Selectively wipe data using app protection policy conditional launch actions in Intune
Conditional launch actions within Intune app protection policies provide organizations the ability to block access or wipe org data when certain device or app conditions aren't met.
You can explicitly choose to wipe your company's corporate data from the end user's device as an action to take for noncompliance by using these settings. For some settings, you're able to configure multiple actions, such as block access and wipe data based on different specified values.
Create an app protection policy using conditional launch actions
- Sign in to the Microsoft Intune admin center.
- Select Apps > Protection.
- Select Create policy and select the platform of the device for your policy.
- Select Configure required settings to see the list of settings available to be configured for the policy.
- By scrolling down in the Settings pane, you'll see a section titled Conditional launch with an editable table.
- Select a Setting and enter the Value that users must meet to sign in to your company app.
- Select the Action you want to take if users don't meet your requirements. In some cases, multiple actions can be configured for a single setting. For more information, see How to create and assign app protection policies.
Policy settings
The app protection policy settings table has columns for Setting, Value, and Action.
Preview: Windows policy settings
For Windows, you're able to configure actions for the following "Health Check" settings using the Setting dropdown:
- Disabled account
- Max OS version
- Min app version
- Min OS version
- Min SDK version
- Offline grace period
- Max allowed device threat level
iOS policy settings
For iOS/iPadOS, you're able to configure actions for the following settings using the Setting dropdown:
- Max PIN attempts
- Offline grace period
- Jailbroken/rooted devices
- Max OS version
- Min OS version
- Min app version
- Min SDK version
- Device model(s)
- Max allowed device threat level
- Disabled account
To use the Device model(s) setting, input a semi-colon separated list of iOS/iPadOS model identifiers. These values aren't case-sensitive. Besides within Intune Reporting for the 'Device model(s)' input, you can find an iOS/iPadOS model identifier in this third-party GitHub repository.
Example input: iPhone5,2;iPhone5,3
On end-user devices, the Intune client would take action based on a simple matching of device model strings specified in Intune for Application Protection Policies. Matching depends entirely on what the device reports. You (the IT administrator) are encouraged to ensure that the intended behavior occurs by testing this setting based on various device manufacturers and models, and targeted to a small user group. The default value is Not configured.
Set one of the following actions:
- Allow specified (Block nonspecified)
- Allow specified (Wipe nonspecified)
What happens if the IT admin inputs a different list of iOS/iPadOS model identifier(s) between policies targeted to the same apps for the same Intune user?
When conflicts arise between two app protection policies for configured values, Intune typically takes the most restrictive approach. The resultant policy sent down to the targeted app opened by the targeted Intune user would be an intersection of the listed iOS/iPadOS model identifiers in Policy A and Policy B targeted to the same app/user combination. For example, Policy A specifies iPhone5,2;iPhone5,3, while Policy B specifies iPhone5,3, the resultant policy that the Intune user targeted by both Policy A and Policy B is iPhone5,3.
Android policy settings
For Android, you're able to configure actions for the following settings using the Setting dropdown:
- Max PIN attempts
- Offline grace period
- Jailbroken/rooted devices
- Min OS version
- Max OS version
- Min app version
- Min patch version
- Device manufacturer(s)
- Play integrity verdict
- Require threat scan on apps
- Min Company Portal version
- Max allowed device threat level
- Disabled account
- Require device lock
By using the Min Company Portal version, you can specify a specific minimum defined version of the Company Portal that is enforced on an end user device. This conditional launch setting allows you to set values to Block access, Wipe data, and Warn as possible actions when each value isn't met. The possible formats for this value follow the pattern [Major].[Minor], [Major].[Minor].[Build], or [Major].[Minor].[Build].[Revision]. Given that some end users may not prefer a forced update of apps on the spot, the 'warn' option may be ideal when configuring this setting. The Google Play Store does a good job of only sending the delta bytes for app updates. However, this can still be a large amount of data that the user may not want to utilize if they are on data at the time of the update. Forcing an update and downloading an updated app could result in unexpected data charges at the time of the update. The Min Company Portal version setting, if configured, will affect any end user who gets version 5.0.4560.0 of the Company Portal and any future versions of the Company Portal. This setting has no effect on users using a version of Company Portal that is older than the version that this feature is released with. End users using app autoupdates on their device will likely not see any dialogs from this feature, given that they'll likely be on the latest Company Portal version. This setting is Android only with app protection for enrolled and unenrolled devices.
To use the Device manufacturer(s) setting, input a semi-colon separated list of Android manufacturers. These values aren't case-sensitive. Besides Intune Reporting, you can find the Android manufacturer of a device under the device settings.
Example input: Manufacturer A;Manufacturer B
Note
The following list are some common manufacturers reported from devices using Intune, and can be used as input: Asus;Blackberry;Bq;Gionee;Google;Hmd global;Htc;Huawei;Infinix;Kyocera;Lemobile;Lenovo;Lge;Motorola;Oneplus;Oppo;Samsung;Sharp;Sony;Tecno;Vivo;Vodafone;Xiaomi;Zte;Zuk
On end-user devices, the Intune client would take action based on a simple matching of device model strings specified in Intune for Application Protection Policies. Matching depends entirely on what the device reports. You (the IT administrator) are encouraged to ensure that the intended behavior occurs by testing this setting based on various device manufacturers and models, and targeted to a small user group. The default value is Not configured.
Set one of the following actions:
- Allow specified (Block on nonspecified)
- Allow specified (Wipe on nonspecified)
What happens if the IT admin inputs a different list of Android manufacturer(s) between policies targeted to the same apps for the same Intune user?
When conflicts arise between two app protection policies for configured values, Intune typically takes the most restrictive approach. The resultant policy sent down to the targeted app being opened by the targeted Intune user would be an intersection of the listed Android manufacturers in Policy A and Policy B targeted to the same app/user combination. For example, Policy A specifies Google;Samsung, while Policy B specifies Google, the resultant policy that the Intune user targeted by both Policy A and Policy B is Google.
Additional settings and actions
By default, the table contains populated rows as settings configured for Offline grace period, and Max PIN attempts, if the Require PIN for access setting is set to Yes.
To configure a setting, select a setting from the dropdown under the Setting column. Once a setting is selected, the editable text box becomes enabled under the Value column in the same row, if a value is required to be set. Also, the dropdown becomes enabled under the Action column with the set of conditional launch actions applicable to the setting.
The following list provides the common list of actions:
- Block access – Block the end user from accessing the corporate app.
- Wipe data – Wipe the corporate data from the end user's device.
- Warn – Provide dialog to end user as a warning message.
In some cases, such as the Min OS version setting, you can configure the setting to perform all applicable actions based on different version numbers.
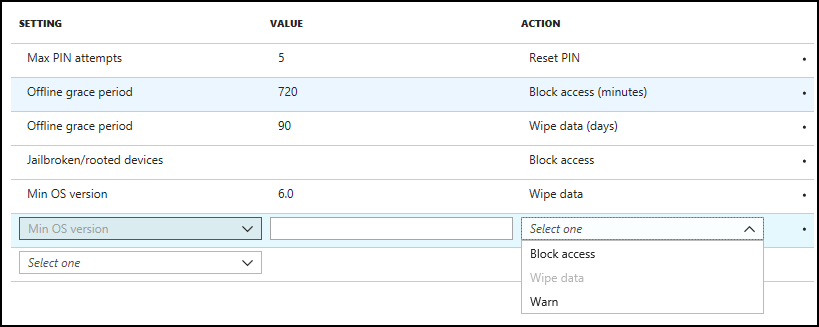
Once a setting is fully configured, the row appears in a read-only view and be available to be edited at any time. In addition, the row appears to have a dropdown available for selection in the Setting column. Configured settings that don't allow multiple actions aren't available for selection in the dropdown.
Next steps
Learn more information on Intune app protection policies, see: