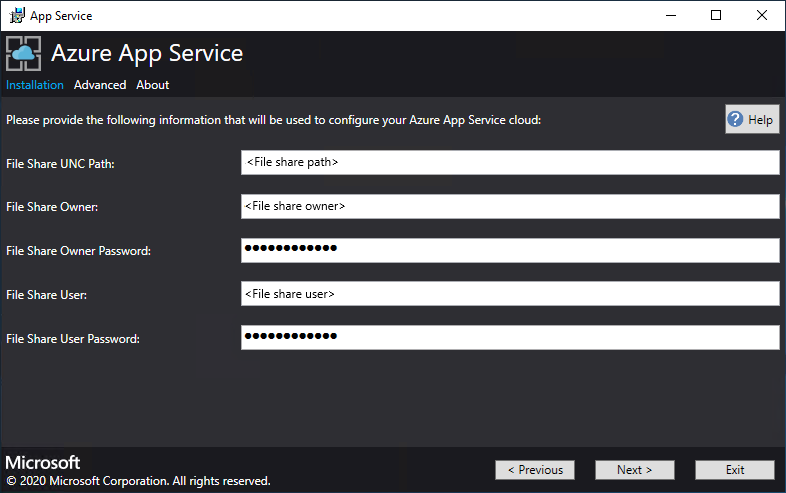
Enter the info for your file share and then select Next. The address of the file share must use the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) or the IP address of your File Server. For example, \\appservicefileserver.local.cloudapp.azurestack.external\websites, or \\10.0.0.1\websites. If you're using a file server, which is domain joined, you must provide the full username including domain. For example, myfileserverdomain\FileShareOwner.
Note
The installer tries to test connectivity to the file share before proceeding. But, if you're deploying to an existing virtual network, this connectivity test might fail. You're given a warning and a prompt to continue. If the file share info is correct, continue the deployment.
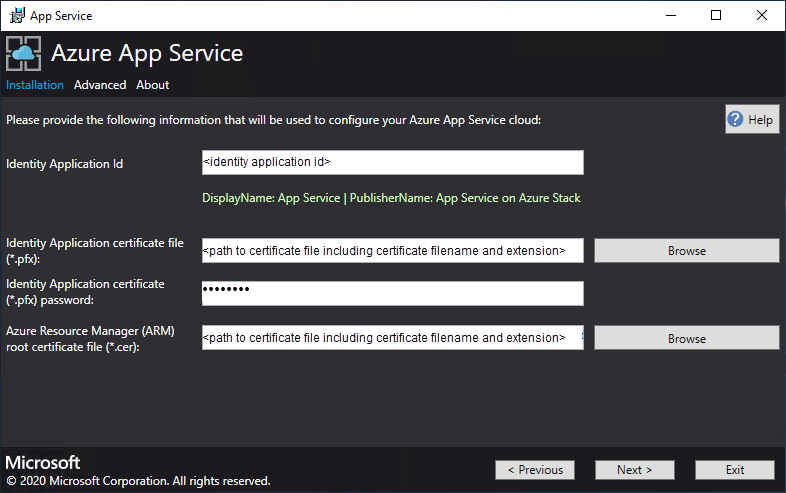
On the next App Service Installer page, follow these steps:
a. In the Identity Application ID box, enter the GUID for the Identity application you created as part of the pre-requisites.
b. In the Identity Application certificate file box, enter (or browse to) the location of the certificate file.
c. In the Identity Application certificate password box, enter the password for the certificate. This password is the one that you made note of when you used the script to create the certificates.
d. In the Azure Resource Manager root certificate file box, enter (or browse to) the location of the certificate file.
e. Select Next.
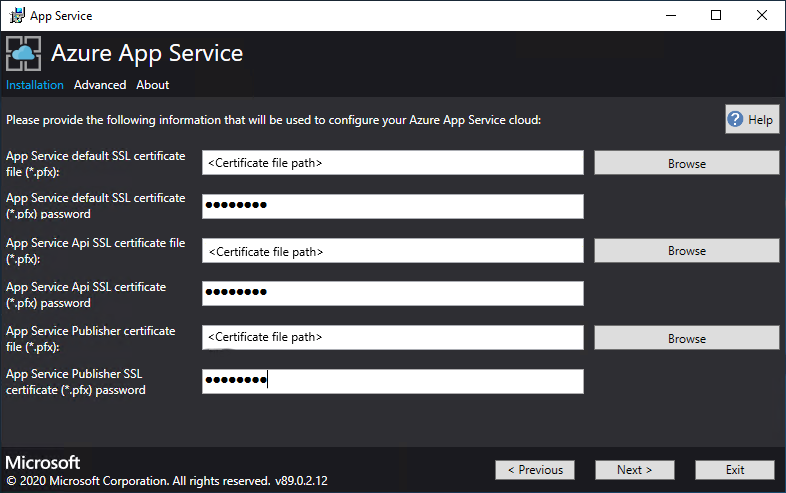
For each of the three certificate file boxes, select Browse and navigate to the appropriate certificate file. You must provide the password for each certificate. These certificates are the ones that you created in Prerequisites for deploying App Service on Azure Stack Hub. Select Next after entering all the information.
Box Certificate file name example App Service default SSL certificate file _.appservice.local.AzureStack.external.pfx App Service API SSL certificate file api.appservice.local.AzureStack.external.pfx App Service Publisher SSL certificate file ftp.appservice.local.AzureStack.external.pfx If you used a different domain suffix when you created the certificates, your certificate file names don't use local.AzureStack.external. Instead, use your custom domain info.
Enter the SQL Server details for the server instance used to host the App Service resource provider database and then select Next. The installer validates the SQL connection properties.
The App Service installer tries to test connectivity to the SQL Server before proceeding. If you're deploying to an existing virtual network, this connectivity test might fail. You're given a warning and a prompt to continue. If the SQL Server info is correct, continue the deployment.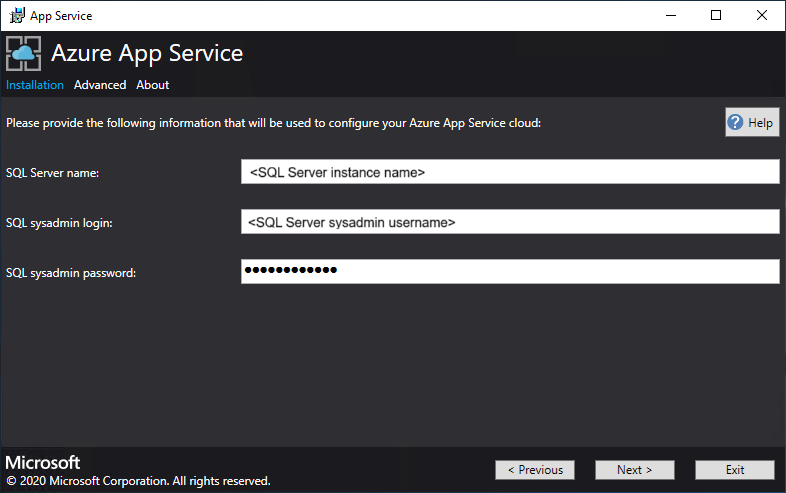
Review the role instance and SKU options. The defaults populate with the minimum number of instances and the minimum SKU for each role in a production deployment. For ASDK deployment, you can scale the instances down to lower SKUs to reduce the core and memory commit but you will experience a performance degradation. A summary of vCPU and memory requirements is provided to help plan your deployment. After you make your selections, select Next.
Note
For production deployments, following the guidance in Capacity planning for Azure App Service server roles in Azure Stack Hub.
Role Minimum instances Minimum SKU Notes Controller 2 Standard_A4_v2 - (4 cores, 8192 MB) Manages and maintains the health of the App Service cloud. Management 1 Standard_D3_v2 - (4 cores, 14336 MB) Manages the App Service Azure Resource Manager and API endpoints, portal extensions (admin, tenant, Functions portal), and the data service. To support failover, increase the recommended instances to 2. Publisher 1 Standard_A2_v2 - (2 cores, 4096 MB) Publishes content via FTP and web deployment. FrontEnd 1 Standard_A4_v2 - (4 cores, 8192 MB) Routes requests to App Service apps. Shared Worker 1 Standard_A4_v2 - (4 cores, 8192 MB) Hosts web or API apps and Azure Functions apps. You might want to add more instances. As an operator, you can define your offering and choose any SKU tier. The tiers must have a minimum of one vCPU. 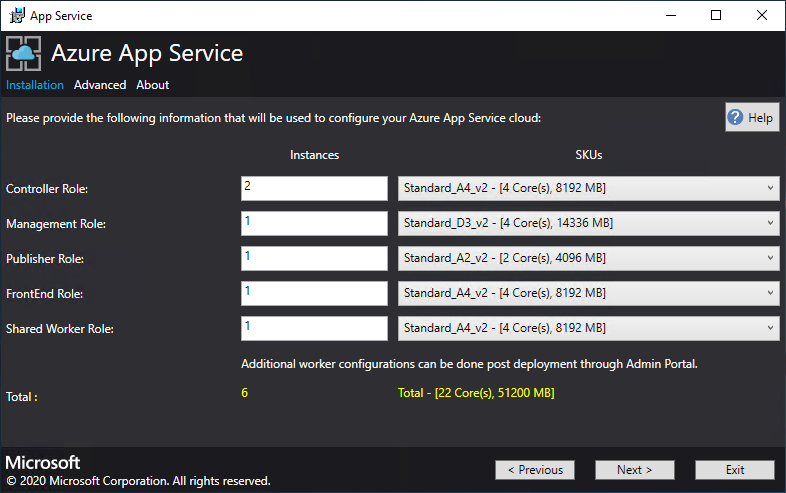
Note
Windows Server 2022 Core isn't a supported platform image for use with Azure App Service on Azure Stack Hub. Don't use evaluation images for production deployments.
In the Select Platform Image box, choose your deployment Windows Server 2022 virtual machine (VM) image from the images available in the compute resource provider for the App Service cloud. Select Next.
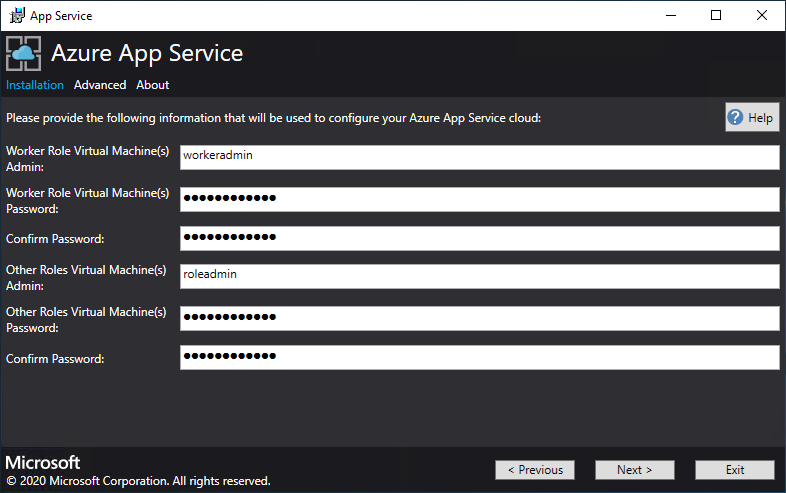
On the next App Service Installer page, follow these steps:
a. Enter the Worker Role VM admin user name and password.
b. Enter the Other Roles VM admin user name and password.
c. Select Next.
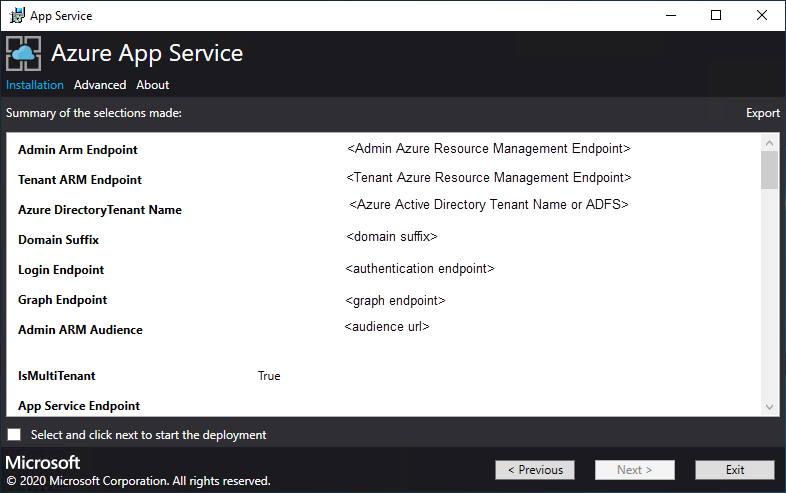
On the App Service Installer summary page, follow these steps:
a. Verify the selections you made. To make changes, use the Previous buttons to visit previous pages.
b. If the configurations are correct, select the check box.
c. To start the deployment, select Next.
On the next App Service Installer page, follow these steps:
a. Track the installation progress. App Service on Azure Stack Hub can take up to 240 minutes to deploy based on the default selections and age of the base Windows 2016 Datacenter image.
b. After the installer successfully finishes, select Exit.
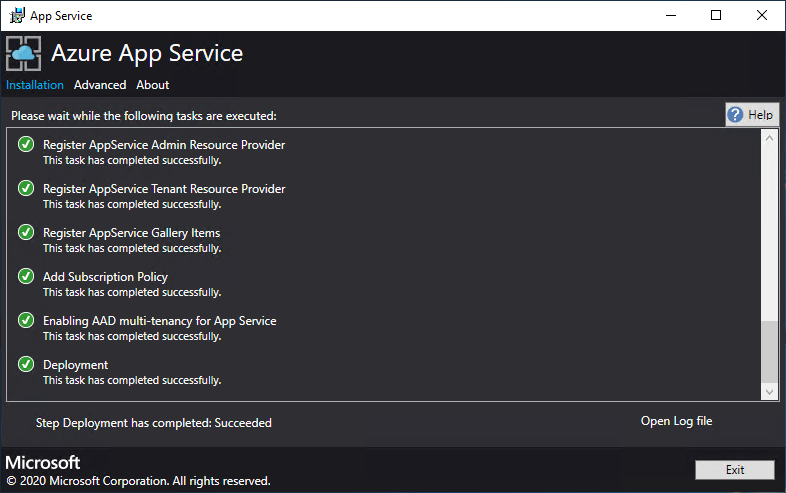
Post-deployment Steps
Important
If you've provided the App Service RP with a SQL Always On Instance you must add the appservice_hosting and appservice_metering databases to an availability group and synchronize the databases to prevent any loss of service in the event of a database failover.
If you're deploying to an existing virtual network and using an internal IP address to connect to your file server, you must add an outbound security rule. This rule enables SMB traffic between the worker subnet and the file server. In the administrator portal, go to the WorkersNsg Network Security Group and add an outbound security rule with the following properties:
- Source: Any
- Source port range: *
- Destination: IP addresses
- Destination IP address range: Range of IPs for your file server
- Destination port range: 445
- Protocol: TCP
- Action: Allow
- Priority: 700
- Name: Outbound_Allow_SMB445
To remove latency when workers are communicating with the file server we also advise adding the following rule to the Worker NSG to allow outbound LDAP and Kerberos traffic to your Active Directory Controllers if securing the file server using Active Directory, for example if you have used the Quickstart template to deploy a HA File Server and SQL Server.
Go to the WorkersNsg in the Admin Portal and add an outbound security rule with the following properties:
- Source: Any
- Source port range: *
- Destination: IP Addresses
- Destination IP address range: Range of IPs for your AD Servers, for example with the Quickstart template 10.0.0.100, 10.0.0.101
- Destination port range: 389,88
- Protocol: Any
- Action: Allow
- Priority: 710
- Name: Outbound_Allow_LDAP_and_Kerberos_to_Domain_Controllers
Validate the App Service on Azure Stack Hub installation
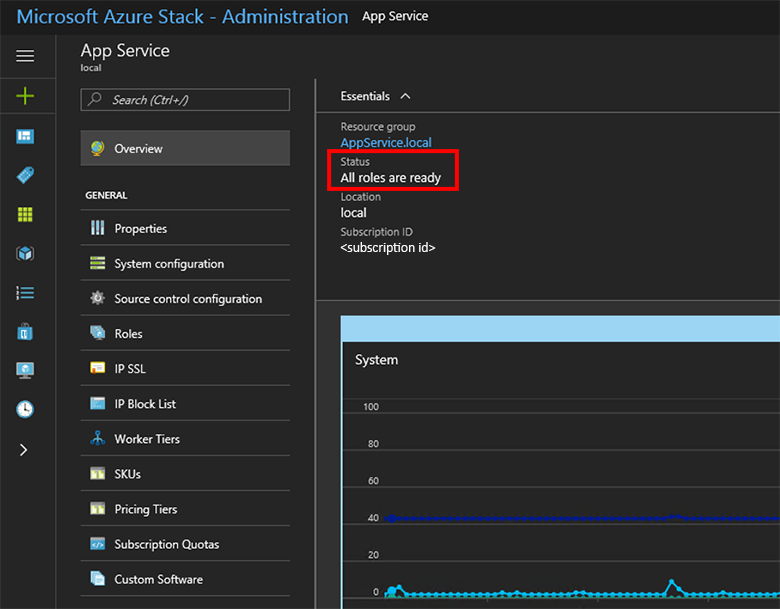
In the Azure Stack Hub administrator portal, go to Administration - App Service.
In the overview, under status, check to see that the Status displays All roles are ready.
Test drive App Service on Azure Stack Hub
After you deploy and register the App Service resource provider, test it to make sure that users can deploy web and API apps.
Note
You need to create an offer that has the Microsoft.Web namespace in the plan. You also need a tenant subscription that subscribes to the offer. For more info, see Create offer and Create plan.
You must have a tenant subscription to create apps that use App Service on Azure Stack Hub. The only tasks that a service admin can complete in the administrator portal are related to the resource provider administration of App Service. This includes adding capacity, configuring deployment sources, and adding Worker tiers and SKUs.
To create web, API, and Azure Functions apps, you must use the user portal and have a tenant subscription.
To create a test web app, follow these steps:
In the Azure Stack Hub user portal, select + Create a resource > Web + Mobile > Web App.
Under Web App, enter a name in Web app.
Under Resource Group, select New. Enter a name for the Resource Group.
Select App Service plan/Location > Create New.
Under App Service plan, enter a name for the App Service plan.
Select Pricing tier > Free-Shared or Shared-Shared > Select > OK > Create.
A tile for the new web app appears on the dashboard. Select the tile.
On Web App, select Browse to view the default website for this app.
Deploy a WordPress, DNN, or Django website (optional)
In the Azure Stack Hub user portal, select +, go to the Azure Marketplace, deploy a Django website, and then wait for the deployment to finish. The Django web platform uses a file system-based database. It doesn't require any additional resource providers, such as SQL or MySQL.
If you also deployed a MySQL resource provider, you can deploy a WordPress website from the Marketplace. When you're prompted for database parameters, enter the user name as User1@Server1, with the user name and server name of your choice.
If you also deployed a SQL Server resource provider, you can deploy a DNN website from the Marketplace. When you're prompted for database parameters, choose a database in the computer running SQL Server that's connected to your resource provider.
In this article you learn how to deploy the Azure App Service resource provider to an Azure Stack Hub environment that is:
- Not connected to the internet.
- Secured by Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS).
To add the Azure App Service resource provider to your offline Azure Stack Hub deployment, you must complete these top-level tasks:
- Complete the prerequisite steps (like purchasing certificates, which can take a few days to receive).
- Download and extract the installation and helper files to a machine that's connected to the internet.
- Create an offline installation package.
- Run the appservice.exe installer file.
Create an offline installation package
To deploy Azure App Service in an offline environment, first create an offline installation package on a machine that's connected to the internet.
Run the AppService.exe installer on a machine that's connected to the internet.
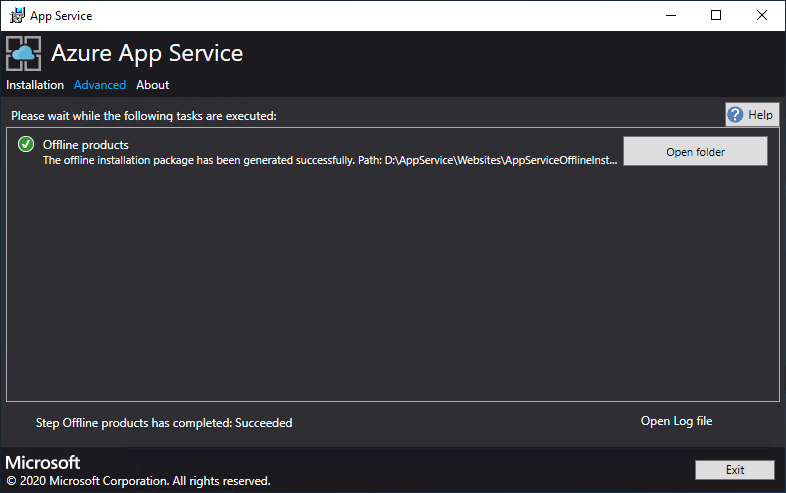
Select Advanced > Create offline installation package. This step will take several minutes to complete.

The Azure App Service installer creates an offline installation package and displays the path to it. You can select Open folder to open the folder in File Explorer.
Copy the installer (AppService.exe) and the offline installation package to a machine that has connectivity to your Azure Stack Hub.
Complete the offline installation of Azure App Service on Azure Stack Hub
Run appservice.exe as an admin from a computer that can reach the Azure Stack Hub Admin Azure Resource Management endpoint.
Select Advanced > Complete offline installation.
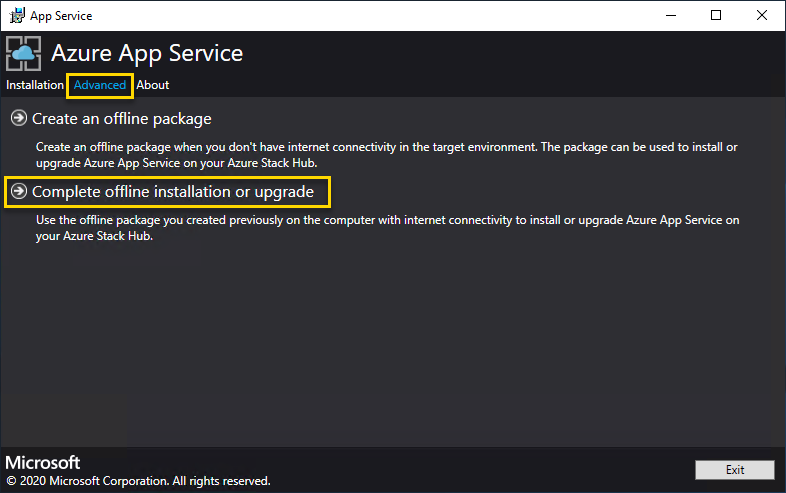
Browse to the location of the offline installation package you previously created, and then select Next.
Review and accept the Microsoft Software License Terms, and then select Next.
Review and accept the third-party license terms, and then select Next.
Make sure the Azure App Service cloud configuration info is correct. If you used the default settings during ASDK deployment, you can accept the default values here. However, if you customized the options when you deployed Azure Stack Hub or are deploying on an integrated system, you must edit the values in this window to reflect those changes. For example, if you use the domain suffix mycloud.com, your Azure Stack Hub Tenant Azure Resource Manager endpoint must change to
management.<region>.mycloud.com. After you confirm your info, select Next.
On the next App Service Installer page you will connect to your Azure Stack Hub:
Select the connection method you wish to use - Credential or Service Principal
- Credential
- If you're using Microsoft Entra ID, enter the Microsoft Entra admin account and password that you provided when you deployed Azure Stack Hub. Select Connect.
- If you're using Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS), provide your admin account. For example, cloudadmin@azurestack.local. Enter your password, and then select Connect.
- Service Principal
- The service principal that you use must have Owner rights on the Default Provider Subscription
- Provide the Service Principal ID, Certificate File, and Password and select Connect.
- Credential
In Azure Stack Hub Subscriptions, select the Default Provider Subscription. Azure App Service on Azure Stack Hub must be deployed in the Default Provider Subscription.
In the Azure Stack Hub Locations, select the location that corresponds to the region you're deploying to. For example, select local if you're deploying to the ASDK.
Administrators can specify a three character Deployment Prefix for the individual instances in each Virtual Machine Scale Set that are deployed. This is useful if managing multiple Azure Stack Hub instances.
You can allow the Azure App Service installer to create a virtual network and associated subnets. Or, you can deploy into an existing virtual network, as configured through these steps.
To use the Azure App Service installer method, select Create VNet with default settings, accept the defaults, and then select Next.
To deploy into an existing network, select Use existing VNet and Subnets, and then:
- Select the Resource Group option that contains your virtual network.
- Choose the Virtual Network name you want to deploy into.
- Select the correct Subnet values for each of the required role subnets.
- Select Next.

Enter the info for your file share and then select Next. The address of the file share must use the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) or IP address of your file server. For example: \\appservicefileserver.local.cloudapp.azurestack.external\websites, or \\10.0.0.1\websites. If you're using a file server that's domain-joined, you must provide the full user name, including the domain. For example:
<myfileserverdomain>\<FileShareOwner>.Note
The installer tries to test connectivity to the file share before proceeding. However, if you choose to deploy into an existing virtual network, the installer might be unable to connect to the file share and displays a warning asking whether you want to continue. Verify the file share info and continue if it's correct.

On the next page:
- In the Identity Application ID box, enter the GUID for the Identity application you created as part of the pre-requisites.
- In the Identity Application certificate file box, enter (or browse to) the location of the certificate file.
- In the Identity Application certificate password box, enter the password for the certificate. This password is the one that you made note of when you used the script to create the certificates.
- In the Azure Resource Manager root certificate file box, enter (or browse to) the location of the certificate file.
- Select Next.

For each of the three certificate file boxes, select Browse and navigate to the appropriate certificate file. You must provide the password for each certificate. These certificates are the ones that you created in Prerequisites for deploying App Service on Azure Stack Hub. Select Next after entering all the information.
Box Certificate file name example App Service default SSL certificate file _.appservice.local.AzureStack.external.pfx App Service API SSL certificate file api.appservice.local.AzureStack.external.pfx App Service Publisher SSL certificate file ftp.appservice.local.AzureStack.external.pfx If you used a different domain suffix when you created the certificates, your certificate file names don't use local.AzureStack.external. Instead, use your custom domain info.

Enter the SQL Server details for the server instance used to host the Azure App Service resource provider databases, and then select Next. The installer validates the SQL connection properties. You must enter either the internal IP or the FQDN for the SQL Server name.
Note
The installer tries to test connectivity to the computer running SQL Server before proceeding. However, if you chose to deploy into an existing virtual network, the installer might not be able to connect to the computer running SQL Server and displays a warning asking whether you want to continue. Verify the SQL Server info and continue if it's correct.
From Azure App Service on Azure Stack Hub 1.3 onward, the installer checks that the computer running SQL Server has database containment enabled at the SQL Server level. If it doesn't, you're prompted with the following exception:
Enable contained database authentication for SQL server by running below command on SQL server (Ctrl+C to copy) *********************************************************** sp_configure 'contained database authentication', 1; GO RECONFIGURE; GO ***********************************************************
Review the role instance and SKU options. The defaults populate with the minimum number of instances and the minimum SKU for each role in a production deployment. For ASDK deployment, you can scale the instances down to lower SKUs to reduce the core and memory commit but you will experience a performance degradation. A summary of vCPU and memory requirements is provided to help plan your deployment. After you make your selections, select Next.
Note
For production deployments, follow the guidance in Capacity planning for Azure App Service server roles in Azure Stack Hub.
Role Minimum instances Minimum SKU Notes Controller 2 Standard_A4_v2 - (4 cores, 8192 MB) Manages and maintains the health of the App Service cloud. Management 1 Standard_D3_v2 - (4 cores, 14336 MB) Manages the App Service Azure Resource Manager and API endpoints, portal extensions (admin, tenant, Functions portal), and the data service. To support failover, increase the recommended instances to 2. Publisher 1 Standard_A2_v2 - (2 cores, 4096 MB) Publishes content via FTP and web deployment. FrontEnd 1 Standard_A4_v2 - (4 cores, 8192 MB) Routes requests to App Service apps. Shared Worker 1 Standard_A4_v2 - (4 cores, 8192 MB) Hosts web or API apps and Azure Functions apps. You might want to add more instances. As an operator, you can define your offering and choose any SKU tier. The tiers must have a minimum of one vCPU. 
In the Select Platform Image box, choose your prepared Windows Server 2022 Datacenter virtual machine (VM) image from the images available on the compute resource provider for the Azure App Service cloud. Select Next.
Note
Windows Server 2022 Core is not a supported platform image for use with Azure App Service on Azure Stack Hub. Don't use evaluation images for production deployments. Azure App Service on Azure Stack Hub requires that Microsoft .NET 3.5.1 SP1 be activated on the image used for deployment. Marketplace-syndicated Windows Server 2022 images don't have this feature enabled. Therefore, you must create and use a Windows Server 2022 image with this feature pre-enabled.
See Prerequisites for deploying App Service on Azure Stack Hub for details on creating a custom image and adding to Marketplace. Be sure to specify the following when adding the image to Marketplace:
- Publisher = MicrosoftWindowsServer
- Offer = WindowsServer
- SKU = AppService
- Version = Specify the "latest" version
On the next page:
- Enter the Worker Role VM admin user name and password.
- Enter the Other Roles VM admin user name and password.
- Select Next.

On the summary page:
- Verify the selections you made. To make changes, use the Previous buttons to visit previous pages.
- If the configurations are correct, select the check box.
- To start the deployment, select Next.

On the next page:
Track the installation progress. App Service on Azure Stack Hub can take up to 240 minutes to deploy based on the default selections and age of the base Windows 2016 Datacenter image.
After the installer finishes running, select Exit.

Post-deployment steps
Important
If you've provided the Azure App Service RP with a SQL Always On Instance, you must add the appservice_hosting and appservice_metering databases to an availability group. You must also synchronize the databases to prevent any loss of service in the event of a database failover.
If you chose to deploy into an existing virtual network and an internal IP address to connect to your file server, you must add an outbound security rule, enabling SMB traffic between the worker subnet and the file server. In the administrator portal, go to the WorkersNsg Network Security Group and add an outbound security rule with the following properties:
- Source: Any
- Source port range: *
- Destination: IP addresses
- Destination IP address range: Range of IPs for your file server
- Destination port range: 445
- Protocol: TCP
- Action: Allow
- Priority: 700
- Name: Outbound_Allow_SMB445
To remove latency when workers are communicating with the file server we also advise adding the following rule to the Worker NSG to allow outbound LDAP and Kerberos traffic to your Active Directory Controllers if securing the file server using Active Directory, for example if you have used the Quickstart template to deploy a HA File Server and SQL Server.
Go to the WorkersNsg in the Admin Portal and add an outbound security rule with the following properties:
- Source: Any
- Source port range: *
- Destination: IP Addresses
- Destination IP address range: Range of IPs for your AD Servers, for example with the Quickstart template 10.0.0.100, 10.0.0.101
- Destination port range: 389,88
- Protocol: Any
- Action: Allow
- Priority: 710
- Name: Outbound_Allow_LDAP_and_Kerberos_to_Domain_Controllers
Validate the Azure App Service on Azure Stack Hub installation
In the Azure Stack Hub administrator portal, go to Administration - App Service.
In the overview, under status, check to see that the Status displays All roles are ready.

Test drive Azure App Service on Azure Stack Hub
After you deploy and register the Azure App Service resource provider, test it to make sure that users can deploy web and API apps.
Note
You must create an offer that has the Microsoft.Web namespace within the plan. Then, you need to have a tenant subscription that subscribes to this offer. For more info, see Create offer and Create plan.
You must have a tenant subscription to create apps that use Azure App Service on Azure Stack Hub. The only capabilities that a service admin can complete within the administrator portal are related to the resource provider administration of Azure App Service. These capabilities include adding capacity, configuring deployment sources, and adding Worker tiers and SKUs.
As of the third technical preview, to create web, API, and Azure Functions apps, you must use the user portal and have a tenant subscription.
In the Azure Stack Hub user portal, select + Create a resource > Web + Mobile > Web App.
On the Web App blade, type a name in the Web app box.
Under Resource Group, select New. Type a name in the Resource Group box.
Select App Service plan/Location > Create New.
On the App Service plan blade, type a name in the App Service plan box.
Select Pricing tier > Free-Shared or Shared-Shared > Select > OK > Create.
In less than a minute, a tile for the new web app appears on the dashboard. Select the tile.
On the Web App blade, select Browse to view the default website for this app.
Deploy a WordPress, DNN, or Django website (optional)
In the Azure Stack Hub user portal, select +, go to Azure Marketplace, deploy a Django website, and wait for successful completion. The Django web platform uses a file system-based database. It doesn't require any additional resource providers, such as SQL or MySQL.
If you also deployed a MySQL resource provider, you can deploy a WordPress website from Azure Marketplace. When you're prompted for database parameters, enter the user name as User1@Server1, with the user name and server name of your choice.
If you also deployed a SQL Server resource provider, you can deploy a DNN website from Azure Marketplace. When you're prompted for database parameters, choose a database on the computer running SQL Server that's connected to your resource provider.
Next steps
Prepare for additional admin operations for App Service on Azure Stack Hub: