使用 StandardUICommand、XamlUICommand 和 ICommand 在 Windows 应用中进行命令控制
本主题介绍 Windows 应用程序中的命令控制。 具体说来,我们讨论如何使用 XamlUICommand 和 StandardUICommand 类(以及 ICommand 接口)在不同的控件类型之间共享和管理命令,不管所用的设备和输入类型是什么。
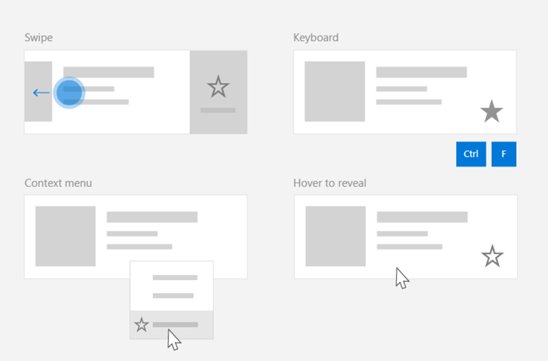
在不同的控件之间共享命令,不管设备和输入类型是什么
重要的 API
概述
命令可以直接通过 UI 交互(例如,在上下文菜单中单击某个按钮或选择某个项)进行调用。 命令还可以通过输入设备(例如键盘快捷方式、手势、语音识别或自动化/辅助功能工具)间接进行调用。 进行调用以后,该命令随后即可由控件处理(在编辑控件中进行文本导航)、由窗口处理(后退导航)或由应用程序处理(退出)。
命令可以在应用的特定上下文中操作(例如,删除文本或撤消某个操作),也可在无上下文的情况下操作(例如,将音频静音或调整亮度)。
下图显示两个共享某些相同命令的命令界面(一个 CommandBar 和一个浮出式上下文 CommandBarFlyout)。
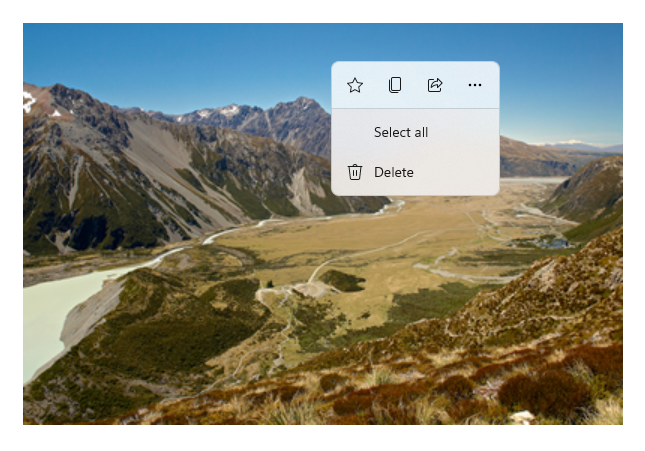
命令栏
Microsoft 照片库中的上下文菜单
命令交互
考虑到可能影响命令调用方式的设备、输入类型和 UI 设计面的多样性,建议通过尽可能多的命令控制图面来公开命令。 可以组合使用轻扫、MenuBar、CommandBar、CommandBarFlyout 和传统上下文菜单。
对于关键命令,请使用特定于输入的快捷方式。 输入快捷方式可以加快用户的操作执行速度,具体取决于所使用的输入设备。
下面是一些常用于不同输入类型的输入快捷方式:
- 指针 - 鼠标和手写笔悬停按钮
- 键盘 - 快捷方式(访问键和快捷键)
- 触控 - 轻扫
- 触控 - 通过下拉操作刷新数据
必须考虑输入类型和用户体验,使应用程序的功能可以使用通用方式进行访问。 例如,集合(尤其是可供用户编辑的集合)通常包含各种特定的命令,这些命令因输入设备的不同在执行时有很大的差异。
下表显示了一些典型集合命令以及用于公开这些命令的方式。
| 命令 | 与输入无关 | 鼠标快捷方式 | 键盘快捷方式 | 触控快捷方式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 删除物品 | 上下文菜单 | 悬停按钮 | DEL 键 | 轻扫删除 |
| 标记项 | 上下文菜单 | 悬停按钮 | Ctrl+Shift+G | 轻扫标记 |
| 刷新数据 | 上下文菜单 | 不可用 | F5 键 | 下拉刷新 |
| 收藏项 | 上下文菜单 | 悬停按钮 | F、Ctrl+S | 轻扫收藏 |
始终提供上下文菜单:建议在传统上下文菜单或 CommandBarFlyout 中包括所有相关的上下文命令,因为所有输入类型都支持这二者。 例如,如果某个命令仅在出现指针悬停事件时公开,则该命令不能用在仅支持触控的设备上。
Windows 应用程序中的命令
可以通过多种方式在 Windows 应用程序中共享和管理命令控制体验。 可以在代码隐藏中为标准交互(例如 Click)定义事件处理程序(这可能相当低效,具体取决于 UI 的复杂程度),可以将标准交互的事件侦听器绑定到共享处理程序,还可以将控件的 Command 属性绑定到某个用于描述命令逻辑的 ICommand 实现。
为了跨命令图面高效地提供丰富且广泛的用户体验并尽量减少重复代码,建议使用本主题中介绍的命令绑定功能(要进行标准事件处理,请参阅各个事件主题)。
要将控件绑定到共享命令资源,可以自行实现 ICommand 接口,也可以通过 XamlUICommand 基类或者通过 StandardUICommand 派生类定义的某个平台命令来构建命令。
- 可以使用 ICommand 接口(Windows.UI.Xaml.Input.ICommand 或 System.Windows.Input.ICommand)在应用中创建完全自定义的可重用命令。
- XamlUICommand 也提供此功能,但可以简化开发过程,因为它会公开一组内置的命令属性,例如命令行为、键盘快捷方式(访问键和快捷键)、图标、标签和说明。
- StandardUICommand 允许你从一组具有预定义属性的标准平台命令中进行选择,进一步进行了简化。
重要
在 UWP 应用程序中,命令是 Windows.UI.Xaml.Input.ICommand (C++) 或 System.Windows.Input.ICommand (C#) 接口的实现,具体取决于所选语言框架。
使用 StandardUICommand 类的命令体验
派生自 XamlUICommand(派生自适用于 C++ 的 Windows.UI.Xaml.Input.ICommand 或适用于 C# 的 System.Windows.Input.ICommand),StandardUICommand 类会公开一组带预定义属性(例如图标、键盘快捷方式、说明)的标准平台命令。
可以使用 StandardUICommand 通过快速且一致的方式定义常见命令,例如 Save 或 Delete。 只需提供 execute 和 canExecute 函数即可。
示例
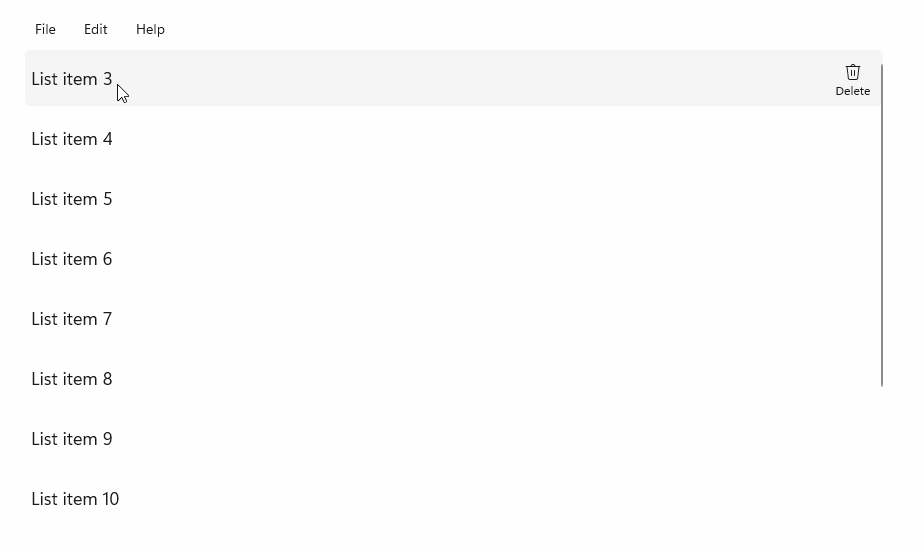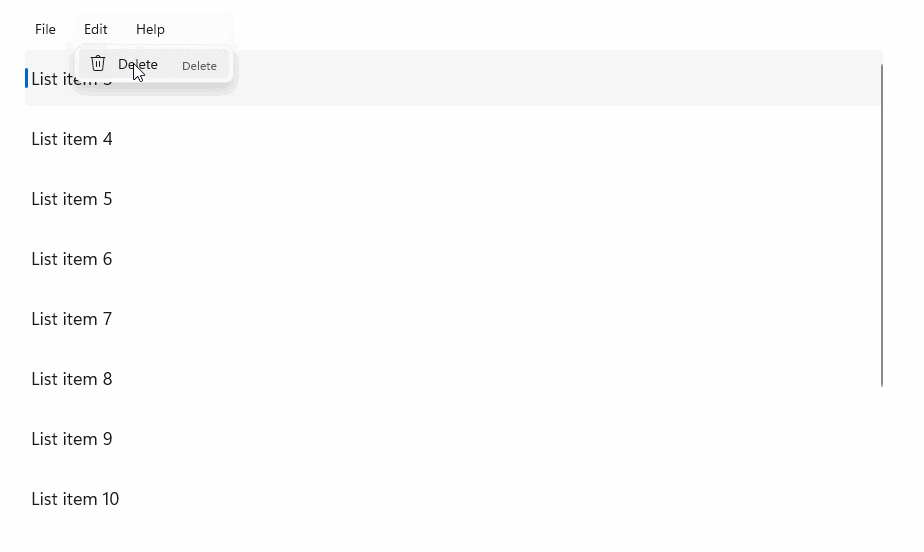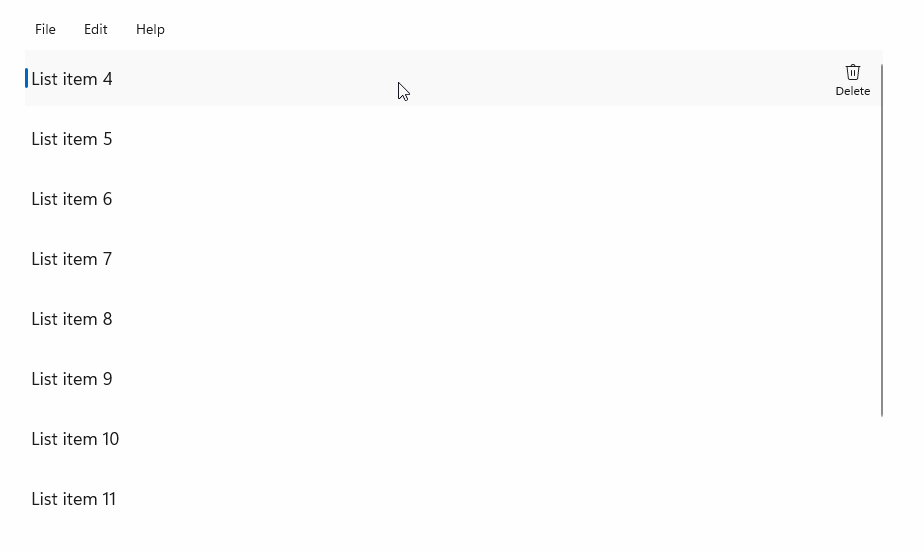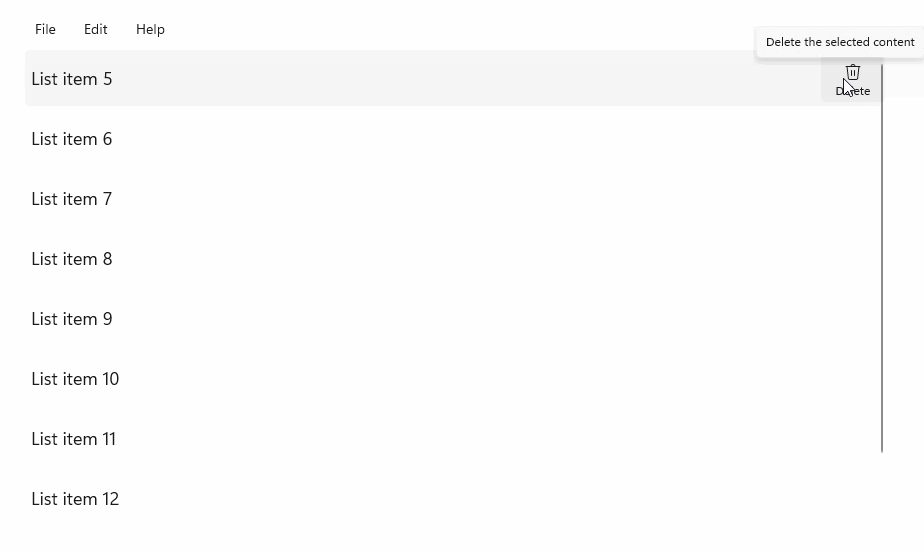
StandardUICommandSample
| 下载此示例的代码 |
|---|
| UWP 命令控制示例 (StandardUICommand) |
在此示例中,我们演示如何使用通过 StandardUICommand 类实现的“删除项”命令来增强基本的 ListView,同时使用 MenuBar、轻扫控件、悬停按钮和上下文菜单优化各种输入类型的用户体验。
注意
此示例需要 Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Controls NuGet 包,它是 WinUI 2 的一部分。
Xaml:
此示例 UI 包含一个有五个项的 ListView。 Delete StandardUICommand 绑定到 MenuBarItem、SwipeItem、AppBarButton 和 ContextFlyout 菜单。
<Page
x:Class="StandardUICommandSample.MainPage"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local="using:StandardUICommandSample"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:muxcontrols="using:Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Controls"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Background="{ThemeResource ApplicationPageBackgroundThemeBrush}">
<Page.Resources>
<Style x:Key="HorizontalSwipe"
TargetType="ListViewItem"
BasedOn="{StaticResource ListViewItemRevealStyle}">
<Setter Property="Height" Value="60"/>
<Setter Property="Padding" Value="0"/>
<Setter Property="HorizontalContentAlignment" Value="Stretch"/>
<Setter Property="VerticalContentAlignment" Value="Stretch"/>
<Setter Property="BorderThickness" Value="0"/>
</Style>
</Page.Resources>
<Grid Loaded="ControlExample_Loaded">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<StackPanel Grid.Row="0"
Padding="10"
BorderThickness="0,0,0,1"
BorderBrush="LightBlue"
Background="AliceBlue">
<TextBlock Style="{StaticResource HeaderTextBlockStyle}">
StandardUICommand sample
</TextBlock>
<TextBlock Style="{StaticResource SubtitleTextBlockStyle}" Margin="0,0,0,10">
This sample shows how to use the StandardUICommand class to
share a platform command and consistent user experiences
across various controls.
</TextBlock>
<TextBlock Style="{StaticResource SubtitleTextBlockStyle}" Margin="0,0,0,0">
Specifically, we define a standard delete command and add it
to a variety of command surfaces, all of which share a common
icon, label, keyboard accelerator, and description.
</TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
<muxcontrols:MenuBar Grid.Row="1" Padding="10">
<muxcontrols:MenuBarItem Title="File">
</muxcontrols:MenuBarItem>
<muxcontrols:MenuBarItem Title="Edit">
<MenuFlyoutItem x:Name="DeleteFlyoutItem"/>
</muxcontrols:MenuBarItem>
<muxcontrols:MenuBarItem Title="Help">
</muxcontrols:MenuBarItem>
</muxcontrols:MenuBar>
<ListView x:Name="ListViewRight" Grid.Row="2"
Loaded="ListView_Loaded"
IsItemClickEnabled="True"
SelectionMode="Single"
SelectionChanged="ListView_SelectionChanged"
ItemContainerStyle="{StaticResource HorizontalSwipe}">
<ListView.ItemTemplate>
<DataTemplate x:DataType="local:ListItemData">
<UserControl PointerEntered="ListViewSwipeContainer_PointerEntered"
PointerExited="ListViewSwipeContainer_PointerExited">
<UserControl.ContextFlyout>
<MenuFlyout>
<MenuFlyoutItem
Command="{x:Bind Command}"
CommandParameter="{x:Bind Text}" />
</MenuFlyout>
</UserControl.ContextFlyout>
<Grid AutomationProperties.Name="{x:Bind Text}">
<VisualStateManager.VisualStateGroups>
<VisualStateGroup x:Name="HoveringStates">
<VisualState x:Name="HoverButtonsHidden" />
<VisualState x:Name="HoverButtonsShown">
<VisualState.Setters>
<Setter Target="HoverButton.Visibility"
Value="Visible" />
</VisualState.Setters>
</VisualState>
</VisualStateGroup>
</VisualStateManager.VisualStateGroups>
<SwipeControl x:Name="ListViewSwipeContainer" >
<SwipeControl.RightItems>
<SwipeItems Mode="Execute">
<SwipeItem x:Name="DeleteSwipeItem"
Background="Red"
Command="{x:Bind Command}"
CommandParameter="{x:Bind Text}"/>
</SwipeItems>
</SwipeControl.RightItems>
<Grid VerticalAlignment="Center">
<TextBlock Text="{x:Bind Text}"
Margin="10"
FontSize="18"
HorizontalAlignment="Left"
VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
<AppBarButton x:Name="HoverButton"
IsTabStop="False"
HorizontalAlignment="Right"
Visibility="Collapsed"
Command="{x:Bind Command}"
CommandParameter="{x:Bind Text}"/>
</Grid>
</SwipeControl>
</Grid>
</UserControl>
</DataTemplate>
</ListView.ItemTemplate>
</ListView>
</Grid>
</Page>
代码隐藏
- 首先,我们定义一个
ListItemData类,其中包含一个文本字符串,以及适用于 ListView 中每个 ListViewItem 的 ICommand。
public class ListItemData
{
public String Text { get; set; }
public ICommand Command { get; set; }
}
- 在 MainPage 类中,我们为 ListView ItemTemplate 的 DataTemplate 定义一组
ListItemData对象。 然后,我们为其填充包含五个项(带有文本和关联的 StandardUICommand Delete)的初始集合。
/// <summary>
/// ListView item collection.
/// </summary>
ObservableCollection<ListItemData> collection =
new ObservableCollection<ListItemData>();
/// <summary>
/// Handler for the layout Grid control load event.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">Source of the control loaded event</param>
/// <param name="e">Event args for the loaded event</param>
private void ControlExample_Loaded(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// Create the standard Delete command.
var deleteCommand = new StandardUICommand(StandardUICommandKind.Delete);
deleteCommand.ExecuteRequested += DeleteCommand_ExecuteRequested;
DeleteFlyoutItem.Command = deleteCommand;
for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
collection.Add(
new ListItemData {
Text = "List item " + i.ToString(),
Command = deleteCommand });
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Handler for the ListView control load event.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">Source of the control loaded event</param>
/// <param name="e">Event args for the loaded event</param>
private void ListView_Loaded(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
var listView = (ListView)sender;
// Populate the ListView with the item collection.
listView.ItemsSource = collection;
}
- 接下来,我们定义 ICommand ExecuteRequested 处理程序,在其中实现项删除命令。
/// <summary>
/// Handler for the Delete command.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">Source of the command event</param>
/// <param name="e">Event args for the command event</param>
private void DeleteCommand_ExecuteRequested(
XamlUICommand sender, ExecuteRequestedEventArgs args)
{
// If possible, remove specified item from collection.
if (args.Parameter != null)
{
foreach (var i in collection)
{
if (i.Text == (args.Parameter as string))
{
collection.Remove(i);
return;
}
}
}
if (ListViewRight.SelectedIndex != -1)
{
collection.RemoveAt(ListViewRight.SelectedIndex);
}
}
- 最后,我们定义各种 ListView 事件(包括 PointerEntered、PointerExited 和 SelectionChanged 事件)的处理程序。 指针事件处理程序用于显示或隐藏每个项的“删除”按钮。
/// <summary>
/// Handler for the ListView selection changed event.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">Source of the selection changed event</param>
/// <param name="e">Event args for the selection changed event</param>
private void ListView_SelectionChanged(object sender, SelectionChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (ListViewRight.SelectedIndex != -1)
{
var item = collection[ListViewRight.SelectedIndex];
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Handler for the pointer entered event.
/// Displays the delete item "hover" buttons.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">Source of the pointer entered event</param>
/// <param name="e">Event args for the pointer entered event</param>
private void ListViewSwipeContainer_PointerEntered(
object sender, PointerRoutedEventArgs e)
{
if (e.Pointer.PointerDeviceType ==
Windows.Devices.Input.PointerDeviceType.Mouse ||
e.Pointer.PointerDeviceType ==
Windows.Devices.Input.PointerDeviceType.Pen)
{
VisualStateManager.GoToState(
sender as Control, "HoverButtonsShown", true);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Handler for the pointer exited event.
/// Hides the delete item "hover" buttons.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender">Source of the pointer exited event</param>
/// <param name="e">Event args for the pointer exited event</param>
private void ListViewSwipeContainer_PointerExited(
object sender, PointerRoutedEventArgs e)
{
VisualStateManager.GoToState(
sender as Control, "HoverButtonsHidden", true);
}
使用 XamlUICommand 类的命令体验
如果需要创建不是由 StandardUICommand 类定义的命令,或者需要对命令外观进行更多的控制,则可使用派生自 ICommand 接口的 XamlUICommand 类来添加各种 UI 属性(例如图标、标签、说明和键盘快捷方式)、方法和事件,以便快速定义自定义命令的 UI 和行为。
XamlUICommand 可以让你通过图标、标签、说明、键盘快捷方式(访问键和键盘快捷键)之类的控件绑定来指定 UI,不需设置单独的属性。
示例

XamlUICommandSample
| 下载此示例的代码 |
|---|
| UWP 命令控制示例 (XamlUICommand) |
此示例共享前面的 StandardUICommand 示例的删除功能,但同时演示了如何使用 XamlUICommand 类通过你自己的字体图标、标签、键盘快捷方式和说明来定义自定义删除命令。 与 StandardUICommand 示例一样,我们使用通过 XamlUICommand 类实现的“删除项”命令来增强基本的 ListView,同时使用 MenuBar、轻扫控件、悬停按钮和上下文菜单优化各种输入类型的用户体验。
许多平台控件实际上使用 XamlUICommand 属性,就像上一部分的 StandardUICommand 示例一样。
注意
此示例需要 Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Controls NuGet 包,它是 WinUI 2 的一部分。
Xaml:
此示例 UI 包含一个有五个项的 ListView。 自定义 XamlUICommand CustomXamlUICommand 绑定到 MenuBarItem、SwipeItem、AppBarButton 和 ContextFlyout 菜单。
<Page
x:Class="XamlUICommand_Sample.MainPage"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local="using:XamlUICommand_Sample"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:muxcontrols="using:Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Controls"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Background="{ThemeResource ApplicationPageBackgroundThemeBrush}">
<Page.Resources>
<XamlUICommand x:Name="CustomXamlUICommand"
ExecuteRequested="DeleteCommand_ExecuteRequested"
Description="Custom XamlUICommand"
Label="Custom XamlUICommand">
<XamlUICommand.IconSource>
<FontIconSource FontFamily="Wingdings" Glyph="M"/>
</XamlUICommand.IconSource>
<XamlUICommand.KeyboardAccelerators>
<KeyboardAccelerator Key="D" Modifiers="Control"/>
</XamlUICommand.KeyboardAccelerators>
</XamlUICommand>
<Style x:Key="HorizontalSwipe"
TargetType="ListViewItem"
BasedOn="{StaticResource ListViewItemRevealStyle}">
<Setter Property="Height" Value="70"/>
<Setter Property="Padding" Value="0"/>
<Setter Property="HorizontalContentAlignment" Value="Stretch"/>
<Setter Property="VerticalContentAlignment" Value="Stretch"/>
<Setter Property="BorderThickness" Value="0"/>
</Style>
</Page.Resources>
<Grid Loaded="ControlExample_Loaded" Name="MainGrid">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<StackPanel Grid.Row="0"
Padding="10"
BorderThickness="0,0,0,1"
BorderBrush="LightBlue"
Background="AliceBlue">
<TextBlock Style="{StaticResource HeaderTextBlockStyle}">
XamlUICommand sample
</TextBlock>
<TextBlock Style="{StaticResource SubtitleTextBlockStyle}" Margin="0,0,0,10">
This sample shows how to use the XamlUICommand class to
share a custom command with consistent user experiences
across various controls.
</TextBlock>
<TextBlock Style="{StaticResource SubtitleTextBlockStyle}" Margin="0,0,0,0">
Specifically, we define a custom delete command and add it
to a variety of command surfaces, all of which share a common
icon, label, keyboard accelerator, and description.
</TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
<muxcontrols:MenuBar Grid.Row="1">
<muxcontrols:MenuBarItem Title="File">
</muxcontrols:MenuBarItem>
<muxcontrols:MenuBarItem Title="Edit">
<MenuFlyoutItem x:Name="DeleteFlyoutItem"
Command="{StaticResource CustomXamlUICommand}"/>
</muxcontrols:MenuBarItem>
<muxcontrols:MenuBarItem Title="Help">
</muxcontrols:MenuBarItem>
</muxcontrols:MenuBar>
<ListView x:Name="ListViewRight" Grid.Row="2"
Loaded="ListView_Loaded"
IsItemClickEnabled="True"
SelectionMode="Single"
SelectionChanged="ListView_SelectionChanged"
ItemContainerStyle="{StaticResource HorizontalSwipe}">
<ListView.ItemTemplate>
<DataTemplate x:DataType="local:ListItemData">
<UserControl PointerEntered="ListViewSwipeContainer_PointerEntered"
PointerExited="ListViewSwipeContainer_PointerExited">
<UserControl.ContextFlyout>
<MenuFlyout>
<MenuFlyoutItem
Command="{x:Bind Command}"
CommandParameter="{x:Bind Text}" />
</MenuFlyout>
</UserControl.ContextFlyout>
<Grid AutomationProperties.Name="{x:Bind Text}">
<VisualStateManager.VisualStateGroups>
<VisualStateGroup x:Name="HoveringStates">
<VisualState x:Name="HoverButtonsHidden" />
<VisualState x:Name="HoverButtonsShown">
<VisualState.Setters>
<Setter Target="HoverButton.Visibility"
Value="Visible" />
</VisualState.Setters>
</VisualState>
</VisualStateGroup>
</VisualStateManager.VisualStateGroups>
<SwipeControl x:Name="ListViewSwipeContainer">
<SwipeControl.RightItems>
<SwipeItems Mode="Execute">
<SwipeItem x:Name="DeleteSwipeItem"
Background="Red"
Command="{x:Bind Command}"
CommandParameter="{x:Bind Text}"/>
</SwipeItems>
</SwipeControl.RightItems>
<Grid VerticalAlignment="Center">
<TextBlock Text="{x:Bind Text}"
Margin="10"
FontSize="18"
HorizontalAlignment="Left"
VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
<AppBarButton x:Name="HoverButton"
IsTabStop="False"
HorizontalAlignment="Right"
Visibility="Collapsed"
Command="{x:Bind Command}"
CommandParameter="{x:Bind Text}"/>
</Grid>
</SwipeControl>
</Grid>
</UserControl>
</DataTemplate>
</ListView.ItemTemplate>
</ListView>
</Grid>
</Page>
代码隐藏
- 首先,我们定义一个
ListItemData类,其中包含一个文本字符串,以及适用于 ListView 中每个 ListViewItem 的 ICommand。
public class ListItemData
{
public String Text { get; set; }
public ICommand Command { get; set; }
}
- 在 MainPage 类中,我们为 ListView ItemTemplate 的 DataTemplate 定义一组
ListItemData对象。 然后,我们为其填充包含五个项(带有文本和关联的 XamlUICommand)的初始集合。
ObservableCollection<ListItemData> collection = new ObservableCollection<ListItemData>();
private void ControlExample_Loaded(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
for (var i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
collection.Add(
new ListItemData { Text = "List item " + i.ToString(), Command = CustomXamlUICommand });
}
}
private void ListView_Loaded(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
var listView = (ListView)sender;
listView.ItemsSource = collection;
}
- 接下来,我们定义 ICommand ExecuteRequested 处理程序,在其中实现项删除命令。
private void DeleteCommand_ExecuteRequested(
XamlUICommand sender, ExecuteRequestedEventArgs args)
{
if (args.Parameter != null)
{
foreach (var i in collection)
{
if (i.Text == (args.Parameter as string))
{
collection.Remove(i);
return;
}
}
}
if (ListViewRight.SelectedIndex != -1)
{
collection.RemoveAt(ListViewRight.SelectedIndex);
}
}
- 最后,我们定义各种 ListView 事件(包括 PointerEntered、PointerExited 和 SelectionChanged 事件)的处理程序。 指针事件处理程序用于显示或隐藏每个项的“删除”按钮。
private void ListView_SelectionChanged(object sender, SelectionChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (ListViewRight.SelectedIndex != -1)
{
var item = collection[ListViewRight.SelectedIndex];
}
}
private void ListViewSwipeContainer_PointerEntered(object sender, PointerRoutedEventArgs e)
{
if (e.Pointer.PointerDeviceType ==
Windows.Devices.Input.PointerDeviceType.Mouse ||
e.Pointer.PointerDeviceType == Windows.Devices.Input.PointerDeviceType.Pen)
{
VisualStateManager.GoToState(sender as Control, "HoverButtonsShown", true);
}
}
private void ListViewSwipeContainer_PointerExited(object sender, PointerRoutedEventArgs e)
{
VisualStateManager.GoToState(sender as Control, "HoverButtonsHidden", true);
}
使用 ICommand 接口的命令体验
标准 UWP 控件(按钮、列表、选择、日历、预测性文本)是许多常见命令体验的基础。 如需控件类型的完整列表,请参阅 Windows 应用的控件和模式。
要为结构化命令控制体验提供支持,最基本的方法是定义 ICommand 接口(适用于 C++ 的 Windows.UI.Xaml.Input.ICommand 或适用于 C# 的 System.Windows.Input.ICommand)的实现。 此 ICommand 实例随后可以绑定到控件(例如按钮)。
注意
在某些情况下,将方法绑定到 Click 事件并将属性绑定到 IsEnabled 属性也同样很高效。
示例
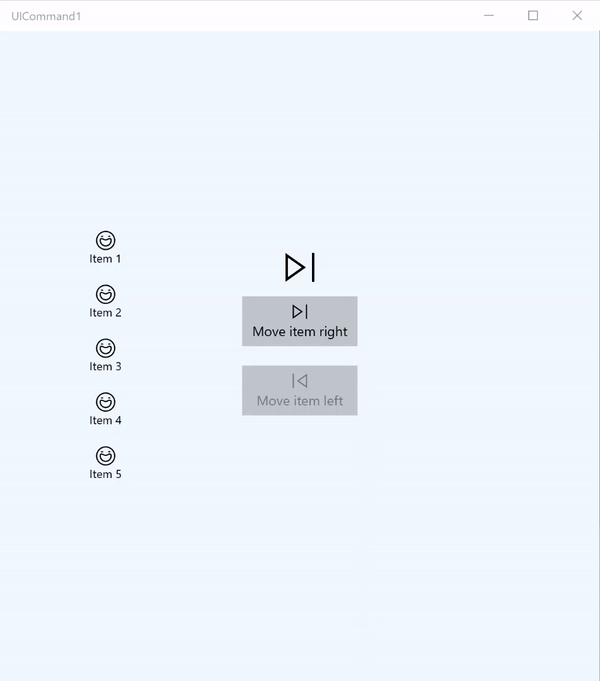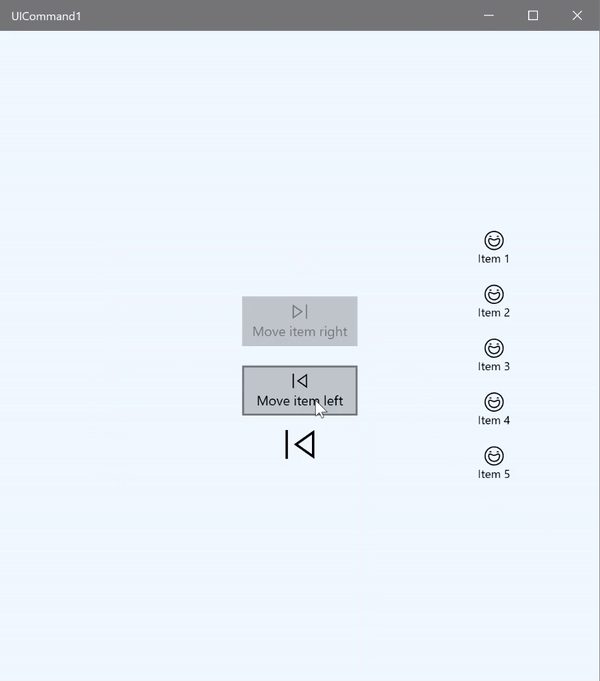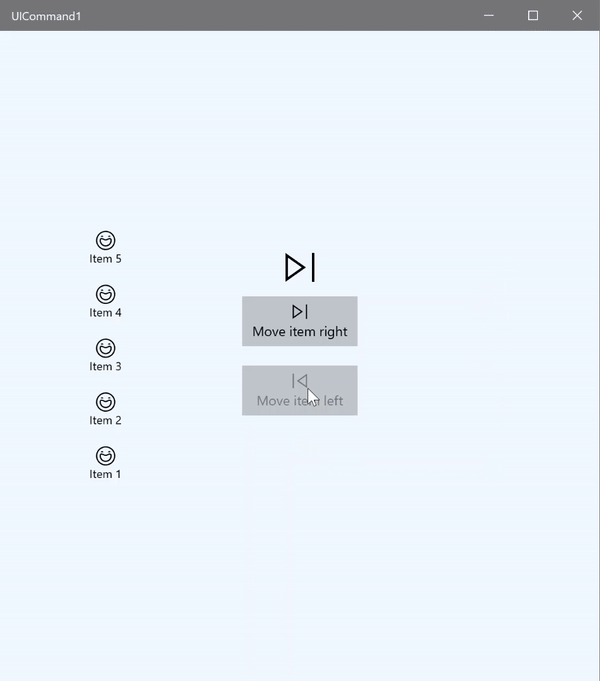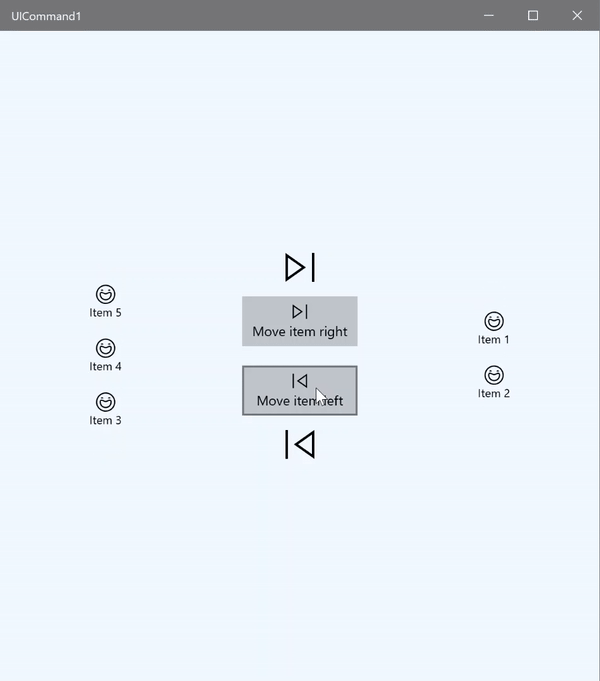
ICommand 示例
| 下载此示例的代码 |
|---|
| UWP 命令控制示例 (ICommand) |
在这个基本示例中,我们演示如何通过单击按钮、键盘快捷方式以及旋转鼠标滚轮来调用单个命令。
我们使用两个 ListView,一个填充了五个项,另一个为空;另外还使用两个按钮,一个用于将项从左侧的 ListView 移到右侧的 ListView,另一个用于将项从右侧移到左侧。 每个按钮绑定到相应的命令(分别为 ViewModel.MoveRightCommand 和 ViewModel.MoveLeftCommand),根据其关联的 ListView 中的项数自动启用或禁用。
以下 XAML 代码定义示例的 UI。
<Page
x:Class="UICommand1.View.MainPage"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:vm="using:UICommand1.ViewModel"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Background="{ThemeResource ApplicationPageBackgroundThemeBrush}">
<Page.Resources>
<vm:OpacityConverter x:Key="opaque" />
</Page.Resources>
<Grid Name="ItemGrid"
Background="AliceBlue"
PointerWheelChanged="Page_PointerWheelChanged">
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="2*"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*"/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ListView Grid.Column="0" VerticalAlignment="Center"
x:Name="CommandListView"
ItemsSource="{x:Bind Path=ViewModel.ListItemLeft}"
SelectionMode="None" IsItemClickEnabled="False"
HorizontalAlignment="Right">
<ListView.ItemTemplate>
<DataTemplate x:DataType="vm:ListItemData">
<Grid VerticalAlignment="Center">
<AppBarButton Label="{x:Bind ListItemText}">
<AppBarButton.Icon>
<SymbolIcon Symbol="{x:Bind ListItemIcon}"/>
</AppBarButton.Icon>
</AppBarButton>
</Grid>
</DataTemplate>
</ListView.ItemTemplate>
</ListView>
<Grid Grid.Column="1" Margin="0,0,0,0"
HorizontalAlignment="Center"
VerticalAlignment="Center">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
<RowDefinition Height="*"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<StackPanel Grid.Row="1">
<FontIcon FontFamily="{StaticResource SymbolThemeFontFamily}"
FontSize="40" Glyph=""
Opacity="{x:Bind Path=ViewModel.ListItemLeft.Count,
Mode=OneWay, Converter={StaticResource opaque}}"/>
<Button Name="MoveItemRightButton"
Margin="0,10,0,10" Width="120" HorizontalAlignment="Center"
Command="{x:Bind Path=ViewModel.MoveRightCommand}">
<Button.KeyboardAccelerators>
<KeyboardAccelerator
Modifiers="Control"
Key="Add" />
</Button.KeyboardAccelerators>
<StackPanel>
<SymbolIcon Symbol="Next"/>
<TextBlock>Move item right</TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
</Button>
<Button Name="MoveItemLeftButton"
Margin="0,10,0,10" Width="120" HorizontalAlignment="Center"
Command="{x:Bind Path=ViewModel.MoveLeftCommand}">
<Button.KeyboardAccelerators>
<KeyboardAccelerator
Modifiers="Control"
Key="Subtract" />
</Button.KeyboardAccelerators>
<StackPanel>
<SymbolIcon Symbol="Previous"/>
<TextBlock>Move item left</TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
</Button>
<FontIcon FontFamily="{StaticResource SymbolThemeFontFamily}"
FontSize="40" Glyph=""
Opacity="{x:Bind Path=ViewModel.ListItemRight.Count,
Mode=OneWay, Converter={StaticResource opaque}}"/>
</StackPanel>
</Grid>
<ListView Grid.Column="2"
x:Name="CommandListViewRight"
VerticalAlignment="Center"
IsItemClickEnabled="False"
SelectionMode="None"
ItemsSource="{x:Bind Path=ViewModel.ListItemRight}"
HorizontalAlignment="Left">
<ListView.ItemTemplate>
<DataTemplate x:DataType="vm:ListItemData">
<Grid VerticalAlignment="Center">
<AppBarButton Label="{x:Bind ListItemText}">
<AppBarButton.Icon>
<SymbolIcon Symbol="{x:Bind ListItemIcon}"/>
</AppBarButton.Icon>
</AppBarButton>
</Grid>
</DataTemplate>
</ListView.ItemTemplate>
</ListView>
</Grid>
</Page>
这是前一 UI 的代码隐藏。
在代码隐藏中,我们连接到包含命令代码的视图模型。 另外,我们还为来自鼠标滚轮的输入定义了一个处理程序,后者也连接到命令代码。
using Windows.UI.Xaml;
using Windows.UI.Xaml.Input;
using Windows.UI.Xaml.Controls;
using UICommand1.ViewModel;
using Windows.System;
using Windows.UI.Core;
namespace UICommand1.View
{
/// <summary>
/// An empty page that can be used on its own or navigated to within a Frame.
/// </summary>
public sealed partial class MainPage : Page
{
// Reference to our view model.
public UICommand1ViewModel ViewModel { get; set; }
// Initialize our view and view model.
public MainPage()
{
this.InitializeComponent();
ViewModel = new UICommand1ViewModel();
}
/// <summary>
/// Handle mouse wheel input and assign our
/// commands to appropriate direction of rotation.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sender"></param>
/// <param name="e"></param>
private void Page_PointerWheelChanged(object sender, PointerRoutedEventArgs e)
{
var props = e.GetCurrentPoint(sender as UIElement).Properties;
// Require CTRL key and accept only vertical mouse wheel movement
// to eliminate accidental wheel input.
if ((Window.Current.CoreWindow.GetKeyState(VirtualKey.Control) !=
CoreVirtualKeyStates.None) && !props.IsHorizontalMouseWheel)
{
bool delta = props.MouseWheelDelta < 0 ? true : false;
switch (delta)
{
case true:
ViewModel.MoveRight();
break;
case false:
ViewModel.MoveLeft();
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
}
}
这是来自视图模型的代码
我们可以使用视图模型为应用中的两个命令定义执行细节、填充一个 ListView,并提供一个不透明度值转换器,以便根据每个 ListView 的项计数来隐藏或显示某个其他的 UI。
using System;
using System.Collections.ObjectModel;
using System.ComponentModel;
using Windows.UI.Xaml.Controls;
using Windows.UI.Xaml.Data;
namespace UICommand1.ViewModel
{
/// <summary>
/// UI properties for our list items.
/// </summary>
public class ListItemData
{
/// <summary>
/// Gets and sets the list item content string.
/// </summary>
public string ListItemText { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Gets and sets the list item icon.
/// </summary>
public Symbol ListItemIcon { get; set; }
}
/// <summary>
/// View Model that sets up a command to handle invoking the move item buttons.
/// </summary>
public class UICommand1ViewModel
{
/// <summary>
/// The command to invoke when the Move item left button is pressed.
/// </summary>
public RelayCommand MoveLeftCommand { get; private set; }
/// <summary>
/// The command to invoke when the Move item right button is pressed.
/// </summary>
public RelayCommand MoveRightCommand { get; private set; }
// Item collections
public ObservableCollection<ListItemData> ListItemLeft { get; } =
new ObservableCollection<ListItemData>();
public ObservableCollection<ListItemData> ListItemRight { get; } =
new ObservableCollection<ListItemData>();
public ListItemData listItem;
/// <summary>
/// Sets up a command to handle invoking the move item buttons.
/// </summary>
public UICommand1ViewModel()
{
MoveLeftCommand =
new RelayCommand(new Action(MoveLeft), CanExecuteMoveLeftCommand);
MoveRightCommand =
new RelayCommand(new Action(MoveRight), CanExecuteMoveRightCommand);
LoadItems();
}
/// <summary>
/// Populate our list of items.
/// </summary>
public void LoadItems()
{
for (var x = 0; x <= 4; x++)
{
listItem = new ListItemData();
listItem.ListItemText = "Item " + (ListItemLeft.Count + 1).ToString();
listItem.ListItemIcon = Symbol.Emoji;
ListItemLeft.Add(listItem);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Move left command valid when items present in the list on right.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>True, if count is greater than 0.</returns>
private bool CanExecuteMoveLeftCommand()
{
return ListItemRight.Count > 0;
}
/// <summary>
/// Move right command valid when items present in the list on left.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>True, if count is greater than 0.</returns>
private bool CanExecuteMoveRightCommand()
{
return ListItemLeft.Count > 0;
}
/// <summary>
/// The command implementation to execute when the Move item right button is pressed.
/// </summary>
public void MoveRight()
{
if (ListItemLeft.Count > 0)
{
listItem = new ListItemData();
ListItemRight.Add(listItem);
listItem.ListItemText = "Item " + ListItemRight.Count.ToString();
listItem.ListItemIcon = Symbol.Emoji;
ListItemLeft.RemoveAt(ListItemLeft.Count - 1);
MoveRightCommand.RaiseCanExecuteChanged();
MoveLeftCommand.RaiseCanExecuteChanged();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// The command implementation to execute when the Move item left button is pressed.
/// </summary>
public void MoveLeft()
{
if (ListItemRight.Count > 0)
{
listItem = new ListItemData();
ListItemLeft.Add(listItem);
listItem.ListItemText = "Item " + ListItemLeft.Count.ToString();
listItem.ListItemIcon = Symbol.Emoji;
ListItemRight.RemoveAt(ListItemRight.Count - 1);
MoveRightCommand.RaiseCanExecuteChanged();
MoveLeftCommand.RaiseCanExecuteChanged();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Views subscribe to this event to get notified of property updates.
/// </summary>
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
/// <summary>
/// Notify subscribers of updates to the named property
/// </summary>
/// <param name="propertyName">The full, case-sensitive, name of a property.</param>
protected void NotifyPropertyChanged(string propertyName)
{
PropertyChangedEventHandler handler = this.PropertyChanged;
if (handler != null)
{
PropertyChangedEventArgs args = new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName);
handler(this, args);
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Convert a collection count to an opacity value of 0.0 or 1.0.
/// </summary>
public class OpacityConverter : IValueConverter
{
/// <summary>
/// Converts a collection count to an opacity value of 0.0 or 1.0.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value">The count passed in</param>
/// <param name="targetType">Ignored.</param>
/// <param name="parameter">Ignored</param>
/// <param name="language">Ignored</param>
/// <returns>1.0 if count > 0, otherwise returns 0.0</returns>
public object Convert(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, string language)
{
return ((int)value > 0 ? 1.0 : 0.0);
}
/// <summary>
/// Not used, converter is not intended for two-way binding.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="value">Ignored</param>
/// <param name="targetType">Ignored</param>
/// <param name="parameter">Ignored</param>
/// <param name="language">Ignored</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public object ConvertBack(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, string language)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
}
最后是 ICommand 接口的实现
在这里,我们定义一个命令来实现 ICommand 接口并直接将其功能中继到其他对象。
using System;
using System.Windows.Input;
namespace UICommand1
{
/// <summary>
/// A command whose sole purpose is to relay its functionality
/// to other objects by invoking delegates.
/// The default return value for the CanExecute method is 'true'.
/// <see cref="RaiseCanExecuteChanged"/> needs to be called whenever
/// <see cref="CanExecute"/> is expected to return a different value.
/// </summary>
public class RelayCommand : ICommand
{
private readonly Action _execute;
private readonly Func<bool> _canExecute;
/// <summary>
/// Raised when RaiseCanExecuteChanged is called.
/// </summary>
public event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged;
/// <summary>
/// Creates a new command that can always execute.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="execute">The execution logic.</param>
public RelayCommand(Action execute)
: this(execute, null)
{
}
/// <summary>
/// Creates a new command.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="execute">The execution logic.</param>
/// <param name="canExecute">The execution status logic.</param>
public RelayCommand(Action execute, Func<bool> canExecute)
{
if (execute == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("execute");
_execute = execute;
_canExecute = canExecute;
}
/// <summary>
/// Determines whether this <see cref="RelayCommand"/> can execute in its current state.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="parameter">
/// Data used by the command. If the command does not require
/// data to be passed, this object can be set to null.
/// </param>
/// <returns>true if this command can be executed; otherwise, false.</returns>
public bool CanExecute(object parameter)
{
return _canExecute == null ? true : _canExecute();
}
/// <summary>
/// Executes the <see cref="RelayCommand"/> on the current command target.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="parameter">
/// Data used by the command. If the command does not require
/// data to be passed, this object can be set to null.
/// </param>
public void Execute(object parameter)
{
_execute();
}
/// <summary>
/// Method used to raise the <see cref="CanExecuteChanged"/> event
/// to indicate that the return value of the <see cref="CanExecute"/>
/// method has changed.
/// </summary>
public void RaiseCanExecuteChanged()
{
var handler = CanExecuteChanged;
if (handler != null)
{
handler(this, EventArgs.Empty);
}
}
}
}
总结
通用 Windows 平台提供了一个强大且灵活的命令控制系统,用于构建可以跨控件类型、设备和输入类型共享和管理命令的应用。
在为 Windows 应用构建命令时,请使用以下方法:
- 在 XAML/代码隐藏中侦听和处理事件
- 绑定到事件处理方法(例如 Click)
- 定义自己的 ICommand 实现
- 使用自己的值为预定义的一组属性创建 XamlUICommand 对象
- 使用一组预定义的平台属性和值创建 StandardUICommand 对象
后续步骤
如果需要一个演示 XamlUICommand 和 StandardUICommand 实现的完整示例,请参阅 WinUI 2 库示例。
