Automatic tuning in Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Managed Instance
Applies to:
Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Managed Instance
SQL database in Fabric
Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Managed Instance automatic tuning provides peak performance and stable workloads through continuous performance tuning based on AI and machine learning.
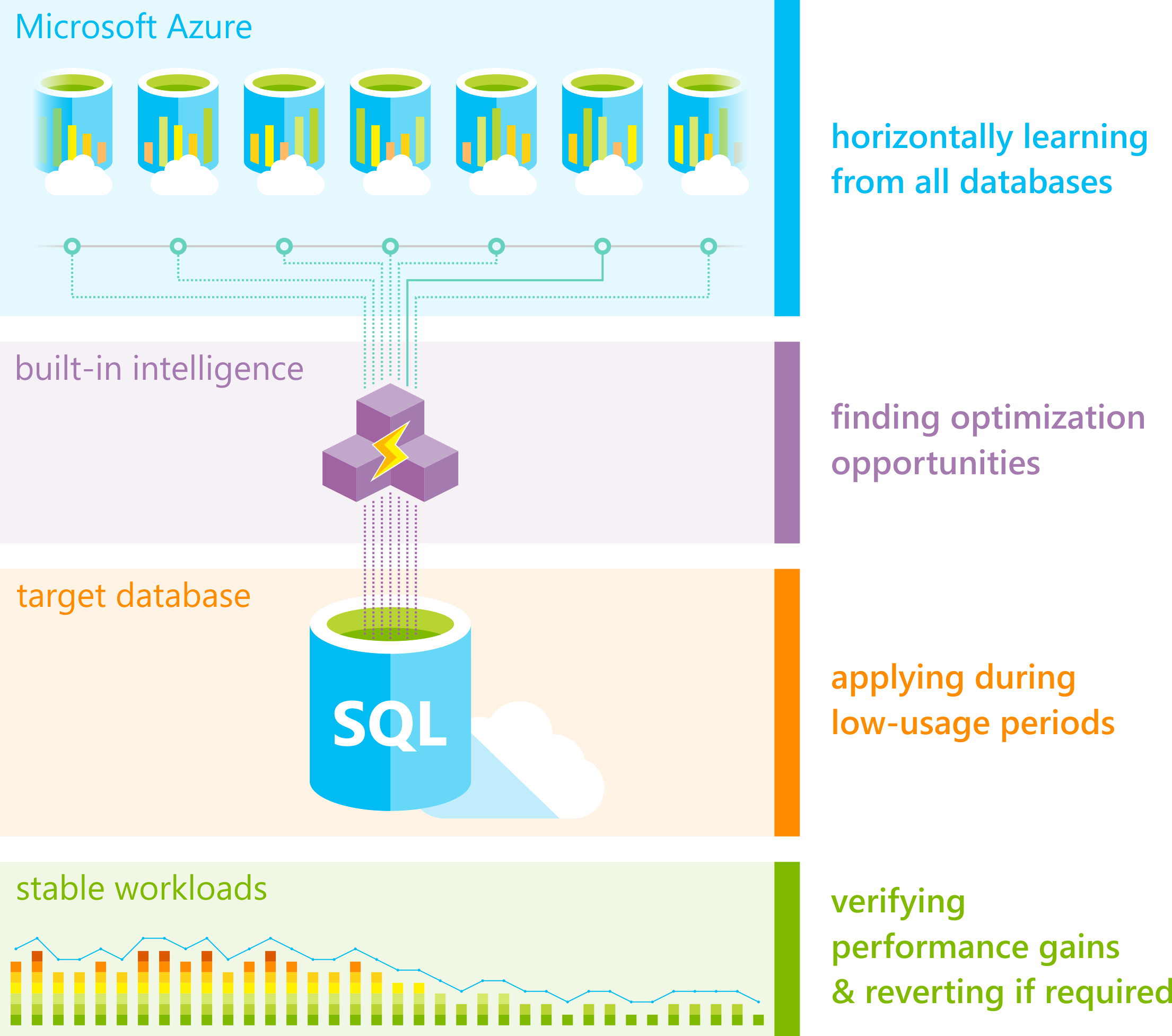
Automatic tuning is a fully managed intelligent performance service that uses built-in intelligence to continuously monitor queries executed on a database and automatically improve their performance. This is achieved through dynamically adapting a database to changing workloads and applying tuning recommendations. Automatic tuning learns horizontally from all databases on Azure through AI, and dynamically improves its tuning actions. The longer a database runs with automatic tuning on, the better it performs.
Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Managed Instance automatic tuning might be one of the most impactful features that you can enable to provide stable and peak performing database workloads.
Azure SQL automatic tuning shares its core logic with the SQL Server automatic tuning feature in the database engine. For additional technical information on the built-in intelligence mechanism, see SQL Server automatic tuning.
What can automatic tuning do for you
- Automated performance tuning of databases
- Automated verification of performance gains
- Automated rollback and self-correction
- Tuning history
- Tuning action Transact-SQL (T-SQL) scripts for manual deployments
- Scale out capability on hundreds of thousands of databases
- Positive impact to DevOps resources and the total cost of ownership
Safe, reliable, and proven
Tuning operations applied to databases are fully safe for performance of your most intense workloads. The system has been designed with care not to interfere with user workloads. Automated tuning recommendations are applied only at the times of a low utilization of CPU, Data IO, and Log IO. The system can also temporarily disable automatic tuning operations to protect workload performance. In such case, "Disabled by the system" message will be shown in Azure portal and in sys.database_automatic_tuning_options DMV. Automatic tuning is designed to give user workloads the highest resource priority.
Automatic tuning mechanisms are mature and have been perfected on several million databases running on Azure. Automated tuning operations applied are verified automatically to ensure there is a notable positive improvement to workload performance. If there is no improvement, or in the unlikely case performance regresses, changes made by automatic tuning are promptly reverted. Through the tuning history recorded, there exists a clear trace of tuning improvements made to each database in Azure SQL Database.
Enable automatic tuning
- Azure SQL Database: Enable automatic tuning in the Azure portal or by using the ALTER DATABASE T-SQL statement.
- Azure SQL Managed Instance: Enable automatic tuning by using the ALTER DATABASE T-SQL statement.
- SQL database in Microsoft Fabric: Enabled by default. For more information, see Performance Dashboard for SQL database in Microsoft Fabric.
Automatic tuning options
The automatic tuning options available in Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Managed Instance are:
| Automatic tuning option | Description | Single database and pooled database support | Instance database support |
|---|---|---|---|
| CREATE INDEX | Identifies indexes that may improve performance of your workload, creates indexes, and automatically verifies that performance of queries has improved. When recommending a new index, the system considers space available in the database. If index addition is estimated to increase space utilization to over 90% toward maximum data size, index recommendation is not generated. Once the system identifies a period of low utilization and starts to create an index, it will not pause or cancel this operation even if resource utilization unexpectedly increases. If index creation fails, it will be retried during a future period of low utilization. Index recommendations are not provided for tables where the clustered index or heap is larger than 10 GB. | Yes | No |
| DROP INDEX | Drops unused (over the last 90 days) and duplicate indexes. Unique indexes, including indexes supporting primary key and unique constraints, are never dropped. This option may be automatically disabled when queries with index hints are present in the workload, or when the workload performs partition switching. On Premium and Business Critical service tiers, this option will never drop unused indexes, but will drop duplicate indexes, if any. | Yes | No |
| FORCE LAST GOOD PLAN (automatic plan correction) | Identifies Azure SQL queries using an execution plan that is slower than the previous good plan, and forces queries to use the last known good plan instead of the regressed plan. | Yes | Yes |
Automatic tuning for Azure SQL Database
Automatic tuning for Azure SQL Database uses the CREATE INDEX, DROP INDEX, and FORCE_LAST_GOOD_PLAN database advisor recommendations to optimize your database performance. For more information, see Database advisor recommendations in the Azure portal, in PowerShell, and in the REST API.
You can either manually apply tuning recommendations using the Azure portal, or you can let automatic tuning autonomously apply tuning recommendations for you. The benefits of letting the system autonomously apply tuning recommendations for you is that it automatically validates there exists a positive gain to workload performance, and if there is no significant performance improvement detected or if performance regresses, the system automatically reverts the changes that were made. Depending on query execution frequency, the validation process can take from 30 minutes to 72 hours, taking longer for less frequently executing queries. If at any point during validation a regression is detected, changes are reverted immediately.
Important
In case you are applying tuning recommendations through T-SQL, the automatic performance validation and reversal mechanisms are not available. Recommendations applied in such way will remain active and shown in the list of tuning recommendations for 24-48 hours before the system automatically withdraws them. If you would like to remove a recommendation sooner, you can discard it from Azure portal.
Automatic tuning options can be independently enabled or disabled for each database, or they can be configured at the server-level and applied on every database that inherits settings from the server. By default, new servers inherit Azure defaults for automatic tuning settings. Azure defaults are set to FORCE_LAST_GOOD_PLAN enabled, CREATE_INDEX disabled, and DROP_INDEX disabled.
Configuring automatic tuning options on a server and inheriting settings for databases belonging to the parent server is the recommended method for configuring automatic tuning. It simplifies management of automatic tuning options for a large number of databases.
To learn about building email notifications for automatic tuning recommendations, see Email notifications for automatic tuning.
Automatic tuning for Azure SQL Managed Instance
Automatic tuning for SQL Managed Instance only supports FORCE LAST GOOD PLAN. For more information about configuring automatic tuning options through T-SQL, see Automatic tuning introduces automatic plan correction and Automatic plan correction.
Automatic tuning for SQL database in Microsoft Fabric
The automatic tuning option to CREATE INDEX is enabled automatically in SQL database in Microsoft Fabric.
Samples to enable
For more information, see ALTER DATABASE SET options.
To inherit the default configuration from the parent logical server, use the following T-SQL. In the Azure portal, this reflects the option to "Inherit from: Server".
ALTER DATABASE CURRENT SET AUTOMATIC_TUNING = INHERIT;
To enable the CREATE INDEX and DROP INDEX automatic tuning options, use the following T-SQL.
ALTER DATABASE CURRENT SET AUTOMATIC_TUNING (CREATE_INDEX = ON, DROP_INDEX = ON);
Automatic tuning history
For Azure SQL Database, the history of changes made by automatic tuning is retained for 21 days. It can be viewed in Azure portal on the Performance recommendations page for a database, or using PowerShell with the Get-AzSqlDatabaseRecommendedAction cmdlet. For longer retention, history data can also be streamed to several types of destinations by enabling the AutomaticTuning diagnostic setting.
Related content
- Read the blog post Artificial Intelligence tunes Azure SQL Database.
- Learn how automatic tuning works under the hood in Automatically indexing millions of databases in Microsoft Azure SQL Database.
- Learn how automatic tuning can proactively help you Diagnose and troubleshoot high CPU on Azure SQL Database