使用 ADO.NET 创建简单的数据应用程序
注意
数据集和相关类是 2000 年代初的旧 .NET Framework 技术,使应用程序能够在应用程序与数据库断开连接时处理内存中的数据。 这些方法对于使用户能够修改数据并持续更改回数据库的应用程序特别有用。 虽然数据集已被证明是一项非常成功的技术,但我们建议新的 .NET 应用程序使用 Entity Framework Core。 实体框架提供了一种更自然的方式来将表格数据作为对象模型,并且具有更简单的编程接口。
当你创建操作数据库中的数据的应用程序时,就执行了如定义连接字符串、插入数据以及运行存储过程等基本任务。 学习本主题后,你可以了解如何使用 Visual C# 或 Visual Basic 和 ADO.NET 从简单的 Windows 窗体“基于数据”应用程序中与数据库进行交互。 所有 .NET 数据技术(包括数据集、LINQ to SQL 和 实体框架)最终执行的步骤与本文中所示的步骤非常相似。
本文演示了一种从数据库快速获取数据的简单方法。 如果应用程序需要以非普通方式修改数据并更新数据库,则应考虑使用“实体框架”以及使用数据绑定自动将用户界面控件与基础数据中的更改同步。
重要
要使代码保持简单,请不要包括生产就绪的异常处理。
注意
可以在 C# 和 Visual Basic 的 Visual Studio 文档 GitHub 存储库中访问本教程的完整代码。
先决条件
要创建应用程序,你将需要:
安装了“.NET 桌面开发”和“数据存储和处理”工作负载的 Visual Studio。 若要安装这些程序,请打开 Visual Studio 安装程序,然后在要修改的 Visual Studio 版本旁选择“修改”(或“更多”>“修改”)。
SQL Server Express LocalDB。 如果尚未安装 SQL Server Express LocalDB,可从 SQL Server 下载页面安装。
本主题假定你已经熟悉 Visual Studio IDE 的基本功能,并能够创建 Windows 窗体应用程序,将窗体添加到项目,将按钮和其他控件安装到这些窗体上,为这些控件设置属性,以及对简单事件进行编码。 如果不熟悉这些任务,建议先完成在 Visual Studio 中使用 Visual Basic 创建 Windows 窗体应用教程或在 Visual Studio 中使用 C# 创建 Windows 窗体应用教程,然后再开始本演练。
设置示例数据库
按照以下步骤创建示例数据库:
在 Visual Studio 中,打开“服务器资源管理器”窗口。
右键单击“数据连接”,然后选择“新建 SQL Server 数据库”。
在“服务器名称”中,输入“(localdb)\mssqllocaldb”。
在“新数据库名称”文本框中,输入 Sales,然后选择“确定”。
将创建空的 Sales 数据库并将其添加到服务器资源管理器中的“数据连接”节点。
右键单击“Sales”数据连接,并选择“新建查询”。
查询编辑器窗口将打开。
将 Sales Transact-SQL 脚本复制到剪贴板。
将 T-SQL 脚本粘贴到查询编辑器中,然后选择“执行”按钮。
很快查询就会完成运行并创建数据库对象。 数据库包含两个表:Customer 和 Orders。 这些表最初不包含数据,但可在运行将创建的应用程序时添加数据。 该数据库还包含四个简单的存储过程。
创建窗体并添加控件
使用 Windows 窗体应用程序 (.NET Framework) 模板创建 C# 或 Visual Basic 项目,然后将其命名为 SimpleDataApp。
Visual Studio 将创建项目以及若干个文件,其中包括名为“Form1”的空 Windows 窗体。
添加两个 Windows 窗体到项目中,以使其具有三个窗体,然后给予它们下列名称:
导航
NewCustomer
FillOrCancel
对于每个窗体,添加文本框、按钮和其他控件,如下图所示。 对于每个控件,设置表中描述的属性。
注意
分组框和标签控件可提高清晰度,但不在代码中使用。
Navigation 窗体
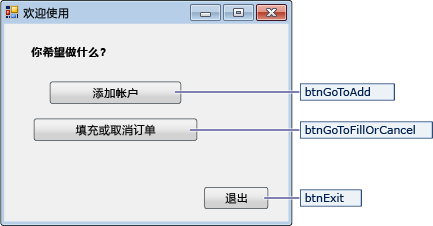
| Navigation 窗体的控件 | 属性 |
|---|---|
| Button | Name = btnGoToAdd |
| Button | Name = btnGoToFillOrCancel |
| Button | Name = btnExit |
NewCustomer 窗体
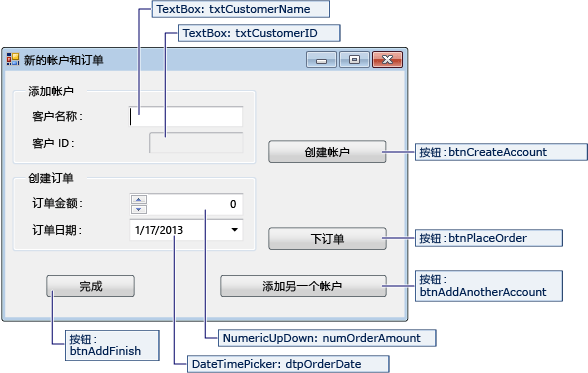
| NewCustomer 窗体的控件 | 属性 |
|---|---|
| TextBox | Name = txtCustomerName |
| TextBox | Name = txtCustomerID Readonly = True |
| Button | Name = btnCreateAccount |
| NumericUpdown | DecimalPlaces = 0 Maximum = 5000 Name = numOrderAmount |
| DateTimePicker | Format = Short Name = dtpOrderDate |
| Button | Name = btnPlaceOrder |
| Button | Name = btnAddAnotherAccount |
| Button | Name = btnAddFinish |
FillOrCancel 窗体
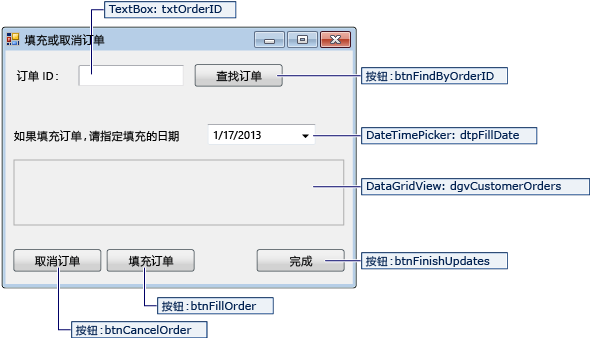
| FillOrCancel 窗体的控件 | 属性 |
|---|---|
| TextBox | Name = txtOrderID |
| Button | Name = btnFindByOrderID |
| DateTimePicker | Format = Short Name = dtpFillDate |
| DataGridView | Name = dgvCustomerOrders Readonly = True RowHeadersVisible = False |
| Button | Name = btnCancelOrder |
| Button | Name = btnFillOrder |
| Button | Name = btnFinishUpdates |
存储连接字符串
当应用程序尝试打开数据库的连接时,应用程序必须能够访问连接字符串。 若要避免在每个窗体中手动输入该字符串,请将该字符串存储在项目的 App.config 文件中,并创建一种方法,当在应用程序任意窗体中调用该方法时都会返回该字符串。
可通过在服务器资源管理器中右键单击 Sales 数据连接,然后选择“属性”来查找连接字符串。 找到 ConnectionString 属性,然后使用 Ctrl+A、Ctrl+C 来选择字符串并将其复制到剪贴板。
如果使用的是 c#,请在解决方案资源管理器中,展开项目下的“属性”节点,然后打开 Settings.settings 文件。 如果使用的是 Visual Basic,请在解决方案资源管理器中,单击“显示所有文件”,展开“我的项目”节点,然后打开 Settings.settings 文件。
在“名称”列中,输入
connString。在“类型”列表中,选择“(连接字符串)”。
在“范围”列表中,选择“应用程序”。
在“值”列中,输入连接字符串(不使用任何引号),然后保存更改。
注意
在实际应用程序中,应安全地存储连接字符串,如连接字符串和配置文件中所述。 为了获得最佳安全性,请使用不依赖于在连接字符串中存储密码的身份验证方法,例如适用于本地 SQL Server 数据库的 Windows 身份验证。 请参阅保存和编辑连接字符串。
编写窗体代码
本部分简要概述了每种窗体的用途。 它还提供了相关代码,单击窗体上的按钮时就会定义基础逻辑。
Navigation 窗体
运行应用程序时,Navigation 窗体将打开。 按“添加帐户”按钮可以打开 NewCustomer 窗体。 按“填写或取消订单”按钮可以打开 FillOrCancel 窗体。 按“退出”按钮可以关闭应用程序。
使 Navigation 窗体成为启动窗体
如果使用 C#,则在“解决方案资源管理器”中,打开 Program.cs,然后将 Application.Run 行更改为 Application.Run(new Navigation());
如果使用的是 Visual Basic,则在“解决方案资源管理器”中,打开“属性”窗口,选择“应用程序”选项卡,然后在“启动窗体”列表上选择 SimpleDataApp.Navigation。
创建自动生成的事件处理程序
双击 Navigation 窗体上的三个按钮,创建空的事件处理程序方法。 双击按钮还会在设计器代码文件中添加自动生成的代码,启用按钮单击就会引发事件。
注意
如果跳过设计器中的双击操作,只是复制代码并将其粘贴到代码文件中,请不要忘记将事件处理程序设置为正确的方法。 可以在“属性”窗口中执行此操作。 切换到“事件”选项卡(使用“闪电”工具栏按钮)并查找“单击”处理程序。
添加适用于 Navigation 窗体逻辑的代码
在 Navigation 窗体的代码页中,完成三个按钮单击事件处理程序的方法主体,如下面的代码所示。
/// <summary>
/// Opens the NewCustomer form as a dialog box,
/// which returns focus to the calling form when it is closed.
/// </summary>
private void btnGoToAdd_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Form frm = new NewCustomer();
frm.Show();
}
/// <summary>
/// Opens the FillorCancel form as a dialog box.
/// </summary>
private void btnGoToFillOrCancel_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Form frm = new FillOrCancel();
frm.ShowDialog();
}
/// <summary>
/// Closes the application (not just the Navigation form).
/// </summary>
private void btnExit_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.Close();
}
注意
本教程的代码提供 C# 和 Visual Basic 版本。 要在 C# 和 Visual Basic 之间切换此页上的代码语言,请使用每个代码示例顶部的代码语言切换器。
NewCustomer 窗体
输入客户名称,然后选择“创建帐户”按钮时,NewCustomer 窗体会创建一个客户帐户,而 SQL Server 则会返回一个 IDENTITY 值作为新的客户 ID。 然后可以通过指定数量和订单日期并选择“下订单”按钮来为新帐户下订单。
创建自动生成的事件处理程序
双击四个按钮,为 NewCustomer 窗体上的每个按钮创建一个空的 Click 事件处理程序。 双击按钮还会在设计器代码文件中添加自动生成的代码,启用按钮单击就会引发事件。
添加适用于 NewCustomer 窗体逻辑的代码
若要完成 NewCustomer 窗体逻辑,请按照以下步骤操作。
将
System.Data.SqlClient命名空间置于范围中,这样就不必完全限定其成员的名称。将一些变量和帮助程序方法添加到类,如以下代码所示。
// Storage for IDENTITY values returned from database. private int parsedCustomerID; private int orderID; /// <summary> /// Verifies that the customer name text box is not empty. /// </summary> private bool IsCustomerNameValid() { if (txtCustomerName.Text == "") { MessageBox.Show("Please enter a name."); return false; } else { return true; } } /// <summary> /// Verifies that a customer ID and order amount have been provided. /// </summary> private bool IsOrderDataValid() { // Verify that CustomerID is present. if (txtCustomerID.Text == "") { MessageBox.Show("Please create customer account before placing order."); return false; } // Verify that Amount isn't 0. else if ((numOrderAmount.Value < 1)) { MessageBox.Show("Please specify an order amount."); return false; } else { // Order can be submitted. return true; } } /// <summary> /// Clears the form data. /// </summary> private void ClearForm() { txtCustomerName.Clear(); txtCustomerID.Clear(); dtpOrderDate.Value = DateTime.Now; numOrderAmount.Value = 0; this.parsedCustomerID = 0; }完成四个按钮单击事件处理程序的方法主体,如以下代码所示。
/// <summary> /// Creates a new customer by calling the Sales.uspNewCustomer stored procedure. /// </summary> private void btnCreateAccount_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (IsCustomerNameValid()) { // Create the connection. using (SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(Properties.Settings.Default.connString)) { // Create a SqlCommand, and identify it as a stored procedure. using (SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand("Sales.uspNewCustomer", connection)) { sqlCommand.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure; // Add input parameter for the stored procedure and specify what to use as its value. sqlCommand.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@CustomerName", SqlDbType.NVarChar, 40)); sqlCommand.Parameters["@CustomerName"].Value = txtCustomerName.Text; // Add the output parameter. sqlCommand.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@CustomerID", SqlDbType.Int)); sqlCommand.Parameters["@CustomerID"].Direction = ParameterDirection.Output; try { connection.Open(); // Run the stored procedure. sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery(); // Customer ID is an IDENTITY value from the database. this.parsedCustomerID = (int)sqlCommand.Parameters["@CustomerID"].Value; // Put the Customer ID value into the read-only text box. this.txtCustomerID.Text = Convert.ToString(parsedCustomerID); } catch { MessageBox.Show("Customer ID was not returned. Account could not be created."); } finally { connection.Close(); } } } } } /// <summary> /// Calls the Sales.uspPlaceNewOrder stored procedure to place an order. /// </summary> private void btnPlaceOrder_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { // Ensure the required input is present. if (IsOrderDataValid()) { // Create the connection. using (SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(Properties.Settings.Default.connString)) { // Create SqlCommand and identify it as a stored procedure. using (SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand("Sales.uspPlaceNewOrder", connection)) { sqlCommand.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure; // Add the @CustomerID input parameter, which was obtained from uspNewCustomer. sqlCommand.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@CustomerID", SqlDbType.Int)); sqlCommand.Parameters["@CustomerID"].Value = this.parsedCustomerID; // Add the @OrderDate input parameter. sqlCommand.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@OrderDate", SqlDbType.DateTime, 8)); sqlCommand.Parameters["@OrderDate"].Value = dtpOrderDate.Value; // Add the @Amount order amount input parameter. sqlCommand.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@Amount", SqlDbType.Int)); sqlCommand.Parameters["@Amount"].Value = numOrderAmount.Value; // Add the @Status order status input parameter. // For a new order, the status is always O (open). sqlCommand.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@Status", SqlDbType.Char, 1)); sqlCommand.Parameters["@Status"].Value = "O"; // Add the return value for the stored procedure, which is the order ID. sqlCommand.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@RC", SqlDbType.Int)); sqlCommand.Parameters["@RC"].Direction = ParameterDirection.ReturnValue; try { //Open connection. connection.Open(); // Run the stored procedure. sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery(); // Display the order number. this.orderID = (int)sqlCommand.Parameters["@RC"].Value; MessageBox.Show("Order number " + this.orderID + " has been submitted."); } catch { MessageBox.Show("Order could not be placed."); } finally { connection.Close(); } } } } } /// <summary> /// Clears the form data so another new account can be created. /// </summary> private void btnAddAnotherAccount_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { this.ClearForm(); } /// <summary> /// Closes the form/dialog box. /// </summary> private void btnAddFinish_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { this.Close(); }
FillOrCancel 窗体
当你输入订单 ID,然后选择查找订单按钮时,FillOrCancel 表单会运行一个查询以返回订单。 返回的行在只读数据网格中显示。 如果选择“取消订单”按钮,则可以将订单标记为已取消 (X);如果选择“填写订单”按钮,则可以将订单标记为已填写 (F)。 如果再次选择“查找订单”按钮,则会显示更新的行。
创建自动生成的事件处理程序
通过双击按钮,为 FillOrCancel 窗体上的四个按钮创建空的 Click 事件处理程序。 双击按钮还会在设计器代码文件中添加自动生成的代码,启用按钮单击就会引发事件。
添加适用于 FillOrCancel 窗体逻辑的代码
若要完成 FillOrCancel 窗体逻辑,请按照以下步骤操作。
将以下两个命名空间置于范围内,这样就无需完全限定其成员的名称。
将变量和帮助程序方法添加到类,如以下代码所示。
// Storage for the order ID value. private int parsedOrderID; /// <summary> /// Verifies that an order ID is present and contains valid characters. /// </summary> private bool IsOrderIDValid() { // Check for input in the Order ID text box. if (txtOrderID.Text == "") { MessageBox.Show("Please specify the Order ID."); return false; } // Check for characters other than integers. else if (Regex.IsMatch(txtOrderID.Text, @"^\D*$")) { // Show message and clear input. MessageBox.Show("Customer ID must contain only numbers."); txtOrderID.Clear(); return false; } else { // Convert the text in the text box to an integer to send to the database. parsedOrderID = Int32.Parse(txtOrderID.Text); return true; } }完成四个按钮单击事件处理程序的方法主体,如以下代码所示。
/// <summary> /// Executes a t-SQL SELECT statement to obtain order data for a specified /// order ID, then displays it in the DataGridView on the form. /// </summary> private void btnFindByOrderID_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (IsOrderIDValid()) { using (SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(Properties.Settings.Default.connString)) { // Define a t-SQL query string that has a parameter for orderID. const string sql = "SELECT * FROM Sales.Orders WHERE orderID = @orderID"; // Create a SqlCommand object. using (SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand(sql, connection)) { // Define the @orderID parameter and set its value. sqlCommand.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@orderID", SqlDbType.Int)); sqlCommand.Parameters["@orderID"].Value = parsedOrderID; try { connection.Open(); // Run the query by calling ExecuteReader(). using (SqlDataReader dataReader = sqlCommand.ExecuteReader()) { // Create a data table to hold the retrieved data. DataTable dataTable = new DataTable(); // Load the data from SqlDataReader into the data table. dataTable.Load(dataReader); // Display the data from the data table in the data grid view. this.dgvCustomerOrders.DataSource = dataTable; // Close the SqlDataReader. dataReader.Close(); } } catch { MessageBox.Show("The requested order could not be loaded into the form."); } finally { // Close the connection. connection.Close(); } } } } } /// <summary> /// Cancels an order by calling the Sales.uspCancelOrder /// stored procedure on the database. /// </summary> private void btnCancelOrder_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (IsOrderIDValid()) { // Create the connection. using (SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(Properties.Settings.Default.connString)) { // Create the SqlCommand object and identify it as a stored procedure. using (SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand("Sales.uspCancelOrder", connection)) { sqlCommand.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure; // Add the order ID input parameter for the stored procedure. sqlCommand.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@orderID", SqlDbType.Int)); sqlCommand.Parameters["@orderID"].Value = parsedOrderID; try { // Open the connection. connection.Open(); // Run the command to execute the stored procedure. sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery(); } catch { MessageBox.Show("The cancel operation was not completed."); } finally { // Close connection. connection.Close(); } } } } } /// <summary> /// Fills an order by calling the Sales.uspFillOrder stored /// procedure on the database. /// </summary> private void btnFillOrder_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (IsOrderIDValid()) { // Create the connection. using (SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(Properties.Settings.Default.connString)) { // Create command and identify it as a stored procedure. using (SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand("Sales.uspFillOrder", connection)) { sqlCommand.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure; // Add the order ID input parameter for the stored procedure. sqlCommand.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@orderID", SqlDbType.Int)); sqlCommand.Parameters["@orderID"].Value = parsedOrderID; // Add the filled date input parameter for the stored procedure. sqlCommand.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@FilledDate", SqlDbType.DateTime, 8)); sqlCommand.Parameters["@FilledDate"].Value = dtpFillDate.Value; try { connection.Open(); // Execute the stored procedure. sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery(); } catch { MessageBox.Show("The fill operation was not completed."); } finally { // Close the connection. connection.Close(); } } } } } /// <summary> /// Closes the form. /// </summary> private void btnFinishUpdates_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { this.Close(); }
测试应用程序
运行应用程序并尝试创建几个客户和订单,以验证一切都按预期工作。 若要验证更改是否已更新到数据库中,请在“服务器资源管理器”中打开“表”节点,右键单击“客户”和“订单”节点,然后选择“显示表数据”。
