本机引擎中的扩展眼动跟踪
扩展眼动跟踪是 HoloLens 2 中的一项新功能。 它是标准眼动跟踪的超集,后者仅提供双眼凝视数据。 扩展眼动跟踪还提供单眼凝视数据,并允许应用程序为凝视数据设置不同的帧速率,例如 30、60 和 90fps。 HoloLens 2 目前不支持其他特征,如睁眼和异向眼动。
扩展眼动跟踪 SDK 使应用程序能够访问扩展眼动跟踪的数据和特征。 它可以与 WinRT API 或 OpenXR API 一起使用。
本文介绍了如何在本机引擎(C# 或 C++/WinRT)中使用扩展眼动跟踪 SDK 以及 WinRT API。
项目设置
- 使用 Visual Studio 2019 或更高版本创建
Holographic DirectX 11 App (Universal Windows)或Holographic DirectX 11 App (Universal Windows) (C++/WinRT)项目,或者打开现有的全息 Visual Studio 项目。 - 将扩展眼动跟踪 SDK 导入项目。
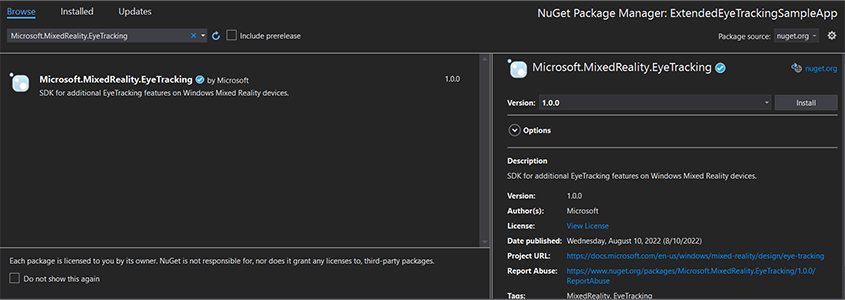
- 在 Visual Studio 解决方案资源管理器中,右键单击你的项目 ->“管理 NuGet 包...”
- 确保右上角的包源指向 nuget.org:https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json
- 单击“浏览器”选项卡,然后搜索
Microsoft.MixedReality.EyeTracking。 - 单击“安装”按钮以安装最新版本的 SDK。
- 设置“凝视输入”功能
- 在解决方案资源管理器中双击 Package.appxmanifest 文件。
- 单击“功能”选项卡,然后检查凝视输入。
- 包括头文件并使用命名空间。
- 对于 C# 项目:
using Microsoft.MixedReality.EyeTracking;- 对于 C++/WinRT 项目:
#include <winrt/Microsoft.MixedReality.EyeTracking.h> using namespace winrt::Microsoft::MixedReality::EyeTracking; - 使用扩展眼动跟踪 SDK API 并实现逻辑。
- 生成并部署到 HoloLens。
获取凝视数据的步骤概述
通过扩展眼动跟踪 SDK API 获取眼睛凝视数据时,需要执行以下步骤:
- 征得用户同意,以获取对眼动跟踪特征的访问权限。
- 注意眼睛凝视追踪仪的连接和断开连接。
- 打开眼睛凝视追踪仪,然后查询其功能。
- 反复从眼睛凝视追踪仪读取凝视数据。
- 将凝视数据传输到其他 SpatialCoordinateSystems。
获取对眼动跟踪特征的访问权限
若要使用任何与眼睛相关的信息,应用程序必须首先请求用户同意。
var status = await Windows.Perception.People.EyesPose.RequestAccessAsync();
bool useGaze = (status == Windows.UI.Input.GazeInputAccessStatus.Allowed);
auto accessStatus = co_await winrt::Windows::Perception::People::EyesPose::RequestAccessAsync();
bool useGaze = (accessStatus.get() == winrt::Windows::UI::Input::GazeInputAccessStatus::Allowed);
检测眼睛凝视追踪仪
眼睛凝视追踪仪检测是通过 EyeGazeTrackerWatcher 类进行的。 检测到眼睛凝视追踪仪或其断开连接时,将分别引发 EyeGazeTrackerAdded 和 EyeGazeTrackerRemoved 事件。
观察程序必须使用 StartAsync() 方法显式启动,这将在已连接的追踪仪通过 EyeGazeTrackerAdded 事件收到信号时异步完成。
当检测到眼睛凝视追踪仪时,会将一个 EyeGazeTracker 实例传递给应用程序中的 EyeGazeTrackerAdded 事件参数;反之,当追踪仪断开连接时,会将相应的 EyeGazeTracker 实例传递给 EyeGazeTrackerRemoved 事件。
EyeGazeTrackerWatcher watcher = new EyeGazeTrackerWatcher();
watcher.EyeGazeTrackerAdded += _watcher_EyeGazeTrackerAdded;
watcher.EyeGazeTrackerRemoved += _watcher_EyeGazeTrackerRemoved;
await watcher.StartAsync();
...
private async void _watcher_EyeGazeTrackerAdded(object sender, EyeGazeTracker e)
{
// Implementation is in next section
}
private void _watcher_EyeGazeTrackerRemoved(object sender, EyeGazeTracker e)
{
...
}
EyeGazeTrackerWatcher watcher;
watcher.EyeGazeTrackerAdded(std::bind(&SampleEyeTrackingNugetClientAppMain::OnEyeGazeTrackerAdded, this, _1, _2));
watcher.EyeGazeTrackerRemoved(std::bind(&SampleEyeTrackingNugetClientAppMain::OnEyeGazeTrackerRemoved, this, _1, _2));
co_await watcher.StartAsync();
...
winrt::Windows::Foundation::IAsyncAction SampleAppMain::OnEyeGazeTrackerAdded(const EyeGazeTrackerWatcher& sender, const EyeGazeTracker& tracker)
{
// Implementation is in next section
}
void SampleAppMain::OnEyeGazeTrackerRemoved(const EyeGazeTrackerWatcher& sender, const EyeGazeTracker& tracker)
{
...
}
打开眼睛凝视追踪仪
接收 EyeGazeTracker 实例时,应用程序必须首先通过调用 OpenAsync() 方法将其打开。 然后,它可以根据需要查询追踪仪功能。 OpenAsync() 方法采用布尔参数;这指示应用程序是否需要访问不属于标准眼动跟踪的特征,例如单眼凝视矢量或更改追踪仪的帧速率。
双眼凝视是所有眼睛凝视追踪仪都必须支持的特征。 其他特征(如对单眼凝视的访问权限)是可选的,可能受支持也可能不受支持,具体取决于追踪仪及其驱动程序。 对于这些可选特征,EyeGazeTracker 类会公开一个属性来指示相应特征是否受支持,例如 AreLeftAndRightGazesSupported 属性,该属性指示设备是否支持单眼凝视信息。
眼睛凝视追踪仪公开的所有空间信息都与追踪仪本身相关,追踪仪本身由“动态节点 ID”进行标识。 使用节点 ID 通过 WinRT API 获取 SpatialCoordinateSystem 时,可以将凝视数据的坐标转换为另一个坐标系统。
private async void _watcher_EyeGazeTrackerAdded(object sender, EyeGazeTracker e)
{
try
{
// Try to open the tracker with access to restricted features
await e.OpenAsync(true);
// If it has succeeded, store it for future use
_tracker = e;
// Check support for individual eye gaze
bool supportsIndividualEyeGaze = _tracker.AreLeftAndRightGazesSupported;
// Get a spatial locator for the tracker, this will be used to transfer the gaze data to other coordinate systems later
var trackerNodeId = e.TrackerSpaceLocatorNodeId;
_trackerLocator = Windows.Perception.Spatial.Preview.SpatialGraphInteropPreview.CreateLocatorForNode(trackerNodeId);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Unable to open the tracker
}
}
winrt::Windows::Foundation::IAsyncAction SampleEyeTrackingNugetClientAppMain::OnEyeGazeTrackerAdded(const EyeGazeTrackerWatcher&, const EyeGazeTracker& tracker)
{
auto newTracker = tracker;
try
{
// Try to open the tracker with access to restricted features
co_await newTracker.OpenAsync(true);
// If it has succeeded, store it for future use
m_gazeTracker = newTracker;
// Check support for individual eye gaze
const bool supportsIndividualEyeGaze = m_gazeTracker.AreLeftAndRightGazesSupported();
// Get a spatial locator for the tracker. This will be used to transfer the gaze data to other coordinate systems later
const auto trackerNodeId = m_gazeTracker.TrackerSpaceLocatorNodeId();
m_trackerLocator = winrt::Windows::Perception::Spatial::Preview::SpatialGraphInteropPreview::CreateLocatorForNode(trackerNodeId);
}
catch (const winrt::hresult_error& e)
{
// Unable to open the tracker
}
}
设置眼睛凝视追踪仪的帧速率
EyeGazeTracker.SupportedTargetFrameRates 属性将返回追踪仪支持的目标帧速率列表。 HoloLens 2 支持 30、60 和 90fps。
请使用 EyeGazeTracker.SetTargetFrameRate() 方法设置目标帧速率。
// This returns a list of supported frame rate: 30, 60, 90 fps in order
var supportedFrameRates = _tracker.SupportedTargetFrameRates;
// Sets the tracker at the highest supported frame rate (90 fps)
var newFrameRate = supportedFrameRates[supportedFrameRates.Count - 1];
_tracker.SetTargetFrameRate(newFrameRate);
uint newFramesPerSecond = newFrameRate.FramesPerSecond;
// This returns a list of supported frame rate: 30, 60, 90 fps in order
const auto supportedFrameRates = m_gazeTracker.SupportedTargetFrameRates();
// Sets the tracker at the highest supported frame rate (90 fps)
const auto newFrameRate = supportedFrameRates.GetAt(supportedFrameRates.Size() - 1);
m_gazeTracker.SetTargetFrameRate(newFrameRate);
const uint32_t newFramesPerSecond = newFrameRate.FramesPerSecond();
从眼睛凝视追踪仪读取凝视数据
眼睛凝视追踪仪会定期在循环缓冲区中发布其状态。 这使应用程序能够以较小的时间跨度读取追踪仪的状态。 例如,它允许检索追踪仪的最新状态,或在某个事件(例如用户手势)时的状态。
将追踪仪状态作为 EyeGazeTrackerReading 实例进行检索的方法:
TryGetReadingAtTimestamp()和TryGetReadingAtSystemRelativeTime()方法将返回离应用程序所传递时间最近的EyeGazeTrackerReading。 追踪仪会控制发布时间表,因此返回的读数可能略早于或晚于请求时间。EyeGazeTrackerReading.Timestamp和EyeGazeTrackerReading.SystemRelativeTime属性使应用程序能够知道相应已发布状态的确切时间。TryGetReadingAfterTimestamp()和TryGetReadingAfterSystemRelativeTime()方法将返回时间戳严格高于作为参数传递的时间的第一个EyeGazeTrackerReading。 这使应用程序能够按顺序读取追踪仪发布的所有状态。 请注意,所有这些方法都将查询现有缓冲区,并立即返回。 如果没有可用状态,它们将返回 null(换句话说,它们不会让应用程序等待状态发布)。
除了时间戳,EyeGazeTrackerReading 实例还具有 IsCalibrationValid 属性,该属性指示眼动追踪仪校准是否有效。
最后,可以通过一组方法(如 TryGetCombinedEyeGazeInTrackerSpace() 或 TryGetLeftEyeGazeInTrackerSpace())检索凝视数据。 所有这些方法都会返回一个表示成功情况的布尔值。 未能获取某些数据可能意味着数据不受支持(EyeGazeTracker 具有检测此情况的属性),或者追踪仪无法获取数据(例如,校准无效或眼睛被挡住)。
例如,如果应用程序想要显示与双眼凝视对应的游标,则可以使用正准备的帧的时间戳查询追踪仪,如下所示。
var holographicFrame = holographicSpace.CreateNextFrame();
var prediction = holographicFrame.CurrentPrediction;
var predictionTimestamp = prediction.Timestamp;
var reading = _tracker.TryGetReadingAtTimestamp(predictionTimestamp.TargetTime.DateTime);
if (reading != null)
{
// Vector3 needs the System.Numerics namespace
if (reading.TryGetCombinedEyeGazeInTrackerSpace(out Vector3 gazeOrigin, out Vector3 gazeDirection))
{
// Use gazeOrigin and gazeDirection to display the cursor
}
}
auto holographicFrame = m_holographicSpace.CreateNextFrame();
auto prediction = holographicFrame.CurrentPrediction();
auto predictionTimestamp = prediction.Timestamp();
const auto reading = m_gazeTracker.TryGetReadingAtTimestamp(predictionTimestamp.TargetTime());
if (reading)
{
float3 gazeOrigin;
float3 gazeDirection;
if (reading.TryGetCombinedEyeGazeInTrackerSpace(gazeOrigin, gazeDirection))
{
// Use gazeOrigin and gazeDirection to display the cursor
}
}
将凝视数据转换为其他 SpatialCoordinateSystem
返回空间数据(如位置)的 WinRT API 始终需要 PerceptionTimestamp 和 SpatialCoordinateSystem。 例如,若要使用 WinRT API 检索 HoloLens 2 的双眼凝视,API SpatialPointerPose.TryGetAtTimestamp() 需要两个参数:SpatialCoordinateSystem 和 PerceptionTimestamp。 然后,当通过 SpatialPointerPose.Eyes.Gaze 访问双眼凝视时,其原点和方向以传入的 SpatialCoordinateSystem 表示。
扩展眼动跟踪 SDK API 无需采用 SpatialCoordinateSystem,凝视数据始终在追踪仪的坐标系统中表示。 但是,你可以将这些凝视数据转换为另一个坐标系统,从而使追踪仪的姿势与其他坐标系统相关的。
如上面名为“打开眼睛凝视追踪仪”的部分所述,若要获取眼睛凝视追踪仪的
SpatialLocator,请使用EyeGazeTracker.TrackerSpaceLocatorNodeId属性调用Windows.Perception.Spatial.Preview.SpatialGraphInteropPreview.CreateLocatorForNode()。通过
EyeGazeTrackerReading检索的凝视原点和方向与眼睛凝视追踪仪相关。SpatialLocator.TryLocateAtTimestamp()将在给定PerceptionTimeStamp返回眼睛凝视追踪仪的完整 6DoF 位置,该位置与给定SpatialCoordinateSystem相关,可用于构造 Matrix4x4 转换矩阵。使用构造的 Matrix4x4 转换矩阵将凝视原点和方向转换到其他 SpatialCoordinateSystem。
以下代码示例显示了如何计算位于双眼凝视方向上、凝视原点前两米处的立方体的位置:
var predictionTimestamp = prediction.Timestamp;
var stationaryCS = stationaryReferenceFrame.CoordinateSystem;
var trackerLocation = _trackerLocator.TryLocateAtTimestamp(predictionTimestamp, stationaryCS);
if (trackerLocation != null)
{
var trackerToStationaryMatrix = Matrix4x4.CreateFromQuaternion(trackerLocation.Orientation) * Matrix4x4.CreateTranslation(trackerLocation.Position);
var reading = _tracker.TryGetReadingAtTimestamp(predictionTimestamp.TargetTime.DateTime);
if (reading != null)
{
if (reading.TryGetCombinedEyeGazeInTrackerSpace(out Vector3 gazeOriginInTrackerSpace, out Vector3 gazeDirectionInTrackerSpace))
{
var cubePositionInTrackerSpace = gazeOriginInTrackerSpace + 2.0f * gazeDirectionInTrackerSpace;
var cubePositionInStationaryCS = Vector3.Transform(cubePositionInTrackerSpace, trackerToStationaryMatrix);
}
}
}
auto predictionTimestamp = prediction.Timestamp();
auto stationaryCS = m_stationaryReferenceFrame.CoordinateSystem();
auto trackerLocation = m_trackerLocator.TryLocateAtTimestamp(predictionTimestamp, stationaryCS);
if (trackerLocation)
{
auto trackerOrientation = trackerLocation.Orientation();
auto trackerPosition = trackerLocation.Position();
auto trackerToStationaryMatrix = DirectX::XMMatrixRotationQuaternion(DirectX::XMLoadFloat4(reinterpret_cast<const DirectX::XMFLOAT4*>(&trackerOrientation))) * DirectX::XMMatrixTranslationFromVector(DirectX::XMLoadFloat3(&trackerPosition));
const auto reading = m_gazeTracker.TryGetReadingAtTimestamp(predictionTimestamp.TargetTime());
if (reading)
{
float3 gazeOriginInTrackerSpace;
float3 gazeDirectionInTrackerSpace;
if (reading.TryGetCombinedEyeGazeInTrackerSpace(gazeOriginInTrackerSpace, gazeDirectionInTrackerSpace))
{
auto cubePositionInTrackerSpace = gazeOriginInTrackerSpace + 2.0f * gazeDirectionInTrackerSpace;
float3 cubePositionInStationaryCS;
DirectX::XMStoreFloat3(&cubePositionInStationaryCS, DirectX::XMVector3TransformCoord(DirectX::XMLoadFloat3(&cubePositionInTrackerSpace), trackerToStationaryMatrix));
}
}
}
扩展眼动跟踪 SDK 的 API 参考
namespace Microsoft.MixedReality.EyeTracking
{
/// <summary>
/// Allow discovery of Eye Gaze Trackers connected to the system
/// This is the only class from Extended Eye Tracking SDK that the application will instantiate,
/// other classes' instances will be returned by method calls or properties.
/// </summary>
public class EyeGazeTrackerWatcher
{
/// <summary>
/// Constructs an instance of the watcher
/// </summary>
public EyeGazeTrackerWatcher();
/// <summary>
/// Starts trackers enumeration.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Task representing async action; completes when the initial enumeration is completed</returns>
public System.Threading.Tasks.Task StartAsync();
/// <summary>
/// Stop listening to trackers additions and removal
/// </summary>
public void Stop();
/// <summary>
/// Raised when an Eye Gaze tracker is connected
/// </summary>
public event System.EventHandler<EyeGazeTracker> EyeGazeTrackerAdded;
/// <summary>
/// Raised when an Eye Gaze tracker is disconnected
/// </summary>
public event System.EventHandler<EyeGazeTracker> EyeGazeTrackerRemoved;
}
/// <summary>
/// Represents an Eye Tracker device
/// </summary>
public class EyeGazeTracker
{
/// <summary>
/// True if Restricted mode is supported, which means the driver supports to provide individual
/// eye gaze vector and framerate
/// </summary>
public bool IsRestrictedModeSupported;
/// <summary>
/// True if Vergence Distance is supported by tracker
/// </summary>
public bool IsVergenceDistanceSupported;
/// <summary>
/// True if Eye Openness is supported by the driver
/// </summary>
public bool IsEyeOpennessSupported;
/// <summary>
/// True if individual gazes are supported
/// </summary>
public bool AreLeftAndRightGazesSupported;
/// <summary>
/// Get the supported target frame rates of the tracker
/// </summary>
public System.Collections.Generic.IReadOnlyList<EyeGazeTrackerFrameRate> SupportedTargetFrameRates;
/// <summary>
/// NodeId of the tracker, used to retrieve a SpatialLocator or SpatialGraphNode to locate the tracker in the scene
/// for Perception API, use SpatialGraphInteropPreview.CreateLocatorForNode
/// for Mixed Reality OpenXR API, use SpatialGraphNode.FromDynamicNodeId
/// </summary>
public Guid TrackerSpaceLocatorNodeId;
/// <summary>
/// Opens the tracker
/// </summary>
/// <param name="restrictedMode">True if restricted mode active</param>
/// <returns>Task representing async action; completes when the initial enumeration is completed</returns>
public System.Threading.Tasks.Task OpenAsync(bool restrictedMode);
/// <summary>
/// Closes the tracker
/// </summary>
public void Close();
/// <summary>
/// Changes the target frame rate of the tracker
/// </summary>
/// <param name="newFrameRate">Target frame rate</param>
public void SetTargetFrameRate(EyeGazeTrackerFrameRate newFrameRate);
/// <summary>
/// Try to get tracker state at a given timestamp
/// </summary>
/// <param name="timestamp">timestamp</param>
/// <returns>State if available, null otherwise</returns>
public EyeGazeTrackerReading TryGetReadingAtTimestamp(DateTime timestamp);
/// <summary>
/// Try to get tracker state at a system relative time
/// </summary>
/// <param name="time">time</param>
/// <returns>State if available, null otherwise</returns>
public EyeGazeTrackerReading TryGetReadingAtSystemRelativeTime(TimeSpan time);
/// <summary>
/// Try to get first first tracker state after a given timestamp
/// </summary>
/// <param name="timestamp">timestamp</param>
/// <returns>State if available, null otherwise</returns>
public EyeGazeTrackerReading TryGetReadingAfterTimestamp(DateTime timestamp);
/// <summary>
/// Try to get the first tracker state after a system relative time
/// </summary>
/// <param name="time">time</param>
/// <returns>State if available, null otherwise</returns>
public EyeGazeTrackerReading TryGetReadingAfterSystemRelativeTime(TimeSpan time);
}
/// <summary>
/// Represents a Frame Rate supported by an Eye Tracker
/// </summary>
public class EyeGazeTrackerFrameRate
{
/// <summary>
/// Frames per second of the frame rate
/// </summary>
public UInt32 FramesPerSecond;
}
/// <summary>
/// Snapshot of Gaze Tracker state
/// </summary>
public class EyeGazeTrackerReading
{
/// <summary>
/// Timestamp of state
/// </summary>
public DateTime Timestamp;
/// <summary>
/// Timestamp of state as system relative time
/// Its SystemRelativeTime.Ticks could provide the QPC time to locate tracker pose
/// </summary>
public TimeSpan SystemRelativeTime;
/// <summary>
/// Indicates user calibration is valid
/// </summary>
public bool IsCalibrationValid;
/// <summary>
/// Tries to get a vector representing the combined gaze related to the tracker's node
/// </summary>
/// <param name="origin">Origin of the gaze vector</param>
/// <param name="direction">Direction of the gaze vector</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool TryGetCombinedEyeGazeInTrackerSpace(out System.Numerics.Vector3 origin, out System.Numerics.Vector3 direction);
/// <summary>
/// Tries to get a vector representing the left eye gaze related to the tracker's node
/// </summary>
/// <param name="origin">Origin of the gaze vector</param>
/// <param name="direction">Direction of the gaze vector</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool TryGetLeftEyeGazeInTrackerSpace(out System.Numerics.Vector3 origin, out System.Numerics.Vector3 direction);
/// <summary>
/// Tries to get a vector representing the right eye gaze related to the tracker's node position
/// </summary>
/// <param name="origin">Origin of the gaze vector</param>
/// <param name="direction">Direction of the gaze vector</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool TryGetRightEyeGazeInTrackerSpace(out System.Numerics.Vector3 origin, out System.Numerics.Vector3 direction);
/// <summary>
/// Tries to read vergence distance
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value">Vergence distance if available</param>
/// <returns>bool if value is valid</returns>
public bool TryGetVergenceDistance(out float value);
/// <summary>
/// Tries to get left Eye openness information
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value">Eye Openness if valid</param>
/// <returns>bool if value is valid</returns>
public bool TryGetLeftEyeOpenness(out float value);
/// <summary>
/// Tries to get right Eye openness information
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value">Eye Openness if valid</param>
/// <returns>bool if value is valid</returns>
public bool TryGetRightEyeOpenness(out float value);
}
}