Set up and configure Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare
Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare includes solutions that are built on capabilities within Microsoft Dynamics 365, Microsoft 365, Microsoft Azure, and Microsoft Power Platform.
You deploy these solutions in Microsoft Cloud Solution Center. Solution Center provides a central place to deploy industry cloud solutions from Microsoft, including solutions that are part of Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare.
Solution Center simplifies the deployment process. It checks for requirements such as licenses, dependencies, and enables you to easily discover and deploy capabilities and solutions in Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare.
Prerequisites
- You must be a tenant admin, Dynamics 365 admin, or Power Platform admin to deploy Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare solutions.
- You must have licenses for the Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare solutions and apps that you’re deploying. If your organization doesn't have the necessary licenses, you're notified during the deployment process in Solution Center. To learn more, see Licensing for Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare.
- Learn more about compliance in Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare and ensure you use services that match your requirements.
Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare solutions
Here are the solutions that are part of Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare, along with deployment information for each solution. Keep in mind that:
- Some solutions have predeployment setup requirements.
- Some solutions require configuration or have more capabilities that you can set up after deployment.
| Solution | Dependencies |
|---|---|
| Care management | Dynamics 365 Customer Service* |
| Data integration toolkit | Power Apps |
| Unified patient view | Power Apps |
| Provider data model | Power Apps |
| Payor data model (preview) | Power Apps |
| Life sciences data model (preview) | Power Apps |
| Virtual Visits | Microsoft Teams |
| Text analytics for health | Azure subscription |
| Azure IoT for healthcare | Azure subscription |
| Azure Health Bot | Azure subscription |
| Azure Health Data Services | Azure subscription |
| Health document intelligence | Azure subscription |
*Dataverse, Power Apps, and Power Automate prerequisites are included in the Dynamics 365 dependency offering.
Important
Effective January 30, 2025, the following solutions will be retired and no longer supported:
- Patient insight cards
- Healthcare database templates
- Device data support in care management (preview)
- Patient population dashboard (preview)
- Healthcare data pipeline template
The following solutions won't be available for deployment via the Microsoft Cloud Solution Center. However, support will continue for existing customers.
- Patient access (and access portal)
- Home health
- Patient outreach - Outbound marketing and Patient outreach - Journeys
- Patient service center
For guidance on alternative implementations and customizing your healthcare platform to address different scenarios and specific requirements, see Build custom healthcare solutions using healthcare data solutions in Power Platform.
Have questions? Reach out to us at Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare.
Deploy solutions
Sign in to Solution Center, and then go to Solutions > Healthcare.
You can see a list of capabilities. From here, you can:
- Select Quick view to learn more about the capability and the solutions, apps, and services that are part of it.
- Select the capability card to view and deploy solutions for that capability. After you select a card, you can select All in the Filter by capability list to see all available solutions.
- For each solution, you can select Quick view to learn more about the solution, dependencies required to deploy it, and get links to more information.
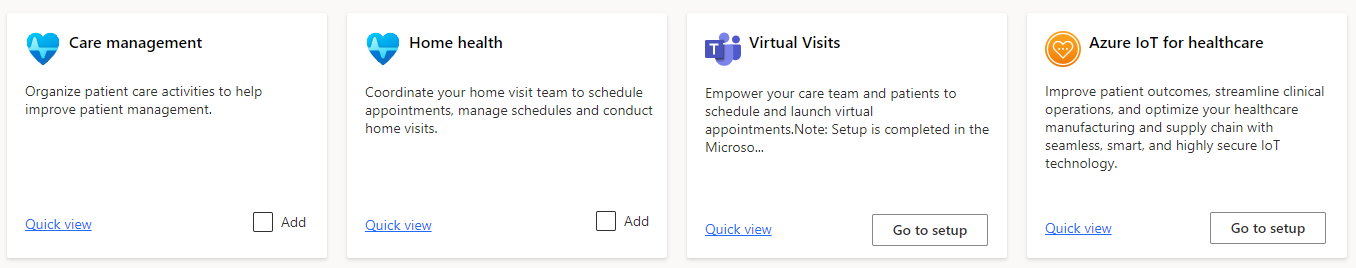
Select the solutions that you want to deploy. You can notice two types of deployment options, Add and Go to setup. Here's an example.
- Add: Solutions powered by Dynamics 365 have this option. Solution Center guides you through the deployment process and the solution is deployed in the background. For step-by-step guidance, see Deploy the Healthcare solutions powered by Dynamics 365.
- Go to setup: Solutions powered by Microsoft 365 and Azure have this option. Depending on the solution you select, you're either taken to the Microsoft 365 admin center or the Azure portal or site for setup.
To learn more, see Use Microsoft Cloud Solution Center.
Configure solutions
Some solutions require configuration after deployment and others have more capabilities that you can set up to enhance the solution.
Configure Dynamics 365 solutions
After deployment is completed, there may be some configuration tasks to do to configure your deployed solutions. Select View documentation next to the solution on the success page in Solution Center.
You can also configure other capabilities to enhance your solutions. For example, you can integrate with Azure Health Bot and Microsoft Teams, sync clinical data in your disparate systems with Azure Health Data Services, and so on.
To learn more, see Post-deployment configurations for healthcare solutions powered by Dynamics 365.
Set up Microsoft 365
You need the following features from Microsoft 365:
| Product or feature | Available with |
|---|---|
| Microsoft Teams | Microsoft 365 Enterprise SKUs and Frontline (E and F) SKUs |
| Microsoft 365 EHR integration. Integration is available with the Cerner and Epic platforms. | Part of the Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare add-on or as a stand-alone. |
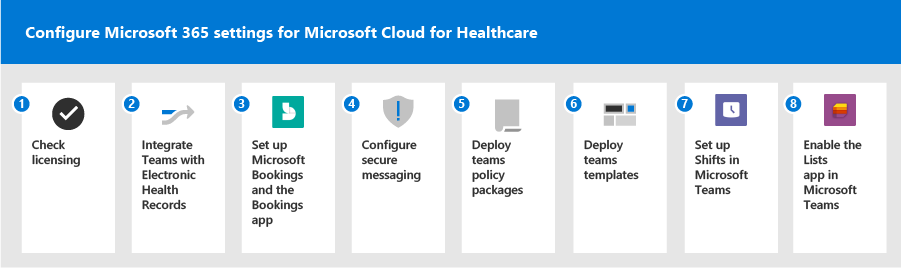
To set up these features and capabilities, you need to:
1. Check licensing
Ensure that you have Microsoft 365, added Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare, and checked your licensing. For more about Microsoft 365 and Microsoft Teams for Healthcare organizations, see Get started with Microsoft 365 for Healthcare organizations.
2. Integrate Teams with Electronic Health Records (EHR)
Microsoft Teams Electronic Healthcare Record (EHR) connector makes it easy for clinicians to launch a virtual patient appointment or consultation with another provider in Teams. Instead of navigating traditionally fragmented systems, clinicians can use the streamlined communication and collaboration features of Teams, so they can focus on providing the best possible care. If you have an EHR system already, you can connect Teams with that EHR system.
Go to the Microsoft 365 admin center to integrate Teams with your Cerner EHR system or Epic EHR system.
3. Set up the Virtual Appointments app or the Bookings app (optional)
If you aren't using an EHR system, you can use the Virtual Appointments app or the Bookings app in Teams to schedule and manage virtual appointments.
See Virtual Appointments with Microsoft Teams.
4. Configure secure messaging
Messaging policies are used to control which chat and channel messaging features are available to users in Teams. These policies are part of the overall deployment of secure messaging for healthcare organizations such as hospitals, clinics, or doctor's offices, where having a message picked up and acted upon in a timely manner is crucial, as is knowing when crucial messages are read.
Configure secure messaging in Teams.
5. Deploy Teams policy packages
A policy package in Teams is a collection of predefined policies and policy settings that you can assign to users who have similar roles in your organization. Policy packages simplify, streamline, and help provide consistency when managing policies. You can customize the settings of the policies in the package to suit the needs of your users. When you change the settings of policies in a policy package, all users who are assigned to that package get the updated settings.
Deploy Teams policy packages.
6. Deploy team templates
Team templates in Teams allow you to quickly and easily create teams by providing a predefined template of settings, channels, and preinstalled apps. For healthcare organizations, templates can be especially powerful, as they provide structure for users to become oriented with how to use Teams effectively. Templates also allow administrators to deploy consistent teams across their organizations.
Deploy team templates in Teams.
7. Enable the Shifts app in Teams (optional)
You can schedule your internal staff using the Shifts app in Teams. Staff members and managers can manage schedules and keep in touch, even on mobile devices.
Enable the Shifts app in Teams.
8. Enable the Lists app in Teams (optional)
The Lists app in Teams helps users in your healthcare organization track information, organize work, and manage workflows. With Lists, you can track data such as issues, inventory, patients, and more using customizable views, rules, and alerts to keep everyone on the team in sync. The Lists app includes a Patients list template created for healthcare.
Enable the Lists app in Teams.
Set up Azure capabilities
Set up the following Azure capabilities to use in Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare:
Azure Health Data Services: Azure Health Data Services lets you quickly connect existing PHI data sources, such as EHRs and research databases. Create new opportunities with analytics, machine learning, and actionable intelligence across your health data.
It powers the following capabilities in Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare:
- Remote patient monitoring
- Clinical analytics
- Operational analytics
- Data management
Azure Health Data Services can also help enhance the following solutions in Microsoft Cloud for Healthcare:
- Care management
- Data integration toolkit
To learn more, see Deploy Azure Health Data Services.
Azure AI Health Bot: The AI Health Bot Service is a cloud platform that empowers developers in healthcare organizations to build and deploy compliant, AI-powered virtual health assistants and health bots that help improve processes and reduce costs. You can use the AI Health Bot to handle patient questions automatically. To learn more, see Use Azure AI Health Bot.
Text Analytics for Health: Accelerate unstructured data insights and supercharge interoperability between healthcare organizations. To learn more, see What is Text Analytics for health in Azure Cognitive Service for Language?.
Azure IoT for healthcare: Improve patient outcomes, streamline clinical operations, and optimize your healthcare manufacturing and supply chain with seamless, smart, and highly secure IoT technology. To learn more, see Tutorial: Deploy and walk through the continuous patient monitoring application template.
Health document intelligence: Extract information from health documents and images to automate and digitize your business processes, enrich knowledge mining, and build solutions with Azure AI Document Intelligence. To learn more, go to What is Azure AI Document Intelligence?
Add users and assign roles
Dynamics 365 solutions
To access the healthcare solutions and apps you deployed, users must be assigned the appropriate security roles. To learn more, see Add users and assign security role.
Microsoft Teams
You manage access to Teams at the user level by assigning or removing a Teams license in the Microsoft 365 admin center. By default, when a licensing plan (for example, Microsoft 365 Enterprise E3) is assigned to a user, a Teams license is automatically assigned, and the user is enabled for Teams. To learn more, see Manage user access to Teams.
You can then set up teams and channels for your health teams and information workers. Admins can set them up in the Teams client or the Microsoft Teams admin center. When you set up a team, you add users and assign them user roles.
Teams has two user roles: owner and member. By default, a user who creates a new team is granted owner status. Team owners can make any member of their team a co-owner. Having multiple team owners lets you share the responsibilities of managing settings and membership, including invitations. To learn more, see Overview of teams and channels in Teams and Assign team owners and members in Teams.
For an overview of deploying Teams, see Teams deployment overview.