Add a search service to a network security perimeter
Important
Azure AI Search support for network security perimeter is in public preview under supplemental terms of use. It's available in regions providing the feature. This preview version is provided without a service level agreement, and it's not recommended for production workloads. Certain features might not be supported or might have constrained capabilities.
Review the limitations and considerations section before you start.
This article explains how to join an Azure AI Search service to a network security perimeter to control network access to your search service. By joining a network security perimeter, you can:
- Log all access to your search service in context with other Azure resources in the same perimeter.
- Block any data exfiltration from a search service to other services outside the perimeter.
- Allow access to your search service using inbound and outbound access capabilities of the network security perimeter.
You can add a search service to a network security perimeter in the Azure portal, as described in this article. Alternatively, you can use the Azure Virtual Network Manager REST API to join a search service, and use the Search Management REST APIs to view and synchronize the configuration settings.
Limitations and considerations
For search services within a network security perimeter, indexers must use a system or user-assigned managed identity and have a role assignment that permits read-access to data sources.
Supported indexer data sources are currently limited to Azure Blob Storage, Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL, and Azure SQL Database.
Currently, within the perimeter, indexer connections to Azure PaaS for data retrieval is the primary use case. For outbound skills-driven API calls to Azure AI services, Azure OpenAI, or the Azure AI Foundry model catalog, or for inbound calls from the Azure AI Foundry for "chat with your data" scenarios you must configure inbound and outbound rules to allow the requests through the perimeter. If you require private connections for structure-aware chunking and vectorization, you should create a shared private link and a private network.
Prerequisites
An existing network security perimeter. You can create one to associate with your search service.
Azure AI Search, any billable tier, in any region.
Assign a search service to a network security perimeter
Azure Network Security Perimeter allows administrators to define a logical network isolation boundary for PaaS resources (for example, Azure Storage and Azure SQL Database) that are deployed outside virtual networks. It restricts communication to resources within the perimeter, and it allows non-perimeter public traffic through inbound and outbound access rules.
You can add Azure AI Search to a network security perimeter so that all indexing and query requests occur within the security boundary.
In the Azure portal, find the network security perimeter service for your subscription.
Select Resources from the left-hand menu.
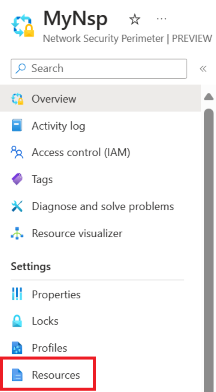
Select Add > Associate resources with an existing profile.
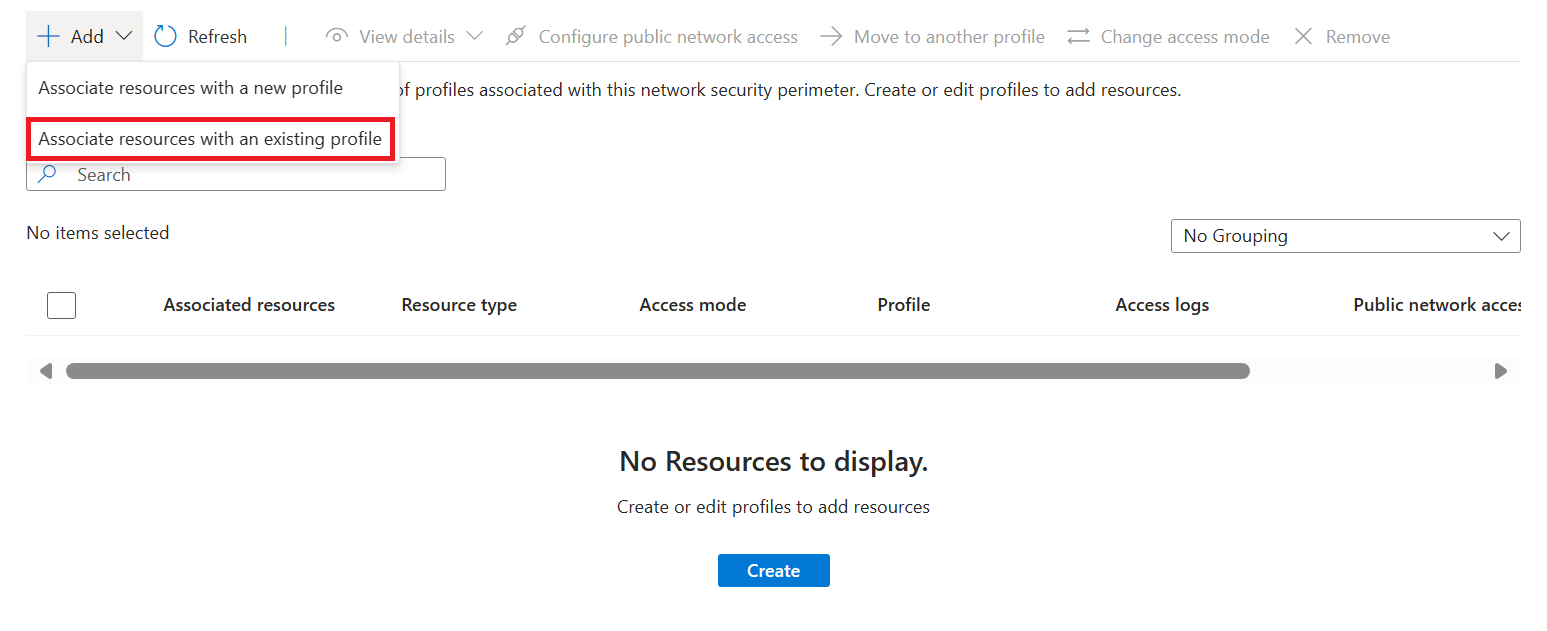
Select the profile you created when you created the network security perimeter for Profile.
Select Associate, and then select the search service you created.
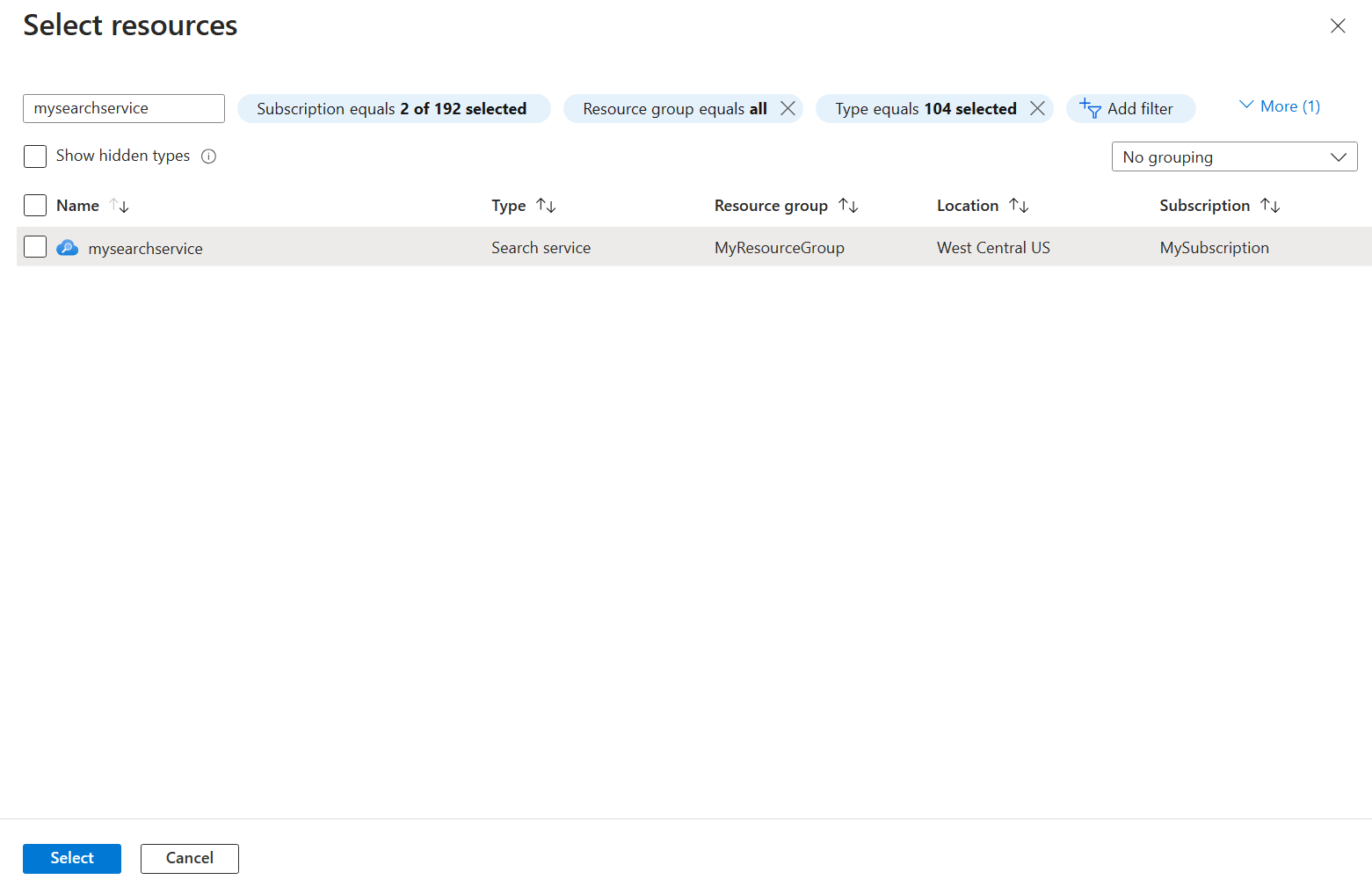
Select Associate in the bottom left-hand section of the screen to create the association.
Network security perimeter access modes
Network security perimeter supports two different access modes for associated resources:
| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| Learning mode | This is the default access mode. In learning mode, network security perimeter logs all traffic to the search service that would have been denied if the perimeter was in enforced mode. This allows network administrators to understand the existing access patterns of the search service before implementing enforcement of access rules. |
| Enforced mode | In Enforced mode, network security perimeter logs and denies all traffic that isn't explicitly allowed by access rules. |
Network security perimeter and search service networking settings
The publicNetworkAccess setting determines search service association with a network security perimeter.
In Learning mode, the
publicNetworkAccesssetting controls public access to the resource.In Enforced mode, the
publicNetworkAccesssetting is overridden by the network security perimeter rules. For example, if a search service with apublicNetworkAccesssetting ofenabledis associated with a network security perimeter in Enforced mode, access to the search service is still controlled by network security perimeter access rules.
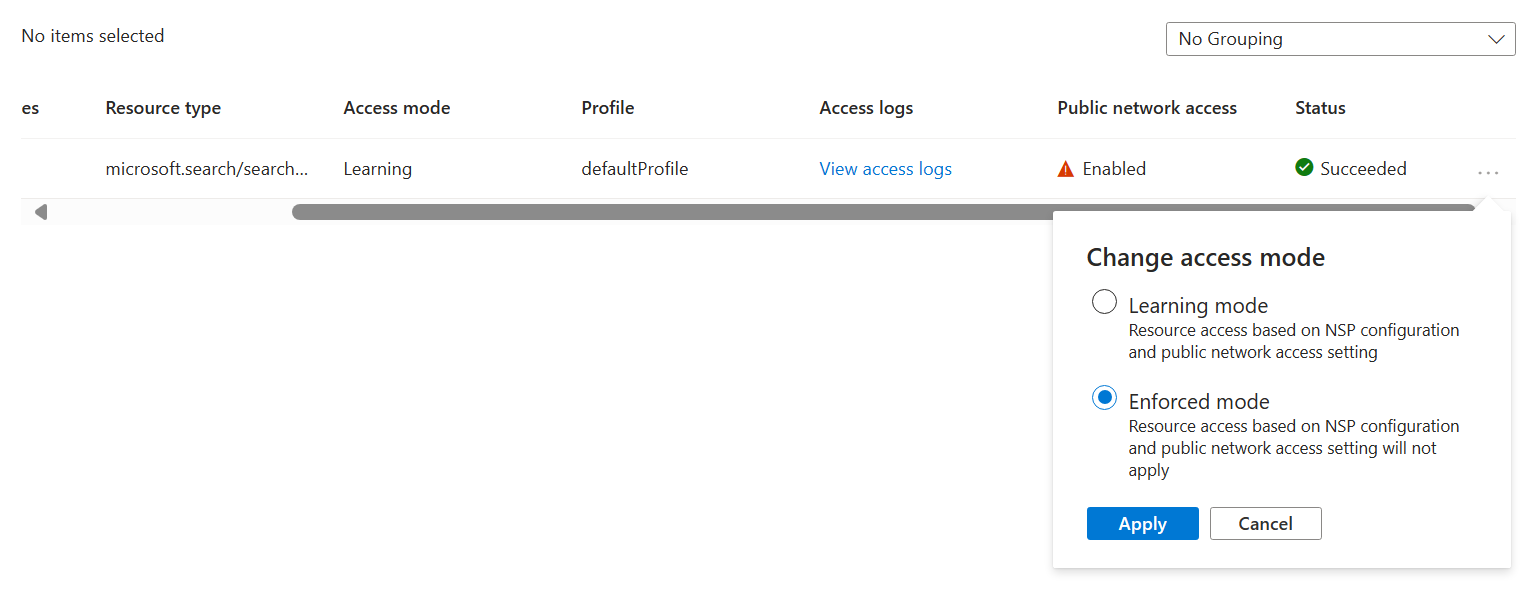
Change the network security perimeter access mode
Navigate to your network security perimeter resource in the Azure portal.
Select Resources in the left-hand menu.

Find your search service in the table.
Select the three dots in the far right of the search service row. Select Change access mode in the popup.`
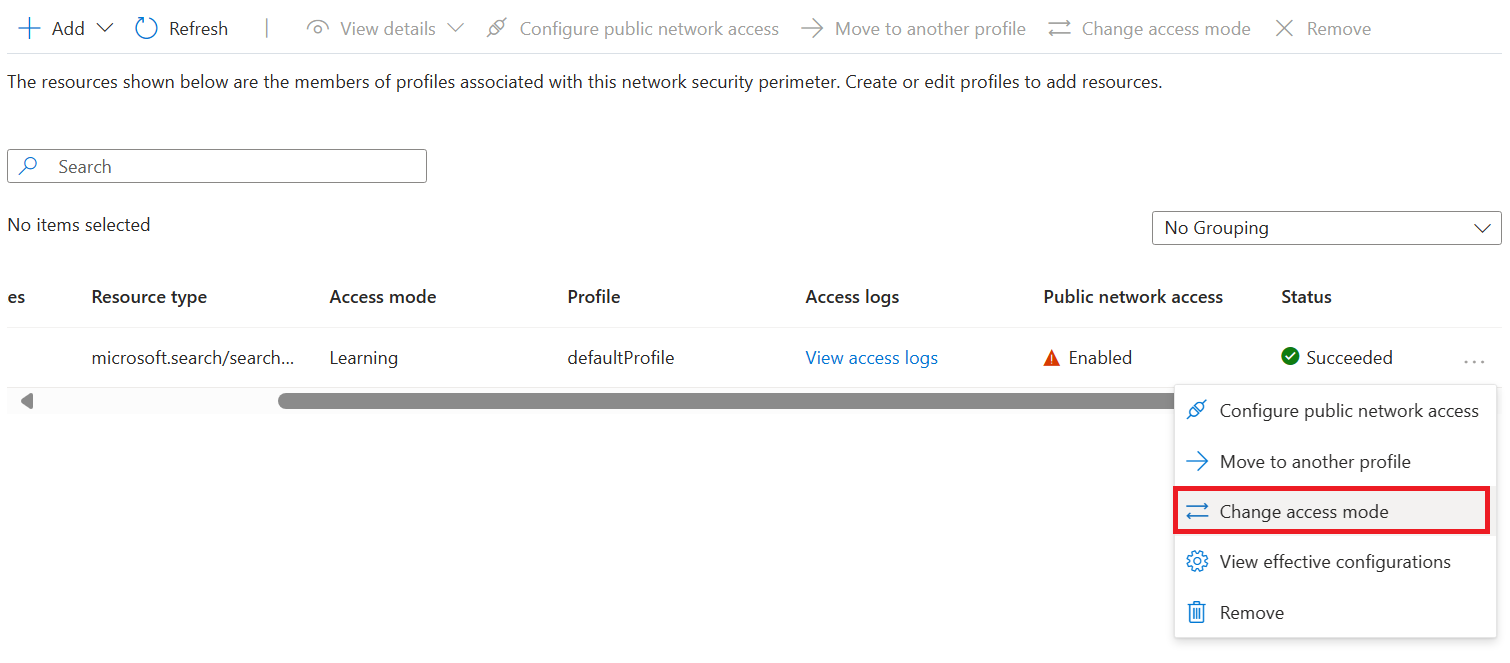
Select the desired access mode and select Apply.
Enable logging network access
Navigate to your network security perimeter resource in the Azure portal.
Select Diagnostic settings in the left-hand menu.
Select Add diagnostic setting.
Enter any name such as "diagnostic" for Diagnostic setting name.
Under Logs, select allLogs. allLogs ensures all inbound and outbound network access to resources in your network security perimeter is logged.
Under Destination details, select Archive to a storage account or Send to Log Analytics workspace. The storage account must be in the same region as the network security perimeter. You can either use an existing storage account or create a new one. A Log Analytics workspace can be in a different region than the one used by the network security perimeter. You can also select any of the other applicable destinations.
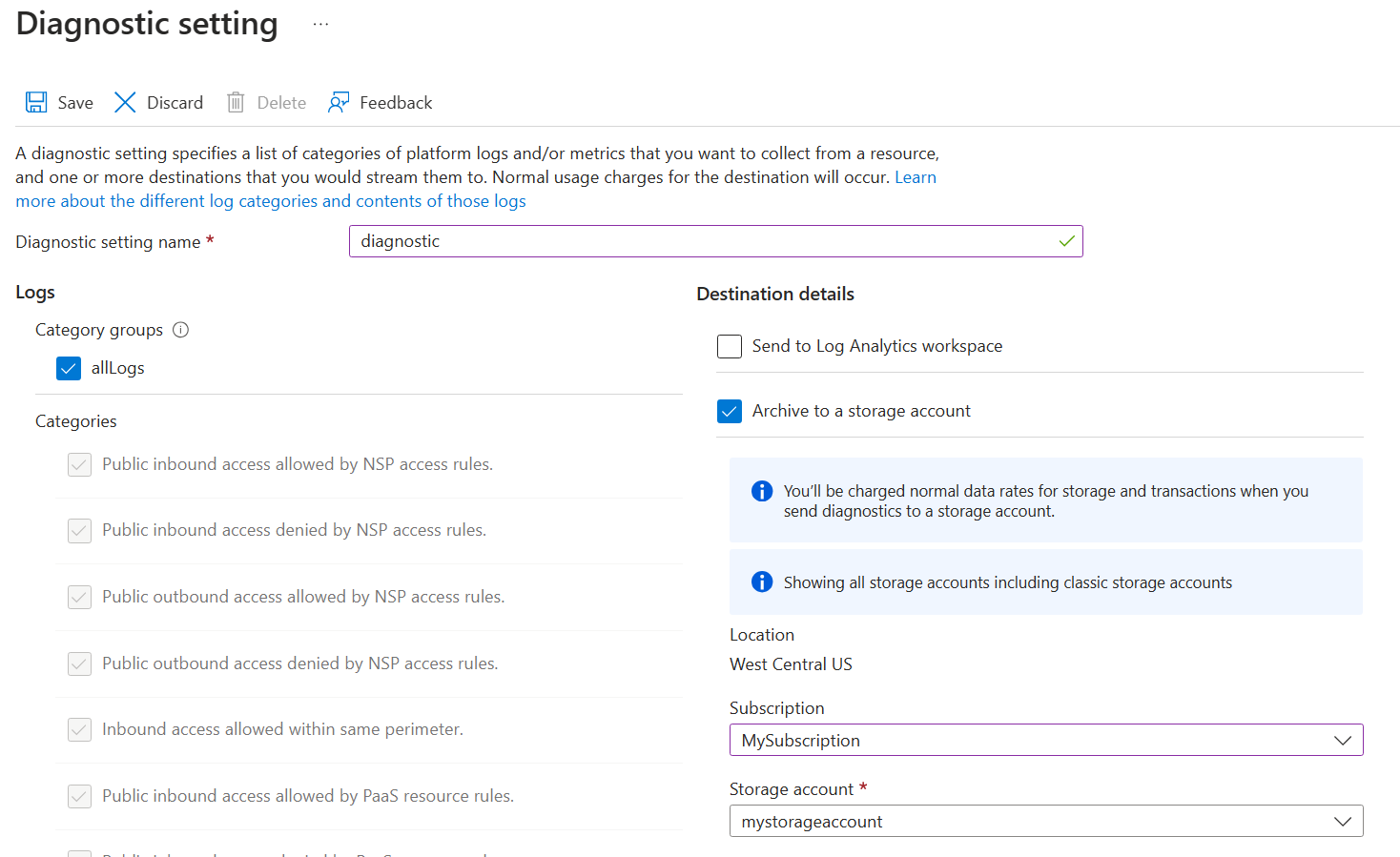
Select Save to create the diagnostic setting and start logging network access.
Reading network access logs
Log Analytics workspace
The network-security-perimeterAccessLogs table contains all the logs for every log category (for example network-security-perimeterPublicInboundResourceRulesAllowed). Every log contains a record of the network security perimeter network access that matches the log category.
Here's an example of the network-security-perimeterPublicInboundResourceRulesAllowed log format:
| Column Name | Meaning | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
| ResultDescription | Name of the network access operation | POST /indexes/my-index/docs/search |
| Profile | Which network security perimeter the search service was associated with | defaultProfile |
| ServiceResourceId | Resource ID of the search service | search-service-resource-id |
| Matched Rule | JSON description of the rule that was matched by the log | { "accessRule": "IP firewall" } |
| SourceIPAddress | Source IP of the inbound network access, if applicable | 1.1.1.1 |
| AccessRuleVersion | Version of the network-security-perimeter access rules used to enforce the network access rules | 0 |
Storage Account
The storage account has containers for every log category (for example insights-logs-network-security-perimeterpublicinboundperimeterrulesallowed). The folder structure inside the container matches the resource ID of the network security perimeter and the time the logs were taken. Each line on the JSON log file contains a record of the network security perimeter network access that matches the log category.
For example, the inbound perimeter rules allowed category log uses the following format:
"properties": {
"ServiceResourceId": "/subscriptions/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/resourceGroups/network-security-perimeter/providers/Microsoft.Search/searchServices/network-security-perimeter-search",
"Profile": "defaultProfile",
"MatchedRule": {
"AccessRule": "myaccessrule"
},
"Source": {
"IpAddress": "255.255.255.255",
}
}
Add an access rule for your search service
A network security perimeter profile specifies rules that allow or deny access through the perimeter.
Within the perimeter, all resources have mutual access at the network level. You must still set up authentication and authorization, but at the network level, connection requests from inside the perimeter are accepted.
For resources outside of the network security perimeter, you must specify inbound and outbound access rules. Inbound rules specify which connections to allow in, and outbound rules specify which requests are allowed out.
A search service accepts inbound requests from apps like Azure AI Foundry portal, Azure Machine Learning prompt flow, and any app that sends indexing or query requests. A search service sends outbound requests during indexer-based indexing and skillset execution. This section explains how to set up inbound and outbound access rules for Azure AI Search scenarios.
Note
Any service associated with a network security perimeter implicitly allows inbound and outbound access to any other service associated with the same network security perimeter when that access is authenticated using managed identities and role assignments. Access rules only need to be created when allowing access outside of the network security perimeter, or for access authenticated using API keys.
Add an inbound access rule
Inbound access rules can allow the internet and resources outside the perimeter to connect with resources inside the perimeter.
Network security perimeter supports two types of inbound access rules:
IP address ranges. IP addresses or ranges must be in the Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) format. An example of CIDR notation is 192.0.2.0/24, which represents the IPs that range from 192.0.2.0 to 192.0.2.255. This type of rule allows inbound requests from any IP address within the range.
Subscriptions. This type of rule allows inbound access authenticated using any managed identity from the subscription.
To add an inbound access rule in the Azure portal:
Navigate to your network security perimeter resource in the Azure portal.
Select Profiles in the left-hand menu.
Select the profile you're using with your network security perimeter
Select Inbound access rules in the left-hand menu.
Select Add.
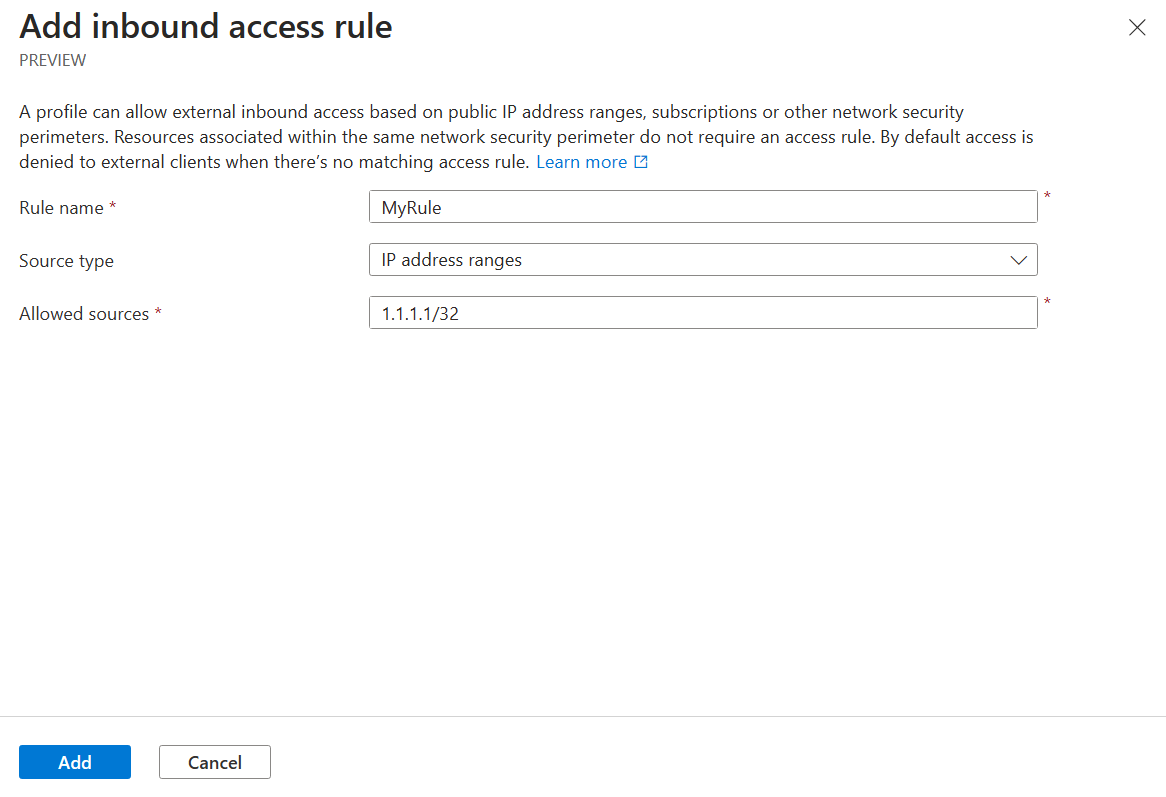
Enter or select the following values:
Setting Value Rule name The name for the inbound access rule (for example, "MyInboundAccessRule"). Source Type Valid values are IP address ranges or subscriptions. Allowed Sources If you selected IP address ranges, enter the IP address range in CIDR format that you want to allow inbound access from. Azure IP ranges are available at this link. If you selected Subscriptions, use the subscription you want to allow inbound access from. Select Add to create the inbound access rule.
Add an outbound access rule
A search service makes outbound calls during indexer-based indexing and skillset execution. If your indexer data sources, Azure AI services, or custom skill logic is outside of the network security perimeter, you should create an outbound access rule that allows your search service to make the connection.
Recall that in public preview, Azure AI Search can only connect to Azure Storage or Azure Cosmos DB within the security perimeter. If your indexers use other data sources, you need an outbound access rule to support that connection.
Network security perimeter supports outbound access rules based on the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) of the destination. For example, you can allow outbound access from any service associated with your network security perimeter to an FQDN such as mystorageaccount.blob.core.windows.net.
To add an outbound access rule in the Azure portal:
Navigate to your network security perimeter resource in the Azure portal.
Select Profiles in the left-hand menu.

Select the profile you're using with your network security perimeter

Select Outbound access rules in the left-hand menu.
Select Add.
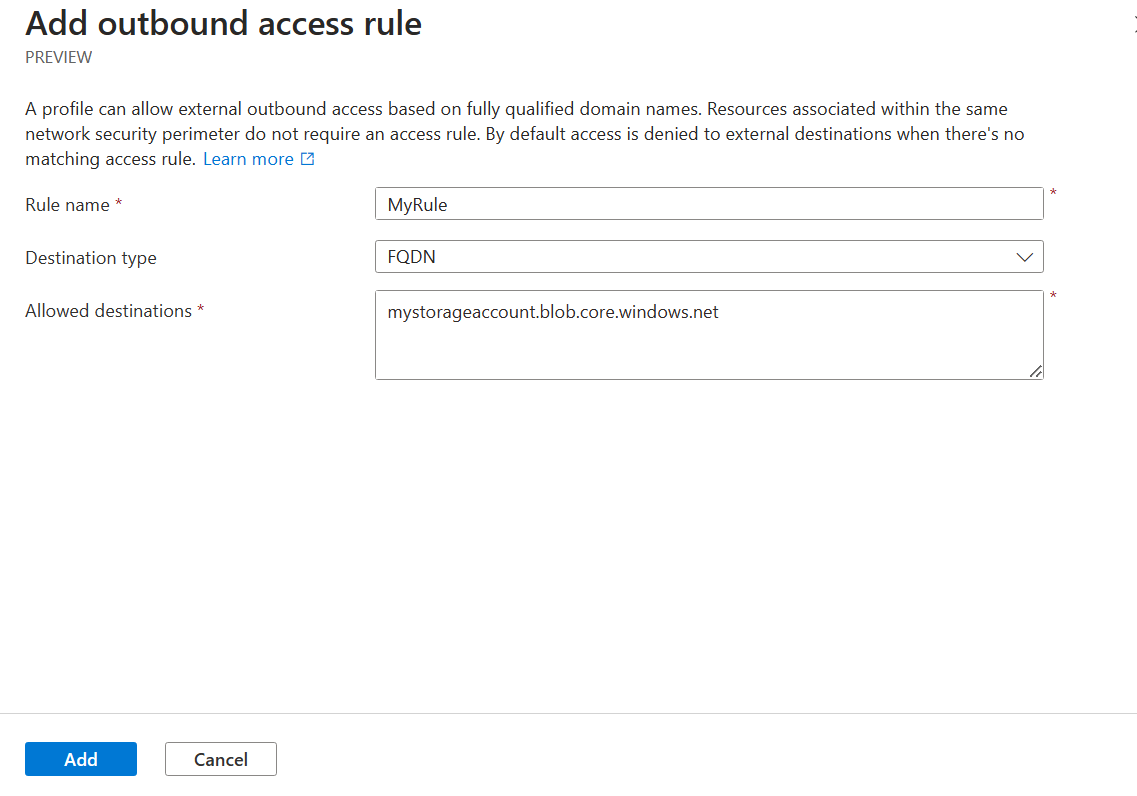
Enter or select the following values:
Setting Value Rule name The name for the outbound access rule (for example, "MyOutboundAccessRule") Destination Type Leave as FQDN Allowed Destinations Enter a comma-separated list of FQDNs you want to allow outbound access to Select Add to create the outbound access rule.
Test your connection through network security perimeter
In order to test your connection through network security perimeter, you need access to a web browser, either on a local computer with an internet connection or an Azure VM.
Change your network security perimeter association to enforced mode to start enforcing network security perimeter requirements for network access to your search service.
Decide if you want to use a local computer or an Azure VM.
- If you're using a local computer, you need to know your public IP address.
- If you're using an Azure VM, you can either use private link or check the IP address using the Azure portal.
Using the IP address, you can create an inbound access rule for that IP address to allow access. You can skip this step if you're using private link.
Finally, try navigating to the search service in the Azure portal. If you can view the indexes successfully, then the network security perimeter is configured correctly.
View and manage network security perimeter configuration
You can use the Network Security Perimeter Configuration REST APIs to review and reconcile perimeter configurations.
Be sure to use preview API version 2024-06-01-preview. Learn how to call the Management REST APIs.