<iterator> 函式
advance
依指定的位置數目遞增迭代器。
template <class InputIterator, class Distance>
void advance(InputIterator& InIt, Distance Off);
參數
InIt
要遞增且必須符合輸入迭代器需求的迭代器。
Off
整數類資料類型,可以轉換為迭代器的差異類型,並指定迭代器位置向前移的增量數目。
備註
範圍必須是非單數,其中反覆運算器必須可取值或超過結尾。
InputIterator如果 符合雙向反覆運算器類型的需求,則 Off 可能是負數。 如果 InputIterator 是輸入或轉送反覆運算器類型, Off 則必須是非負值。
當滿足隨機存取反覆運算器的需求時 InputIterator ,進階函式具有常數複雜度;否則,它具有線性複雜度,因此可能很昂貴。
範例
// iterator_advance.cpp
// compile with: /EHsc
#include <iterator>
#include <list>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
list<int> L;
for (int i = 1; i < 9; ++i)
{
L.push_back(i);
}
list<int>::iterator LPOS = L.begin();
cout << "The list L is: ( ";
for (auto L_Iter = L.begin(); L_Iter != L.end(); L_Iter++)
{
cout << *L_Iter << " ";
}
cout << ")." << endl;
cout << "The iterator LPOS initially points to the first element: "
<< *LPOS << "." << endl;
advance(LPOS, 4);
cout << "LPOS is advanced 4 steps forward to point"
<< " to the fifth element: "
<< *LPOS << "." << endl;
advance(LPOS, -3);
cout << "LPOS is moved 3 steps back to point to the "
<< "2nd element: " << *LPOS << "." << endl;
}
The list L is: ( 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ).
The iterator LPOS initially points to the first element: 1.
LPOS is advanced 4 steps forward to point to the fifth element: 5.
LPOS is moved 3 steps back to point to the 2nd element: 2.
back_inserter
建立可以在指定的容器背面插入項目的迭代器。
template <class Container>
back_insert_iterator<Container> back_inserter(Container& Cont);
參數
Cont
要在其中執行背後插入的容器。
傳回值
與容器物件 Cont 關聯的 back_insert_iterator。
備註
在C++標準連結庫中,自變數必須參考具有成員函push_back式的三個序列容器之一: deque Class、listClass 或vector Class。
範例
// iterator_back_inserter.cpp
// compile with: /EHsc
#include <iterator>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
vector<int> vec;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
vec.push_back(i);
}
cout << "The initial vector vec is: ( ";
for (auto vIter = vec.begin(); vIter != vec.end(); vIter++)
{
cout << *vIter << " ";
}
cout << ")." << endl;
// Insertions can be done with template function
back_insert_iterator<vector<int> > backiter(vec);
*backiter = 30;
backiter++;
*backiter = 40;
// Alternatively, insertions can be done with the
// back_insert_iterator member function
back_inserter(vec) = 500;
back_inserter(vec) = 600;
cout << "After the insertions, the vector vec is: ( ";
for (auto vIter = vec.begin(); vIter != vec.end(); vIter++)
{
cout << *vIter << " ";
}
cout << ")." << endl;
}
The initial vector vec is: ( 0 1 2 ).
After the insertions, the vector vec is: ( 0 1 2 30 40 500 600 ).
begin
擷取在指定的容器中第一個項目的迭代器。
template <class Container>
auto begin(Container& cont) `
-> decltype(cont.begin());
template <class Container>
auto begin(const Container& cont) `
-> decltype(cont.begin());
template <class Ty, class Size>
Ty *begin(Ty (& array)[Size]);
參數
cont
容器。
array
Ty 類型的物件陣列。
傳回值
前兩個樣板函式會傳回 cont.begin()。 第一個函式是非常數,第二個是常數。
第三個樣板函式會傳回 array。
範例
需要更泛型的行為時,建議您使用這個樣板函式取代容器成員 begin()。
// cl.exe /EHsc /nologo /W4 /MTd
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <vector>
template <typename C> void reverse_sort(C& c)
{
std::sort(std::begin(c), std::end(c), std::greater<>());
}
template <typename C> void print(const C& c)
{
for (const auto& e : c)
{
std::cout << e << " ";
}
std::cout << "\n";
}
int main()
{
std::vector<int> v = { 11, 34, 17, 52, 26, 13, 40, 20, 10, 5, 16, 8, 4, 2, 1 };
print(v);
reverse_sort(v);
print(v);
std::cout << "--\n";
int arr[] = { 23, 70, 35, 106, 53, 160, 80, 40, 20, 10, 5, 16, 8, 4, 2, 1 };
print(arr);
reverse_sort(arr);
print(arr);
}
11 34 17 52 26 13 40 20 10 5 16 8 4 2 1
52 40 34 26 20 17 16 13 11 10 8 5 4 2 1
--
23 70 35 106 53 160 80 40 20 10 5 16 8 4 2 1
160 106 80 70 53 40 35 23 20 16 10 8 5 4 2 1
因為它會呼叫非成員版本的 reverse_sort,除了標準陣列之外,begin() 函式支援任何種類的容器。 撰寫程式代碼 reverse_sort 以使用容器成員 begin():
template <typename C>
void reverse_sort(C& c) {
using std::begin;
using std::end;
std::sort(c.begin(), c.end(), std::greater<>());
}
然後傳送陣列給它,造成這個編譯程序錯誤:
error C2228: left of '.begin' must have class/struct/union
cbegin
將 const (只讀) 反覆運算器擷取至指定容器中的第一個專案。
template <class Container>
auto cbegin(const Container& cont)
-> decltype(cont.begin());
參數
cont
容器或 initializer_list。
傳回值
cont.begin() 常數。
備註
此函式適用於所有C++標準連結庫容器和 。initializer_list
您可以使用此成員函式取代 begin() 樣板函式,以確保傳回值是 const_iterator。 一般而言,它會與類型推算關鍵詞搭配 auto 使用,如下列範例所示。 在此範例中,請將 Container 視為任何一種支援 begin() 和 cbegin() 的可修改 (非 const) 容器或 initializer_list。
auto i1 = Container.begin();
// i1 is Container<T>::iterator
auto i2 = Container.cbegin();
// i2 is Container<T>::const_iterator
cend
將 const (只讀) 反覆運算器擷取到指定容器中最後一個元素之後的專案。
template <class Container>
auto cend(const Container& cont)
-> decltype(cont.end());
參數
cont
容器或 initializer_list。
傳回值
cont.end() 常數。
備註
此函式適用於所有C++標準連結庫容器和 。initializer_list
您可以使用此成員函式取代 end() 樣板函式,以確保傳回值是 const_iterator。 一般而言,它會與類型推算關鍵詞搭配 auto 使用,如下列範例所示。 在此範例中,請將 Container 視為任何一種支援 end() 和 cend() 的可修改 (非 const) 容器或 initializer_list。
auto i1 = Container.end();
// i1 is Container<T>::iterator
auto i2 = Container.cend();
// i2 is Container<T>::const_iterator
crbegin
從容器結尾開始,取得容器專案的反向只讀反覆運算器。
template <class C> constexpr auto crbegin(const C& c) -> decltype(std::rbegin(c));
參數
C
容器的類型。
c
容器實例。
傳回值
此反覆運算器會以反向順序傳回容器的專案,從容器結尾開始。
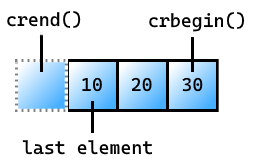
範例: crbegin
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::vector<int> v{10, 20, 30};
for (auto i = std::crbegin(v); i != std::crend(v); ++i)
{
std::cout << *i << ' '; // outputs 30 20 10
}
// v[1] = 100; // error because the iterator is const
}
30 20 10
crend
取得唯讀反轉專案序列結尾的 sentinel。
template <class C> constexpr auto crend(const C& c) -> decltype(std::rend(c));
參數
C
容器的類型。
c
容器實例。
傳回值
sentinel 會遵循容器反轉檢視中的最後一個專案。

crend 例
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::vector<int> v{10, 20, 30};
auto vi = std::crend(v);
--vi; // get off the sentinel and onto the last element in the reversed range
std::cout << *vi; // outputs 10
// vi[0] = 300; // error because the iterator is const
}
10
data
取得容器中第一個專案的指標。
1) template <class C> constexpr auto data(C& c) -> decltype(c.data());
2) template <class C> constexpr auto data(const C& c) -> decltype(c.data());
3) template <class T, size_t N> constexpr T* data(T (&array)[N]) noexcept;
4) template <class E> constexpr const E* data(initializer_list<E> il) noexcept;
參數
C
容器的類型。
c
容器的實例。
E
初始化表達式清單的項目類型。
il
初始化表達式清單。
N
陣列中的項目數。
T
陣列中數據的型別。
傳回值
1, 2) 根據容器類型指向第一個專案的指標。 例如,如果容器是整數的向量,傳回值的型別就是 int *。
3) 第一個專案的指標做為陣列。
4) 初始化表示式清單第一個專案的指標。
例 data
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::vector<int> v{ 10, 20, 30 };
std::string src{ "a string" };
const char *charPtr = std::data(src);
int* intPtr = std::data(v);
std::cout << charPtr << ", " << *intPtr << '\n'; // a string, 10
}
a string, 10
distance
判斷在兩個迭代器定址的位置之間的增量數。
template <class InputIterator>
typename iterator_traits<InputIterator>::difference_type distance(InputIterator first, InputIterator last);
參數
first
要判斷與第二個迭代器之距離的第一個迭代器。
last
要判斷與第一個迭代器之距離的第二個迭代器。
傳回值
必須遞增的次數, first 直到等於 last為止。
備註
當滿足隨機存取反覆運算器的需求時 InputIterator ,distance 函式具有常數複雜度;否則,它具有線性複雜度,因此可能很昂貴。
範例
// iterator_distance.cpp
// compile with: /EHsc
#include <iterator>
#include <list>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
list<int> L;
for (int i = -1; i < 9; ++i)
{
L.push_back(2 * i);
}
list <int>::iterator L_Iter, LPOS = L.begin();
cout << "The list L is: ( ";
for (L_Iter = L.begin(); L_Iter != L.end(); L_Iter++)
{
cout << *L_Iter << " ";
}
cout << ")." << endl;
cout << "The iterator LPOS initially points to the first element: "
<< *LPOS << "." << endl;
advance(LPOS, 7);
cout << "LPOS is advanced 7 steps forward to point "
<< " to the eighth element: "
<< *LPOS << "." << endl;
list<int>::difference_type Ldiff;
Ldiff = distance(L.begin(), LPOS);
cout << "The distance from L.begin( ) to LPOS is: "
<< Ldiff << "." << endl;
}
The list L is: ( -2 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 ).
The iterator LPOS initially points to the first element: -2.
LPOS is advanced 7 steps forward to point to the eighth element: 12.
The distance from L.begin( ) to LPOS is: 7.
empty
template <class C> constexpr auto empty(const C& c) -> decltype(c.empty());
template <class T, size_t N> constexpr bool empty(const T (&array)[N]) noexcept;
template <class E> constexpr bool empty(initializer_list<E> il) noexcept;
參數
C
容器的類型。
c
容器的實例。
E
初始化表達式清單的項目類型。
il
初始化表達式清單。
N
陣列中的項目數。
T
陣列中數據的型別。
傳回值
如果容器沒有專案,則傳 true 回 ,否則 false傳回 。
範例
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::vector<int> v{ 10,20,30 };
std::vector<int> v2;
std::cout << std::boolalpha << std::empty(v); // outputs false
std::cout << std::boolalpha << ", " << std::empty(v2); // outputs true
}
false, true
end
擷取迭代器,指向在指定的容器中最後一個項目後面的項目。
template <class Container>
auto end(Container& cont)
-> decltype(cont.end());
template <class Container>
auto end(const Container& cont)
-> decltype(cont.end());
template <class Ty, class Size>
Ty *end(Ty (& array)[Size]);
參數
cont
容器。
array
Ty 類型的物件陣列。
傳回值
前兩個樣板函式會傳回 cont.end() (第一個函式是非常數,而第二個函式是常數)。
第三個樣板函式會傳回 array + Size。
備註
如需程式碼範例,請參閱begin。
front_inserter
建立可以在指定的容器前面插入項目的迭代器。
template <class Container>
front_insert_iterator<Container> front_inserter(Container& Cont);
參數
Cont
其前面要插入元素的容器物件。
傳回值
與容器物件 Cont 關聯的 front_insert_iterator。
備註
也可以使用 front_insert_iterator 類別的成員函式 front_insert_iterator。
在「C++ 標準程式庫」內,引數必須參考具有成員函式 push_back 的下列兩個序列容器其中之一:deque 類別 或「list 類別」。
範例
// iterator_front_inserter.cpp
// compile with: /EHsc
#include <iterator>
#include <list>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
list<int> L;
for (int i = -1; i < 9; ++i)
{
L.push_back(i);
}
cout << "The list L is:\n ( ";
for (auto L_Iter = L.begin(); L_Iter != L.end(); L_Iter++)
{
cout << *L_Iter << " ";
}
cout << ")." << endl;
// Using the template function to insert an element
front_insert_iterator<list <int>> Iter(L);
*Iter = 100;
// Alternatively, you may use the front_insert member function
front_inserter(L) = 200;
cout << "After the front insertions, the list L is:\n ( ";
for (auto L_Iter = L.begin(); L_Iter != L.end(); L_Iter++)
{
cout << *L_Iter << " ";
}
cout << ")." << endl;
}
The list L is:
( -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ).
After the front insertions, the list L is:
( 200 100 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ).
inserter
協助程式範本函式,可讓您使用 inserter(Cont, Where) 而非 insert_iterator<Container>(Cont, Where)。
template <class Container>
insert_iterator<Container>
inserter(
Container& Cont,
typename Container::iterator Where);
參數
Cont
要新增新元素的容器。
Where
找出插入點的迭代器。
備註
此範本函式會傳回 insert_iterator<Container>(Cont, Where)。
範例
// iterator_inserter.cpp
// compile with: /EHsc
#include <iterator>
#include <list>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
list<int> L;
for (int i = 2; i < 5; ++i)
{
L.push_back(10 * i);
}
cout << "The list L is:\n ( ";
for (auto L_Iter = L.begin(); L_Iter != L.end(); L_Iter++)
{
cout << *L_Iter << " ";
}
cout << ")." << endl;
// Using the template version to insert an element
insert_iterator<list<int>> Iter(L, L.begin());
*Iter = 1;
// Alternatively, using the member function to insert an element
inserter(L, L.end()) = 500;
cout << "After the insertions, the list L is:\n ( ";
for (auto L_Iter = L.begin(); L_Iter != L.end(); L_Iter++)
{
cout << *L_Iter << " ";
}
cout << ")." << endl;
}
The list L is:
( 20 30 40 ).
After the insertions, the list L is:
( 1 20 30 40 500 ).
make_checked_array_iterator
建立其他演算法可使用的 checked_array_iterator。
注意
這個函式是「C++ 標準程式庫」的 Microsoft 擴充功能。 透過使用這個函式實作的程式碼不可移植到不支援此 Microsoft 擴充功能的 C++ Standard 建置環境。
template <class Iter>
checked_array_iterator<Iter>
make_checked_array_iterator(
Iter Ptr,
size_t Size,
size_t Index = 0);
參數
Ptr
目的陣列的指標。
Size
目的陣列的大小。
Index
陣列中選擇性的索引。
傳回值
checked_array_iterator 的執行個體。
備註
make_checked_array_iterator 函式是在 stdext 命名空間中定義。
這個函式會接受原始指標 (通常會導致溢出界限的顧慮),並將其包裝在執行檢查的 checked_array_iterator 類別中。 由於該類別已標記為已檢查,因此「C++ 標準程式庫」不會發出它的相關警告。 如需詳細資訊與程式碼範例,請參閱已檢查的迭代器。
範例
在下列範例中,會建立一個向量並填入 10 個項目。 向量的內容是透過使用複製演算法複製到陣列,然後 make_checked_array_iterator 會用來指定目的。 接著界限故意違規檢查,以便觸發偵錯判斷提示失敗。
// make_checked_array_iterator.cpp
// compile with: /EHsc /W4 /MTd
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator> // stdext::make_checked_array_iterator
#include <memory> // std::make_unique
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
template <typename C> void print(const string& s, const C& c)
{
cout << s;
for (const auto& e : c)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
const size_t dest_size = 10;
// Old-school but not exception safe, favor make_unique<int[]>
// int* dest = new int[dest_size];
unique_ptr<int[]> updest = make_unique<int[]>(dest_size);
int* dest = updest.get(); // get a raw pointer for the demo
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < dest_size; ++i)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
print("vector v: ", v);
copy(v.begin(), v.end(), stdext::make_checked_array_iterator(dest, dest_size));
cout << "int array dest: ";
for (int i = 0; i < dest_size; ++i)
{
cout << dest[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// Add another element to the vector to force an overrun.
v.push_back(10);
// ! The next line causes a debug assertion when it executes.
copy(v.begin(), v.end(), stdext::make_checked_array_iterator(dest, dest_size));
}
make_move_iterator
建立一個包含所提供迭代器作為stored迭代器的 move iterator。
template <class Iterator>
move_iterator<Iterator>
make_move_iterator(const Iterator& It);
參數
It
儲存在新移動迭代器中的迭代器。
備註
樣本函式會傳move_iterator<Iterator>(_It)回 。
make_unchecked_array_iterator
建立其他演算法可使用的 unchecked_array_iterator。
注意
這個函式是「C++ 標準程式庫」的 Microsoft 擴充功能。 透過使用這個函式實作的程式碼不可移植到不支援此 Microsoft 擴充功能的 C++ Standard 建置環境。
template <class Iter>
unchecked_array_iterator<Iter>
make_unchecked_array_iterator(Iter Ptr);
參數
Ptr
目的陣列的指標。
傳回值
unchecked_array_iterator 的執行個體。
備註
make_unchecked_array_iterator 函式是在 stdext 命名空間中定義。
這個函式會使用原始指標,並將它包裝在不執行任何檢查的類別中,因此會最佳化到極精簡的程度,但它也會關閉編譯器警告,例如 C4996。 因此,這是處理未檢查指標警告的目標方式,而不需要全域關閉警告訊息或產生檢查成本。 如需詳細資訊與程式碼範例,請參閱已檢查的迭代器。
範例
在下列範例中,會建立一個向量並填入 10 個項目。 向量的內容是透過使用複製演算法複製到陣列,然後 make_unchecked_array_iterator 會用來指定目的。
// make_unchecked_array_iterator.cpp
// compile with: /EHsc /W4 /MTd
#include <algorithm>
#include <iterator> // stdext::make_unchecked_array_iterator
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
template <typename C> void print(const string& s, const C& c)
{
cout << s;
for (const auto& e : c)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
const size_t dest_size = 10;
int* dest = new int[dest_size];
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < dest_size; ++i)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
print("vector v: ", v);
// COMPILER WARNING SILENCED: stdext::unchecked_array_iterator is marked as checked in debug mode
// (it performs no checking, so an overrun will trigger undefined behavior)
copy(v.begin(), v.end(), stdext::make_unchecked_array_iterator(dest));
cout << "int array dest: ";
for (int i = 0; i < dest_size; ++i)
{
cout << dest[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
delete[] dest;
}
vector v: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
int array dest: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
next
反覆運算指定的次數,並傳回新的迭代器位置。
template <class InputIterator>
InputIterator next(
InputIterator first,
typename iterator_traits<InputIterator>::difference_type off = 1);
參數
first
目前位置。
off
要逐一查看的次數。
傳回值
在逐一查看 off 次之後,傳回新的迭代器位置。
備註
此範本函式會傳回遞增 off 次後的 next
prev
以反向方向反覆運算指定的次數,並傳回新的迭代器位置。
template <class BidirectionalIterator>
BidirectionalIterator prev(
BidirectionalIterator first,
typename iterator_traits<BidirectionalIterator>::difference_type off = 1);
參數
first
目前位置。
off
要逐一查看的次數。
備註
此範本函式會傳回遞減 off 次後的 next。
rbegin
取得反覆運算器,它會以反向順序傳回容器的專案。
template <class C> constexpr auto rbegin(C& c) -> decltype(c.rbegin());
template <class C> constexpr auto rbegin(const C& c) -> decltype(c.rbegin());
參數
C
容器的類型。
c
容器實例。
傳回值
傳回的反覆運算器會以反向順序呈現容器的專案,從反向範圍結尾開始。
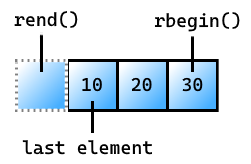
例 rbegin
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::vector<int> v{ 10, 20, 30 };
for (auto e = std::rbegin(v); e != std::rend(v); ++e)
{
std::cout << *e << ' '; // outputs 30 20 10
}
}
30 20 10
rend
取得反轉專案序列結尾的 sentinel。
template <class C> constexpr auto rend(C& c)-> decltype(c.rend());
template <class C> constexpr auto rend(const C& c) -> decltype(c.rend());
參數
C
容器的類型。
c
容器實例。
傳回值
容器結尾之 sentinel 的反向反覆運算器。 sentinel 會遵循容器反向檢視中的最後一個專案:

rend 例
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::vector<int> v{10, 20, 30};
auto vi = std::rend(v);
--vi; // get off the sentinel and onto the last element in the reversed range
std::cout << *vi; // outputs 10
}
10
size
template <class C> constexpr auto size(const C& c)
-> decltype(c.size());
template <class T, size_t N> constexpr size_t size(const T (&array)[N]) noexcept;
參數
C
容器的類型。
c
容器的實例。
N
陣列中的項目數。
T
陣列中數據的型別。
傳回值
容器中的元素數目,做為無符號整數值。
例 size
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::vector<int> v{ 10, 20, 30 };
size_t s = std::size(v);
std::cout << s; // outputs 3
}
3