Build a bot with SSO authentication
Conversational bots in Microsoft Teams perform repetitive automated tasks initiated by users, such as customer service. The user needs to sign in multiple times without single sign-on (SSO) authentication. With SSO authentication methods, the users don't need to sign in to the bot multiple times.
A bot behaves differently depending on the conversation it's involved in:
- Bots in channel and group chat conversations require the users to @mention the bot.
- Bots in a one-to-one conversation don't require an @mention. All messages sent by the user routes to the bot.
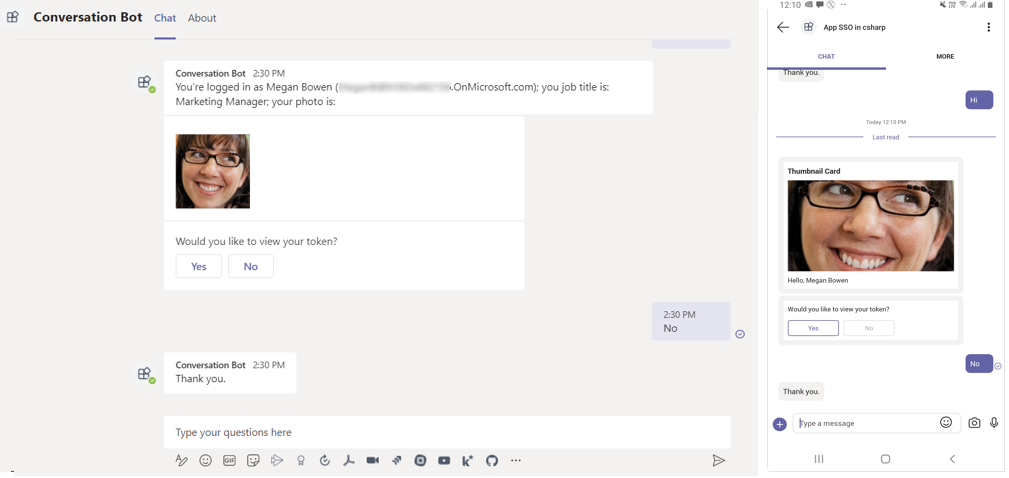
This step-by-step guide helps you to build a bot with SSO authentication. You'll see the following output:
Prerequisites
Ensure that you install the following tools and set up your development environment:
| Install | For using... | |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Teams | Microsoft Teams to collaborate with everyone you work with through apps for chat, meetings, and calls all in one place. | |
| Visual Studio 2022 | You can install the enterprise version in Visual Studio 2022, and install the ASP.NET and web development workloads. Use the latest version. | |
| Microsoft 365 developer account | Access to Teams account with the appropriate permissions to install an app. | |
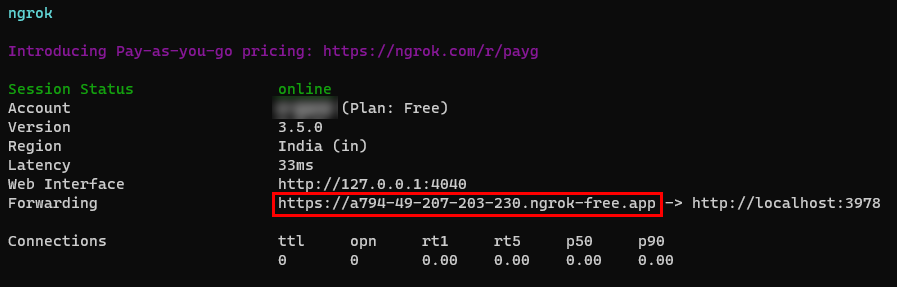
| Dev tunnel | Teams app features (conversational bots, message extensions, and incoming webhooks) need inbound connections. A tunnel connects your development system to Teams. Dev tunnel is a powerful tool to securely open your localhost to the internet and control who has access. Dev tunnel is available in Visual Studio 2022 version 17.7.0 or later. or You can also use ngrok as a tunnel to connect your development system to Teams. It isn't required for apps that only include tabs. This package is installed within the project directory (using npm devDependencies). |
Note
After downloading ngrok, sign up and install authtoken.
Set up your Teams development tenant
A tenant is like a space or a container where you chat, share files, and run meetings for your organization in Teams. You can also upload and test the custom app.
Check for custom app upload option
After creating the app, you must load your app in Teams without distributing it. This process is known as custom app upload. Sign in to your Microsoft 365 account to view this option.
Note
Custom app upload is necessary for previewing and testing apps in Teams local environment. Enable app upload to preview and test your app in Teams locally.
Do you already have a tenant, and do you have the admin access? Let's check if you really do!
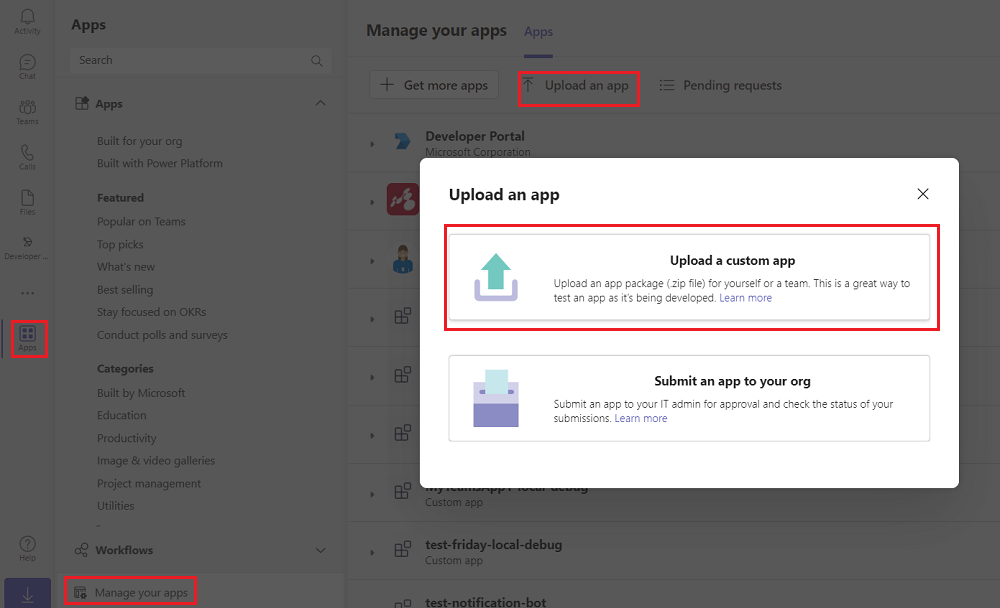
To verify custom upload apps in Teams:
In the Teams client, select the Apps icon.
Select Manage your apps.
Select Upload an app
Look for the option Upload a custom app. If you see the option, custom app upload is enabled.
Note
Contact Teams administrator, if you don't have the option to upload a custom app.
Create a free Teams developer tenant (optional)
If you don't have a Teams developer account, you can get it for free. Join the Microsoft 365 developer program!
Go to the Microsoft 365 developer program.
Select Join Now and follow the onscreen instructions.
In the welcome screen, select Setup E5 subscription.
Set up an administrator account. After you finish, the following screen displays.
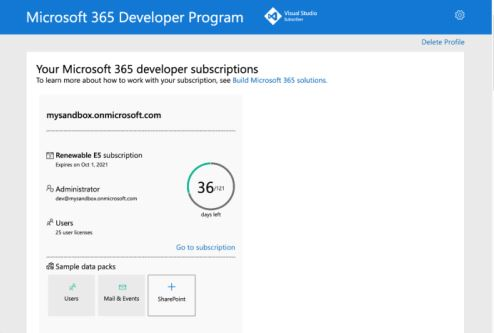
Sign in to Teams using the new administrator account you just set up. Verify that you have the Upload a custom app option in Teams.
Set up local environment
Open Microsoft-Teams-Samples.
Select Code.
From the dropdown menu, select Open with GitHub Desktop.
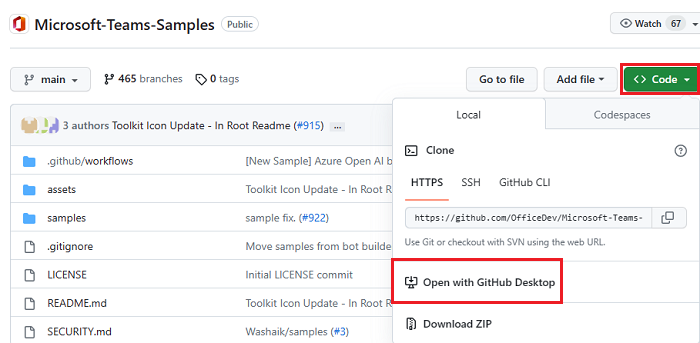
Select Clone.
Register Microsoft Entra app
The following steps help you to create and register your bot in the Azure portal:
- Create and register your Azure app.
- Create client secret to enable SSO authentication of the bot.
- Add Teams channel to deploy the bot.
- Create a tunnel to your web server's endpoints using dev tunnel (recommended) or ngrok.
- Add messaging endpoint to the dev tunnel that you created.
Add App registration
Go to Azure portal.
Select App registrations.

Select + New registration.

Enter the name of your app.
Select Accounts in any organizational directory (Any Microsoft Entra ID tenant - Multitenant).
Select Register.
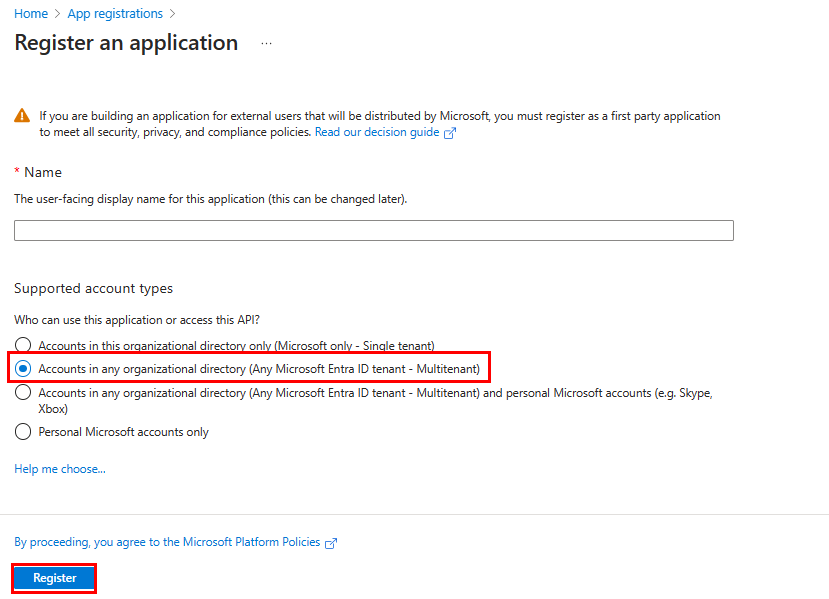
Your app is registered in Microsoft Entra ID. The app overview page appears.
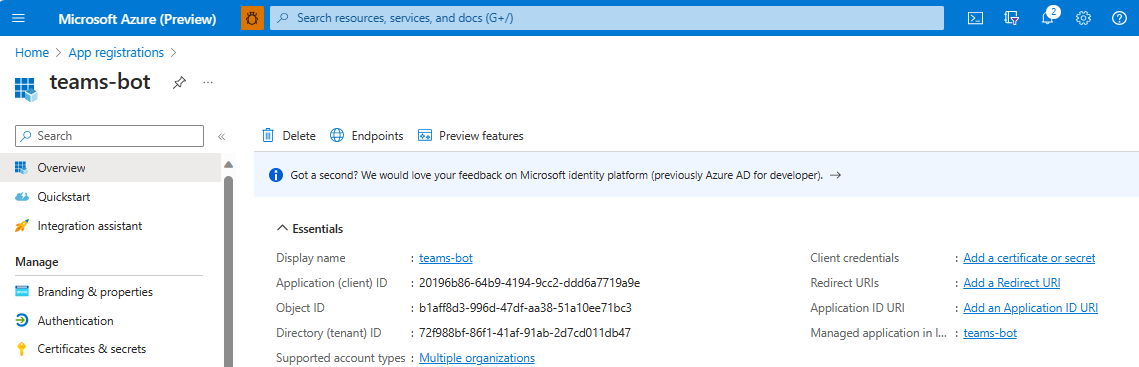
Note
Save the app ID from Application (client) ID and Directory (tenant) ID for further use.
Create a tunnel
Open Visual Studio.
Select Create a new project.
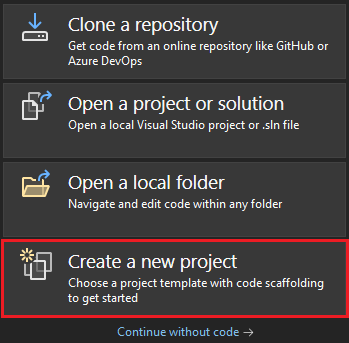
In the search box, enter ASP.NET. From the search results, select ASP.NET Core Web App.
Select Next.
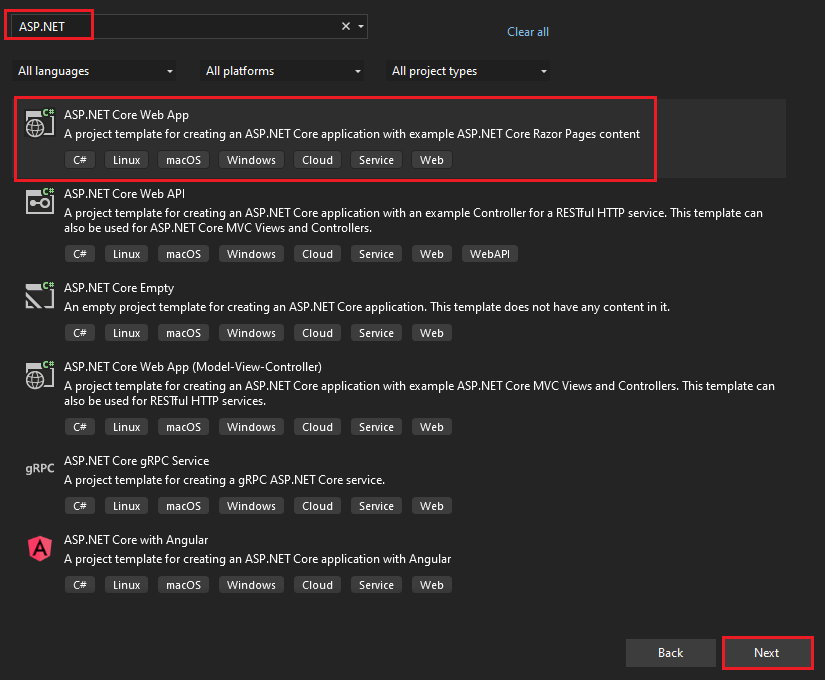
Enter Project name and select Next.
Select Create.
An overview window appears.
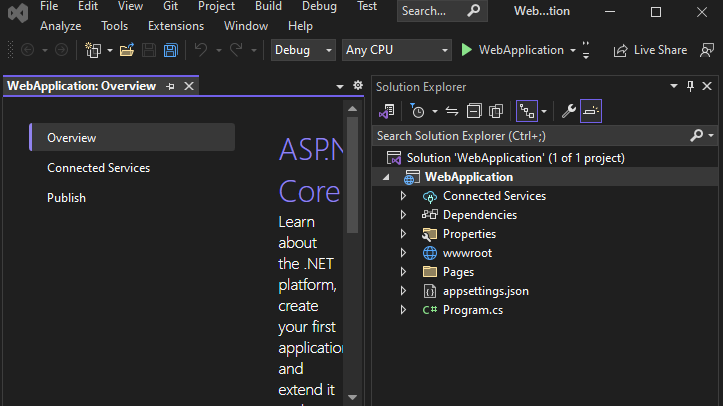
In the debug dropdown list, select Dev Tunnels (no active tunnel) > Create a Tunnel....
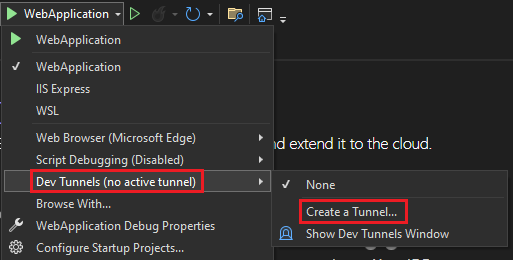
A pop-up window appears.
Update the following details in the pop-up window:
- Account: Enter a Microsoft or GitHub account.
- Name: Enter a name for your tunnel.
- Tunnel Type: From the dropdown list, select Temporary.
- Access: From the dropdown list, select Public.
Select OK.
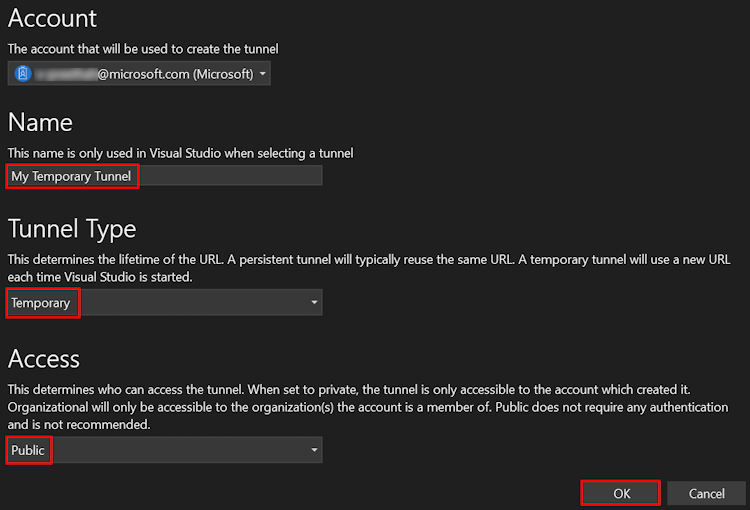
A pop-up window appears showing that dev tunnel is successfully created.
Select OK.
You can find the tunnel you've created in the debug dropdown list as follows:
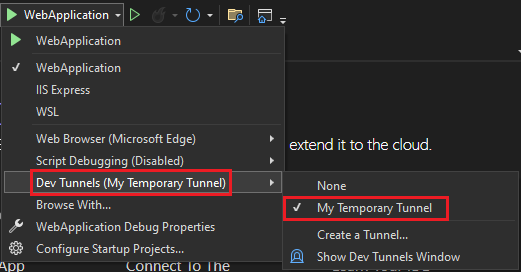
Select F5 to run the application in the debug mode.
If a Security Warning dialog appears, select Yes.
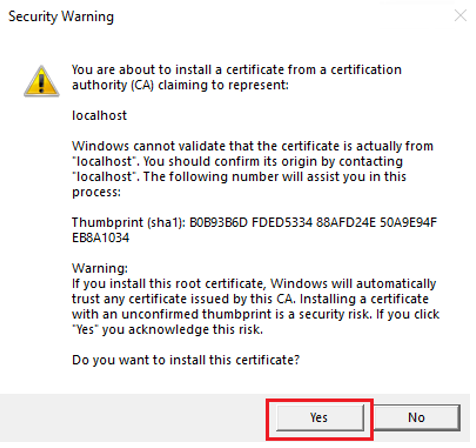
A pop-up window appears.
Select Continue.
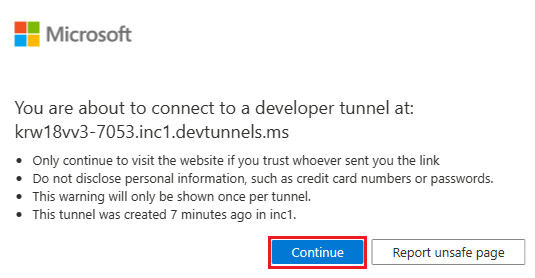
The dev tunnel home page opens in a new browser window and the dev tunnel is now active.
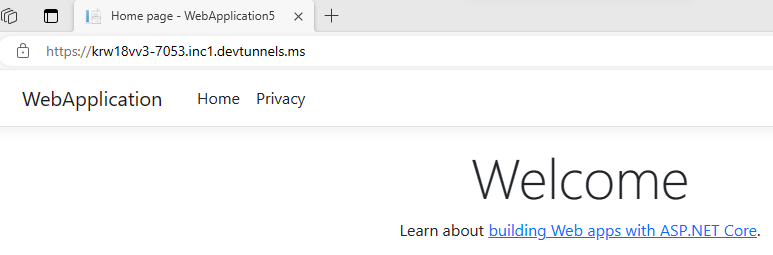
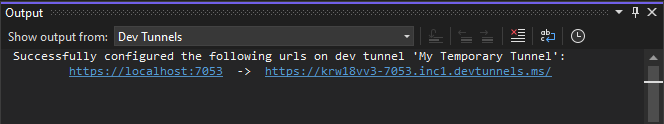
Go to Visual Studio, select View > Output.
From the Output console dropdown menu, select Dev Tunnels.
The Output console shows the dev tunnel URL.
Add a web authentication
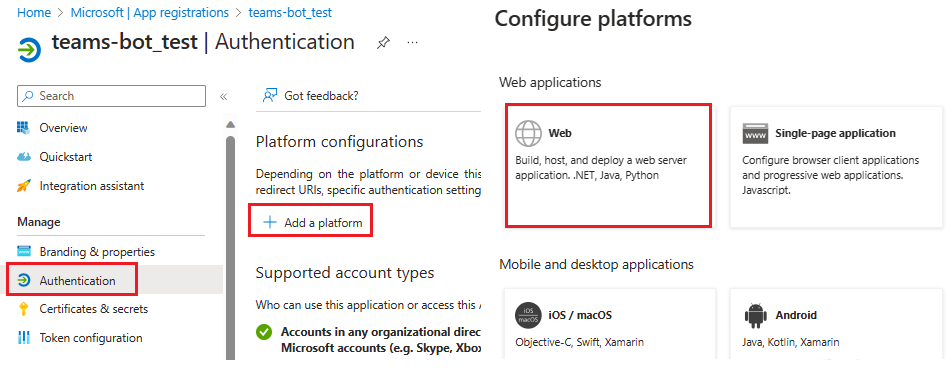
In the left pane, under Manage, select Authentication.
Select Add a platform > Web.
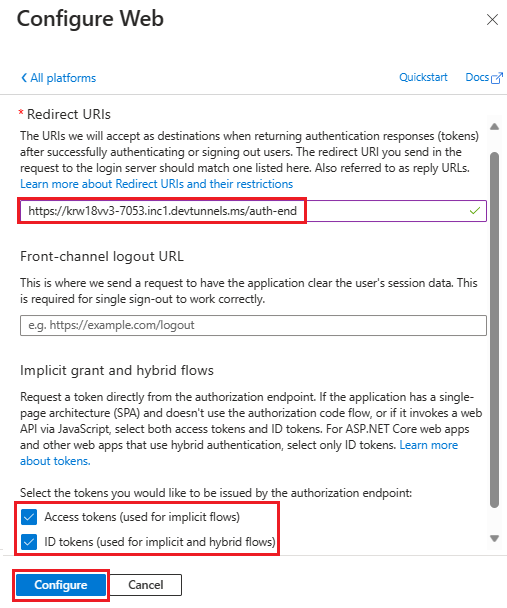
Enter the redirect URI for your app by appending
auth-endto the fully qualified domain name. For example,https://your-devtunnel-domain/auth-endorhttps://your-ngrok-domain/auth-end.Under Implicit grant and hybrid flows, select the Access tokens and ID tokens checkboxes.
Select Configure.
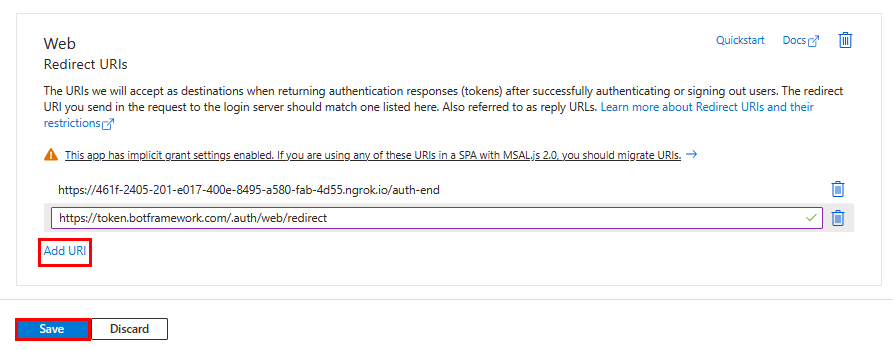
Under Web, select Add URI.
Enter
https://token.botframework.com/.auth/web/redirect.Select Save.
Create a client secret
In the left pane, under Manage, select Certificates & secrets.
Under Client secrets, select + New client secret.
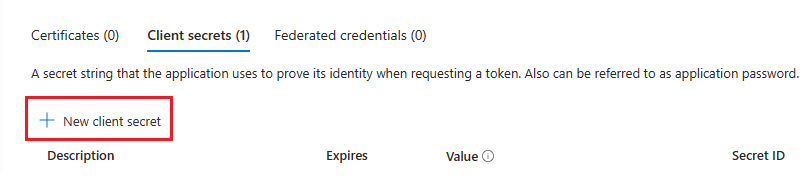
The Add a client secret window appears.
Enter Description.
Select Add.
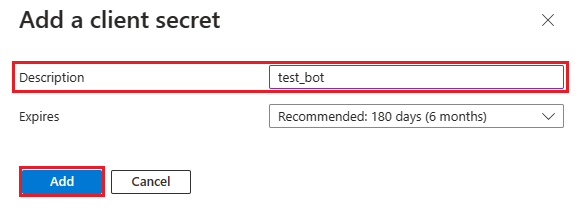
Under Value, select Copy to clipboard to save the client secret value for further use.
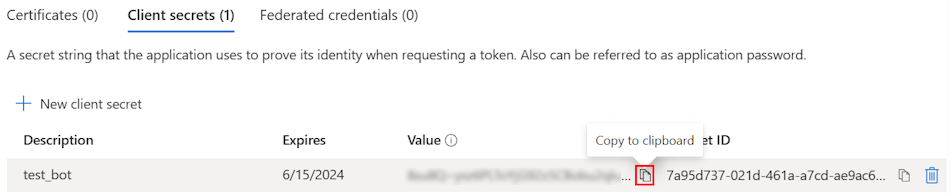
Add API permissions
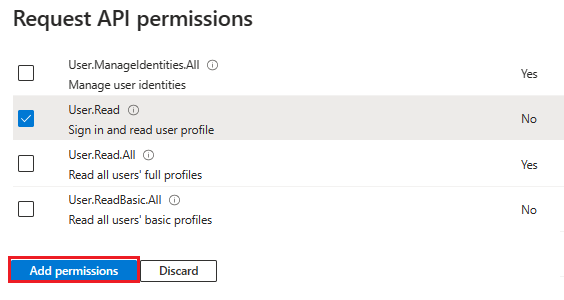
In the left pane, select API permissions.
Select + Add a permission.
Select Microsoft Graph.
Select Delegated permissions.
Select User > User.Read.
Select Add permissions.
Note
If an app isn't granted IT admin consent, users must provide consent the first time they use an app. Users need to consent to the API permissions only if the Microsoft Entra app is registered in a different tenant.
Application ID URI
In the left pane, under Manage, select Expose an API.
Next to Application ID URI, select Add.

Update the Application ID URI in the
api://botid-{AppID}format and select Save.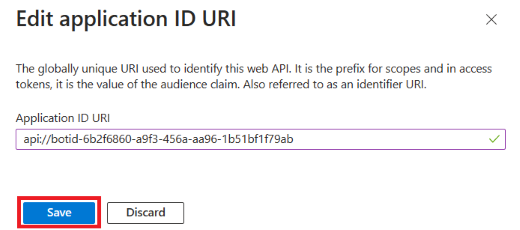
Add a scope
In the left pane, under Manage, select Expose an API.
Select + Add a scope.
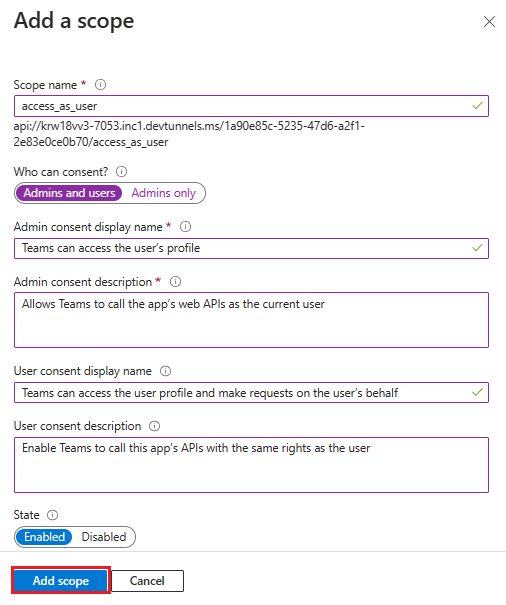
Enter access_as_user as the Scope name.
Under Who can consent?, select Admins and users.
Update the values for the rest of the fields as follows:
Enter Teams can access the user’s profile as Admin consent display name.
Enter Allows Teams to call the app’s web APIs as the current user as Admin consent description.
Enter Teams can access the user profile and make requests on the user’s behalf as User consent display name.
Enter Enable Teams to call this app’s APIs with the same rights as the user as User consent description.
Ensure that State is set to Enabled.
Select Add scope.
The following image shows the fields and the values:
Note
The Scope name must match with the Application ID URI with
/access_as_userappended at the end.
Add client application
In the left pane, under Manage, select Expose an API.
Under Authorized client applications, identify the applications that you want to authorize for your app’s web application.
Select + Add a client application.
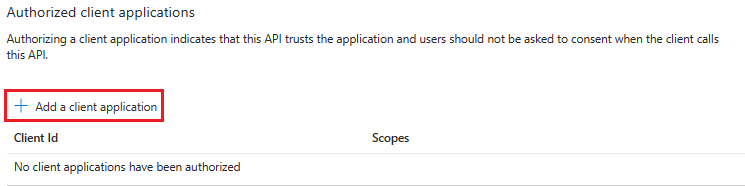
Add Teams mobile or desktop and Teams web application.
For Teams mobile or desktop: Enter the Client ID as
1fec8e78-bce4-4aaf-ab1b-5451cc387264.
For Teams web: Enter the Client ID as
5e3ce6c0-2b1f-4285-8d4b-75ee78787346.
Select the Authorized scopes checkbox.
Select Add application.
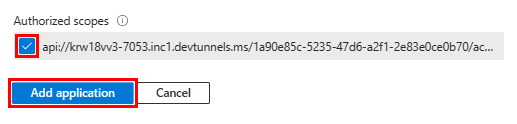
The following image displays the Client Id:
Update the manifest
In the left pane, select Manifest.
Set the value for the
accessTokenAcceptedVersionto2and select Save.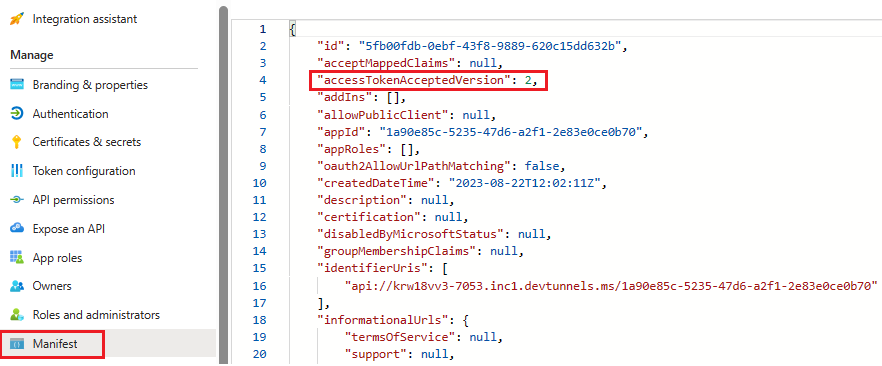
Create your bot
Create an Azure bot resource
Note
If you're already testing your bot in Teams, sign out of this app and Teams. To see this change, sign in again.
Go to Home.
Select + Create a resource.
In the search box, enter Azure Bot.
Select Enter.
Select Azure Bot.
Select Create.

Enter the bot name in Bot handle.
Select your Subscription from the dropdown list.
Select your Resource group from the dropdown list.
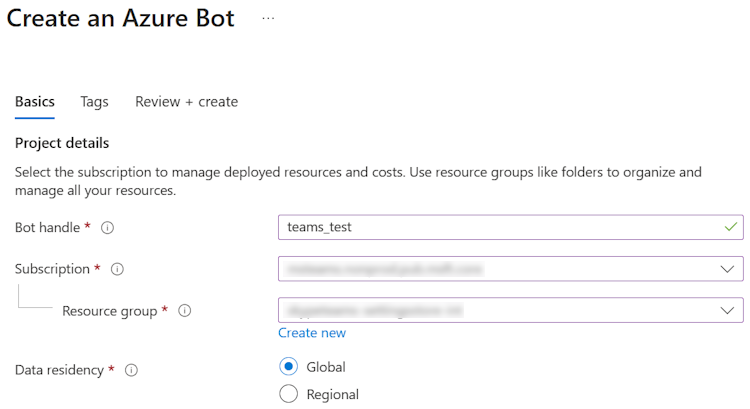
If you don't have an existing resource group, you can create a new resource group. To create a new resource group, follow these steps:
- Select Create new.
- Enter the resource name and select OK.
- Select a location from New resource group location dropdown list.

Under Pricing, select Change plan.
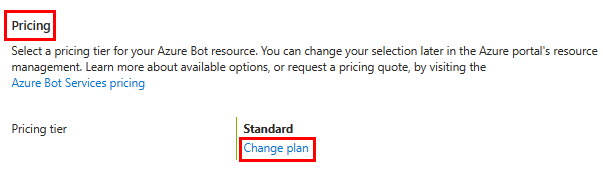
Select FO Free > Select.
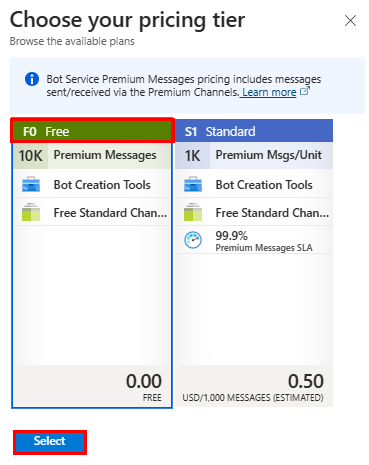
Under Microsoft App ID, select Type of App as Multi Tenant.
In the Creation type, select Use existing app registration.
Enter the App ID.
Note
You can't create more than one bot with the same Microsoft App ID.
Select Review + create.
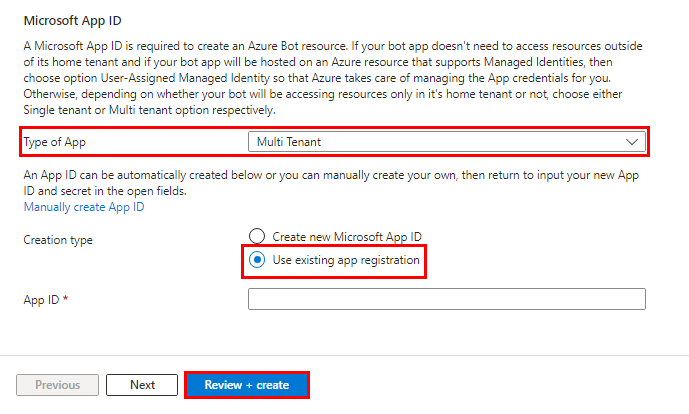
After the validation passes, select Create.
The bot takes a few minutes to provision.
Select Go to resource.
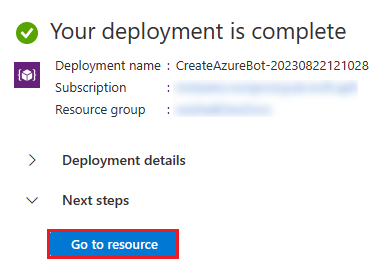
You've successfully created your Azure bot.
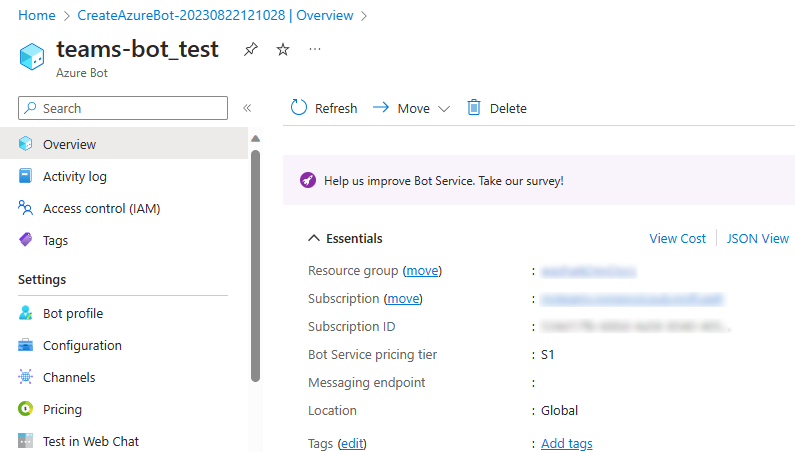
Add a Teams channel
In the left pane, select Channels.
Under Available Channels, select Microsoft Teams.
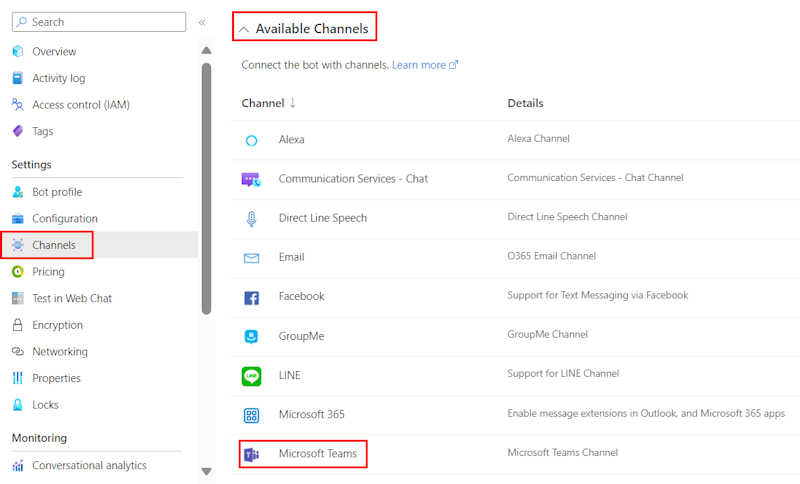
Select the checkbox to accept the Terms of Service.
Select Agree.
Select Apply.
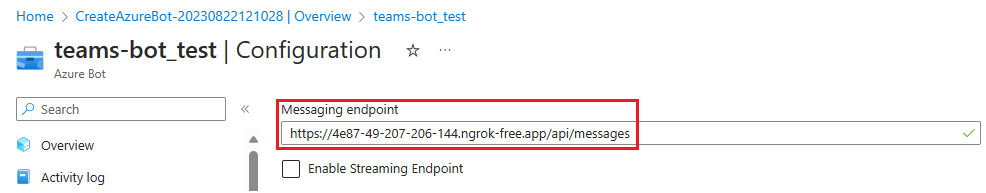
To add a messaging endpoint
Use the dev tunnel URL in the Output console as the messaging endpoint.

In the left pane, under Settings, select Configuration.
Update the Messaging endpoint in the format
https://your-devtunnel-domain/api/messages.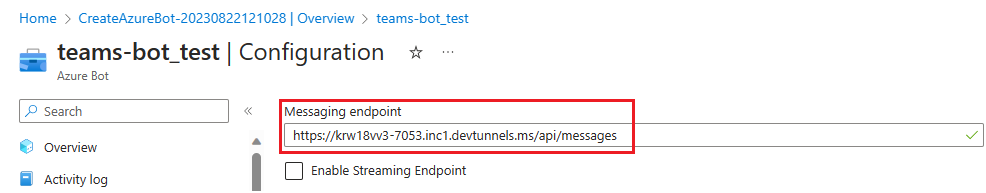
Select Apply.
You've successfully set up a bot in Azure Bot service.
Note
If the Application Insights Instrumentation key shows an error, update with App ID.
Add an OAuth connection settings
In the left pane, select Configuration.
Select Add OAuth Connection Settings.
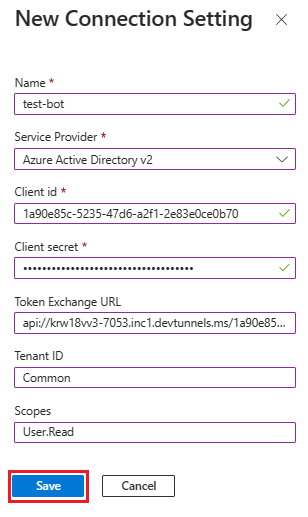
Under New Connection Setting, update the following details:
- Name: Enter a name for your new connection setting. You can use the name in the settings of your bot service code.
- Service Provider: From the dropdown list, select Azure Active Directory v2.
- Client id: Update your Microsoft App ID.
- Client secret: Update the client secrets Value.
- Token Exchange URL: Update the Application ID URI.
- Tenant ID: Enter Common.
- Scopes: Enter User.Read.
Select Save.
Set up app settings and manifest files
Go to the appsettings.json file in the cloned repository.
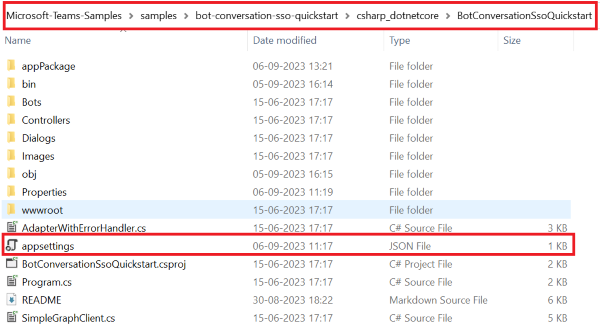
Open the appsettings.json file and update the following information:
- Set
"MicrosoftAppId"to your bot's Microsoft App ID. - Set
"MicrosoftAppPassword"to your bot's client secret ID value. - Set
ConnectionNameas OAuth connection name. - Set
"MicrosoftAppType"to MultiTenant. - Set
"MicrosoftAppTenantId"to common.
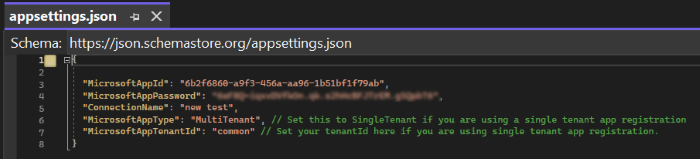
- Set
Go to the manifest.json file in the cloned repository.
Open the manifest.json file and update the following changes:
- Replace all occurrences of
"{TODO: MicrosoftAppId}"with your Microsoft App ID. - Set
"<<domain-name>>"to your ngrok or dev tunnel domain.
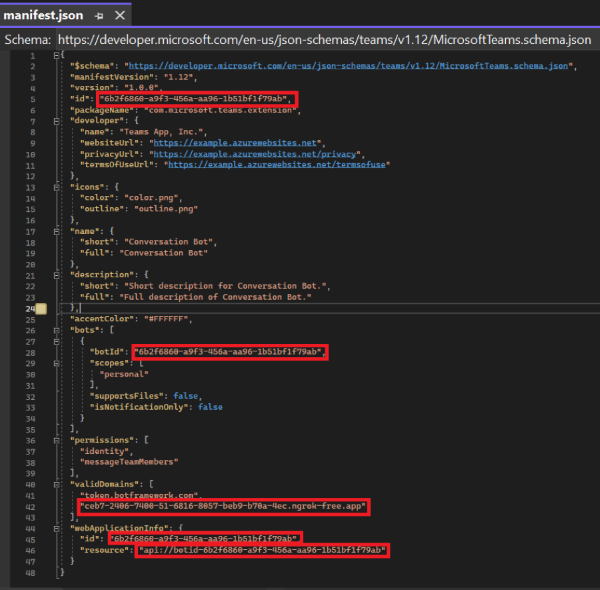
- Replace all occurrences of
Build and run the service
Open Visual Studio.
Go to File > Open > Project/Solution....
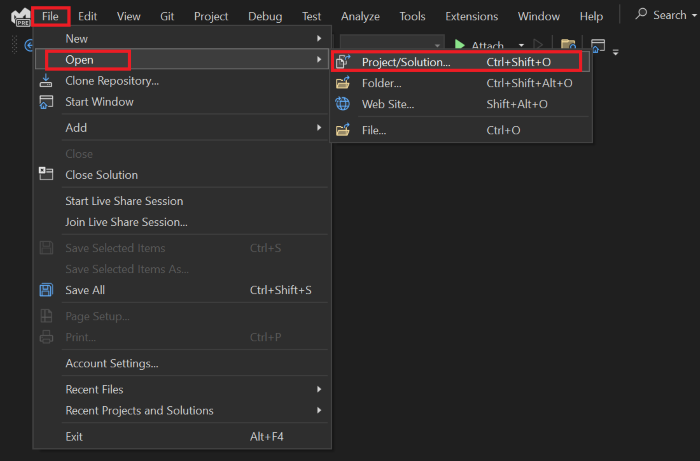
From bot-conversation-sso-quickstart > csharp_dotnetcore folder, and select BotConversationSsoQuickstart.sln file.
Select F5 to run the project.
If a Security Warning dialog appears, select Yes.
A webpage opens with a message Your bot is ready!.
Troubleshooting
If you get the Unable to find package error, follow these steps:
- Go to Tools > NuGet Package Manager > Package Manager Settings.
- In the Options window that appears, select NuGet Package Manager > Package Sources.
- Select Add.
- In Name, enter
nuget.organd in Source, enterhttps://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json. - Select Update and OK.
- Rebuild your project.
Upload the bot in Teams
In your cloned repository, go to Microsoft-Teams-Samples > samples > bot-conversation-sso-quickstart > csharp_dotnetcore > BotConversationSsoQuickstart.
Create a .zip file with the following files that are present in the appPackage folder:
- manifest.json
- outline.png
- color.png
Go to Microsoft Teams.
In the Teams client, select Apps.
Select Manage your apps.
Select Upload an app.
Look for the option to Upload a custom app.
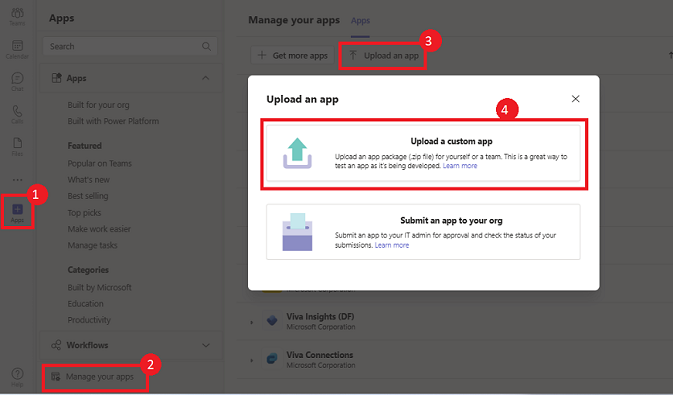
Select Open to upload the .zip file that you've created in the Manifest folder.
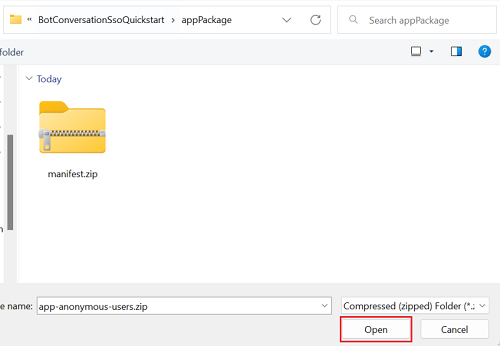
Select Add to add the bot to your chat.
Select Open.
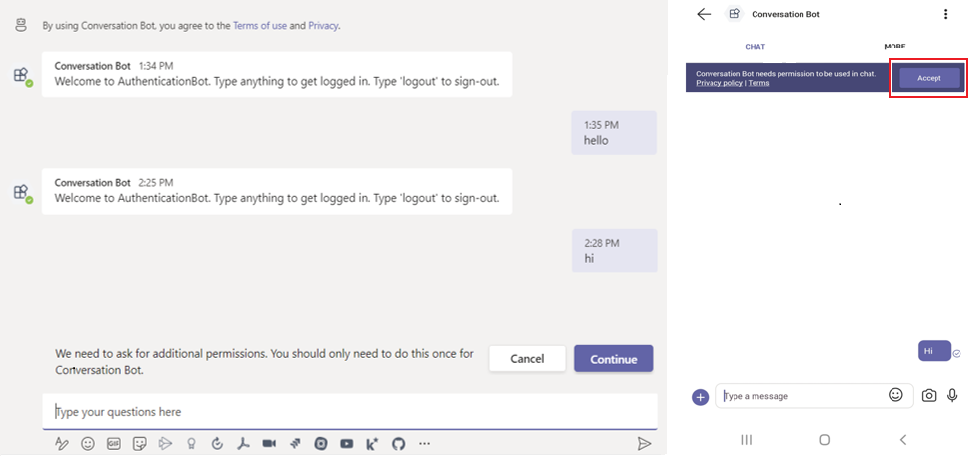
You can interact with the bot by sending it a message. The bot exchanges an SSO token and calls the Graph API on your behalf. It keeps you signed in unless you send a message to sign out.
Send a message to the bot. The conversation bot asks for consent for the first time.
For desktop: Select Continue to give permissions to Teams client for accessing the bot.

Note
Now you’ve configured SSO with your bot app and it's the only time you'll have to give consent.
For mobile: Select Accept.
Note
Now you’ve configured SSO with your bot app in mobile, and it's the only time you'll have to give consent.
Complete challenge
Did you come up with something like this?

Congratulations!
You've completed the tutorial to get started with build a bot with SSO authentication.
Have an issue with this section? If so, please give us some feedback so we can improve this section.