Create an Azure AI Search service in the Azure portal
Azure AI Search is an information retrieval platform for the enterprise. It supports traditional search and conversational, AI-driven search for "chat with your data" experiences across your proprietary content.
The easiest way to create a search service is through the Azure portal, which is covered in this article.
You can also use:
Before you start
Some properties are fixed for the lifetime of the search service. Before creating your service, decide on the following properties:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Becomes part of the URL endpoint. The name must be unique and follow naming rules. |
| Region | Determines data residency and availability of certain features. For example, semantic ranker and Azure AI integration have region requirements. Choose a region that supports the features you need. |
| Tier | Determines infrastructure, service limits, and billing. Some features aren't available on lower or specialized tiers. |
Subscribe to Azure
Azure AI Search requires a free or pay-as-you-go Azure subscription.
To try Azure AI Search for free, start a trial subscription and then create your search service on the Free tier. Each Azure subscription can have one free search service, which is intended for short-term, non-production evaluation of the product. You can complete all of our quickstarts and most of our tutorials on the Free tier. For more information, see Try Azure AI Search for free.
Important
To make room for other services, Microsoft might delete free services that are inactive for an extended period of time.
Find the Azure AI Search offering
Sign in to the Azure portal.
In the upper-left corner of your dashboard, select Create a resource.
Use the search box to find Azure AI Search.
Choose a subscription
If you have multiple Azure subscriptions, choose one for your search service.
If you're implementing customer-managed encryption or using other features that rely on managed service identities for external data access, choose the same subscription you use for Azure Key Vault or other services that use managed identities.
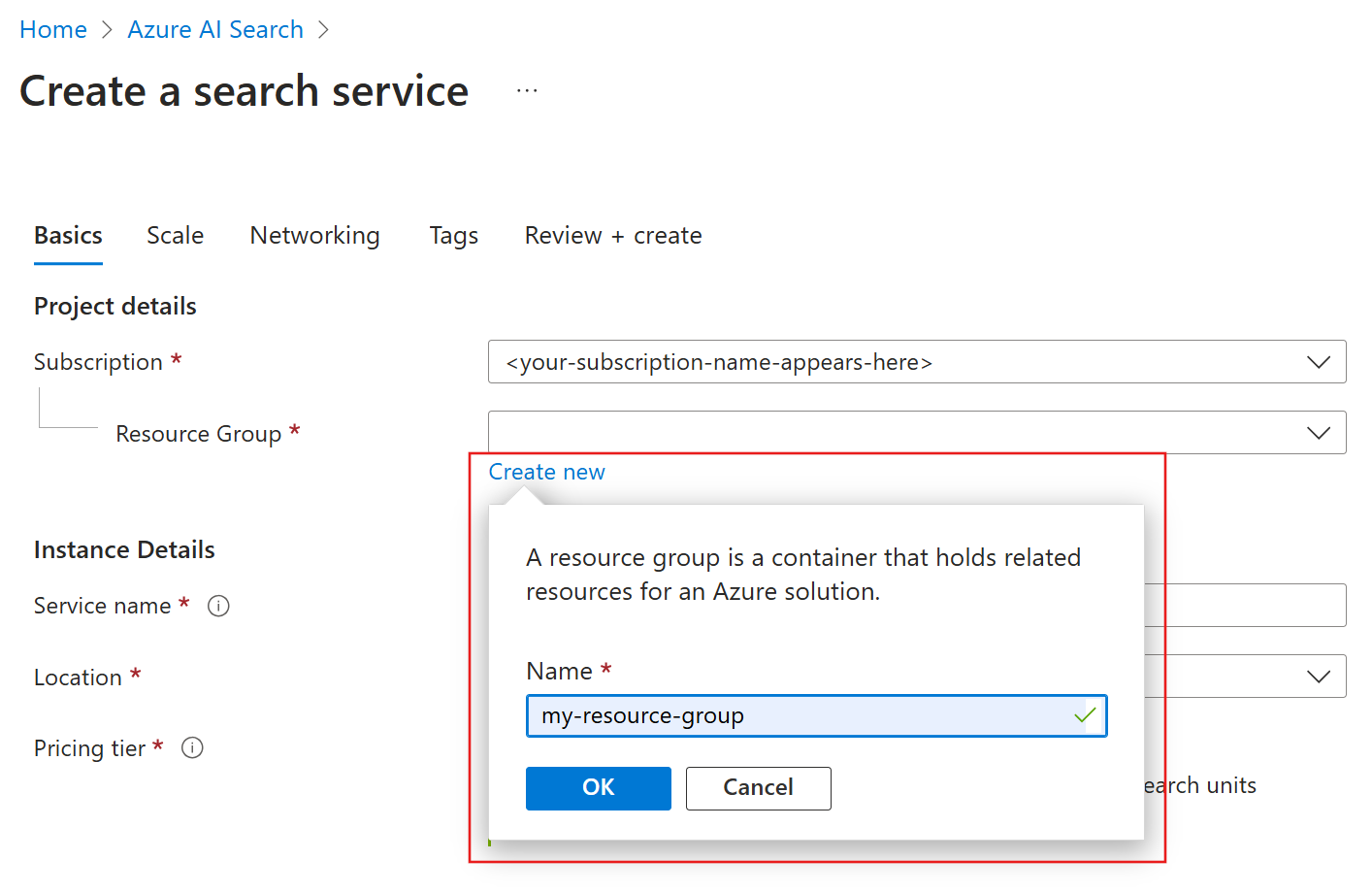
Set a resource group
A resource group is a container that holds related resources for an Azure solution. Use it to consolidate same-solution resources, monitor costs, and check the creation date of your search service.
Over time, you can track current and projected costs for individual resources and for the overall resource group. The following screenshot shows the cost information that's available when you combine multiple resources into one group:
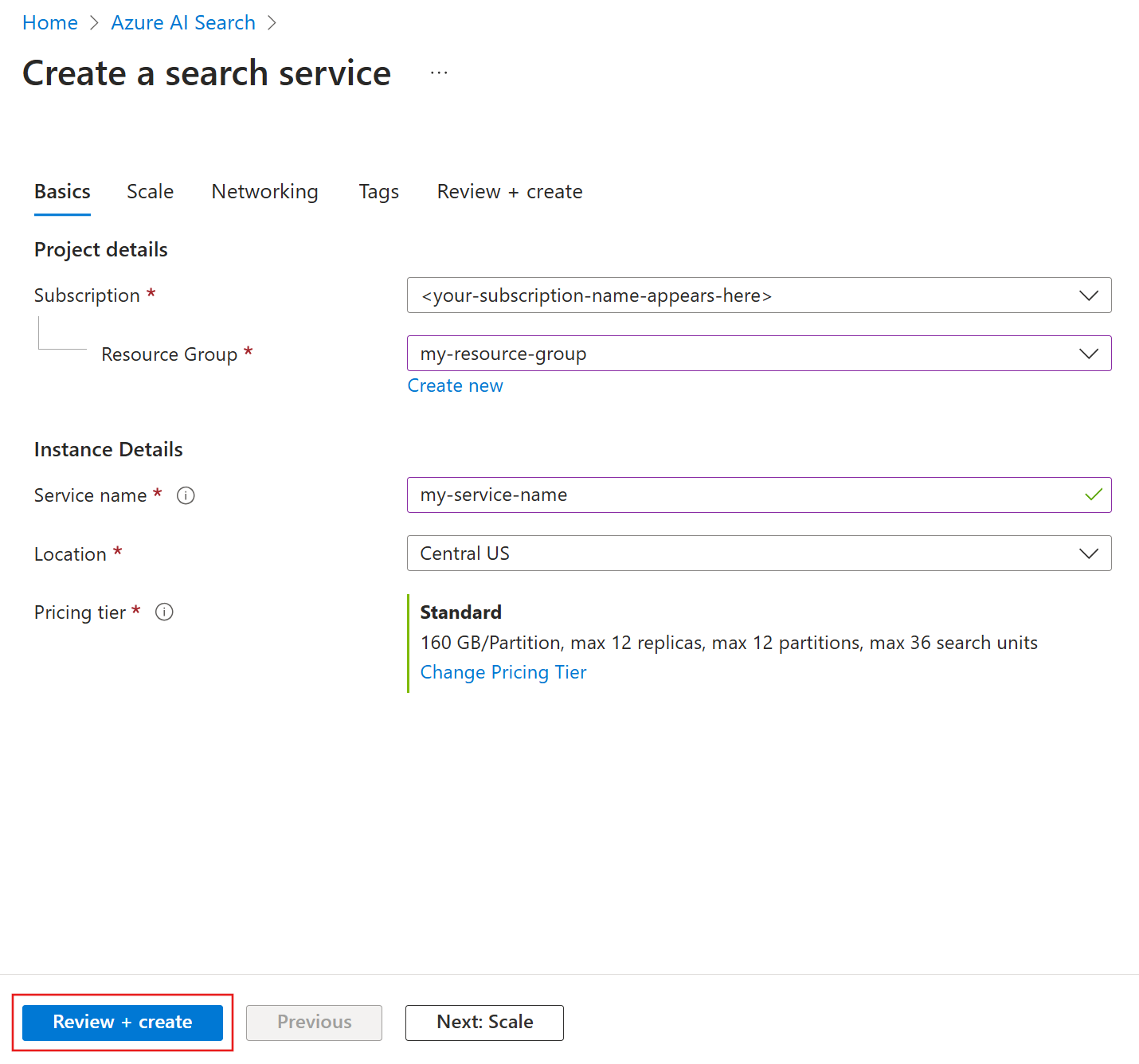
Name your service
Enter a name for your search service. The name is part of the endpoint against which API calls are issued: https://your-service-name.search.windows.net. For example, if you enter myservice, the endpoint becomes https://myservice.search.windows.net.
When naming your service, follow these rules:
- Use a name that's unique within the
search.windows.netnamespace. - Use between 2 and 60 characters.
- Use only lowercase letters, digits, and dashes (-).
- Don't use dashes as the first two characters or the last character.
- Don't use consecutive dashes.
Tip
If you have multiple search services, it's helpful to include the region in the service name. For example, when deciding how to combine or attach resources, the name myservice-westus might save you a trip to the Properties page.
Choose a region
Important
Due to high demand, Azure AI Search is currently unavailable for new instances in some regions.
If you use multiple Azure services, putting all of them in the same region minimizes or voids bandwidth charges. There are no charges for data egress among same-region services.
In most cases, choose a region near you, unless any of the following apply:
Your nearest region is at capacity. The Azure portal has the advantage of hiding unavailable regions and tiers during resource setup.
You want to use integrated data chunking and vectorization or built-in skills for AI enrichment. Integrated operations have region requirements.
You want to use Azure Storage for indexer-based indexing, or you want to store application data that isn't in an index. Debug session state, enrichment caches, and knowledge stores are Azure AI Search features that depend on Azure Storage. The region you choose for Azure Storage has implications for network security. If you're setting up a firewall, you should place the resources in separate regions. For more information, see Outbound connections from Azure AI Search to Azure Storage.
Checklist for choosing a region
Is Azure AI Search available in a nearby region? Check the list of supported regions.
Do you have a specific tier in mind? Check region availability by tier.
Do you have business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR) requirements? Create two or more search services in regional pairs within availability zones. For example, if you're operating in North America, you might choose East US and West US, or North Central US and South Central US, for each search service.
Do you need AI enrichment, integrated data chunking and vectorization, or multimodal image search? Azure AI Search, Azure OpenAI, and Azure AI multiservice must coexist in the same region.
Start with Azure OpenAI regions because they have the most variability. Azure OpenAI provides embedding models and chat models for RAG and integrated vectorization.
Check Azure AI Search regions for a match to your Azure OpenAI region. If you're using OCR, entity recognition, or other skills backed by Azure AI, the AI service integration column indicates whether Azure AI multiservice and Azure AI Search are in the same region.
Check multimodal embedding regions for multimodal APIs and image search. This API is accessed through an Azure AI multiservice account, but in general, it's available in fewer regions than Azure AI multiservice.
Regions with the most overlap
Currently, the following regions offer cross-regional availability for Azure AI Search, Azure OpenAI, and Azure AI Vision multimodal:
- Americas: West US, East US
- Europe: Switzerland North, Sweden Central
This list isn't definitive, and depending on your tier, you might have more choices. Region status can also change quickly, so confirm your region choice before creating your search service.
Choose a tier
Azure AI Search is offered in multiple pricing tiers:
- Free
- Basic
- Standard
- Storage Optimized
Each tier has its own capacity and limits, and some features are tier dependent. For information about computing characteristics, feature availability, and region availability, see Choose a service tier for Azure AI Search.
The Basic and Standard tiers are the most common for production workloads, but many customers start with the Free tier. The billable tiers differ primarily in partition size, partition speed, and limits on the number of objects you can create.
Note
- You can't change the tier after creating your search service, so choose carefully.
- Search services created after April 3, 2024 have larger partitions and higher vector quotas at every billable tier.
Create your service
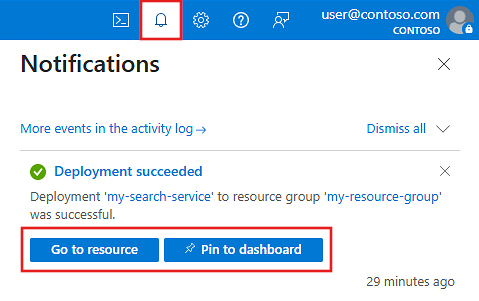
After providing the necessary inputs, create your search service.
Your service is deployed within minutes, and you can monitor its progress with Azure notifications. Consider pinning the service to your dashboard for easy access in the future.
Configure authentication
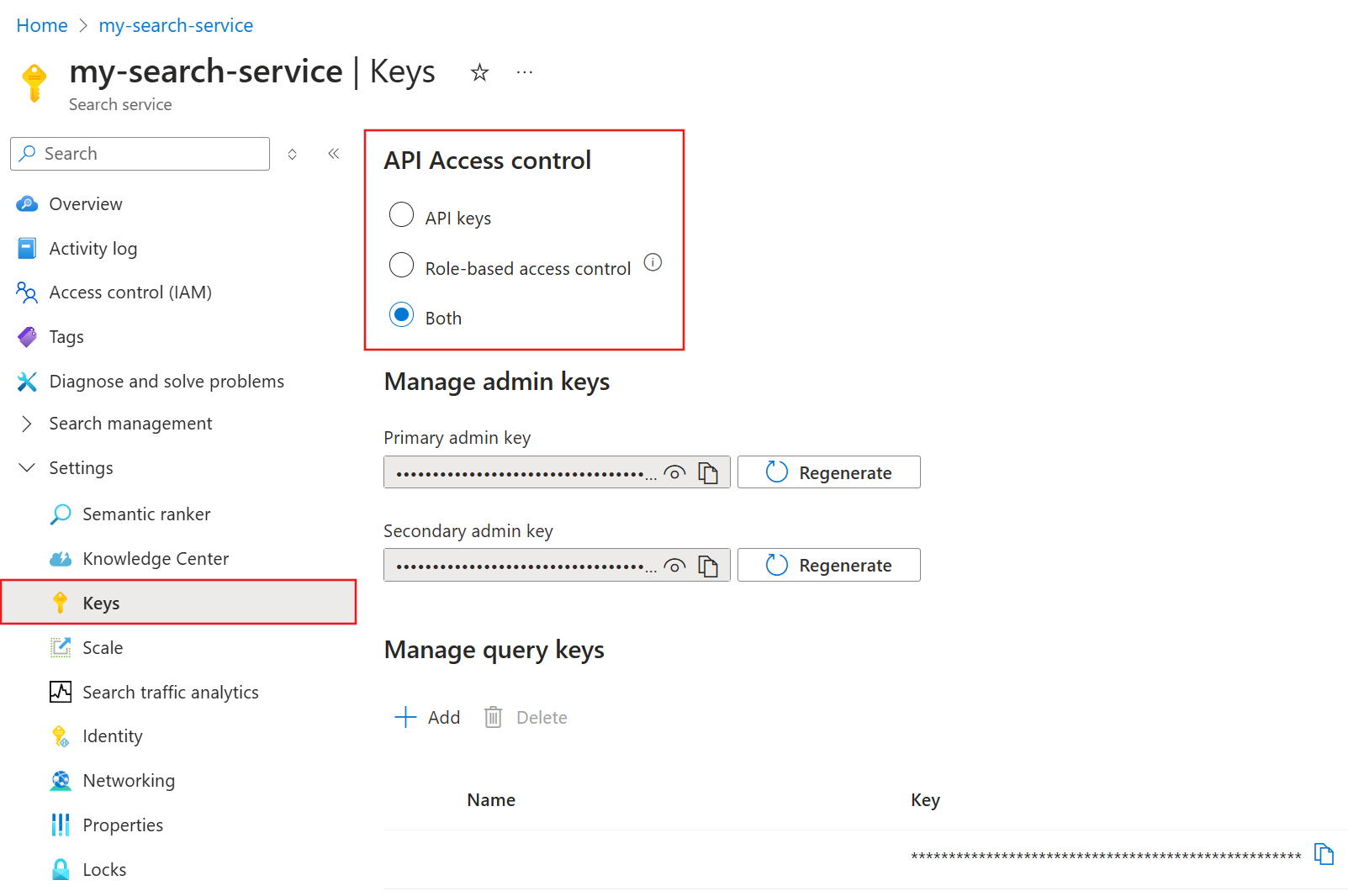
When you create a search service, key-based authentication is the default, but it's not the most secure option. We recommend that you replace it with role-based access.
To enable role-based access for your service:
Go to your search service in the Azure portal.
From the left pane, select Settings > Keys. You can connect to your service using API keys, Azure roles, or both. Select Both until you assign roles, after which you can select Role-based access control.
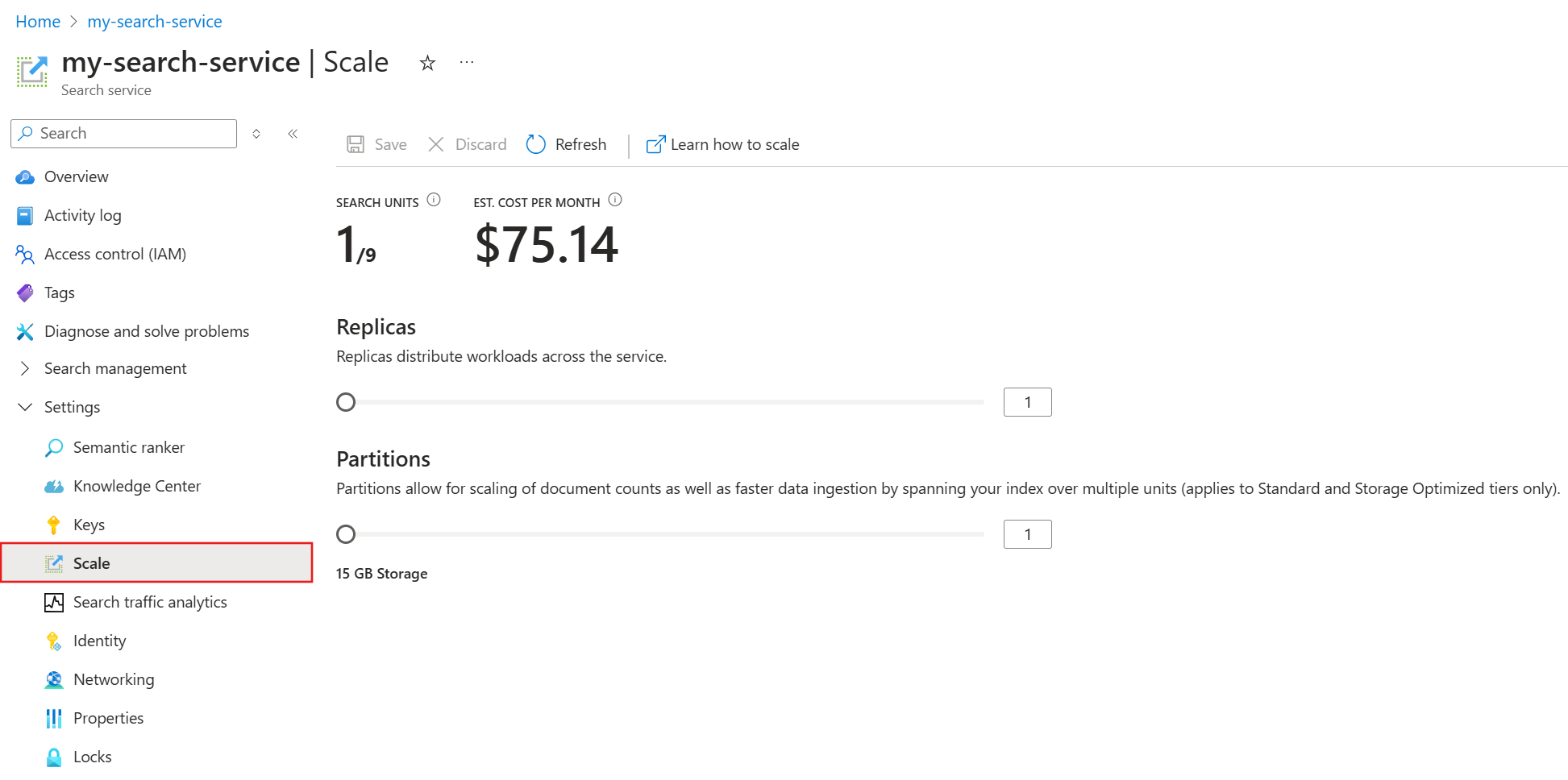
Scale your service
After deploying your search service, you can scale it to meet your needs. Azure AI Search offers two scaling dimensions: replicas and partitions. Replicas allow your service to handle a higher load of search queries, while partitions allow your service to store and search through more documents.
Scaling is available only on billable tiers. On the Free tier, you can't scale your service or configure replicas and partitions.
Important
Your service must have two replicas for read-only SLA and three replicas for read/write SLA.
Adding resources will increase your monthly bill. Use the pricing calculator to understand the billing implications. You can adjust resources based on load, such as increasing resources for initial indexing and decreasing them later for incremental indexing.
To scale your service:
Go to your search service in the Azure portal.
From the left pane, select Settings > Scale.
Use the sliders to add replicas and partitions.
When to add a second service
Most customers use a single search service at a tier sufficient for the expected load. One service can host multiple indexes, each isolated from the others, within the maximum limits of your chosen tier. In Azure AI Search, you can direct requests to only one index, reducing the chance of retrieving data from other indexes in the same service.
However, you might need a second service for the following operational requirements:
- Business continuity and disaster recovery (BCDR). If there's an outage, Azure AI Search won't provide instant failover.
- Multitenant architectures that require two or more services.
- Globally deployed applications that require services in each geography to minimize latency.
Note
In Azure AI Search, you can't separate indexing and querying operations, so don't create multiple services for separate workloads. An index is always queried on the service in which it was created, and you can't copy an index to another service.
A second service isn't required for high availability. You achieve high availability for queries by using two or more replicas in the same service. Because the replicas are updated sequentially, at least one is operational when a service update is rolled out. For more information about uptime, see Service Level Agreements.
Add more services to your subscription
Azure AI Search limits the number of search services you can initially create in a subscription. If you reach your limit, you can request more quotas.
You must have Owner or Contributor permissions for the subscription to request quota. Depending on your region and data center capacity, you might be able to automatically request quota to add services to your subscription. If the request fails, reduce the number or file a support ticket. Expect a one-month turnaround for a large quota increase, such as more than 30 extra services.
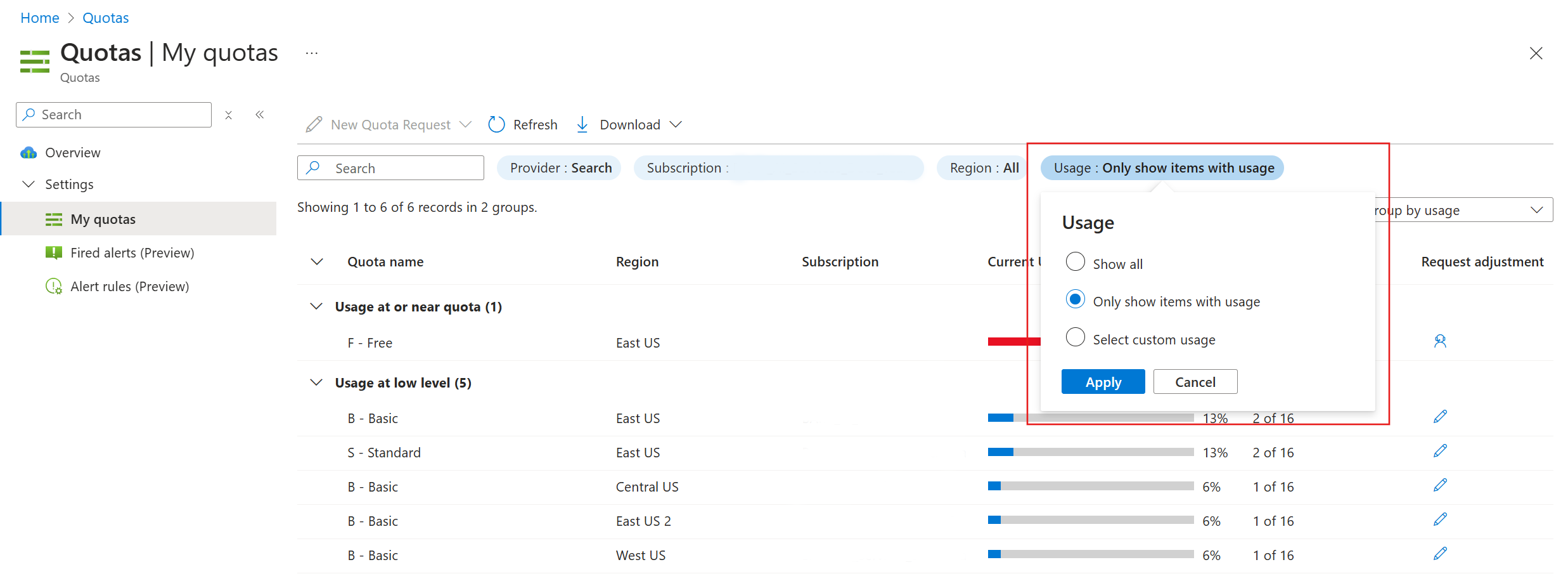
To request more subscription quota:
Go to your dashboard in the Azure portal.
Use the search box to find the Quotas service.
On the Overview tab, select the Search tile.
Set filters to review the existing quota for search services in your current subscription. We recommend filtering by usage.
Next to the tier and region that need more quotas, select Request adjustment
 .
.In New Quota Request, enter a new limit for your subscription quota. The new limit must be greater than your current limit. If regional capacity is constrained, your request won't be automatically approved, and an incident report will be generated on your behalf for investigation and resolution.
Submit your request.
Monitor notifications in the Azure portal for updates on the new limit. Most requests are approved within 24 hours.
Next steps
Now that you've deployed your search service, continue in the Azure portal to create your first index:
Want to optimize and save on your cloud spending?