教程:生成条形图
本教程介绍如何开发一个以简单条形图的形式显示数据的 Power BI 视觉对象。 此视觉对象支持最小量的自定义。 本文档的其他页面介绍了如何添加进一步自定义,如上下文菜单、工具提示等。
在本教程中,你将了解:
- 定义视觉对象的功能
- 了解用于生成视觉对象的源代码
- 呈现视觉对象
- 将对象添加到“属性”窗格中
- 打包视觉对象
设置环境
在开始开发 Power BI 视觉对象之前,请验证本部分中是否已列出所有内容。
Power BI Pro 或 Premium Per User (PPU) 帐户 。 如果没有订阅密钥,可以注册免费试用版。
Visual Studio Code (VS Code)。 VS Code 是用于开发 JavaScript 和 TypeScript 应用程序的理想集成开发环境 (IDE)。
Windows PowerShell 版本 4 或更高版本(适用于 Windows)。 或 终端 (适用于 Mac)。
准备好开发 Power BI 视觉对象的环境。 设置用于开发 Power BI 视觉对象的环境。
本教程使用“美国销售额分析”报表。 你可以下载此报表并将其上传到 Power BI 服务,或使用自己的报表。 如果需要有关 Power BI 服务和上传文件的详细信息,请参阅开始在 Power BI 服务中创建教程。
注意
如果未在安装过程中安装 D3 JavaScript 库,请立即安装。 从 PowerShell 运行 npm i d3@latest --save
创建条形图视觉对象涉及以下步骤:
- 创建新项目
- 定义 capabilities 文件 -
capabilities.json - 创建视觉对象 API
- 打包视觉对象 - pbiviz.json
创建新项目
本教程的目的是帮助你了解视觉对象的架构方式和编写方式。 可按照这些说明从头开始创建一个条码视觉对象,或者可克隆源代码存储库,并使用它来继续进行操作,而无需创建自己的视觉对象。
打开 PowerShell 并导航到要在其中创建项目的文件夹。
输入以下命令:
pbiviz new BarChart现在,你应该有一个名为 BarChart 的文件夹,其中包含视觉对象的文件。
在 VS Code 中,打开 [tsconfig.json](visual-project-structure.md#tsconfigjson) 文件,将“files”的名称更改为“src/barChart.ts”。
"files": [ "src/barChart.ts" ]tsconfig.json 的“files”对象指向视觉对象的主类所在的文件。
最终的 tsconfig.js文件应如此所示。
package.json 文件包含一系列项目依赖项。 将 package.json 文件替换为此文件。
现在,你应该有一个包含以下文件和文件夹的新视觉对象文件夹:
有关其中每个文件的功能的详细说明,请参阅 Power BI 视觉对象项目结构。
本教程将重点介绍的两个文件是 capabilities.json 文件和 src/barchart.ts 文件,前者描述了主机的视觉对象,后者则包含视觉对象的 API。
定义功能
capabilities.json 文件是将数据绑定到主机的位置。 我们将介绍它接受的数据字段类型,以及视觉对象应该具有的功能。

定义数据角色
变量在 capabilities 文件的 dataRoles 部分中定义和绑定。 我们希望条形图接受两种类型的变量:
- 分类数据,由图上不同的条形表示
- 数值或测量数据,由每个条的高度表示
在 Visual Studio Code 中的 capabilities.json 文件中,确认以下 JSON 片段出现在标记为“dataRoles”的对象中。
"dataRoles": [
{
"displayName": "Category Data",
"name": "category",
"kind": "Grouping"
},
{
"displayName": "Measure Data",
"name": "measure",
"kind": "Measure"
}
],
映射数据
接下来,添加数据映射,告知主机如何处理这些变量:
将“dataViewMappings”对象的内容替换为以下代码:
"dataViewMappings": [
{
"conditions": [
{
"category": {
"max": 1
},
"measure": {
"max": 1
}
}
],
"categorical": {
"categories": {
"for": {
"in": "category"
}
},
"values": {
"select": [
{
"bind": {
"to": "measure"
}
}
]
}
}
}
],
上述代码创建了每个数据角色对象一次只能保存一个字段的“条件”。 注意,我们使用数据角色的内部 name 引用每个字段。
它还设置分类数据映射,使每个字段映射到正确的变量。
定义“属性”窗格的对象
capabilities 文件的“objects”部分是定义应该出现在“格式”窗格上的可定制功能的位置。 这些功能不会影响图的内容,但可以更改其观感。
有关对象及其工作方法详细信息,请参阅对象。
以下对象是可选对象。 如果要完成本教程的可选部分以添加颜色和呈现 X 轴,请添加它们。
将“objects”部分的内容替换为以下代码:
"objects": {
"enableAxis": {
"properties": {
"show": {
"type": {
"bool": true
}
},
"fill": {
"type": {
"fill": {
"solid": {
"color": true
}
}
}
}
}
},
"colorSelector": {
"properties": {
"fill": {
"type": {
"fill": {
"solid": {
"color": true
}
}
}
}
}
}
},
保存“capabilities.json”文件。
最终的 capabilities 文件应该类似于此示例中的文件。
视觉对象 API
所有视觉对象都以实现 IVisual 接口的类开头。 src/visual.ts 文件是包含该类的默认文件。
在本教程中,我们将 IVisual 文件称为 barChart.ts。 下载该文件并将其保存到 /src 文件夹(如果没有这样做)。 本部分将详细介绍此文件,并描述其各个部分。
导入
文件的第一个部分导入了该视觉对象所需的模块。 请注意,除了 Power BI 视觉对象模块之外,我们还导入了 d3 库。
以下模块将导入到 barChart.ts 文件:
import {
BaseType,
select as d3Select,
Selection as d3Selection
} from "d3-selection";
import {
ScaleBand,
ScaleLinear,
scaleBand,
scaleLinear
} from "d3-scale";
import "./../style/visual.less";
import { Axis, axisBottom } from "d3-axis";
import powerbi from "powerbi-visuals-api";
type Selection<T extends BaseType> = d3Selection<T, any, any, any>;
// powerbi.visuals
import DataViewCategoryColumn = powerbi.DataViewCategoryColumn;
import Fill = powerbi.Fill;
import ISandboxExtendedColorPalette = powerbi.extensibility.ISandboxExtendedColorPalette;
import ISelectionId = powerbi.visuals.ISelectionId;
import IVisual = powerbi.extensibility.IVisual;
import IVisualHost = powerbi.extensibility.visual.IVisualHost;
import PrimitiveValue = powerbi.PrimitiveValue;
import VisualUpdateOptions = powerbi.extensibility.visual.VisualUpdateOptions;
import VisualConstructorOptions = powerbi.extensibility.visual.VisualConstructorOptions;
import DataViewObjectPropertyIdentifier = powerbi.DataViewObjectPropertyIdentifier;
import { textMeasurementService } from "powerbi-visuals-utils-formattingutils";
import { FormattingSettingsService } from "powerbi-visuals-utils-formattingmodel";
import { BarChartSettingsModel } from "./barChartSettingsModel";
import { dataViewObjects} from "powerbi-visuals-utils-dataviewutils";
接口
接下来,定义视觉对象接口。 以下接口用于描述条形图视觉对象:
- BarChartDataPoint
此接口定义如下:
/**
* Interface for BarChart data points.
*
* @interface
* @property {PrimitiveValue} value - Data value for point.
* @property {string} category - Corresponding category of data value.
* @property {string} color - Color corresponding to data point.
* @property {string} strokeColor - Stroke color for data point column.
* @property {number} strokeWidth - Stroke width for data point column.
* @property {ISelectionId} selectionId - Id assigned to data point for cross filtering
* and visual interaction.
*/
interface BarChartDataPoint {
value: PrimitiveValue;
category: string;
color: string;
strokeColor: string;
strokeWidth: number;
selectionId: ISelectionId;
}
视觉对象转换
定义数据结构后,需要使用 createSelectorDataPoints 函数将数据映射到数据结构上。 此函数从数据视图接收数据,并将数据转换为视觉对象可使用的格式。 在这种情况下,它将返回前一部分中所述的 BarChartDataPoint[] 接口。
DataView 包含要可视化的数据。 此数据可采用不同的形式,例如分类形式或表格形式。 若要生成类似于条形图的分类视觉对象,使用 上的“分类”属性。
每当视觉对象更新时,都会调用此函数。
/**
* Function that converts queried data into a viewmodel that will be used by the visual.
*
* @function
* @param {VisualUpdateOptions} options - Contains references to the size of the container
* and the dataView which contains all the data
* the visual had queried.
* @param {IVisualHost} host - Contains references to the host which contains services
*/
function createSelectorDataPoints(options: VisualUpdateOptions, host: IVisualHost): BarChartDataPoint[] {
const barChartDataPoints: BarChartDataPoint[] = []
const dataViews = options.dataViews;
if (!dataViews
|| !dataViews[0]
|| !dataViews[0].categorical
|| !dataViews[0].categorical.categories
|| !dataViews[0].categorical.categories[0].source
|| !dataViews[0].categorical.values
) {
return barChartDataPoints;
}
const categorical = dataViews[0].categorical;
const category = categorical.categories[0];
const dataValue = categorical.values[0];
const colorPalette: ISandboxExtendedColorPalette = host.colorPalette;
const strokeColor: string = getColumnStrokeColor(colorPalette);
const strokeWidth: number = getColumnStrokeWidth(colorPalette.isHighContrast);
for (let i = 0, len = Math.max(category.values.length, dataValue.values.length); i < len; i++) {
const color: string = getColumnColorByIndex(category, i, colorPalette);
const selectionId: ISelectionId = host.createSelectionIdBuilder()
.withCategory(category, i)
.createSelectionId();
barChartDataPoints.push({
color,
strokeColor,
strokeWidth,
selectionId,
value: dataValue.values[i],
category: `${category.values[i]}`,
});
}
return barChartDataPoints;
}
注意
barChart.ts 文件中接下来的几个函数处理颜色和创建 X 轴。 这些是可选的函数,将在本教程中进一步讨论。 本教程将从 IVisual 函数继续。
呈现视觉对象
定义数据后,我们使用实现 IVisual 接口的 BarChart 类呈现视觉对象。 IVisual 页上介绍了 接口。 它包含一个创建视觉对象的 constructor 方法,以及一个每次视觉对象重载都会调用的 update 方法。
在呈现视觉对象之前,必须声明类的成员:
export class BarChart implements IVisual {
private svg: Selection<SVGSVGElement>;
private host: IVisualHost;
private barContainer: Selection<SVGElement>;
private xAxis: Selection<SVGGElement>;
private barDataPoints: BarChartDataPoint[];
private formattingSettings: BarChartSettingsModel;
private formattingSettingsService: FormattingSettingsService;
private barSelection: Selection<BaseType>;
static Config = {
xScalePadding: 0.1,
solidOpacity: 1,
transparentOpacity: 1,
margins: {
top: 0,
right: 0,
bottom: 25,
left: 30,
},
xAxisFontMultiplier: 0.04,
};
}
构造视觉对象
首次呈现视觉对象时,只调用一次构造函数。 它为条形图和 X 轴创建空的 SVG 容器。 注意,它使用 d3 库来呈现 SVG。
/**
* Creates instance of BarChart. This method is only called once.
*
* @constructor
* @param {VisualConstructorOptions} options - Contains references to the element that will
* contain the visual and a reference to the host
* which contains services.
*/
constructor(options: VisualConstructorOptions) {
this.host = options.host;
//Creating the formatting settings service.
const localizationManager = this.host.createLocalizationManager();
this.formattingSettingsService = new FormattingSettingsService(localizationManager);
this.svg = d3Select(options.element)
.append('svg')
.classed('barChart', true);
this.barContainer = this.svg
.append('g')
.classed('barContainer', true);
this.xAxis = this.svg
.append('g')
.classed('xAxis', true);
}
更新视觉对象
每次视觉对象的大小或它的一个值发生更改时,都会调用 update 方法。
缩放
需缩放视觉对象,使条数和当前值适合视觉对象的定义宽度和高度限制。 这类似于教程中的 update 方法。
为了计算规模,我们使用之前从 scaleLinear 库中导入的 scaleBand 和 d3-scale 方法。
options.dataViews[0].categorical.values[0].maxLocal 值保留所有当前数据点的最大值。 此值用于确定 Y 轴的高度。 X 轴宽度的缩放由 barchartdatapoint 接口中绑定到视觉对象的类别数决定。
对于呈现 X 轴的情况,此视觉对象还会处理断字,以防没有足够的空间在 X 轴上写出整个名称。
其他更新功能
除了缩放外,此 update 方法还会处理所选项和颜色。 这些功能是可选功能,稍后将进行讨论:
/**
* Updates the state of the visual. Every sequential databinding and resize will call update.
*
* @function
* @param {VisualUpdateOptions} options - Contains references to the size of the container
* and the dataView which contains all the data
* the visual had queried.
*/
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
this.formattingSettings = this.formattingSettingsService.populateFormattingSettingsModel(BarChartSettingsModel, options.dataViews?.[0]);
this.barDataPoints = createSelectorDataPoints(options, this.host);
this.formattingSettings.populateColorSelector(this.barDataPoints);
const width = options.viewport.width;
let height = options.viewport.height;
this.svg
.attr("width", width)
.attr("height", height);
if (this.formattingSettings.enableAxis.show.value) {
const margins = BarChart.Config.margins;
height -= margins.bottom;
}
this.xAxis
.style("font-size", Math.min(height, width) * BarChart.Config.xAxisFontMultiplier)
.style("fill", this.formattingSettings.enableAxis.fill.value.value);
const yScale: ScaleLinear<number, number> = scaleLinear()
.domain([0, <number>options.dataViews[0].categorical.values[0].maxLocal])
.range([height, 0]);
const xScale: ScaleBand<string> = scaleBand()
.domain(this.barDataPoints.map(d => d.category))
.rangeRound([0, width])
.padding(0.2);
const xAxis: Axis<string> = axisBottom(xScale);
this.xAxis.attr('transform', 'translate(0, ' + height + ')')
.call(xAxis)
.attr("color", this.formattingSettings.enableAxis.fill.value.value);
const textNodes: Selection<SVGElement> = this.xAxis.selectAll("text");
BarChart.wordBreak(textNodes, xScale.bandwidth(), height);
this.barSelection = this.barContainer
.selectAll('.bar')
.data(this.barDataPoints);
const barSelectionMerged = this.barSelection
.enter()
.append('rect')
.merge(<any>this.barSelection);
barSelectionMerged.classed('bar', true);
barSelectionMerged
.attr("width", xScale.bandwidth())
.attr("height", (dataPoint: BarChartDataPoint) => height - yScale(<number>dataPoint.value))
.attr("y", (dataPoint: BarChartDataPoint) => yScale(<number>dataPoint.value))
.attr("x", (dataPoint: BarChartDataPoint) => xScale(dataPoint.category))
.style("fill", (dataPoint: BarChartDataPoint) => dataPoint.color)
.style("stroke", (dataPoint: BarChartDataPoint) => dataPoint.strokeColor)
.style("stroke-width", (dataPoint: BarChartDataPoint) => `${dataPoint.strokeWidth}px`);
this.barSelection
.exit()
.remove();
}
private static wordBreak(
textNodes: Selection<SVGElement>,
allowedWidth: number,
maxHeight: number
) {
textNodes.each(function () {
textMeasurementService.wordBreak(
this,
allowedWidth,
maxHeight);
});
}
使用格式设置模型 Utils 填充属性窗格
IVisual 函数中的最后一个方法是 getFormattingModel。 此方法生成并返回包含所有格式窗格组件和属性的新式“格式窗格格式设置模型”对象。 然后,它将对象置于“格式”窗格中。 在本例中,我们将根据 capabilities.json 文件中的“对象”创建 enableAxis 和 colorSelector 的格式卡片,其中包括 show 和 fill 的格式设置属性。 若要在“属性”窗格中为每个类别添加颜色选取器,请在 上添加一个 for 循环,并为每个类别向格式设置模型添加新的颜色选取器格式属性。
要生成格式设置模型,开发人员应熟悉其所有组件。 查看 Format Pane 中格式窗格的组件。 查看getFormattingModel中 FormattingModel utils 的 API。
下载该文件并将其保存到 /src 文件夹。 在格式设置类中声明格式设置属性及其值:
import { formattingSettings } from "powerbi-visuals-utils-formattingmodel";
import { BarChartDataPoint } from "./barChart";
import Card = formattingSettings.SimpleCard;
import Model = formattingSettings.Model;
import Slice = formattingSettings.Slice;
import ColorPicker = formattingSettings.ColorPicker;
import ToggleSwitch = formattingSettings.ToggleSwitch;
/**
* Enable Axis Formatting Card
*/
class EnableAxisCardSettings extends Card {
show = new ToggleSwitch({
name: "show",
displayName: undefined,
value: false,
});
fill = new ColorPicker({
name: "fill",
displayName: "Color",
value: { value: "#000000" }
});
topLevelSlice: ToggleSwitch = this.show;
name: string = "enableAxis";
displayName: string = "Enable Axis";
slices: Slice[] = [this.fill];
}
/**
* Color Selector Formatting Card
*/
class ColorSelectorCardSettings extends Card {
name: string = "colorSelector";
displayName: string = "Data Colors";
// slices will be populated in barChart settings model `populateColorSelector` method
slices: Slice[] = [];
}
/**
* BarChart formatting settings model class
*/
export class BarChartSettingsModel extends Model {
// Create formatting settings model formatting cards
enableAxis = new EnableAxisCardSettings();
colorSelector = new ColorSelectorCardSettings();
cards: Card[] = [this.enableAxis, this.colorSelector];
/**
* populate colorSelector object categories formatting properties
* @param dataPoints
*/
populateColorSelector(dataPoints: BarChartDataPoint[]) {
const slices: Slice[] = this.colorSelector.slices;
if (dataPoints) {
dataPoints.forEach(dataPoint => {
slices.push(new ColorPicker({
name: "fill",
displayName: dataPoint.category,
value: { value: dataPoint.color },
selector: dataPoint.selectionId.getSelector(),
}));
});
}
}
}
在视觉对象的构造函数方法中生成和创建格式设置服务模型。 格式设置服务接收 barChart 格式设置,并将其转换为 API 中返回的 FormattingModel 对象。
若要使用本地化功能,请将本地化管理器添加到格式设置服务。
import { FormattingSettingsService } from "powerbi-visuals-utils-formattingmodel";
// ...
// declare utils formatting settings service
private formattingSettingsService: FormattingSettingsService;
//...
constructor(options: VisualConstructorOptions) {
this.host = options.host;
const localizationManager = this.host.createLocalizationManager();
this.formattingSettingsService = new FormattingSettingsService(localizationManager);
// Add here rest of your custom visual constructor code
}
使用更新 API 更新格式化设置模型。 每次更改属性窗格中的格式设置属性时都调用更新 API。 创建条形图选择器数据点,并在格式化设置模型中填充它们:
// declare formatting settings model for bar chart
private formattingSettings: BarChartSettingsModel;
// ...
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
this.formattingSettings = this.formattingSettingsService.populateFormattingSettingsModel(BarChartSettingsModel, options.dataViews[0]);
this.barDataPoints = createSelectorDataPoints(options, this.host);
this.formattingSettings.populateColorSelector(this.barDataPoints);
// Add the rest of your custom visual update API code here
}
最后,新 API getFormattingModel 是一个简单的代码行,它使用在上述更新 API 中创建的格式设置服务和当前格式设置模型。
public getFormattingModel(): powerbi.visuals.FormattingModel {
return this.formattingSettingsService.buildFormattingModel(this.formattingSettings);
}
(可选)呈现 X 轴(静态对象)
可以将对象添加到“属性”窗格中以进一步自定义视觉对象。 这些自定义项可以是用户界面更改,或与查询的数据相关的更改。
可在“属性”窗格中打开或关闭这些对象。
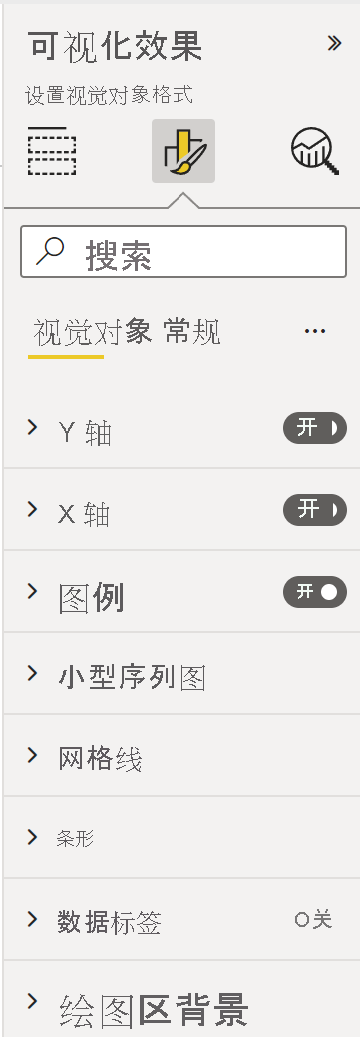
此示例将条形图上的 X 轴呈现为静态对象。
我们已将 enableAxis 属性添加到 capabilities 文件和 barChartSettings 接口。
(可选)添加颜色(数据绑定对象)
数据绑定对象类似于静态对象,但通常处理数据选择。 例如,可使用数据绑定对象以交互方式选择与每个数据点关联的颜色。
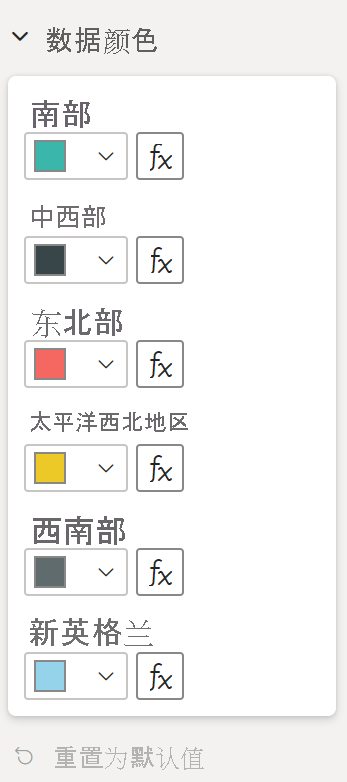
已在 capabilities 文件中定义了 colorSelector 对象。
每个数据点以一种不同颜色表示。 我们在 BarChartDataPoint 接口中包含了颜色,并在 IVisualHost 中定义每个数据点时为其分配了默认颜色。
function getColumnColorByIndex(
category: DataViewCategoryColumn,
index: number,
colorPalette: ISandboxExtendedColorPalette,
): string {
if (colorPalette.isHighContrast) {
return colorPalette.background.value;
}
const defaultColor: Fill = {
solid: {
color: colorPalette.getColor(`${category.values[index]}`).value,
}
};
const prop: DataViewObjectPropertyIdentifier = {
objectName: "colorSelector",
propertyName: "fill"
};
let colorFromObjects: Fill;
if(category.objects?.[index]){
colorFromObjects = dataViewObjects.getValue(category?.objects[index], prop);
}
return colorFromObjects?.solid.color ?? defaultColor.solid.color;
}
function getColumnStrokeColor(colorPalette: ISandboxExtendedColorPalette): string {
return colorPalette.isHighContrast
? colorPalette.foreground.value
: null;
}
function getColumnStrokeWidth(isHighContrast: boolean): number {
return isHighContrast
? 2
: 0;
}
colorPalette 函数中的 createSelectorDataPoints 服务管理这些颜色。 由于 createSelectorDataPoints 会循环访问每个数据点,因此它是分配分类对象(如颜色)的理想位置。
有关如何向条形图添加颜色的更详细说明,请转到向 Power BI 视觉对象添加颜色。
注意
验证你的最终 barChart.ts 文件类似于此 barChart.ts 源代码,或者下载 barChart.ts 源代码并用它替换你的文件 。
测试视觉对象
在 Power BI Server 中运行视觉对象,查看其外观:
在 PowerShell 中,导航到项目的文件夹并启动开发应用。
pbiviz start托管在计算机上的视觉对象现在正在运行。
重要
在本教程结束之前,请不要关闭 PowerShell 窗口。 若要停止运行视觉对象,请输入 Ctrl+C,若系统提示终止批处理作业,请输入 Y,然后按 Enter。
通过从“可视化效果”窗格中选择“开发人员视觉对象”,查看 Power BI 服务中的视觉对象 。
向视觉对象添加数据
拖动视觉对象的边缘可更改大小,并注意规模的调整方式。
打开和关闭 X 轴。

更改不同类别的颜色。
添加其他功能
可通过添加更多功能来进一步自定义视觉对象。 可添加用于增加视觉对象的功能、增强其观感或让用户更好地控制其外观的功能。 例如,你能够:
打包视觉对象
将视觉对象加载到 Power BI Desktop 中或者在 Power BI 视觉对象库中与社区共享视觉对象之前,必须将视觉对象打包。
要准备用于共享的视觉对象,请按照打包 Power BI 视觉对象中的说明操作。
注意
有关包含更多功能(包括工具提示和上下文菜单)的条形图的完整源代码,请参阅 Power BI 视觉对象示例条形图。