你当前正在访问 Microsoft Azure Global Edition 技术文档网站。 如果需要访问由世纪互联运营的 Microsoft Azure 中国技术文档网站,请访问 https://docs.azure.cn。
开始在 Java 中使用中继混合连接 HTTP 请求
在本快速入门中,请创建 Java 发送者和接收者应用程序,用于通过 HTTP 协议发送和接收消息。 这些应用程序使用 Azure 中继的混合连接功能。 若要了解 Azure 中继的常规信息,请参阅 Azure 中继。
在本快速入门中,你将执行以下步骤:
- 使用 Azure 门户创建中继命名空间。
- 使用 Azure 门户在该命名空间中创建混合连接。
- 编写服务器(侦听器)控制台应用程序,用于接收消息。
- 编写客户端(发送方)控制台应用程序,用于发送消息。
- 运行应用程序。
先决条件
- Java。 确保运行的是 JDK 1.8+
- Maven。 确保已安装 Maven
- Azure 中继 SDK。 评审 Java SDK
- Azure 订阅。 如果没有订阅,请在开始之前创建一个免费帐户。
使用 Azure 门户创建命名空间
登录 Azure 门户。
在左侧菜单中,选择“所有服务” 。 选择“集成”,搜索“中继”,将鼠标移到“中继”上方,然后选择“创建”。
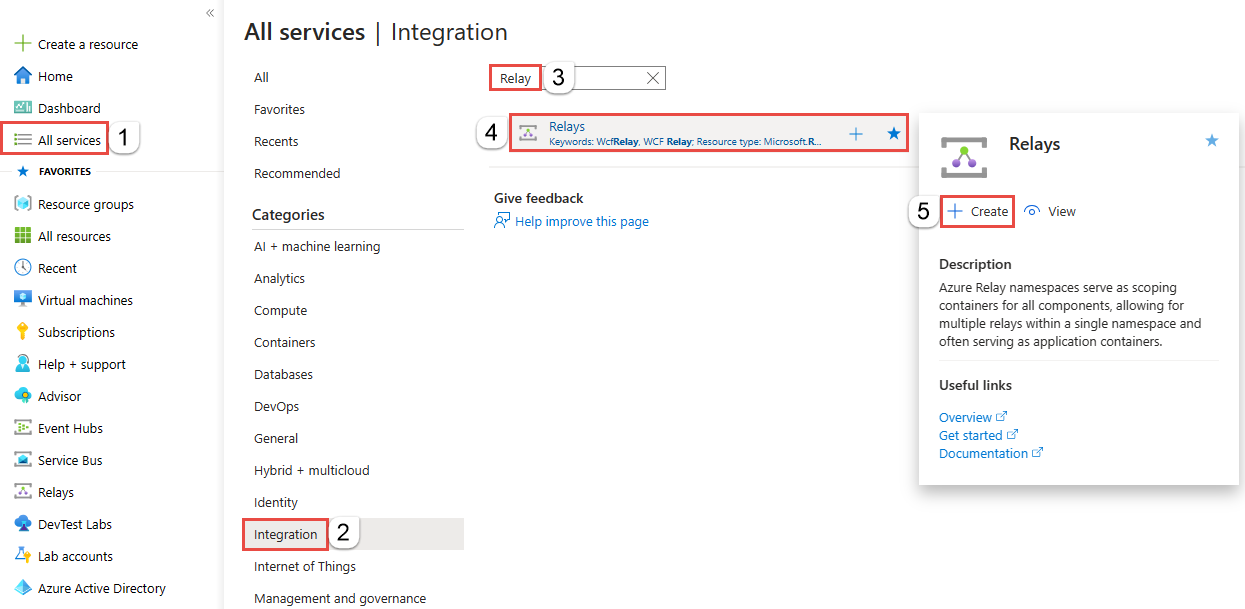
在“创建命名空间”页上,执行以下步骤:
选择要在其中创建命名空间的 Azure 订阅。
对于资源组,选择一个要在其中放置命名空间的现有资源组,或创建一个新资源组。
输入中继命名空间的名称。
选择应托管该命名空间的区域。
在页面底部选择查看 + 创建。

在“查看 + 创建”页面上,选择“创建”。
几分钟后,将看到该命名空间的“中继”页面。

获取管理凭据
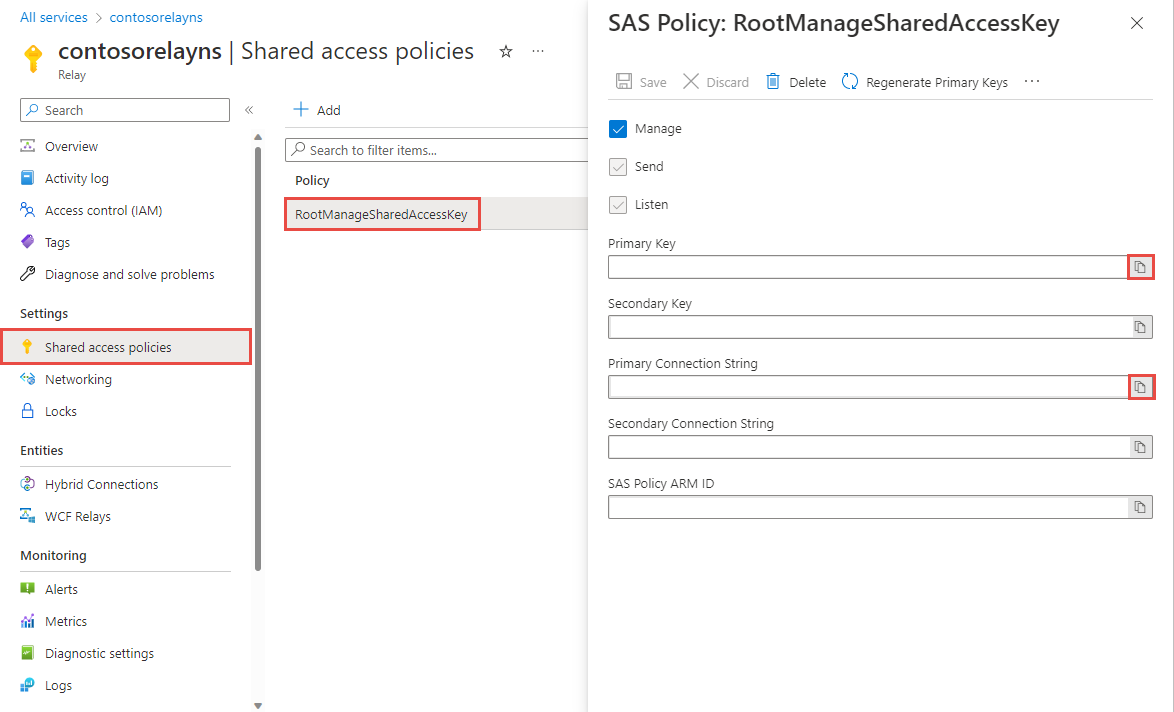
在“中继”页上,选择左侧菜单的“共享访问策略”。
在“共享访问策略”页,选择“RootManageSharedAccessKey” 。
在“SAS 策略:RootManageSharedAccessKey”下,选择“主连接字符串”旁边的“复制”按钮。 此操作会将连接字符串复制到剪贴板,供以后使用。 将此值粘贴到记事本或其他某个临时位置。
重复上述步骤,将主密钥的值复制和粘贴到临时位置,供以后使用。
使用 Azure 门户创建混合连接
在命名空间的“中继”页上,按照以下步骤创建混合连接。
请在左侧菜单中的“实体”下选择“混合连接”,然后选择“+ 混合连接”。
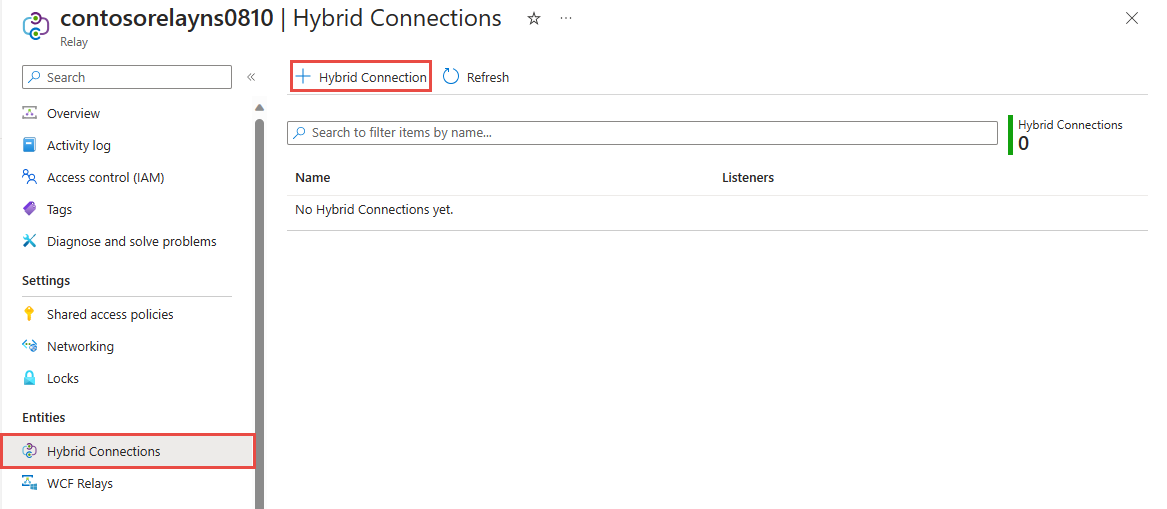
在“创建混合连接”页上,输入混合连接的名称,然后选择“创建”。

创建服务器应用程序(侦听程序)
若要侦听和接收来自中继的消息,请编写 Java 控制台应用程序。
创建 Java 应用程序
如果创建中继时已禁用“需要客户端授权”选项,可使用任何浏览器向混合连接 URL 发送请求。 若要访问受保护的终结点,需在 ServiceBusAuthorization 标头中创建并传递令牌,如下所示。
下面是一个简单的 Maven 项目结构和一个 Java 类,该类演示如何使用 Azure 中继库通过客户端授权将请求发送到混合连接 URL。
添加中继包
修改 maven 应用程序包中的 pom.xml 文件,以包括 Azure 中继包。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft.azure</groupId>
<artifactId>azure-relay</artifactId>
<version>0.0.6</version>
</dependency>
在 mvn 项目中运行 mvn dependency:copy-dependencies -DoutputDirectory=lib,以在项目的 lib 目录中添加依赖项 jar 文件。 它导入 azure-relay mvn 包的所有依赖项。 此包提供用于构造中继统一资源标识符 (URI) 和令牌的函数。
编写一些代码来发送消息
将依赖项 jar 文件添加到
Listener.java文件的 ClassPath。javac -cp lib/* src/main/java/com/example/listener/Listener.Java导入
Listener.java类中的依赖项。import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.URI; import java.net.URISyntaxException; import java.util.Scanner; import com.microsoft.azure.relay.HybridConnectionListener; import com.microsoft.azure.relay.RelayConnectionStringBuilder; import com.microsoft.azure.relay.RelayedHttpListenerResponse; import com.microsoft.azure.relay.TokenProvider;将以下
constants添加到createConnectionStringjava 函数Listener.java文件的顶部,以获取混合连接详细信息。public static String createConnectionString(){ StringBuilder connectionString = new StringBuilder(); connectionString.append("Endpoint=sb://"); connectionString.append("{namespace}"); connectionString.append(".servicebus.windows.net/;SharedAccessKeyName="); connectionString.append("{keyrule}"); connectionString.append(";SharedAccessKey="); connectionString.append("{key}"); connectionString.append(";EntityPath="); connectionString.append("{path}"); return connectionString.toString(); }将括号中的占位符替换为在创建混合连接时获得的值。
namespace- 中继命名空间。 请务必使用完全限定的命名空间名称,例如{namespace}.servicebus.windows.net。path- 混合连接的名称。keyrule- 共享访问策略密钥的名称,默认为RootManageSharedAccessKey。nst key- 先前保存的命名空间的主密钥。
将以下代码添加到
Listener.java文件。 main 函数应类似于以下代码:public static void main( String[] args ) throws URISyntaxException { String CONNECTION_STRING_ENV_VARIABLE_NAME = createConnectionString(); RelayConnectionStringBuilder connectionParams = new RelayConnectionStringBuilder(CONNECTION_STRING_ENV_VARIABLE_NAME); TokenProvider tokenProvider = TokenProvider.createSharedAccessSignatureTokenProvider( connectionParams.getSharedAccessKeyName(), connectionParams.getSharedAccessKey()); HybridConnectionListener listener = new HybridConnectionListener(new URI(connectionParams.getEndpoint().toString() + connectionParams.getEntityPath()), tokenProvider); // The "context" object encapsulates both the incoming request and the outgoing response listener.setRequestHandler((context) -> { String receivedText = ""; if (context.getRequest().getInputStream() != null) { try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(context.getRequest().getInputStream(), "UTF8"))) { StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); String inputLine; while ((inputLine = reader.readLine()) != null) { builder.append(inputLine); } receivedText = builder.toString(); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } System.out.println("requestHandler received " + receivedText); RelayedHttpListenerResponse response = context.getResponse(); response.setStatusCode(202); response.setStatusDescription("OK"); try { response.getOutputStream().write(("Echo: " + receivedText).getBytes()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // The context MUST be closed for the message to be sent response.close(); }); listener.openAsync().join(); Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Press ENTER to terminate this program."); in.nextLine(); listener.close(); in.close(); }Listener.java文件的内容应如下所示:package com.example.listener; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.net.URI; import java.net.URISyntaxException; import java.util.Scanner; import com.microsoft.azure.relay.HybridConnectionListener; import com.microsoft.azure.relay.RelayConnectionStringBuilder; import com.microsoft.azure.relay.RelayedHttpListenerResponse; import com.microsoft.azure.relay.TokenProvider; public class Listener { public static String createConnectionString(){ StringBuilder connectionString = new StringBuilder(); connectionString.append("Endpoint=sb://"); connectionString.append("{namespace}"); connectionString.append(".servicebus.windows.net/;SharedAccessKeyName="); connectionString.append("{keyrule}"); connectionString.append(";SharedAccessKey="); connectionString.append("{key}"); connectionString.append(";EntityPath="); connectionString.append("{path}"); return connectionString.toString(); } public static void main( String[] args ) throws URISyntaxException { String CONNECTION_STRING_ENV_VARIABLE_NAME = createConnectionString(); RelayConnectionStringBuilder connectionParams = new RelayConnectionStringBuilder(CONNECTION_STRING_ENV_VARIABLE_NAME); TokenProvider tokenProvider = TokenProvider.createSharedAccessSignatureTokenProvider( connectionParams.getSharedAccessKeyName(), connectionParams.getSharedAccessKey()); HybridConnectionListener listener = new HybridConnectionListener(new URI(connectionParams.getEndpoint().toString() + connectionParams.getEntityPath()), tokenProvider); // The "context" object encapsulates both the incoming request and the outgoing response listener.setRequestHandler((context) -> { String receivedText = ""; if (context.getRequest().getInputStream() != null) { try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(context.getRequest().getInputStream(), "UTF8"))) { StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); String inputLine; while ((inputLine = reader.readLine()) != null) { builder.append(inputLine); } receivedText = builder.toString(); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage()); } } System.out.println("requestHandler received " + receivedText); RelayedHttpListenerResponse response = context.getResponse(); response.setStatusCode(202); response.setStatusDescription("OK"); try { response.getOutputStream().write(("Echo: " + receivedText).getBytes()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // The context MUST be closed for the message to be sent response.close(); }); listener.openAsync().join(); Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Press ENTER to terminate this program."); in.nextLine(); listener.close(); in.close(); } }
创建客户端应用程序(发送程序)
若要将消息发送到中继,可使用任何 HTTP 客户端,或编写 Java 控制台应用程序。
创建 Java 应用程序
如果创建中继时已禁用“需要客户端授权”选项,可使用任何浏览器向混合连接 URL 发送请求。 若要访问受保护的终结点,需在 ServiceBusAuthorization 标头中创建并传递令牌,如下所示。
下面是一个简单的 Maven 项目结构和一个 Java 类,该类演示如何使用 Azure 中继库通过客户端授权将请求发送到混合连接 URL。
添加中继包
修改 maven 应用程序包中的 pom.xml 文件,以包括 Azure 中继包。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft.azure</groupId>
<artifactId>azure-relay</artifactId>
<version>0.0.6</version>
</dependency>
在 mvn 项目中运行 mvn dependency:copy-dependencies -DoutputDirectory=lib,以在项目的 lib 目录中添加依赖项 jar 文件。 它也导入 azure-relay mvn 包的所有依赖项。 此包提供用于构造中继统一资源标识符 (URI) 和令牌的函数。
编写一些代码来发送消息
将依赖项 jar 文件添加到
Sender.java文件的 ClassPath。javac -cp lib/* src/main/java/com/example/sender/Sender.Java导入
Sender.java类中的依赖项。import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; import java.net.HttpURLConnection; import java.net.MalformedURLException; import java.net.URL; import java.time.Duration; import java.util.Scanner; import com.microsoft.azure.relay.RelayConnectionStringBuilder; import com.microsoft.azure.relay.TokenProvider;将以下
constants添加到createConnectionStringjava 函数Sender.java文件的顶部,以获取混合连接详细信息。public static String createConnectionString(){ StringBuilder connectionString = new StringBuilder(); connectionString.append("Endpoint=sb://"); connectionString.append("{namespace}"); connectionString.append(".servicebus.windows.net/;SharedAccessKeyName="); connectionString.append("{keyrule}"); connectionString.append(";SharedAccessKey="); connectionString.append("{key}"); connectionString.append(";EntityPath="); connectionString.append("{path}"); return connectionString.toString(); }将括号中的占位符替换为在创建混合连接时获得的值。
namespace- 中继命名空间。 请务必使用完全限定的命名空间名称,例如{namespace}.servicebus.windows.net。path- 混合连接的名称。keyrule- 共享访问策略密钥的名称,默认为RootManageSharedAccessKey。nst key- 先前保存的命名空间的主密钥。
将以下代码添加到
Sender.java文件。 main 函数应类似于以下代码。public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String CONNECTION_STRING_ENV_VARIABLE_NAME = createConnectionString(); if (CONNECTION_STRING_ENV_VARIABLE_NAME == null || CONNECTION_STRING_ENV_VARIABLE_NAME.isEmpty()){ System.err.println("Connection string is null or empty. Please check your createConnectionString method."); return; } RelayConnectionStringBuilder connectionParams = new RelayConnectionStringBuilder(CONNECTION_STRING_ENV_VARIABLE_NAME); TokenProvider tokenProvider = TokenProvider.createSharedAccessSignatureTokenProvider( connectionParams.getSharedAccessKeyName(), connectionParams.getSharedAccessKey()); URL url = buildHttpConnectionURL(connectionParams.getEndpoint().toString(), connectionParams.getEntityPath()); String tokenString = tokenProvider.getTokenAsync(url.toString(), Duration.ofHours(1)).join().getToken(); Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); while (true) { System.out.println("Press ENTER to terminate this program."); String message = in.nextLine(); int value = System.in.read(); if (value == '\n' || value == '\r') { System.out.println("Terminating the program..."); break;} // Starting a HTTP connection to the listener HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection(); // Sending an HTTP request to the listener // To send a message body, use POST conn.setRequestMethod((message == null || message.length() == 0) ? "GET" : "POST"); conn.setRequestProperty("ServiceBusAuthorization", tokenString); conn.setDoOutput(true); OutputStreamWriter out = new OutputStreamWriter(conn.getOutputStream()); out.write(message, 0, message.length()); out.flush(); out.close(); // Reading the HTTP response String inputLine; BufferedReader reader = null; StringBuilder responseBuilder = new StringBuilder(); try { InputStream inputStream = conn.getInputStream(); reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream)); System.out.println("status code: " + conn.getResponseCode()); while ((inputLine = reader.readLine()) != null) { responseBuilder.append(inputLine); } System.out.println("received back " + responseBuilder.toString()); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("The listener is offline or could not be reached."); break; } finally { if (reader != null) { reader.close(); } } } in.close(); } static URL buildHttpConnectionURL(String endpoint, String entity) throws MalformedURLException { StringBuilder urlBuilder = new StringBuilder(endpoint + entity); // For HTTP connections, the scheme must be https:// int schemeIndex = urlBuilder.indexOf("://"); if (schemeIndex < 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid scheme from the given endpoint."); } urlBuilder.replace(0, schemeIndex, "https"); return new URL(urlBuilder.toString()); }Sender.java文件的内容应如下所示:package com.example.sender; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.OutputStreamWriter; import java.net.HttpURLConnection; import java.net.MalformedURLException; import java.net.URL; import java.time.Duration; import java.util.Scanner; import com.microsoft.azure.relay.RelayConnectionStringBuilder; import com.microsoft.azure.relay.TokenProvider; public class Sender { public static String createConnectionString(){ StringBuilder connectionString = new StringBuilder(); connectionString.append("Endpoint=sb://"); connectionString.append("{namespace}"); connectionString.append(".servicebus.windows.net/;SharedAccessKeyName="); connectionString.append("{keyrule}"); connectionString.append(";SharedAccessKey="); connectionString.append("{key}"); connectionString.append(";EntityPath="); connectionString.append("{path}"); return connectionString.toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String CONNECTION_STRING_ENV_VARIABLE_NAME = createConnectionString(); if (CONNECTION_STRING_ENV_VARIABLE_NAME == null || CONNECTION_STRING_ENV_VARIABLE_NAME.isEmpty()){ System.err.println("Connection string is null or empty. Please check your createConnectionString method."); return; } RelayConnectionStringBuilder connectionParams = new RelayConnectionStringBuilder(CONNECTION_STRING_ENV_VARIABLE_NAME); TokenProvider tokenProvider = TokenProvider.createSharedAccessSignatureTokenProvider( connectionParams.getSharedAccessKeyName(), connectionParams.getSharedAccessKey()); URL url = buildHttpConnectionURL(connectionParams.getEndpoint().toString(), connectionParams.getEntityPath()); String tokenString = tokenProvider.getTokenAsync(url.toString(), Duration.ofHours(1)).join().getToken(); Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); while (true) { System.out.println("Press ENTER to terminate this program."); String message = in.nextLine(); int value = System.in.read(); if (value == '\n' || value == '\r') { System.out.println("Terminating the program..."); break;} // Starting a HTTP connection to the listener HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection(); // Sending an HTTP request to the listener // To send a message body, use POST conn.setRequestMethod((message == null || message.length() == 0) ? "GET" : "POST"); conn.setRequestProperty("ServiceBusAuthorization", tokenString); conn.setDoOutput(true); OutputStreamWriter out = new OutputStreamWriter(conn.getOutputStream()); out.write(message, 0, message.length()); out.flush(); out.close(); // Reading the HTTP response String inputLine; BufferedReader reader = null; StringBuilder responseBuilder = new StringBuilder(); try { InputStream inputStream = conn.getInputStream(); reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream)); System.out.println("status code: " + conn.getResponseCode()); while ((inputLine = reader.readLine()) != null) { responseBuilder.append(inputLine); } System.out.println("received back " + responseBuilder.toString()); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("The listener is offline or could not be reached."); break; } finally { if (reader != null) { reader.close(); } } } in.close(); } static URL buildHttpConnectionURL(String endpoint, String entity) throws MalformedURLException { StringBuilder urlBuilder = new StringBuilder(endpoint + entity); // For HTTP connections, the scheme must be https:// int schemeIndex = urlBuilder.indexOf("://"); if (schemeIndex < 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid scheme from the given endpoint."); } urlBuilder.replace(0, schemeIndex, "https"); return new URL(urlBuilder.toString()); } }
注意
本文中的示例代码使用连接字符串对 Azure 中继命名空间进行身份验证,以简化教程。 建议在生产环境中使用 Microsoft Entra ID 身份验证,而不要使用更容易泄密的连接字符串或共享访问签名。 有关使用 Microsoft Entra ID 身份验证的详细信息和示例代码,请参阅使用 Microsoft Entra ID 对访问 Azure 中继实体的应用程序进行身份验证和授权和使用 Microsoft Entra ID 对访问 Azure 中继资源的托管标识进行身份验证。
运行应用程序
- 运行服务器应用程序:在 Java 命令提示符或应用程序类型处,键入
java -cp <jar_dependency_path> com.example.listener.Listener.java。 - 运行客户端应用程序:在 Java 命令提示符或应用程序类型处,键入
java -cp <jar_dependency_path> com.example.sender.Sender.java,并输入某些文本。 - 确保服务器应用程序控制台输出了客户端应用程序中输入的文本。
恭喜,现已使用 Java 创建端到端混合连接应用程序!
后续步骤
在本快速入门中,你创建了 Java 客户端和服务器应用程序,此类程序使用 HTTP 来发送和接收消息。 Azure 中继的混合连接功能也支持使用 WebSocket 发送和接收消息。 若要了解如何将 WebSocket 与 Azure 中继混合连接配合使用,请参阅 WebSocket 快速入门。
在本快速入门中,你使用了 Java 来创建客户端和服务器应用程序。 若要了解如何使用 .NET Framework 编写客户端和服务器应用程序,请参阅 .NET WebSocket 快速入门或 .NET HTTP 快速入门。