Windows 應用程式中使用 StandardUICommand、XamlUICommand 和 ICommand 的命令
在本主題中,我們會說明 Windows 應用程式中的命令。 我們特別討論如何使用 XamlUICommand 和 StandardUICommand 類別 (連同 ICommand 介面) 來共用及管理各種控制項類型的命令 (不論所使用的裝置和輸入類型為何)。
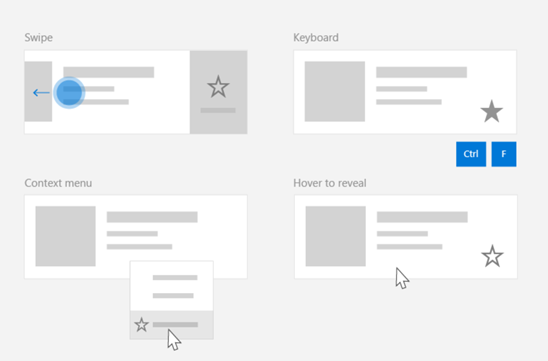
跨各種控制項共用命令 (不論裝置與輸入類型為何)
重要 API
概觀
您可以透過 UI 互動直接叫用命令,例如按一下按鈕,或從操作功能表中選取項目。 也可以透過輸入裝置間接叫用,例如鍵盤快速操作鍵、手勢、語音辨識或自動化工具/協助工具。 一旦叫用,命令即可接著由控制項 (編輯控制項中的文字瀏覽)、視窗 (向後瀏覽) 或應用程式 (結束) 處理。
您可以在您應用程式內的特定內容上操作命令,例如刪除文字或復原動作,也可以進行免內容的操作,例如靜音音訊或調整亮度。
下圖顯示兩個共用一些相同命令的命令介面 (CommandBar 及浮動關聯式 CommandBarFlyout)。
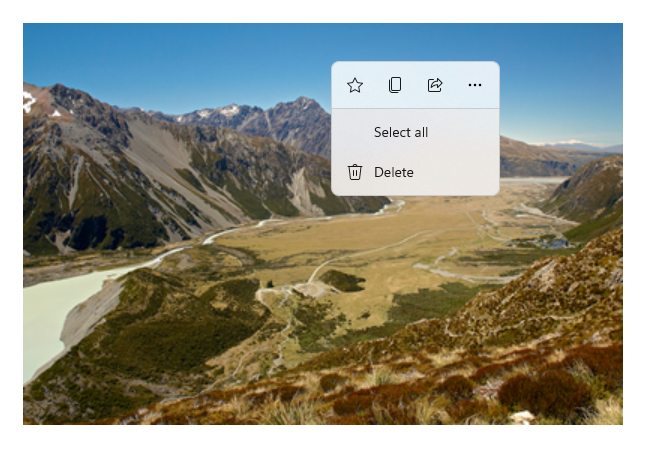
命令列
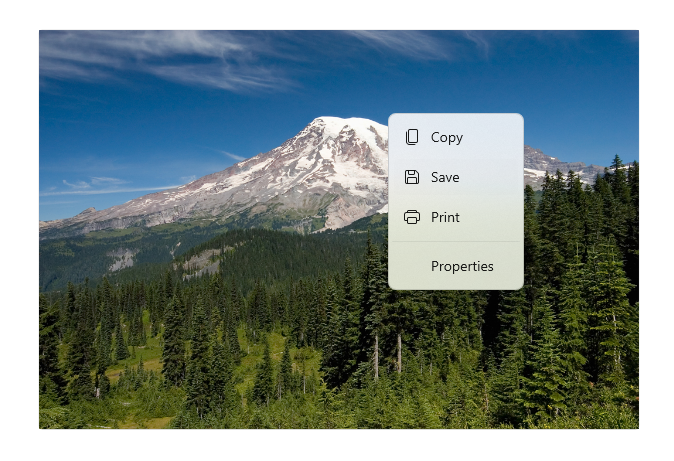
Microsoft 相片圖庫中的內容功能表
命令互動
由於有各式各樣可能影響命令叫用方式的裝置、輸入類型及 UI 介面,我們建議盡可能透過多個命令介面公開您的命令。 這些可以包含 Swipe、MenuBar、CommandBar、CommandBarFlyout 和傳統操作功能表的組合。
對於重要命令,請使用輸入專用加速器。 輸入加速器可讓使用者根據其所使用的輸入裝置,更快速地執行動作。
以下是各種輸入類型的一些常見輸入加速器:
- 指標 - 滑鼠和畫筆動態顯示按鈕
- 鍵盤 - 快速鍵 (便捷鍵和快速操作鍵)
- 觸控 - 撥動
- 觸控 - 拖動以重新整理資料
您必須考量輸入類型和使用者體驗,讓您的應用程式功能可隨處存取。 例如,集合 (尤其是使用者可編輯的集合) 通常包含各種特定命令,其執行方式因輸入裝置而相當不同。
下表列出了一些常見的集合命令,以及公開這些命令的方式。
| Command | 不限輸入類型 | 滑鼠快速操作 | 鍵盤快速操作鍵 | 觸控快速操作 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 刪除項目 | 內容功能表 | 暫留按鈕 | DEL 鍵 | 撥動以刪除 |
| 為項目加上旗標 | 內容功能表 | 暫留按鈕 | Ctrl+Shift+G | 撥動以加上旗標 |
| 重新整理資料 | 內容功能表 | N/A | F5 鍵 | 提取以重新整理 |
| 將項目加入我的最愛 | 內容功能表 | 暫留按鈕 | F、Ctrl+S | 撥動以加入我的最愛 |
一律提供操作功能表 我們建議在傳統操作功能表或 CommandBarFlyout 中包含所有相關的關聯式命令,因為所有輸入類型都支援這兩者。 比方說,如果某個命令僅在指標暫留事件期間公開,它就無法在只能觸控的裝置上使用。
Windows 應用程式中的命令
您可以使用一些方式來共用及管理 Windows 應用程式中的命令體驗。 您可以在程式碼後置中定義適用於標準互動 (例如 Click ) 的事件處理常式 (視您的 UI 複雜度而定,這可能相當沒有效率)、可以將適用於標準互動的事件接聽程式繫結至共用處理常式,也可以將控制項的 Command 屬性繫結至可描述命令邏輯的 ICommand 實作。
若要透過命令介面和最少的程式碼複製,有效率地提供豐富且完整的使用者體驗,我們建議使用本主題所述的命令繫結功能 (如需標準事件處理,請參閱個別的事件主題)。
若要將控制項繫結至共用命令資源,您可以自行實作 ICommand 介面,也可以從 XamlUICommand 基底類別或 StandardUICommand 衍生類別所定義的其中一個平台命令建置您的命令。
- ICommand 介面 (Windows.UI.Xaml.Input.ICommand 或 System.Windows.Input.ICommand) 可讓您在應用程式中建立完全自訂、可重複使用的命令。
- XamlUICommand 也提供這項功能,但藉由公開一組內建命令屬性,例如命令行為、鍵盤快速鍵 (便捷鍵和快速操作鍵)、圖示、標籤及描述,簡化開發作業。
- StandardUICommand 可讓您從一組已預先定義屬性的標準平台命令中選擇,進一步簡化作業。
重要
在 UWP 應用程式中,命令是 Windows.UI.Xaml.Input.ICommand (C++) 或 System.Windows.Input.ICommand (C#) 介面的實作,這取決於您所選擇的語言架構。
使用 StandardUICommand 類別的命令體驗
衍生自 XamlUiCommand (衍生自適用於 C++ 的 Windows.UI.Xaml.Input.ICommand 或適用於 C# 的 System.Windows.Input.ICommand),StandardUICommand 類別會公開一組標準平台命令,其具有使用預先定義的屬性,例如圖示、鍵盤快速操作鍵及描述。
StandardUICommand 提供快速且一致的方式來定義通用命令,例如 Save 或 Delete。 您只需要提供 execute 和 canExecute 函式。
範例
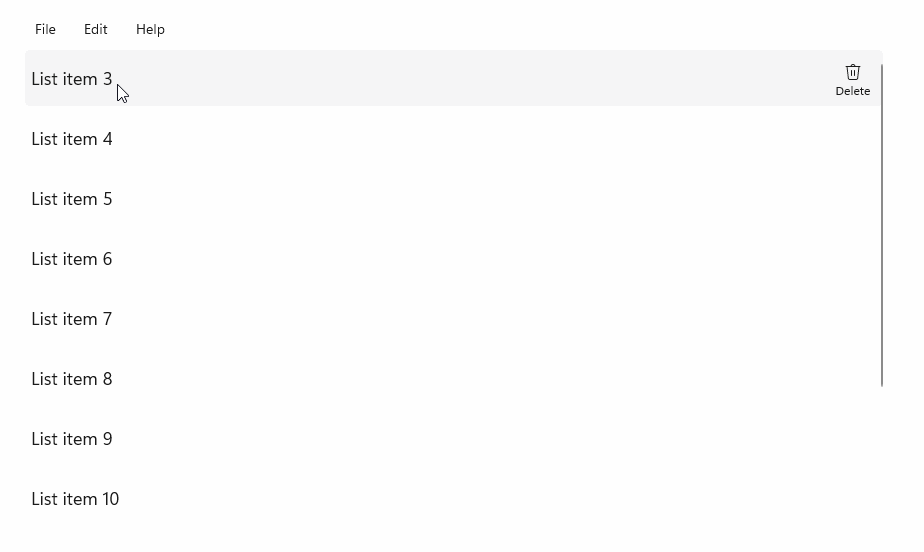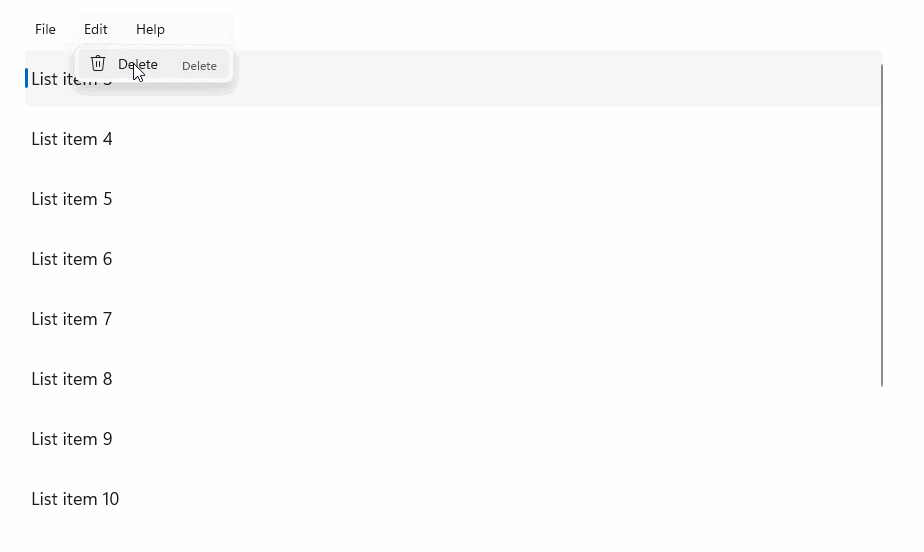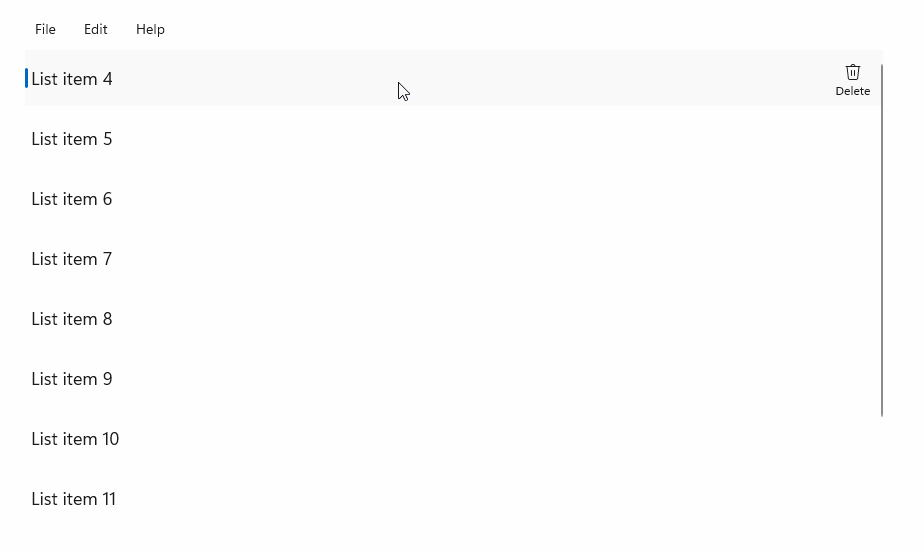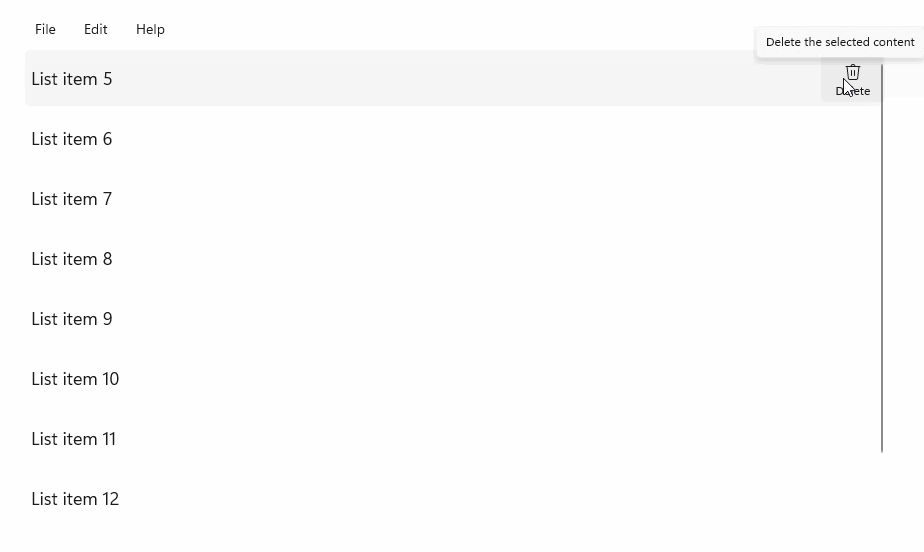
StandardUICommandSample
| 下載此範例的程式碼 |
|---|
| UWP 命令範例 (StandardUICommand) |
在此範例中,我們示範如何以透過 StandardUICommand 類別實作的 Delete 項目命令增強基本 ListView,同時使用 MenuBar、Swipe 控制項、動態顯示按鈕及操作功能表,將各種輸入類型的使用者體驗最佳化。
注意
此範例需要 Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Controls NuGet 套件,屬於 WinUI 2。
Xaml:
範例 UI 包含五個項目的 ListView。 Delete StandardUICommand 會繫結至 MenuBarItem、SwipeItem、AppBarButton 和 ContextFlyout 功能表。
<Page
x:Class="StandardUICommandSample.MainPage"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local="using:StandardUICommandSample"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:muxcontrols="using:Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Controls"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Background="{ThemeResource ApplicationPageBackgroundThemeBrush}">
<Page.Resources>
<Style x:Key="HorizontalSwipe"
TargetType="ListViewItem"
BasedOn="{StaticResource ListViewItemRevealStyle}">
<Setter Property="Height" Value="60"/>
<Setter Property="Padding" Value="0"/>
<Setter Property="HorizontalContentAlignment" Value="Stretch"/>
<Setter Property="VerticalContentAlignment" Value="Stretch"/>
<Setter Property="BorderThickness" Value="0"/>
</Style>
</Page.Resources>
<Grid Loaded="ControlExample_Loaded">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<StackPanel Grid.Row="0"
Padding="10"
BorderThickness="0,0,0,1"
BorderBrush="LightBlue"
Background="AliceBlue">
<TextBlock Style="{StaticResource HeaderTextBlockStyle}">
StandardUICommand sample
</TextBlock>
<TextBlock Style="{StaticResource SubtitleTextBlockStyle}" Margin="0,0,0,10">
This sample shows how to use the StandardUICommand class to
share a platform command and consistent user experiences
across various controls.
</TextBlock>
<TextBlock Style="{StaticResource SubtitleTextBlockStyle}" Margin="0,0,0,0">
Specifically, we define a standard delete command and add it
to a variety of command surfaces, all of which share a common
icon, label, keyboard accelerator, and description.
</TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
<muxcontrols:MenuBar Grid.Row="1" Padding="10">
<muxcontrols:MenuBarItem Title="File">
</muxcontrols:MenuBarItem>
<muxcontrols:MenuBarItem Title="Edit">
<MenuFlyoutItem x:Name="DeleteFlyoutItem"/>
</muxcontrols:MenuBarItem>
<muxcontrols:MenuBarItem Title="Help">
</muxcontrols:MenuBarItem>
</muxcontrols:MenuBar>
<ListView x:Name="ListViewRight" Grid.Row="2"
Loaded="ListView_Loaded"
IsItemClickEnabled="True"
SelectionMode="Single"
SelectionChanged="ListView_SelectionChanged"
ItemContainerStyle="{StaticResource HorizontalSwipe}">
<ListView.ItemTemplate>
<DataTemplate x:DataType="local:ListItemData">
<UserControl PointerEntered="ListViewSwipeContainer_PointerEntered"
PointerExited="ListViewSwipeContainer_PointerExited">
<UserControl.ContextFlyout>
<MenuFlyout>
<MenuFlyoutItem
Command="{x:Bind Command}"
CommandParameter="{x:Bind Text}" />
</MenuFlyout>
</UserControl.ContextFlyout>
<Grid AutomationProperties.Name="{x:Bind Text}">
<VisualStateManager.VisualStateGroups>
<VisualStateGroup x:Name="HoveringStates">
<VisualState x:Name="HoverButtonsHidden" />
<VisualState x:Name="HoverButtonsShown">
<VisualState.Setters>
<Setter Target="HoverButton.Visibility"
Value="Visible" />
</VisualState.Setters>
</VisualState>
</VisualStateGroup>
</VisualStateManager.VisualStateGroups>
<SwipeControl x:Name="ListViewSwipeContainer" >
<SwipeControl.RightItems>
<SwipeItems Mode="Execute">
<SwipeItem x:Name="DeleteSwipeItem"
Background="Red"
Command="{x:Bind Command}"
CommandParameter="{x:Bind Text}"/>
</SwipeItems>
</SwipeControl.RightItems>
<Grid VerticalAlignment="Center">
<TextBlock Text="{x:Bind Text}"
Margin="10"
FontSize="18"
HorizontalAlignment="Left"
VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
<AppBarButton x:Name="HoverButton"
IsTabStop="False"
HorizontalAlignment="Right"
Visibility="Collapsed"
Command="{x:Bind Command}"
CommandParameter="{x:Bind Text}"/>
</Grid>
</SwipeControl>
</Grid>
</UserControl>
</DataTemplate>
</ListView.ItemTemplate>
</ListView>
</Grid>
</Page>
程式碼後置
- 首先,我們會定義
ListItemData類別,其中包含 ListView 中每個 ListViewItem 的文字字串和 ICommand。
public class ListItemData
{
public String Text { get; set; }
public ICommand Command { get; set; }
}
- 在 MainPage 類別中,我們會針對 ListViewItemTemplate 的 DataTemplate 定義
ListItemData物件集合。 我們會接著在其中填入 5 個項目的初始集合 (使用文字和相關聯的 StandardUICommand Delete)。
/// <summary>
/// ListView item collection.
/// </summary>
ObservableCollection<ListItemData> collection =
new ObservableCollection<ListItemData>();
/// <summary>
/// Handler for the layout Grid control load event.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">Source of the control loaded event</param>
/// <param name="e">Event args for the loaded event</param>
private void ControlExample_Loaded(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// Create the standard Delete command.
var deleteCommand = new StandardUICommand(StandardUICommandKind.Delete);
deleteCommand.ExecuteRequested += DeleteCommand_ExecuteRequested;
DeleteFlyoutItem.Command = deleteCommand;
for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
collection.Add(
new ListItemData {
Text = "List item " + i.ToString(),
Command = deleteCommand });
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Handler for the ListView control load event.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">Source of the control loaded event</param>
/// <param name="e">Event args for the loaded event</param>
private void ListView_Loaded(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
var listView = (ListView)sender;
// Populate the ListView with the item collection.
listView.ItemsSource = collection;
}
- 接下來,我們會定義用來實作項目刪除命令的 ICommand ExecuteRequested 處理常式。
/// <summary>
/// Handler for the Delete command.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">Source of the command event</param>
/// <param name="e">Event args for the command event</param>
private void DeleteCommand_ExecuteRequested(
XamlUICommand sender, ExecuteRequestedEventArgs args)
{
// If possible, remove specified item from collection.
if (args.Parameter != null)
{
foreach (var i in collection)
{
if (i.Text == (args.Parameter as string))
{
collection.Remove(i);
return;
}
}
}
if (ListViewRight.SelectedIndex != -1)
{
collection.RemoveAt(ListViewRight.SelectedIndex);
}
}
- 最後,我們會定義各種 ListView 事件的處理常式,包括 PointerEntered、PointerExited和 SelectionChanged 事件。 指標事件處理常式用來顯示或隱藏每個項目的 Delete 按鈕。
/// <summary>
/// Handler for the ListView selection changed event.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">Source of the selection changed event</param>
/// <param name="e">Event args for the selection changed event</param>
private void ListView_SelectionChanged(object sender, SelectionChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (ListViewRight.SelectedIndex != -1)
{
var item = collection[ListViewRight.SelectedIndex];
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Handler for the pointer entered event.
/// Displays the delete item "hover" buttons.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">Source of the pointer entered event</param>
/// <param name="e">Event args for the pointer entered event</param>
private void ListViewSwipeContainer_PointerEntered(
object sender, PointerRoutedEventArgs e)
{
if (e.Pointer.PointerDeviceType ==
Windows.Devices.Input.PointerDeviceType.Mouse ||
e.Pointer.PointerDeviceType ==
Windows.Devices.Input.PointerDeviceType.Pen)
{
VisualStateManager.GoToState(
sender as Control, "HoverButtonsShown", true);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Handler for the pointer exited event.
/// Hides the delete item "hover" buttons.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">Source of the pointer exited event</param>
/// <param name="e">Event args for the pointer exited event</param>
private void ListViewSwipeContainer_PointerExited(
object sender, PointerRoutedEventArgs e)
{
VisualStateManager.GoToState(
sender as Control, "HoverButtonsHidden", true);
}
使用 XamlUICommand 類別的命令體驗
如果您需要建立一個不是由 StandardUICommand 類別所定義的命令,或您想要更充分掌控命令外觀,XamlUiCommand 類別會衍生自 ICommand 介面,並新增各種 UI 屬性 (例如圖示、標籤、描述和鍵盤快速鍵)、方法和事件,以快速定義自訂命令的 UI 和行為。
XamlUICommand 可讓您透過控制項繫結來指定 UI,例如圖示、標籤、描述和鍵盤快速鍵 (便捷鍵和鍵盤快速操作鍵),而不需設定個別的屬性。
範例

XamlUICommandSample
| 下載此範例的程式碼 |
|---|
| UWP 命令範例 (XamlUICommand) |
此範例共用前一個 StandardUICommand 範例的 Delete 功能,但會顯示 XamlUICommand 類別如何讓您以自己的字型圖示、標籤、鍵盤快速操作鍵和描述來定義自訂 delete 命令。 如同 StandardUICommand範例,我們以透過 XamlUICommand類別實作的 Delete 項目命令增強基本 ListView,同時使用 MenuBar、Swipe 控制項、動態顯示按鈕及操作功能表,將各種輸入類型的使用者體驗最佳化。
實際上,許多平台控制項會使用 XamlUICommand 屬性,就像上一節中的 StandardUICommand 範例一樣。
注意
此範例需要 Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Controls NuGet 套件,屬於 WinUI 2。
Xaml:
範例 UI 包含五個項目的 ListView。 自訂 XamlUICommand Delete 會繫結至 MenuBarItem、SwipeItem、AppBarButton 和 ContextFlyout 功能表。
<Page
x:Class="XamlUICommand_Sample.MainPage"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local="using:XamlUICommand_Sample"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:muxcontrols="using:Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Controls"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Background="{ThemeResource ApplicationPageBackgroundThemeBrush}">
<Page.Resources>
<XamlUICommand x:Name="CustomXamlUICommand"
ExecuteRequested="DeleteCommand_ExecuteRequested"
Description="Custom XamlUICommand"
Label="Custom XamlUICommand">
<XamlUICommand.IconSource>
<FontIconSource FontFamily="Wingdings" Glyph="M"/>
</XamlUICommand.IconSource>
<XamlUICommand.KeyboardAccelerators>
<KeyboardAccelerator Key="D" Modifiers="Control"/>
</XamlUICommand.KeyboardAccelerators>
</XamlUICommand>
<Style x:Key="HorizontalSwipe"
TargetType="ListViewItem"
BasedOn="{StaticResource ListViewItemRevealStyle}">
<Setter Property="Height" Value="70"/>
<Setter Property="Padding" Value="0"/>
<Setter Property="HorizontalContentAlignment" Value="Stretch"/>
<Setter Property="VerticalContentAlignment" Value="Stretch"/>
<Setter Property="BorderThickness" Value="0"/>
</Style>
</Page.Resources>
<Grid Loaded="ControlExample_Loaded" Name="MainGrid">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<StackPanel Grid.Row="0"
Padding="10"
BorderThickness="0,0,0,1"
BorderBrush="LightBlue"
Background="AliceBlue">
<TextBlock Style="{StaticResource HeaderTextBlockStyle}">
XamlUICommand sample
</TextBlock>
<TextBlock Style="{StaticResource SubtitleTextBlockStyle}" Margin="0,0,0,10">
This sample shows how to use the XamlUICommand class to
share a custom command with consistent user experiences
across various controls.
</TextBlock>
<TextBlock Style="{StaticResource SubtitleTextBlockStyle}" Margin="0,0,0,0">
Specifically, we define a custom delete command and add it
to a variety of command surfaces, all of which share a common
icon, label, keyboard accelerator, and description.
</TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
<muxcontrols:MenuBar Grid.Row="1">
<muxcontrols:MenuBarItem Title="File">
</muxcontrols:MenuBarItem>
<muxcontrols:MenuBarItem Title="Edit">
<MenuFlyoutItem x:Name="DeleteFlyoutItem"
Command="{StaticResource CustomXamlUICommand}"/>
</muxcontrols:MenuBarItem>
<muxcontrols:MenuBarItem Title="Help">
</muxcontrols:MenuBarItem>
</muxcontrols:MenuBar>
<ListView x:Name="ListViewRight" Grid.Row="2"
Loaded="ListView_Loaded"
IsItemClickEnabled="True"
SelectionMode="Single"
SelectionChanged="ListView_SelectionChanged"
ItemContainerStyle="{StaticResource HorizontalSwipe}">
<ListView.ItemTemplate>
<DataTemplate x:DataType="local:ListItemData">
<UserControl PointerEntered="ListViewSwipeContainer_PointerEntered"
PointerExited="ListViewSwipeContainer_PointerExited">
<UserControl.ContextFlyout>
<MenuFlyout>
<MenuFlyoutItem
Command="{x:Bind Command}"
CommandParameter="{x:Bind Text}" />
</MenuFlyout>
</UserControl.ContextFlyout>
<Grid AutomationProperties.Name="{x:Bind Text}">
<VisualStateManager.VisualStateGroups>
<VisualStateGroup x:Name="HoveringStates">
<VisualState x:Name="HoverButtonsHidden" />
<VisualState x:Name="HoverButtonsShown">
<VisualState.Setters>
<Setter Target="HoverButton.Visibility"
Value="Visible" />
</VisualState.Setters>
</VisualState>
</VisualStateGroup>
</VisualStateManager.VisualStateGroups>
<SwipeControl x:Name="ListViewSwipeContainer">
<SwipeControl.RightItems>
<SwipeItems Mode="Execute">
<SwipeItem x:Name="DeleteSwipeItem"
Background="Red"
Command="{x:Bind Command}"
CommandParameter="{x:Bind Text}"/>
</SwipeItems>
</SwipeControl.RightItems>
<Grid VerticalAlignment="Center">
<TextBlock Text="{x:Bind Text}"
Margin="10"
FontSize="18"
HorizontalAlignment="Left"
VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
<AppBarButton x:Name="HoverButton"
IsTabStop="False"
HorizontalAlignment="Right"
Visibility="Collapsed"
Command="{x:Bind Command}"
CommandParameter="{x:Bind Text}"/>
</Grid>
</SwipeControl>
</Grid>
</UserControl>
</DataTemplate>
</ListView.ItemTemplate>
</ListView>
</Grid>
</Page>
程式碼後置
- 首先,我們會定義
ListItemData類別,其中包含 ListView 中每個 ListViewItem 的文字字串和 ICommand。
public class ListItemData
{
public String Text { get; set; }
public ICommand Command { get; set; }
}
- 在 MainPage 類別中,我們會針對 ListViewItemTemplate 的 DataTemplate 定義
ListItemData物件集合。 我們會接著在其中填入 5 個項目的初始集合 (使用文字和相關聯的 XamlUICommand)。
ObservableCollection<ListItemData> collection = new ObservableCollection<ListItemData>();
private void ControlExample_Loaded(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
collection.Add(
new ListItemData { Text = "List item " + i.ToString(), Command = CustomXamlUICommand });
}
}
private void ListView_Loaded(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
var listView = (ListView)sender;
listView.ItemsSource = collection;
}
- 接下來,我們會定義用來實作項目刪除命令的 ICommand ExecuteRequested 處理常式。
private void DeleteCommand_ExecuteRequested(
XamlUICommand sender, ExecuteRequestedEventArgs args)
{
if (args.Parameter != null)
{
foreach (var i in collection)
{
if (i.Text == (args.Parameter as string))
{
collection.Remove(i);
return;
}
}
}
if (ListViewRight.SelectedIndex != -1)
{
collection.RemoveAt(ListViewRight.SelectedIndex);
}
}
- 最後,我們會定義各種 ListView 事件的處理常式,包括 PointerEntered、PointerExited和 SelectionChanged 事件。 指標事件處理常式用來顯示或隱藏每個項目的 Delete 按鈕。
private void ListView_SelectionChanged(object sender, SelectionChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (ListViewRight.SelectedIndex != -1)
{
var item = collection[ListViewRight.SelectedIndex];
}
}
private void ListViewSwipeContainer_PointerEntered(object sender, PointerRoutedEventArgs e)
{
if (e.Pointer.PointerDeviceType ==
Windows.Devices.Input.PointerDeviceType.Mouse ||
e.Pointer.PointerDeviceType == Windows.Devices.Input.PointerDeviceType.Pen)
{
VisualStateManager.GoToState(sender as Control, "HoverButtonsShown", true);
}
}
private void ListViewSwipeContainer_PointerExited(object sender, PointerRoutedEventArgs e)
{
VisualStateManager.GoToState(sender as Control, "HoverButtonsHidden", true);
}
使用 ICommand 介面的命令體驗
標準 UWP 控制項 (按鈕、清單、選取項目、行事曆、預測文字) 提供許多常見命令體驗的基礎。 如需完整的控制項類型清單,請參閱適用於 Windows 應用程式的控制項和模式。
支援結構化命令體驗的最基本方式就是定義 ICommand 介面實作 (適用於 C++ 的 Windows.UI.Xaml.Input.ICommand或適用於 C# 的 System.Windows.Input.ICommand)。 此 ICommand 執行個體可以接著繫結至按鈕等控制項。
注意
在某些情況下,就如同將方法繫結至 Click 事件以及將屬性繫結至 IsEnabled 屬性一樣有效率。
範例
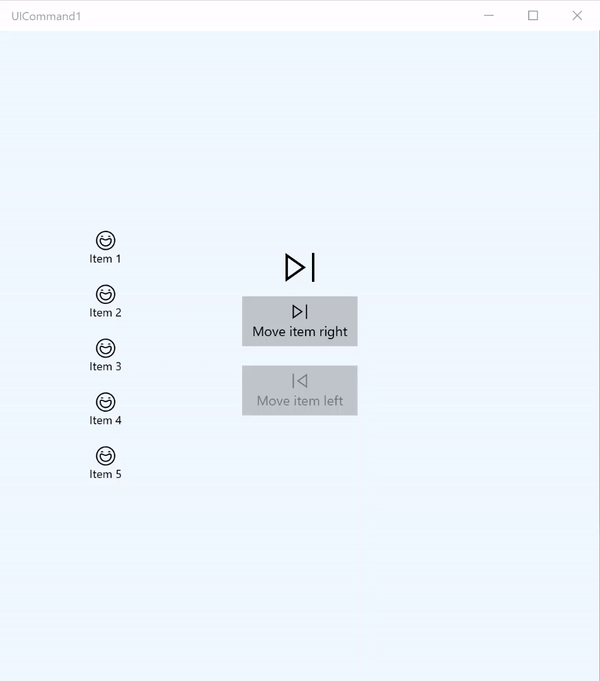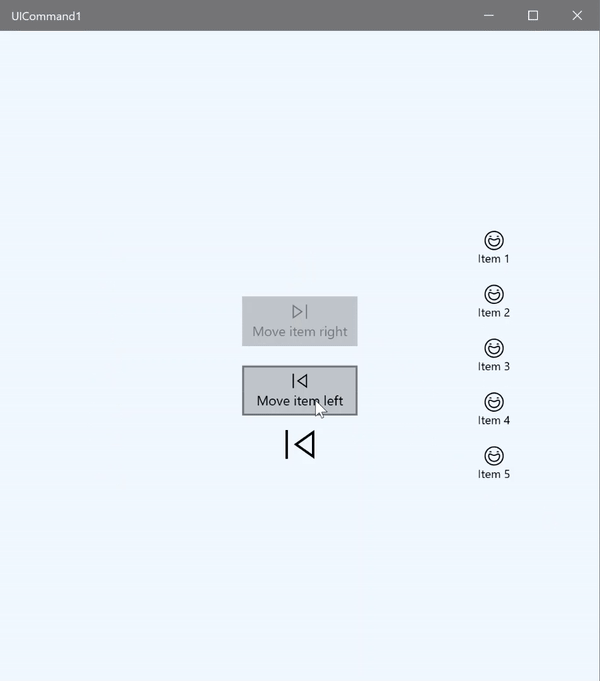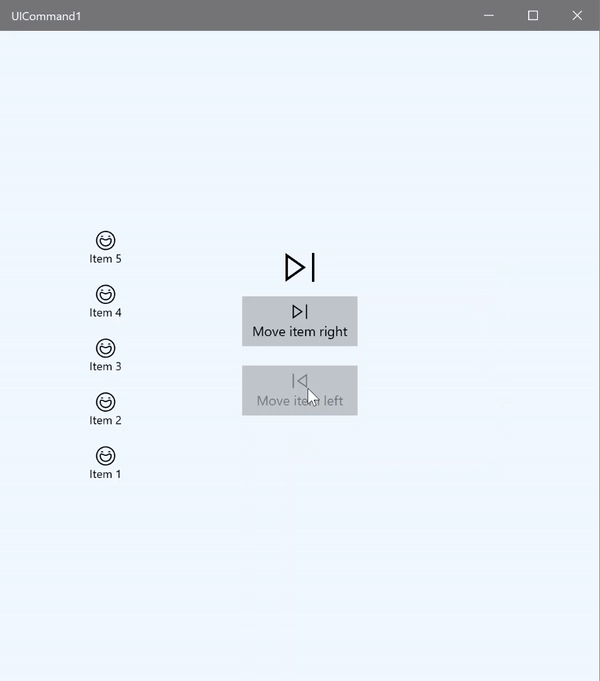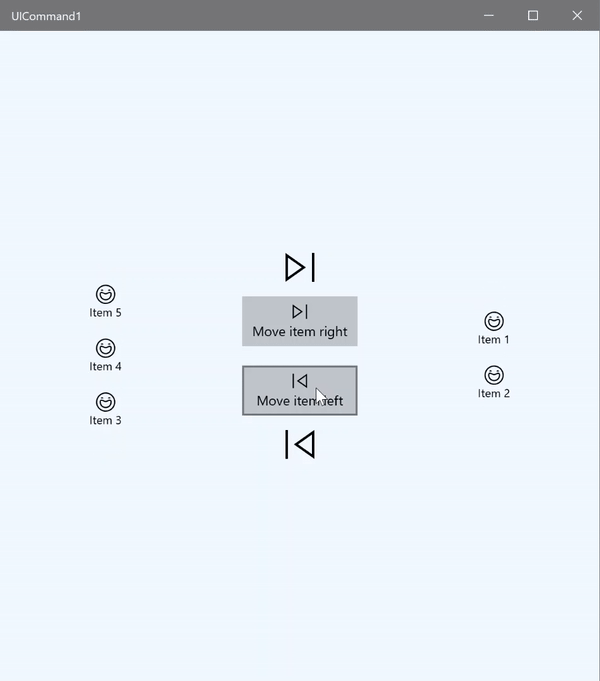
ICommand example
| 下載此範例的程式碼 |
|---|
| UWP 命令範例 (ICommand) |
在此基本範例中,我們會示範如何透過按一下按鈕、鍵盤快速操作鍵及轉動滑鼠滾輪來叫用單一命令。
我們使用兩個 Listview(一個填入五個項目,另一個是空的),以及兩個按鈕 (一個用於將項目從左邊 ListView 移到右邊 ListView,另一個用於將項目從右邊移到左邊)。 每個按鈕都會繫結至對應的命令 (分別是 ViewModel.MoveRightCommand 和 ViewModel.MoveLeftCommand),並且會根據其相關 ListView 中的項目數自動啟用和停用。
下列 XAML 程式碼針對我們的範例定義 UI。
<Page
x:Class="UICommand1.View.MainPage"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:vm="using:UICommand1.ViewModel"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Background="{ThemeResource ApplicationPageBackgroundThemeBrush}">
<Page.Resources>
<vm:OpacityConverter x:Key="opaque" />
</Page.Resources>
<Grid Name="ItemGrid"
Background="AliceBlue"
PointerWheelChanged="Page_PointerWheelChanged">
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="2*"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ListView Grid.Column="0" VerticalAlignment="Center"
x:Name="CommandListView"
ItemsSource="{x:Bind Path=ViewModel.ListItemLeft}"
SelectionMode="None" IsItemClickEnabled="False"
HorizontalAlignment="Right">
<ListView.ItemTemplate>
<DataTemplate x:DataType="vm:ListItemData">
<Grid VerticalAlignment="Center">
<AppBarButton Label="{x:Bind ListItemText}">
<AppBarButton.Icon>
<SymbolIcon Symbol="{x:Bind ListItemIcon}"/>
</AppBarButton.Icon>
</AppBarButton>
</Grid>
</DataTemplate>
</ListView.ItemTemplate>
</ListView>
<Grid Grid.Column="1" Margin="0,0,0,0"
HorizontalAlignment="Center"
VerticalAlignment="Center">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<StackPanel Grid.Row="1">
<FontIcon FontFamily="{StaticResource SymbolThemeFontFamily}"
FontSize="40" Glyph=""
Opacity="{x:Bind Path=ViewModel.ListItemLeft.Count,
Mode=OneWay, Converter={StaticResource opaque}}"/>
<Button Name="MoveItemRightButton"
Margin="0,10,0,10" Width="120" HorizontalAlignment="Center"
Command="{x:Bind Path=ViewModel.MoveRightCommand}">
<Button.KeyboardAccelerators>
<KeyboardAccelerator
Modifiers="Control"
Key="Add" />
</Button.KeyboardAccelerators>
<StackPanel>
<SymbolIcon Symbol="Next"/>
<TextBlock>Move item right</TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
</Button>
<Button Name="MoveItemLeftButton"
Margin="0,10,0,10" Width="120" HorizontalAlignment="Center"
Command="{x:Bind Path=ViewModel.MoveLeftCommand}">
<Button.KeyboardAccelerators>
<KeyboardAccelerator
Modifiers="Control"
Key="Subtract" />
</Button.KeyboardAccelerators>
<StackPanel>
<SymbolIcon Symbol="Previous"/>
<TextBlock>Move item left</TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
</Button>
<FontIcon FontFamily="{StaticResource SymbolThemeFontFamily}"
FontSize="40" Glyph=""
Opacity="{x:Bind Path=ViewModel.ListItemRight.Count,
Mode=OneWay, Converter={StaticResource opaque}}"/>
</StackPanel>
</Grid>
<ListView Grid.Column="2"
x:Name="CommandListViewRight"
VerticalAlignment="Center"
IsItemClickEnabled="False"
SelectionMode="None"
ItemsSource="{x:Bind Path=ViewModel.ListItemRight}"
HorizontalAlignment="Left">
<ListView.ItemTemplate>
<DataTemplate x:DataType="vm:ListItemData">
<Grid VerticalAlignment="Center">
<AppBarButton Label="{x:Bind ListItemText}">
<AppBarButton.Icon>
<SymbolIcon Symbol="{x:Bind ListItemIcon}"/>
</AppBarButton.Icon>
</AppBarButton>
</Grid>
</DataTemplate>
</ListView.ItemTemplate>
</ListView>
</Grid>
</Page>
以下是上述 UI 的程式碼後置。
在程式碼後置中,我們會連線到包含命令碼的檢視模型。 此外,我們會定義從滑鼠滾輪輸入的處理常式,其也會連線我們的命令碼。
using Windows.UI.Xaml;
using Windows.UI.Xaml.Input;
using Windows.UI.Xaml.Controls;
using UICommand1.ViewModel;
using Windows.System;
using Windows.UI.Core;
namespace UICommand1.View
{
/// <summary>
/// An empty page that can be used on its own or navigated to within a Frame.
/// </summary>
public sealed partial class MainPage : Page
{
// Reference to our view model.
public UICommand1ViewModel ViewModel { get; set; }
// Initialize our view and view model.
public MainPage()
{
this.InitializeComponent();
ViewModel = new UICommand1ViewModel();
}
/// <summary>
/// Handle mouse wheel input and assign our
/// commands to appropriate direction of rotation.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void Page_PointerWheelChanged(object sender, PointerRoutedEventArgs e)
{
var props = e.GetCurrentPoint(sender as UIElement).Properties;
// Require CTRL key and accept only vertical mouse wheel movement
// to eliminate accidental wheel input.
if ((Window.Current.CoreWindow.GetKeyState(VirtualKey.Control) !=
CoreVirtualKeyStates.None) && !props.IsHorizontalMouseWheel)
{
bool delta = props.MouseWheelDelta < 0 ? true : false;
switch (delta)
{
case true:
ViewModel.MoveRight();
break;
case false:
ViewModel.MoveLeft();
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
}
}
以下是我們的檢視模型中的程式碼
在我們的檢視模型中,我們為應用程式中的兩個命令定義執行詳細資料、填入一個 ListView,以及提供不透明度值轉換器,以便根據每個 ListView 的項目計數來隱藏或顯示額外一些 UI。
using System;
using System.Collections.ObjectModel;
using System.ComponentModel;
using Windows.UI.Xaml.Controls;
using Windows.UI.Xaml.Data;
namespace UICommand1.ViewModel
{
/// <summary>
/// UI properties for our list items.
/// </summary>
public class ListItemData
{
/// <summary>
/// Gets and sets the list item content string.
/// </summary>
public string ListItemText { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets and sets the list item icon.
/// </summary>
public Symbol ListItemIcon { get; set; }
}
/// <summary>
/// View Model that sets up a command to handle invoking the move item buttons.
/// </summary>
public class UICommand1ViewModel
{
/// <summary>
/// The command to invoke when the Move item left button is pressed.
/// </summary>
public RelayCommand MoveLeftCommand { get; private set; }
/// <summary>
/// The command to invoke when the Move item right button is pressed.
/// </summary>
public RelayCommand MoveRightCommand { get; private set; }
// Item collections
public ObservableCollection<ListItemData> ListItemLeft { get; } =
new ObservableCollection<ListItemData>();
public ObservableCollection<ListItemData> ListItemRight { get; } =
new ObservableCollection<ListItemData>();
public ListItemData listItem;
/// <summary>
/// Sets up a command to handle invoking the move item buttons.
/// </summary>
public UICommand1ViewModel()
{
MoveLeftCommand =
new RelayCommand(new Action(MoveLeft), CanExecuteMoveLeftCommand);
MoveRightCommand =
new RelayCommand(new Action(MoveRight), CanExecuteMoveRightCommand);
LoadItems();
}
/// <summary>
/// Populate our list of items.
/// </summary>
public void LoadItems()
{
for (var x = 0; x <= 4; x++)
{
listItem = new ListItemData();
listItem.ListItemText = "Item " + (ListItemLeft.Count + 1).ToString();
listItem.ListItemIcon = Symbol.Emoji;
ListItemLeft.Add(listItem);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Move left command valid when items present in the list on right.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>True, if count is greater than 0.</returns>
private bool CanExecuteMoveLeftCommand()
{
return ListItemRight.Count > 0;
}
/// <summary>
/// Move right command valid when items present in the list on left.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>True, if count is greater than 0.</returns>
private bool CanExecuteMoveRightCommand()
{
return ListItemLeft.Count > 0;
}
/// <summary>
/// The command implementation to execute when the Move item right button is pressed.
/// </summary>
public void MoveRight()
{
if (ListItemLeft.Count > 0)
{
listItem = new ListItemData();
ListItemRight.Add(listItem);
listItem.ListItemText = "Item " + ListItemRight.Count.ToString();
listItem.ListItemIcon = Symbol.Emoji;
ListItemLeft.RemoveAt(ListItemLeft.Count - 1);
MoveRightCommand.RaiseCanExecuteChanged();
MoveLeftCommand.RaiseCanExecuteChanged();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// The command implementation to execute when the Move item left button is pressed.
/// </summary>
public void MoveLeft()
{
if (ListItemRight.Count > 0)
{
listItem = new ListItemData();
ListItemLeft.Add(listItem);
listItem.ListItemText = "Item " + ListItemLeft.Count.ToString();
listItem.ListItemIcon = Symbol.Emoji;
ListItemRight.RemoveAt(ListItemRight.Count - 1);
MoveRightCommand.RaiseCanExecuteChanged();
MoveLeftCommand.RaiseCanExecuteChanged();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Views subscribe to this event to get notified of property updates.
/// </summary>
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
/// <summary>
/// Notify subscribers of updates to the named property
/// </summary>
/// <param name="propertyName">The full, case-sensitive, name of a property.</param>
protected void NotifyPropertyChanged(string propertyName)
{
PropertyChangedEventHandler handler = this.PropertyChanged;
if (handler != null)
{
PropertyChangedEventArgs args = new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName);
handler(this, args);
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Convert a collection count to an opacity value of 0.0 or 1.0.
/// </summary>
public class OpacityConverter : IValueConverter
{
/// <summary>
/// Converts a collection count to an opacity value of 0.0 or 1.0.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value">The count passed in</param>
/// <param name="targetType">Ignored.</param>
/// <param name="parameter">Ignored</param>
/// <param name="language">Ignored</param>
/// <returns>1.0 if count > 0, otherwise returns 0.0</returns>
public object Convert(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, string language)
{
return ((int)value > 0 ? 1.0 : 0.0);
}
/// <summary>
/// Not used, converter is not intended for two-way binding.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value">Ignored</param>
/// <param name="targetType">Ignored</param>
/// <param name="parameter">Ignored</param>
/// <param name="language">Ignored</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public object ConvertBack(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, string language)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
}
最後,以下是我們的 ICommand 介面實作
在此,我們會定義一個命令,以實作 ICommand 介面並將其功能轉送到其他物件。
using System;
using System.Windows.Input;
namespace UICommand1
{
/// <summary>
/// A command whose sole purpose is to relay its functionality
/// to other objects by invoking delegates.
/// The default return value for the CanExecute method is 'true'.
/// <see cref="RaiseCanExecuteChanged"/> needs to be called whenever
/// <see cref="CanExecute"/> is expected to return a different value.
/// </summary>
public class RelayCommand : ICommand
{
private readonly Action _execute;
private readonly Func<bool> _canExecute;
/// <summary>
/// Raised when RaiseCanExecuteChanged is called.
/// </summary>
public event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged;
/// <summary>
/// Creates a new command that can always execute.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="execute">The execution logic.</param>
public RelayCommand(Action execute)
: this(execute, null)
{
}
/// <summary>
/// Creates a new command.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="execute">The execution logic.</param>
/// <param name="canExecute">The execution status logic.</param>
public RelayCommand(Action execute, Func<bool> canExecute)
{
if (execute == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("execute");
_execute = execute;
_canExecute = canExecute;
}
/// <summary>
/// Determines whether this <see cref="RelayCommand"/> can execute in its current state.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="parameter">
/// Data used by the command. If the command does not require
/// data to be passed, this object can be set to null.
/// </param>
/// <returns>true if this command can be executed; otherwise, false.</returns>
public bool CanExecute(object parameter)
{
return _canExecute == null ? true : _canExecute();
}
/// <summary>
/// Executes the <see cref="RelayCommand"/> on the current command target.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="parameter">
/// Data used by the command. If the command does not require
/// data to be passed, this object can be set to null.
/// </param>
public void Execute(object parameter)
{
_execute();
}
/// <summary>
/// Method used to raise the <see cref="CanExecuteChanged"/> event
/// to indicate that the return value of the <see cref="CanExecute"/>
/// method has changed.
/// </summary>
public void RaiseCanExecuteChanged()
{
var handler = CanExecuteChanged;
if (handler != null)
{
handler(this, EventArgs.Empty);
}
}
}
}
摘要
通用 Windows 平台提供強大且富有彈性的命令系統,可讓您建置應用程式來共用及管理各種控制項類型、裝置和輸入類型的命令。
建立 Windows 應用程式的命令時,請使用下列方法:
- 在 XAML/程式碼後置中接聽和處理事件
- 繫結至事件處理常式方法,例如 Click
- 定義您自己的 ICommand 實作
- 使用您自己的一組預先定義屬性值來建立 XamlUICommand 物件
- 使用一組預先定義的平台屬性和值來建立 StandardUICommand 物件
下一步
如需示範 XamlUICommand 和 StandardUICommand 實作的完整範例,請參閱 XAML 控制項庫範例。
