路径几何图形概述
本主题介绍如何使用 Direct2D 路径几何图形创建复杂绘图。 其中包含以下各节。
先决条件
本概述假定你熟悉如何创建基本的 Direct2D 应用程序,如 创建简单的 Direct2D 应用程序中所述。 它还假定你熟悉 Direct2D 几何图形的基本功能,如 几何图形概述中所述。
Direct2D 中的路径几何图形
路径几何图形由 ID2D1PathGeometry 接口表示。 若要实例化路径几何图形,请调用 ID2D1Factory::CreatePathGeometry 方法。 这些对象可用于描述由弧线、曲线和线条等线段组成的复杂几何图形。 若要使用图形和段填充路径几何图形,请调用 Open 方法来检索 ID2D1GeometrySink ,并使用 geometry 接收器的 方法将图形和段添加到路径几何图形。
使用 ID2D1GeometrySink 填充路径几何图形
ID2D1GeometrySink 描述可以包含直线、弧、三次方贝塞尔曲线和二次贝塞尔曲线的几何路径。
几何接收器由一个或多个图形组成。 每个图形由一个或多个线条、曲线或弧线段组成。 若要创建图表,请调用 BeginFigure 方法,传入图表的起点,然后使用其 Add 方法 ((如 AddLine 和 AddBezier) )添加段。 添加完段后,调用 EndFigure 方法。 可以重复此序列以创建其他图形。 创建完图表后,调用 Close 方法。
示例:创建复杂绘图
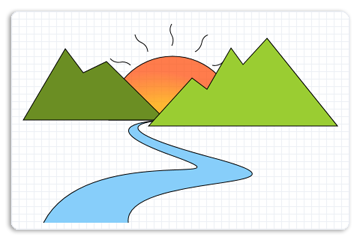
下图显示了一个包含线条、弧线和贝塞尔曲线的复杂绘图。 下面的代码示例演示如何使用四个路径几何对象创建绘图,一个用于左山,一个用于右侧山,一个用于河流,一个用于带有耀斑的太阳。
为左山创建路径几何图形
该示例首先为左山创建路径几何图形,如下图所示。
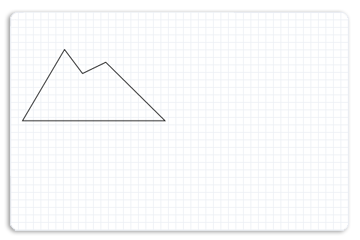
为了创建左山,此示例调用 ID2D1Factory::CreatePathGeometry 方法来创建 ID2D1PathGeometry。
hr = m_pD2DFactory->CreatePathGeometry(&m_pLeftMountainGeometry);
然后,该示例使用 Open 方法从 ID2D1PathGeometry 获取几何接收器,并将其存储在 pSink 变量中。
ID2D1GeometrySink *pSink = NULL;
hr = m_pLeftMountainGeometry->Open(&pSink);
然后,该示例调用 BeginFigure,传入指示此图已填充 D2D1_FIGURE_BEGIN_FILLED , 然后调用 AddLines,传入 D2D1_POINT_2F 点数组, (267、177) 、 (236、192) 、 (212、160) 、 (156、255) 和 (346、255) 。
下面的代码演示如何执行此操作。
pSink->SetFillMode(D2D1_FILL_MODE_WINDING);
pSink->BeginFigure(
D2D1::Point2F(346,255),
D2D1_FIGURE_BEGIN_FILLED
);
D2D1_POINT_2F points[5] = {
D2D1::Point2F(267, 177),
D2D1::Point2F(236, 192),
D2D1::Point2F(212, 160),
D2D1::Point2F(156, 255),
D2D1::Point2F(346, 255),
};
pSink->AddLines(points, ARRAYSIZE(points));
pSink->EndFigure(D2D1_FIGURE_END_CLOSED);
为右山创建路径几何图形
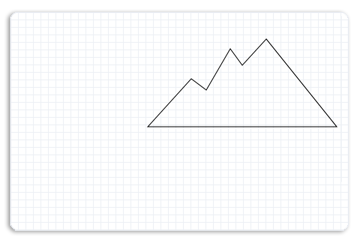
然后,该示例为右山创建另一个路径几何图形,其点 (481,146) , (449、181) 、 (433、159) 、 (401、214) 、 (381、199) 、 (323、263) 和 (575、263) 。 下图显示了右侧山的显示方式。
下面的代码演示如何执行此操作。
hr = m_pD2DFactory->CreatePathGeometry(&m_pRightMountainGeometry);
if(SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
ID2D1GeometrySink *pSink = NULL;
hr = m_pRightMountainGeometry->Open(&pSink);
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
pSink->SetFillMode(D2D1_FILL_MODE_WINDING);
pSink->BeginFigure(
D2D1::Point2F(575,263),
D2D1_FIGURE_BEGIN_FILLED
);
D2D1_POINT_2F points[] = {
D2D1::Point2F(481, 146),
D2D1::Point2F(449, 181),
D2D1::Point2F(433, 159),
D2D1::Point2F(401, 214),
D2D1::Point2F(381, 199),
D2D1::Point2F(323, 263),
D2D1::Point2F(575, 263)
};
pSink->AddLines(points, ARRAYSIZE(points));
pSink->EndFigure(D2D1_FIGURE_END_CLOSED);
}
hr = pSink->Close();
SafeRelease(&pSink);
}
为太阳创建路径几何图形
然后,该示例为太阳填充另一个路径几何图形,如下图所示。
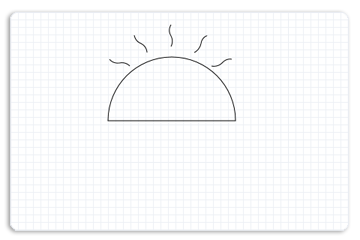
为此,路径几何图形将创建一个接收器,并将弧形图和每个耀斑的图形添加到接收器。 通过重复 BeginFigure 的序列、其 Add ((如 AddBezier) 方法)和 EndFigure,将多个图形添加到接收器。
下面的代码演示如何执行此操作。
hr = m_pD2DFactory->CreatePathGeometry(&m_pSunGeometry);
if(SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
ID2D1GeometrySink *pSink = NULL;
hr = m_pSunGeometry->Open(&pSink);
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
pSink->SetFillMode(D2D1_FILL_MODE_WINDING);
pSink->BeginFigure(
D2D1::Point2F(270, 255),
D2D1_FIGURE_BEGIN_FILLED
);
pSink->AddArc(
D2D1::ArcSegment(
D2D1::Point2F(440, 255), // end point
D2D1::SizeF(85, 85),
0.0f, // rotation angle
D2D1_SWEEP_DIRECTION_CLOCKWISE,
D2D1_ARC_SIZE_SMALL
));
pSink->EndFigure(D2D1_FIGURE_END_CLOSED);
pSink->BeginFigure(
D2D1::Point2F(299, 182),
D2D1_FIGURE_BEGIN_HOLLOW
);
pSink->AddBezier(
D2D1::BezierSegment(
D2D1::Point2F(299, 182),
D2D1::Point2F(294, 176),
D2D1::Point2F(285, 178)
));
pSink->AddBezier(
D2D1::BezierSegment(
D2D1::Point2F(276, 179),
D2D1::Point2F(272, 173),
D2D1::Point2F(272, 173)
));
pSink->EndFigure(D2D1_FIGURE_END_OPEN);
pSink->BeginFigure(
D2D1::Point2F(354, 156),
D2D1_FIGURE_BEGIN_HOLLOW
);
pSink->AddBezier(
D2D1::BezierSegment(
D2D1::Point2F(354, 156),
D2D1::Point2F(358, 149),
D2D1::Point2F(354, 142)
));
pSink->AddBezier(
D2D1::BezierSegment(
D2D1::Point2F(349, 134),
D2D1::Point2F(354, 127),
D2D1::Point2F(354, 127)
));
pSink->EndFigure(D2D1_FIGURE_END_OPEN);
pSink->BeginFigure(
D2D1::Point2F(322,164),
D2D1_FIGURE_BEGIN_HOLLOW
);
pSink->AddBezier(
D2D1::BezierSegment(
D2D1::Point2F(322, 164),
D2D1::Point2F(322, 156),
D2D1::Point2F(314, 152)
));
pSink->AddBezier(
D2D1::BezierSegment(
D2D1::Point2F(306, 149),
D2D1::Point2F(305, 141),
D2D1::Point2F(305, 141)
));
pSink->EndFigure(D2D1_FIGURE_END_OPEN);
pSink->BeginFigure(
D2D1::Point2F(385, 164),
D2D1_FIGURE_BEGIN_HOLLOW
);
pSink->AddBezier(
D2D1::BezierSegment(
D2D1::Point2F(385,164),
D2D1::Point2F(392,161),
D2D1::Point2F(394,152)
));
pSink->AddBezier(
D2D1::BezierSegment(
D2D1::Point2F(395,144),
D2D1::Point2F(402,141),
D2D1::Point2F(402,142)
));
pSink->EndFigure(D2D1_FIGURE_END_OPEN);
pSink->BeginFigure(
D2D1::Point2F(408,182),
D2D1_FIGURE_BEGIN_HOLLOW
);
pSink->AddBezier(
D2D1::BezierSegment(
D2D1::Point2F(408,182),
D2D1::Point2F(416,184),
D2D1::Point2F(422,178)
));
pSink->AddBezier(
D2D1::BezierSegment(
D2D1::Point2F(428,171),
D2D1::Point2F(435,173),
D2D1::Point2F(435,173)
));
pSink->EndFigure(D2D1_FIGURE_END_OPEN);
}
hr = pSink->Close();
SafeRelease(&pSink);
}
为河流创建路径几何图形
然后,该示例为包含贝塞尔曲线的河流创建另一条几何路径。 下图显示了河流的显示方式。

下面的代码演示如何执行此操作。
hr = m_pD2DFactory->CreatePathGeometry(&m_pRiverGeometry);
if(SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
ID2D1GeometrySink *pSink = NULL;
hr = m_pRiverGeometry->Open(&pSink);
if (SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
pSink->SetFillMode(D2D1_FILL_MODE_WINDING);
pSink->BeginFigure(
D2D1::Point2F(183, 392),
D2D1_FIGURE_BEGIN_FILLED
);
pSink->AddBezier(
D2D1::BezierSegment(
D2D1::Point2F(238, 284),
D2D1::Point2F(472, 345),
D2D1::Point2F(356, 303)
));
pSink->AddBezier(
D2D1::BezierSegment(
D2D1::Point2F(237, 261),
D2D1::Point2F(333, 256),
D2D1::Point2F(333, 256)
));
pSink->AddBezier(
D2D1::BezierSegment(
D2D1::Point2F(335, 257),
D2D1::Point2F(241, 261),
D2D1::Point2F(411, 306)
));
pSink->AddBezier(
D2D1::BezierSegment(
D2D1::Point2F(574, 350),
D2D1::Point2F(288, 324),
D2D1::Point2F(296, 392)
));
pSink->EndFigure(D2D1_FIGURE_END_OPEN);
}
将路径几何图形呈现到显示器上
以下代码演示如何在显示器上呈现填充的路径几何图形。 它首先绘制和绘制太阳几何图形,然后绘制左山几何图形,然后绘制河流几何图形,最后绘制右山几何图形。
m_pRenderTarget->BeginDraw();
m_pRenderTarget->SetTransform(D2D1::Matrix3x2F::Identity());
m_pRenderTarget->Clear(D2D1::ColorF(D2D1::ColorF::White));
D2D1_SIZE_F rtSize = m_pRenderTarget->GetSize();
m_pRenderTarget->FillRectangle(
D2D1::RectF(0, 0, rtSize.width, rtSize.height),
m_pGridPatternBitmapBrush
);
m_pRenderTarget->FillGeometry(m_pSunGeometry, m_pRadialGradientBrush);
m_pSceneBrush->SetColor(D2D1::ColorF(D2D1::ColorF::Black, 1.f));
m_pRenderTarget->DrawGeometry(m_pSunGeometry, m_pSceneBrush, 1.f);
m_pSceneBrush->SetColor(D2D1::ColorF(D2D1::ColorF::OliveDrab, 1.f));
m_pRenderTarget->FillGeometry(m_pLeftMountainGeometry, m_pSceneBrush);
m_pSceneBrush->SetColor(D2D1::ColorF(D2D1::ColorF::Black, 1.f));
m_pRenderTarget->DrawGeometry(m_pLeftMountainGeometry, m_pSceneBrush, 1.f);
m_pSceneBrush->SetColor(D2D1::ColorF(D2D1::ColorF::LightSkyBlue, 1.f));
m_pRenderTarget->FillGeometry(m_pRiverGeometry, m_pSceneBrush);
m_pSceneBrush->SetColor(D2D1::ColorF(D2D1::ColorF::Black, 1.f));
m_pRenderTarget->DrawGeometry(m_pRiverGeometry, m_pSceneBrush, 1.f);
m_pSceneBrush->SetColor(D2D1::ColorF(D2D1::ColorF::YellowGreen, 1.f));
m_pRenderTarget->FillGeometry(m_pRightMountainGeometry, m_pSceneBrush);
m_pSceneBrush->SetColor(D2D1::ColorF(D2D1::ColorF::Black, 1.f));
m_pRenderTarget->DrawGeometry(m_pRightMountainGeometry, m_pSceneBrush, 1.f);
hr = m_pRenderTarget->EndDraw();
完整示例输出下图。

相关主题