Enable offline sync for your Windows app
Overview
This tutorial shows you how to add offline support to a Universal Windows Platform (UWP) app using an Azure Mobile App backend. Offline sync allows end users to interact with a mobile app--viewing, adding, or modifying data - even when there is no network connection. Changes are stored in a local database. Once the device is back online, these changes are synced with the remote backend.
In this tutorial, you update the UWP app project from the tutorial Create a Windows app to support the offline features of Azure Mobile Apps. If you do not use the downloaded quick start server project, you must add the data access extension packages to your project. For more information about server extension packages, see Work with the .NET backend server SDK for Azure Mobile Apps.
To learn more about the offline sync feature, see the topic Offline Data Sync in Azure Mobile Apps.
Requirements
This tutorial requires the following pre-requisites:
- Visual Studio 2013 running on Windows 8.1 or later.
- Completion of Create a Windows app.
- Azure Mobile Services SQLite Store
- SQLite for Universal Windows Platform development
Update the client app to support offline features
Azure Mobile App offline features allow you to interact with a local database when you are in an offline scenario. To use these features in your app, you initialize a SyncContext to a local store. Then reference your table through the IMobileServiceSyncTable interface. SQLite is used as the local store on the device.
Install the SQLite runtime for the Universal Windows Platform.
In Visual Studio, open the NuGet package manager for the UWP app project that you completed in the Create a Windows app tutorial. Search for and install the Microsoft.Azure.Mobile.Client.SQLiteStore NuGet package.
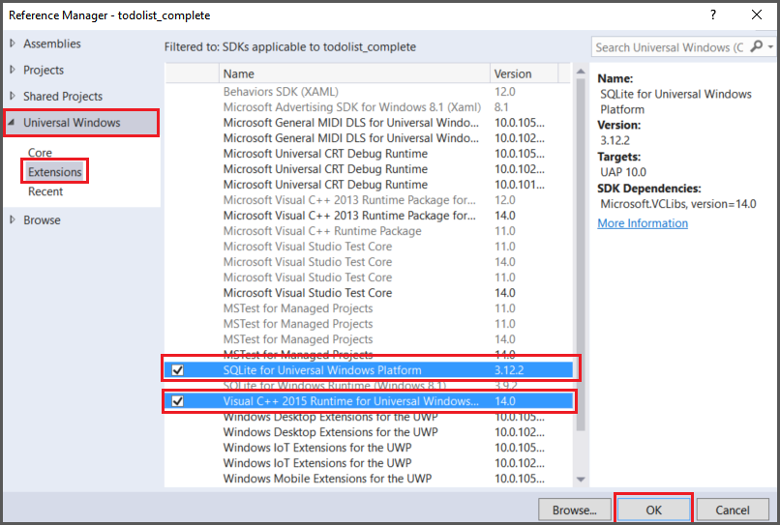
In Solution Explorer, right-click References > Add Reference... > Universal Windows > Extensions, then enable both SQLite for Universal Windows Platform and Visual C++ 2015 Runtime for Universal Windows Platform apps.
Open the MainPage.xaml.cs file and uncomment the
#define OFFLINE_SYNC_ENABLEDdefinition.In Visual Studio, press the F5 key to rebuild and run the client app. The app works the same as it did before you enabled offline sync. However, the local database is now populated with data that can be used in an offline scenario.
Update the app to disconnect from the backend
In this section, you break the connection to your Mobile App backend to simulate an offline situation. When you add data items, your exception handler tells you that the app is in offline mode. In this state, new items added in the local store and will be synced to the mobile app backend when push is next run in a connected state.
Edit App.xaml.cs in the shared project. Comment out the initialization of the MobileServiceClient and add the following line, which uses an invalid mobile app URL:
public static MobileServiceClient MobileService = new MobileServiceClient("https://your-service.azurewebsites.fail");You can also demonstrate offline behavior by disabling wifi and cellular networks on the device or use airplane mode.
Press F5 to build and run the app. Notice your sync failed on refresh when the app launched.
Enter new items and notice that push fails with a CancelledByNetworkError status each time you click Save. However, the new todo items exist in the local store until they can be pushed to the mobile app backend. In a production app, if you suppress these exceptions the client app behaves as if it's still connected to the mobile app backend.
Close the app and restart it to verify that the new items you created are persisted to the local store.
(Optional) In Visual Studio, open Server Explorer. Navigate to your database in Azure->SQL Databases. Right-click your database and select Open in SQL Server Object Explorer. Now you can browse to your SQL database table and its contents. Verify that the data in the backend database has not changed.
(Optional) Use a REST tool such as Fiddler or Postman to query your mobile backend, using a GET query in the form
https://<your-mobile-app-backend-name>.azurewebsites.net/tables/TodoItem.
Update the app to reconnect your Mobile App backend
In this section, you reconnect the app to the mobile app backend. These changes simulate a network reconnection on the app.
When you first run the application, the OnNavigatedTo event handler calls InitLocalStoreAsync. This method in turn calls SyncAsync to sync your
local store with the backend database. The app attempts to sync on startup.
Open App.xaml.cs in the shared project, and uncomment your previous initialization of
MobileServiceClientto use the correct the mobile app URL.Press the F5 key to rebuild and run the app. The app syncs your local changes with the Azure Mobile App backend using push and pull operations when the
OnNavigatedToevent handler executes.(Optional) View the updated data using either SQL Server Object Explorer or a REST tool like Fiddler. Notice the data has been synchronized between the Azure Mobile App backend database and the local store.
In the app, click the check box beside a few items to complete them in the local store.
UpdateCheckedTodoItemcallsSyncAsyncto sync each completed item with the Mobile App backend.SyncAsynccalls both push and pull. However, whenever you execute a pull against a table that the client has made changes to, a push is always executed automatically. This behavior ensures all tables in the local store along with relationships remain consistent. This behavior may result in an unexpected push. For more information on this behavior, see Offline Data Sync in Azure Mobile Apps.
API Summary
To support the offline features of mobile services, we used the IMobileServiceSyncTable interface and initialized MobileServiceClient.SyncContext with a local SQLite database. When offline, the normal CRUD operations for Mobile Apps work as if the app is still connected while the operations occur against the local store. The following methods are used to synchronize the local store with the server:
- PushAsync Because this method is a member of IMobileServicesSyncContext, changes across all tables are pushed to the backend. Only records with local changes are sent to the server.
- PullAsync A pull is started from a IMobileServiceSyncTable. When there are tracked changes in the table, an implicit push is run to make sure that all tables in the local store along with relationships remain consistent. The pushOtherTables parameter controls whether other tables in the context are pushed in an implicit push. The query parameter takes an IMobileServiceTableQuery<T> or OData query string to filter the returned data. The queryId parameter is used to define incremental sync. For more information, see Offline Data Sync in Azure Mobile Apps.
- PurgeAsync Your app should periodically call this method to purge stale data from the local store. Use the force parameter when you need to purge any changes that have not yet been synced.
For more information about these concepts, see Offline Data Sync in Azure Mobile Apps.
More info
The following topics provide additional background information on the offline sync feature of Mobile Apps: