Quickstart: Keyword search using REST
In this quickstart, you call the Search REST APIs to create, load, and query a search index. The REST APIs in Azure AI Search provide programmatic access to all of its capabilities, including preview features, and are an easy way to learn how features work.
Prerequisites
An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
An Azure AI Search service. Create a service or find an existing service in your current subscription. For this quickstart, you can use a free service.
Visual Studio Code with a REST client.
Download files
Download a REST sample from GitHub to send the requests in this quickstart. Instructions can be found at Downloading files from GitHub.
You can also start a new file on your local system and create requests manually by using the instructions in this article.
Get a search service endpoint
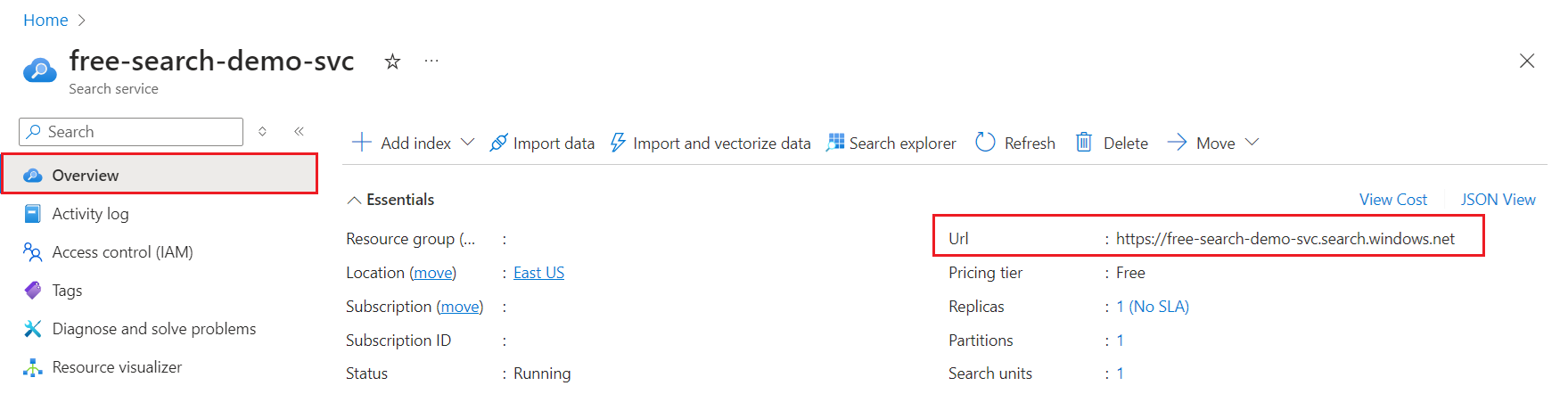
You can find the search service endpoint in the Azure portal.
Sign in to the Azure portal and find your search service.
On the Overview home page, find the URL. An example endpoint might look like
https://mydemo.search.windows.net.
You're pasting this endpoint into the .rest or .http file in a later step.
Configure access
Requests to the search endpoint must be authenticated and authorized. You can use API keys or roles for this task. Keys are easier to start with, but roles are more secure.
For a role-based connection, the following instructions have you connecting to Azure AI Search under your identity, not the identity of a client app.
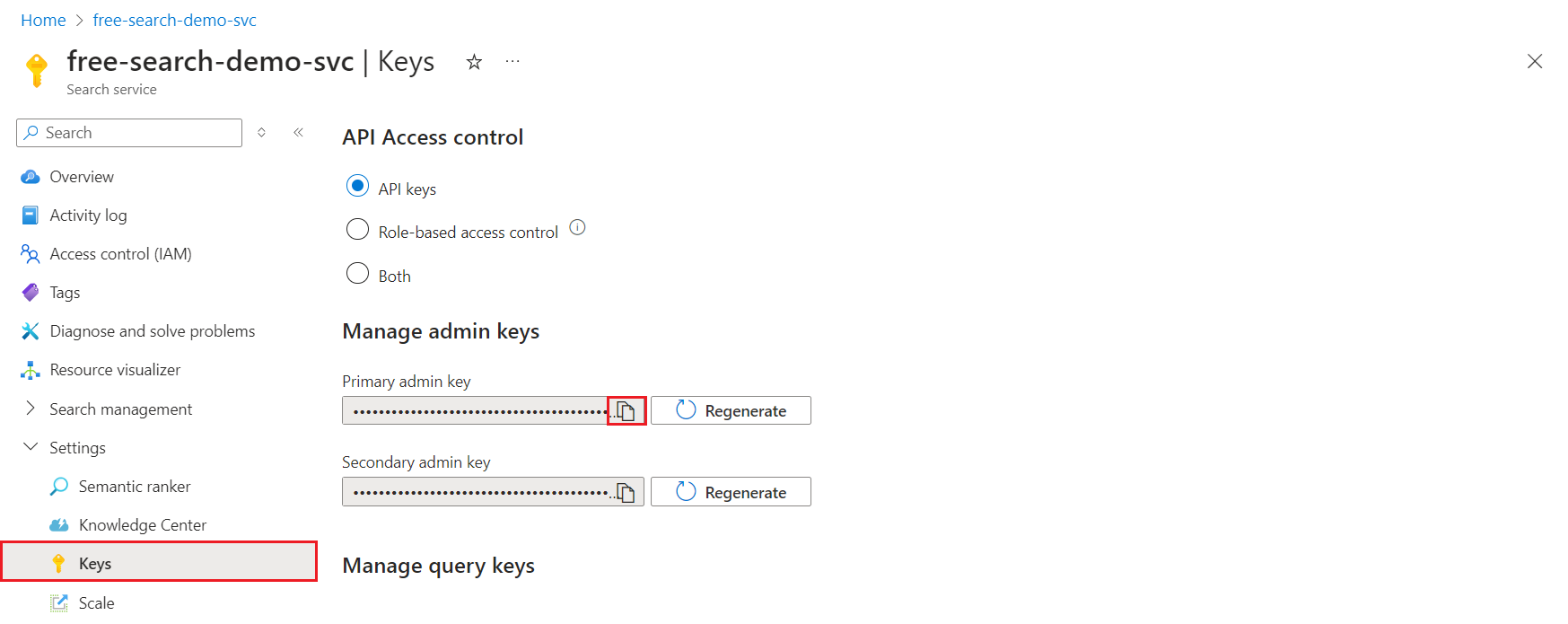
Option 1: Use keys
Select Settings > Keys and then copy an admin key. Admin keys are used to add, modify, and delete objects. There are two interchangeable admin keys. Copy either one. For more information, see Connect to Azure AI Search using key authentication.
You're pasting this key into the .rest or .http file in a later step.
Option 2: Use roles
Make sure your search service is configured for role-based access. You must have preconfigured role-assignments for developer access. Your role assignments must grant permission to create, load, and query a search index.
In this section, obtain your personal identity token using either the Azure CLI, Azure PowerShell, or the Azure portal.
Sign in to Azure CLI.
az loginGet your personal identity token.
az account get-access-token --scope https://search.azure.com/.default
You're pasting your personal identity token into the .rest or .http file in a later step.
Note
This section assumes you're using a local client that connects to Azure AI Search on your behalf. An alternative approach is getting a token for the client app, assuming your application is registered with Microsoft Entra ID.
Set up Visual Studio Code
If you're not familiar with the REST client for Visual Studio Code, this section includes setup so that you can complete the tasks in this quickstart.
Start Visual Studio Code and select the Extensions tile.
Search for the REST client and select Install.

Open or create a new file named with either a
.restor.httpfile extension.Paste in the following example if you're using API keys. Replace the
@baseUrland@apiKeyplaceholders with the values you copied earlier, without quotes.@baseUrl = PUT-YOUR-SEARCH-SERVICE-ENDPOINT-HERE @apiKey = PUT-YOUR-SEARCH-SERVICE-API-KEY-HERE ### List existing indexes by name GET {{baseUrl}}/indexes?api-version=2024-07-01&$select=name HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/json api-key: {{apiKey}}Or, paste in this example if you're using roles. Replace the
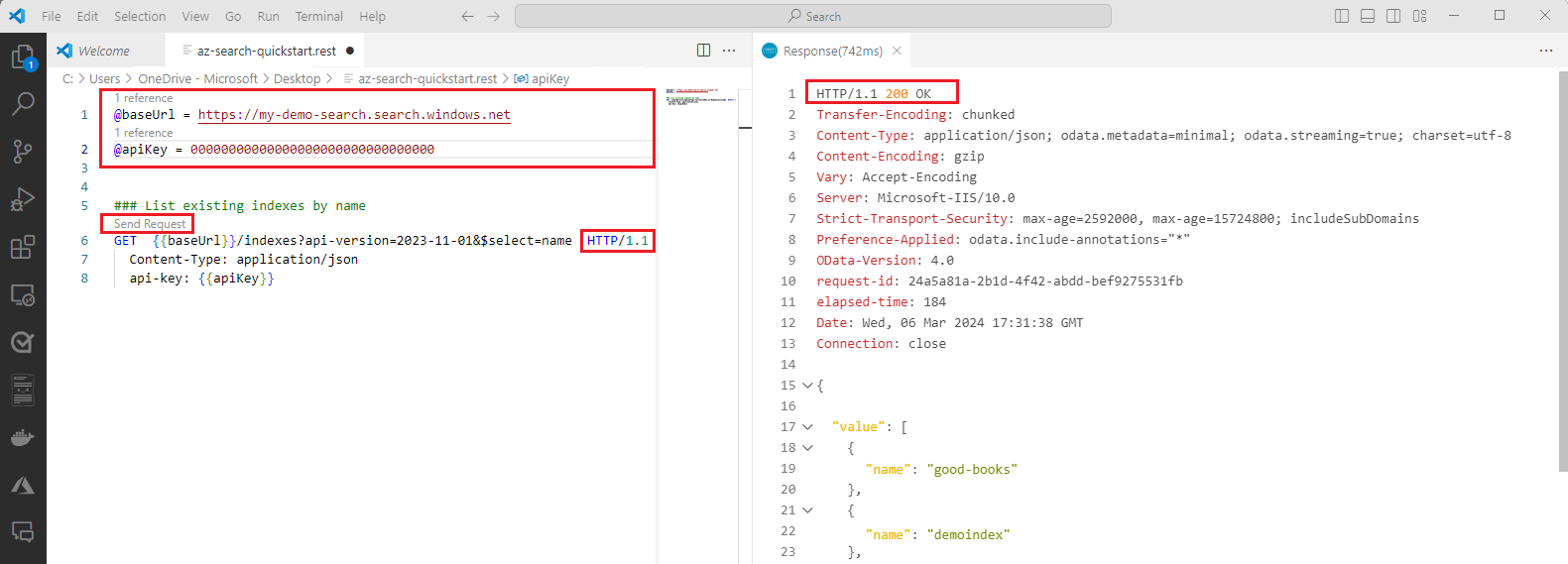
@baseUrland@tokenplaceholders with the values you copied earlier, without quotes.@baseUrl = PUT-YOUR-SEARCH-SERVICE-ENDPOINT-HERE @token = PUT-YOUR-PERSONAL-IDENTITY-TOKEN-HERE ### List existing indexes by name GET {{baseUrl}}/indexes?api-version=2024-07-01&$select=name HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/json Authorization: Bearer {{token}}Select Send request. A response should appear in an adjacent pane. If you have existing indexes, they're listed. Otherwise, the list is empty. If the HTTP code is
200 OK, you're ready for the next steps.If you get
WWW-Authenticate: Bearer realm="Azure Cognitive Search" error="invalid_token" error_description="Authentication token failed validation.", remove the quotes around the token, save the file, and retry your request.Key points:
- Parameters are specified by using an
@prefix. ###designates a REST call. The next line contains the request, which must includeHTTP/1.1.Send requestshould appear above the request.
- Parameters are specified by using an
Create an index
Add a second request to your .rest file. Create Index (REST) creates a search index and sets up the physical data structures on your search service.
Paste in the following example to create the
hotels-quickstartindex on your search service.### Create a new index POST {{baseUrl}}/indexes?api-version=2024-07-01 HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/json Authorization: Bearer {{token}} { "name": "hotels-quickstart", "fields": [ {"name": "HotelId", "type": "Edm.String", "key": true, "filterable": true}, {"name": "HotelName", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "filterable": false, "sortable": true, "facetable": false}, {"name": "Description", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "filterable": false, "sortable": false, "facetable": false, "analyzer": "en.lucene"}, {"name": "Category", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "filterable": true, "sortable": true, "facetable": true}, {"name": "Tags", "type": "Collection(Edm.String)", "searchable": true, "filterable": true, "sortable": false, "facetable": true}, {"name": "ParkingIncluded", "type": "Edm.Boolean", "filterable": true, "sortable": true, "facetable": true}, {"name": "LastRenovationDate", "type": "Edm.DateTimeOffset", "filterable": true, "sortable": true, "facetable": true}, {"name": "Rating", "type": "Edm.Double", "filterable": true, "sortable": true, "facetable": true}, {"name": "Address", "type": "Edm.ComplexType", "fields": [ {"name": "StreetAddress", "type": "Edm.String", "filterable": false, "sortable": false, "facetable": false, "searchable": true}, {"name": "City", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "filterable": true, "sortable": true, "facetable": true}, {"name": "StateProvince", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "filterable": true, "sortable": true, "facetable": true}, {"name": "PostalCode", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "filterable": true, "sortable": true, "facetable": true}, {"name": "Country", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "filterable": true, "sortable": true, "facetable": true} ] } ] }Select Send request. You should have an
HTTP/1.1 201 Createdresponse and the response body should include the JSON representation of the index schema.If you get a
Header name must be a valid HTTP token ["{"]error, make sure there's an empty line betweenapi-keyand the body of the request. If you get HTTP 504, verify that the URL specifies HTTPS. If you see HTTP 400 or 404, check the request body to verify there were no copy-paste errors. An HTTP 403 typically indicates a problem with the API key. It's either an invalid key or a syntax problem with how the API key is specified.You now have several requests in your file. Recall that
###starts a new request and each request runs independently.
About the index definition
Within the index schema, the fields collection defines document structure. Each document that you upload must have these fields. Each field must be assigned to an Entity Data Model (EDM) data type. String fields are used in full text search. If you want numeric data to be searchable, make sure the data type is Edm.String. Other data types such as Edm.Int32 are filterable, sortable, facetable, and retrievable but not full-text searchable.
Attributes on the field determine allowed actions. The REST APIs allow many actions by default. For example, all strings are searchable and retrievable by default. For REST APIs, you might only have attributes if you need to turn off a behavior.
{
"name": "hotels-quickstart",
"fields": [
{"name": "HotelId", "type": "Edm.String", "key": true, "filterable": true},
{"name": "HotelName", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "filterable": false, "sortable": true, "facetable": false},
{"name": "Description", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "filterable": false, "sortable": false, "facetable": false, "analyzer": "en.lucene"},
{"name": "Category", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "filterable": true, "sortable": true, "facetable": true},
{"name": "Tags", "type": "Collection(Edm.String)", "searchable": true, "filterable": true, "sortable": false, "facetable": true},
{"name": "ParkingIncluded", "type": "Edm.Boolean", "filterable": true, "sortable": true, "facetable": true},
{"name": "LastRenovationDate", "type": "Edm.DateTimeOffset", "filterable": true, "sortable": true, "facetable": true},
{"name": "Rating", "type": "Edm.Double", "filterable": true, "sortable": true, "facetable": true},
{"name": "Address", "type": "Edm.ComplexType",
"fields": [
{"name": "StreetAddress", "type": "Edm.String", "filterable": false, "sortable": false, "facetable": false, "searchable": true},
{"name": "City", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "filterable": true, "sortable": true, "facetable": true},
{"name": "StateProvince", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "filterable": true, "sortable": true, "facetable": true},
{"name": "PostalCode", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "filterable": true, "sortable": true, "facetable": true},
{"name": "Country", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "filterable": true, "sortable": true, "facetable": true}
]
}
]
}
Load documents
Creating and loading the index are separate steps. In Azure AI Search, the index contains all searchable data and queries run on the search service. For REST calls, the data is provided as JSON documents. Use Documents- Index REST API for this task.
The URI is extended to include the docs collections and index operation.
Paste in the following example to upload JSON documents to the search index.
### Upload documents POST {{baseUrl}}/indexes/hotels-quickstart/docs/index?api-version=2024-07-01 HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/json Authorization: Bearer {{token}} { "value": [ { "@search.action": "upload", "HotelId": "1", "HotelName": "Stay-Kay City Hotel", "Description": "The hotel is ideally located on the main commercial artery of the city in the heart of New York. A few minutes away is Time's Square and the historic centre of the city, as well as other places of interest that make New York one of America's most attractive and cosmopolitan cities.", "Category": "Boutique", "Tags": [ "pool", "air conditioning", "concierge" ], "ParkingIncluded": false, "LastRenovationDate": "1970-01-18T00:00:00Z", "Rating": 3.60, "Address": { "StreetAddress": "677 5th Ave", "City": "New York", "StateProvince": "NY", "PostalCode": "10022", "Country": "USA" } }, { "@search.action": "upload", "HotelId": "2", "HotelName": "Old Century Hotel", "Description": "The hotel is situated in a nineteenth century plaza, which has been expanded and renovated to the highest architectural standards to create a modern, functional and first-class hotel in which art and unique historical elements coexist with the most modern comforts.", "Category": "Boutique", "Tags": [ "pool", "free wifi", "concierge" ], "ParkingIncluded": false, "LastRenovationDate": "1979-02-18T00:00:00Z", "Rating": 3.60, "Address": { "StreetAddress": "140 University Town Center Dr", "City": "Sarasota", "StateProvince": "FL", "PostalCode": "34243", "Country": "USA" } }, { "@search.action": "upload", "HotelId": "3", "HotelName": "Gastronomic Landscape Hotel", "Description": "The Hotel stands out for its gastronomic excellence under the management of William Dough, who advises on and oversees all of the Hotel’s restaurant services.", "Category": "Resort and Spa", "Tags": [ "air conditioning", "bar", "continental breakfast" ], "ParkingIncluded": true, "LastRenovationDate": "2015-09-20T00:00:00Z", "Rating": 4.80, "Address": { "StreetAddress": "3393 Peachtree Rd", "City": "Atlanta", "StateProvince": "GA", "PostalCode": "30326", "Country": "USA" } }, { "@search.action": "upload", "HotelId": "4", "HotelName": "Sublime Palace Hotel", "Description": "Sublime Palace Hotel is located in the heart of the historic center of Sublime in an extremely vibrant and lively area within short walking distance to the sites and landmarks of the city and is surrounded by the extraordinary beauty of churches, buildings, shops and monuments. Sublime Palace is part of a lovingly restored 1800 palace.", "Category": "Boutique", "Tags": [ "concierge", "view", "24-hour front desk service" ], "ParkingIncluded": true, "LastRenovationDate": "1960-02-06T00:00:00Z", "Rating": 4.60, "Address": { "StreetAddress": "7400 San Pedro Ave", "City": "San Antonio", "StateProvince": "TX", "PostalCode": "78216", "Country": "USA" } } ] }Select Send request. In a few seconds, you should see an HTTP 201 response in the adjacent pane.
If you get a 207, at least one document failed to upload. If you get a 404, you have a syntax error in either the header or body of the request. Verify that you changed the endpoint to include
/docs/index.
Run queries
Now that documents are loaded, you can issue queries against them by using Documents - Search Post (REST).
The URI is extended to include a query expression, which is specified by using the /docs/search operator.
Paste in the following example to query the search index. Then select Send request. A text search request always includes a
searchparameter. This example includes an optionalsearchFieldsparameter that constrains text search to specific fields.### Run a query POST {{baseUrl}}/indexes/hotels-quickstart/docs/search?api-version=2024-07-01 HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/json Authorization: Bearer {{token}} { "search": "lake view", "select": "HotelId, HotelName, Tags, Description", "searchFields": "Description, Tags", "count": true }Review the response in the adjacent pane. You should have a count that indicates the number of matches found in the index, a search score that indicates relevance, and values for each field listed in the
selectstatement.{ "@odata.context": "https://my-demo.search.windows.net/indexes('hotels-quickstart')/$metadata#docs(*)", "@odata.count": 1, "value": [ { "@search.score": 0.6189728, "HotelId": "4", "HotelName": "Sublime Palace Hotel", "Description": "Sublime Palace Hotel is located in the heart of the historic center of Sublime in an extremely vibrant and lively area within short walking distance to the sites and landmarks of the city and is surrounded by the extraordinary beauty of churches, buildings, shops and monuments. Sublime Palace is part of a lovingly restored 1800 palace.", "Tags": [ "concierge", "view", "24-hour front desk service" ] } ] }
Get index properties
You can also use Get Statistics to query for document counts and index size.
Paste in the following example to query the search index. Then select Send request.
### Get index statistics GET {{baseUrl}}/indexes/hotels-quickstart/stats?api-version=2024-07-01 HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/json Authorization: Bearer {{token}}Review the response. This operation is an easy way to get details about index storage.
{ "@odata.context": "https://my-demo.search.windows.net/$metadata#Microsoft.Azure.Search.V2023_11_01.IndexStatistics", "documentCount": 4, "storageSize": 34707, "vectorIndexSize": 0 }
Clean up resources
When you're working in your own subscription, it's a good idea at the end of a project to identify whether you still need the resources you created. Resources left running can cost you money. You can delete resources individually or delete the resource group to delete the entire set of resources.
You can find and manage resources in the Azure portal by using the All resources or Resource groups link in the leftmost pane.
You can also try this DELETE command:
### Delete an index
DELETE {{baseUrl}}/indexes/hotels-quickstart?api-version=2024-07-01 HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
api-key: {{apiKey}}
Next step
Now that you're familiar with the REST client and making REST calls to Azure AI Search, try another quickstart that demonstrates vector support: