教學課程第 3 部分:訓練和註冊機器學習模型
在本教學課程中,您將了解如何訓練多個機器學習模型,以選取最佳模型,進而預測哪些銀行客戶可能會離開。
在本教學課程中,您將會:
- 訓練隨機樹系和 LightGBM 模型。
- 使用 Microsoft Fabric 與 MLflow 架構的原生整合,記錄訓練的機器學習模型、使用的超參數和評估計量。
- 註冊訓練的機器學習模型。
- 評估驗證資料集上訓練機器學習模型的效能。
MLflow 是一個開放原始碼平台,可藉助追蹤、模型和模型登錄等功能來管理機器學習生命週期。 MLflow 原生與 Fabric 資料科學體驗整合。
必要條件
取得 Microsoft Fabric 訂用帳戶。 或註冊免費的 Microsoft Fabric 試用版。
登入 Microsoft Fabric。
使用首頁左下方的體驗切換器,切換至 Fabric。
![體驗切換器功能表的螢幕擷取畫面,顯示選取 [資料科學] 的位置。](media/tutorial-data-science-prepare-system/switch-to-data-science.png)
這是教學課程系列 5 部分中的第 3 部分。 若要完成本教學課程,請先完成:
- 第 1 部分:使用 Apache Spark 將資料內嵌至 Microsoft Fabric Lakehouse。
- 第 2 部分:使用 Microsoft Fabric 筆記本探索和視覺化資料,以深入了解資料。
遵循筆記本中的指示
3-train-evaluate.ipynb 是本教學課程隨附的筆記本。
若要開啟本教學課程隨附的筆記本,請遵循 準備系統以進行數據科學教學課程中的指示, 將筆記本匯入工作區。
如果您想要複製並貼上此頁面中的程式碼,則可以建立新的筆記本。
開始執行程式碼之前,請務必將 Lakehouse 連結至筆記本。
重要
連結您在第 1 部分和第 2 部分中使用的相同 Lakehouse。
安裝自訂程式庫
針對此筆記本,您將使用 imblearn 安裝 Imbalanced-learn (匯入為 %pip install)。 Imbalanced-learn 是 Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE) 的程式庫,用於處理不平衡的資料集。 PySpark 核心會在 %pip install 之後重新啟動,因此您必須先安裝程式庫,再執行任何其他資料格。
您將使用 imblearn 程式庫來存取 SMOTE。 立即使用內嵌安裝功能進行安裝 (例如 %pip、%conda)。
# Install imblearn for SMOTE using pip
%pip install imblearn
重要
每次重新啟動筆記本時,請執行此安裝。
當您在筆記本中安裝程式庫時,僅適用於筆記本工作階段,而非工作區中的持續時間。 如果您重新啟動筆記本,您需要再次安裝程式庫。
如果您有經常使用的程式庫,而且想要將其提供給工作區中的所有筆記本,您可以針對該用途使用 Fabric 環境。 您可以建立環境、在其中安裝程式庫,然後您的工作區管理員可以將環境連結至工作區作為其預設環境。 如需將環境設定為工作區預設值的詳細資訊,請參閱管理員設定工作區的預設程式庫。
如需將現有工作區程式庫和 Spark 屬性遷移至環境的資訊,請參閱將工作區程式庫和 Spark 屬性遷移至預設環境。
載入資料
在訓練任何機器學習模型之前,您需要從 Lakehouse 載入 Delta 資料表,才能讀取您在上一個筆記本中建立的清理資料。
import pandas as pd
SEED = 12345
df_clean = spark.read.format("delta").load("Tables/df_clean").toPandas()
使用 MLflow 產生追蹤和記錄模型的實驗
本節示範如何產生實驗、指定機器學習模型和訓練參數,以及對計量評分、訓練機器學習模型、記錄模型,以及儲存訓練模型以供日後使用。
import mlflow
# Setup experiment name
EXPERIMENT_NAME = "bank-churn-experiment" # MLflow experiment name
擴充 MLflow 自動記錄功能,自動記錄的運作方式是自動擷取機器學習模型在訓練時的輸入參數和輸出計量。 此資訊接著會記錄到您的工作區,您可在其中使用 MLflow API 或工作區中的對應實驗來存取和視覺化該資訊。
系統會記錄具有其各自名稱的所有實驗,而且您能夠追蹤其參數和效能計量。 若要深入了解自動記錄,請參閱 Microsoft Fabric 中的自動記錄。
設定實驗和自動記錄規格
mlflow.set_experiment(EXPERIMENT_NAME)
mlflow.autolog(exclusive=False)
匯入 scikit-learn 和 LightGBM
設置您的資料後,您現在可定義機器學習模型。 您將在此筆記本中套用隨機樹系和 LightGBM 模型。 使用 scikit-learn 和 lightgbm,只需幾行程式碼即可實作模型。
# Import the required libraries for model training
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from lightgbm import LGBMClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, f1_score, precision_score, confusion_matrix, recall_score, roc_auc_score, classification_report
準備訓練、驗證和測試的資料
使用 train_test_split 中的 scikit-learn 函數,將資料分割成訓練、驗證和測試集。
y = df_clean["Exited"]
X = df_clean.drop("Exited",axis=1)
# Split the dataset to 60%, 20%, 20% for training, validation, and test datasets
# Train-Test Separation
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.20, random_state=SEED)
# Train-Validation Separation
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(X_train, y_train, test_size=0.25, random_state=SEED)
將測試資料儲存至 Delta 資料表
將測試資料儲存至 Delta 資料表,以供下一個筆記本使用。
table_name = "df_test"
# Create PySpark DataFrame from Pandas
df_test=spark.createDataFrame(X_test)
df_test.write.mode("overwrite").format("delta").save(f"Tables/{table_name}")
print(f"Spark test DataFrame saved to delta table: {table_name}")
將 SMOTE 套用至訓練資料,以合成少數類別的新樣本
第 2 部分的資料探索顯示,在對應到 10,000 個客戶的 10,000 個資料點中,只有 2,037 個客戶 (約 20%) 已經離開銀行。 這表示資料集高度不平衡。 不平衡分類的問題在於,少數類別的範例太少,模型無法有效地了解決策邊界。 SMOTE 是合成少數類別新樣本最廣泛使用的方法。 在這裡和這裡深入了解 SMOTE。
提示
請注意,SMOTE 應僅套用至訓練資料集。 您必須將測試資料集保留在原始不平衡分佈中,才能取得機器學習模型如何在原始資料上執行的有效近似值,這代表生產環境中的情況。
from collections import Counter
from imblearn.over_sampling import SMOTE
sm = SMOTE(random_state=SEED)
X_res, y_res = sm.fit_resample(X_train, y_train)
new_train = pd.concat([X_res, y_res], axis=1)
提示
您可以放心地忽略執行此資料格時出現的 MLflow 警告訊息。
如果您看到 ModuleNotFoundError 訊息,則錯過了執行此筆記本中的第一個資料格,這會安裝 imblearn 程式庫。 每次重新啟動筆記本時,都需要安裝此程式庫。 返回並重新執行從此筆記本中第一個資料格開始的所有資料格。
模型訓練
- 使用隨機樹系來訓練模型,深度上限為 4,並具有 4 個特徵
mlflow.sklearn.autolog(registered_model_name='rfc1_sm') # Register the trained model with autologging
rfc1_sm = RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=4, max_features=4, min_samples_split=3, random_state=1) # Pass hyperparameters
with mlflow.start_run(run_name="rfc1_sm") as run:
rfc1_sm_run_id = run.info.run_id # Capture run_id for model prediction later
print("run_id: {}; status: {}".format(rfc1_sm_run_id, run.info.status))
# rfc1.fit(X_train,y_train) # Imbalanaced training data
rfc1_sm.fit(X_res, y_res.ravel()) # Balanced training data
rfc1_sm.score(X_val, y_val)
y_pred = rfc1_sm.predict(X_val)
cr_rfc1_sm = classification_report(y_val, y_pred)
cm_rfc1_sm = confusion_matrix(y_val, y_pred)
roc_auc_rfc1_sm = roc_auc_score(y_res, rfc1_sm.predict_proba(X_res)[:, 1])
- 使用隨機樹系來訓練模型,深度上限為 8,並具有 6 個特徵
mlflow.sklearn.autolog(registered_model_name='rfc2_sm') # Register the trained model with autologging
rfc2_sm = RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=8, max_features=6, min_samples_split=3, random_state=1) # Pass hyperparameters
with mlflow.start_run(run_name="rfc2_sm") as run:
rfc2_sm_run_id = run.info.run_id # Capture run_id for model prediction later
print("run_id: {}; status: {}".format(rfc2_sm_run_id, run.info.status))
# rfc2.fit(X_train,y_train) # Imbalanced training data
rfc2_sm.fit(X_res, y_res.ravel()) # Balanced training data
rfc2_sm.score(X_val, y_val)
y_pred = rfc2_sm.predict(X_val)
cr_rfc2_sm = classification_report(y_val, y_pred)
cm_rfc2_sm = confusion_matrix(y_val, y_pred)
roc_auc_rfc2_sm = roc_auc_score(y_res, rfc2_sm.predict_proba(X_res)[:, 1])
- 使用 LightGBM 訓練模型
# lgbm_model
mlflow.lightgbm.autolog(registered_model_name='lgbm_sm') # Register the trained model with autologging
lgbm_sm_model = LGBMClassifier(learning_rate = 0.07,
max_delta_step = 2,
n_estimators = 100,
max_depth = 10,
eval_metric = "logloss",
objective='binary',
random_state=42)
with mlflow.start_run(run_name="lgbm_sm") as run:
lgbm1_sm_run_id = run.info.run_id # Capture run_id for model prediction later
# lgbm_sm_model.fit(X_train,y_train) # Imbalanced training data
lgbm_sm_model.fit(X_res, y_res.ravel()) # Balanced training data
y_pred = lgbm_sm_model.predict(X_val)
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_val, y_pred)
cr_lgbm_sm = classification_report(y_val, y_pred)
cm_lgbm_sm = confusion_matrix(y_val, y_pred)
roc_auc_lgbm_sm = roc_auc_score(y_res, lgbm_sm_model.predict_proba(X_res)[:, 1])
追蹤模型效能的實驗成品
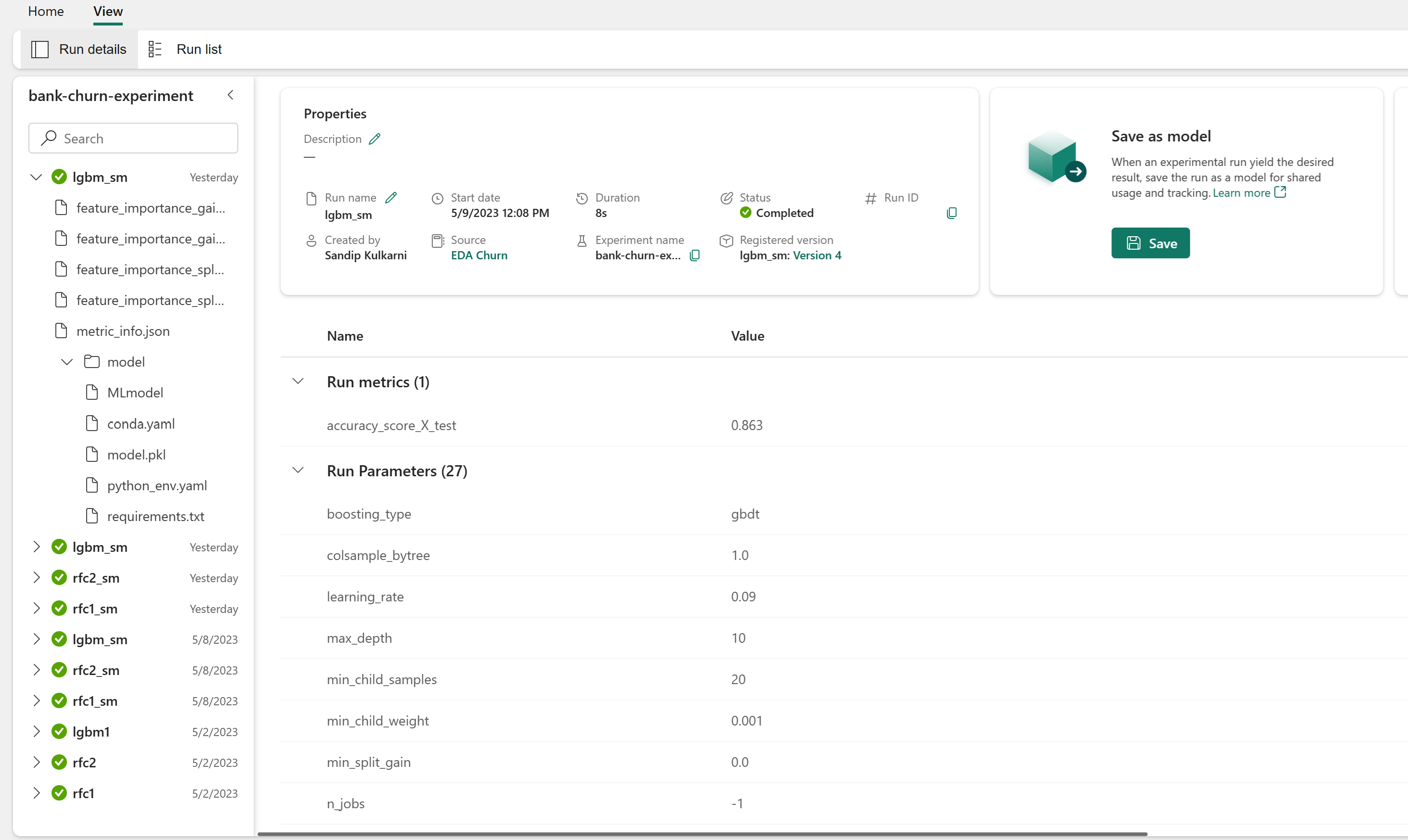
實驗執行會自動儲存在可從工作區找到的實驗成品中。 系統會根據用於設定實驗的名稱來對其命名。 系統會記錄所有訓練的機器學習模型、其執行、效能計量和模型參數。
要檢視您的實驗:
在左側面板中,選取您的工作區。
在右上方,篩選條件僅顯示實驗,以便您更輕鬆地尋找您要尋找的實驗。
尋找並選取實驗名稱,在此案例中為 bank-churn-experiment。 如果您沒有在工作區中看到實驗,請重新整理瀏覽器。
評估驗證資料集上訓練模型的效能
機器學習模型訓練完成之後,您可透過兩種方式來評估訓練模型的效能。
從工作區開啟儲存的實驗、載入機器學習模型,然後在驗證資料集上評估載入模型的效能。
# Define run_uri to fetch the model # mlflow client: mlflow.model.url, list model load_model_rfc1_sm = mlflow.sklearn.load_model(f"runs:/{rfc1_sm_run_id}/model") load_model_rfc2_sm = mlflow.sklearn.load_model(f"runs:/{rfc2_sm_run_id}/model") load_model_lgbm1_sm = mlflow.lightgbm.load_model(f"runs:/{lgbm1_sm_run_id}/model") # Assess the performance of the loaded model on validation dataset ypred_rfc1_sm_v1 = load_model_rfc1_sm.predict(X_val) # Random Forest with max depth of 4 and 4 features ypred_rfc2_sm_v1 = load_model_rfc2_sm.predict(X_val) # Random Forest with max depth of 8 and 6 features ypred_lgbm1_sm_v1 = load_model_lgbm1_sm.predict(X_val) # LightGBM直接評估驗證資料集上訓練機器學習模型的效能。
ypred_rfc1_sm_v2 = rfc1_sm.predict(X_val) # Random Forest with max depth of 4 and 4 features ypred_rfc2_sm_v2 = rfc2_sm.predict(X_val) # Random Forest with max depth of 8 and 6 features ypred_lgbm1_sm_v2 = lgbm_sm_model.predict(X_val) # LightGBM
根據您的喜好設定,任一種方法都沒問題,而且應提供相同的效能。 在此筆記本中,您將選擇第一種方法,以便更好地示範 Microsoft Fabric 中的 MLflow 自動記錄功能。
使用混淆矩陣顯示確判/誤判
接著,您將開發指令碼來繪製混淆矩陣,以便使用驗證資料集來評估分類的正確性。 也可使用 SynapseML 工具來繪製混淆矩陣,如這裡提供的詐騙偵測範例所示。
import seaborn as sns
sns.set_theme(style="whitegrid", palette="tab10", rc = {'figure.figsize':(9,6)})
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.ticker as mticker
from matplotlib import rc, rcParams
import numpy as np
import itertools
def plot_confusion_matrix(cm, classes,
normalize=False,
title='Confusion matrix',
cmap=plt.cm.Blues):
print(cm)
plt.figure(figsize=(4,4))
plt.rcParams.update({'font.size': 10})
plt.imshow(cm, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap)
plt.title(title)
plt.colorbar()
tick_marks = np.arange(len(classes))
plt.xticks(tick_marks, classes, rotation=45, color="blue")
plt.yticks(tick_marks, classes, color="blue")
fmt = '.2f' if normalize else 'd'
thresh = cm.max() / 2.
for i, j in itertools.product(range(cm.shape[0]), range(cm.shape[1])):
plt.text(j, i, format(cm[i, j], fmt),
horizontalalignment="center",
color="red" if cm[i, j] > thresh else "black")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.ylabel('True label')
plt.xlabel('Predicted label')
- 隨機樹系分類器的混淆矩陣,最大上限為 4,並具有 4 個特徵
cfm = confusion_matrix(y_val, y_pred=ypred_rfc1_sm_v1)
plot_confusion_matrix(cfm, classes=['Non Churn','Churn'],
title='Random Forest with max depth of 4')
tn, fp, fn, tp = cfm.ravel()
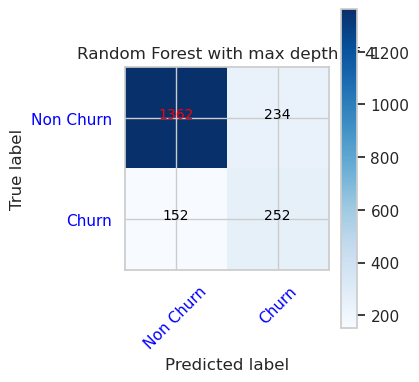
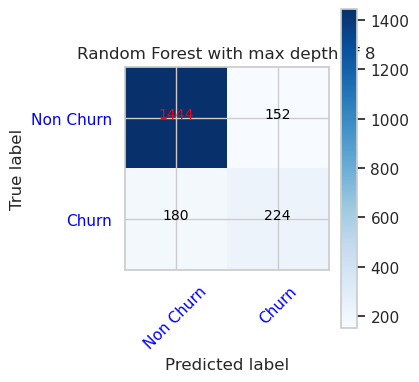
- 隨機樹系分類器的混淆矩陣,最大上限為 8,並具有 6 個特徵
cfm = confusion_matrix(y_val, y_pred=ypred_rfc2_sm_v1)
plot_confusion_matrix(cfm, classes=['Non Churn','Churn'],
title='Random Forest with max depth of 8')
tn, fp, fn, tp = cfm.ravel()
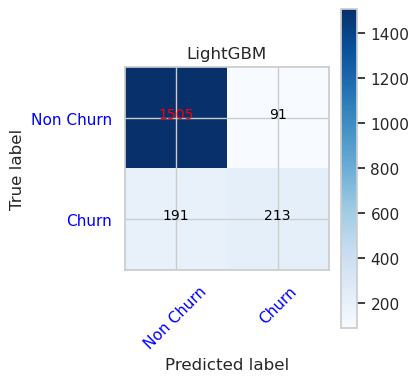
- LightGBM 的混淆矩陣
cfm = confusion_matrix(y_val, y_pred=ypred_lgbm1_sm_v1)
plot_confusion_matrix(cfm, classes=['Non Churn','Churn'],
title='LightGBM')
tn, fp, fn, tp = cfm.ravel()