Create and manage routing rules in Omnichannel Administration
Omnichannel for Customer Service offers a suite of capabilities that extend the power of Dynamics 365 Customer Service Enterprise to enable organizations to instantly connect and engage with their customers across digital messaging channels. An additional license is required to access Omnichannel for Customer Service. For more information, see the Dynamics 365 Customer Service pricing overview and Dynamics 365 Customer Service pricing plan pages.
Important
- Support for the Omnichannel Administration app ended on April 30, 2022. We recommend that you use the Customer Service admin center app to configure the latest features, such as unified routing and voice channel. For more information about the deprecation announcement, see Omnichannel Administration app is deprecated.
- Additionally, workstreams that you create in the Omnichannel Administration app can't be modified in the Customer Service admin center app. You'll need to migrate the existing workstreams and then manage them in the Customer Service admin center app. More information: Migrate workstreams created in Omnichannel Administration
Introduction
Routing rules define how conversations are routed to different queues. Each routing rule has a condition and a destination queue. If the rule condition is evaluated as True, then the conversation is routed to the destination queue.
Important
Routing rules for entity records are defined at the entity record channel level. To learn more, see Entity records routing.
A single work stream can have multiple routing rules that are evaluated in the order of definition. For example, if a work stream called Chat contains 5 routing rules, an incoming chat conversation will be evaluated against all the 5 routing rules in the defined order. While you can define as many rules as your business requires, the application processes only the first 100 rules.
Routing rules are evaluated from top to bottom. If a rule condition is evaluated as True, the chat gets routed to the destination queue and skips further evaluation. If a rule condition is evaluated as False, further rules are evaluated.
Routing rule conditions could be based on channel context, pre-chat context, and contact, account, or case context. For example, you can define a routing rule so that chats from high priority customers who have specific queries about investments can be routed to a specific queue.
Important
If all the rule conditions are evaluated as False for a conversation, it goes to the Default queue. For more information, see Queues in Omnichannel for Customer Service.
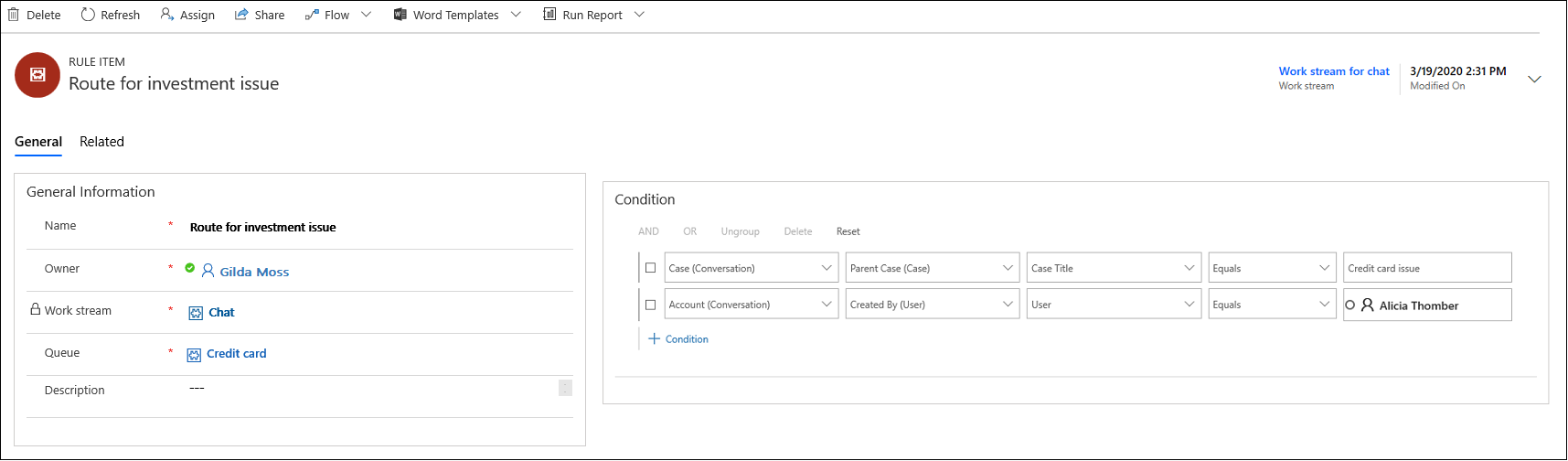
Create a routing rule
To create a routing rule, select a work stream by navigating to Work Distribution Management > Work Streams, and define a new rule in the Routing Rule Items tab.
Select Add. The New Rule Item page appears.
- In the General information section of the General tab, provide the following information:
- Name. Name of the rule item
- Work Stream is auto populated
- Queue. Look up a queue or select New to add a new queue. For more information, see Create a queue in Omnichannel for Customer Service
- Name. Name of the rule item
- Description. A brief description of the rule item.
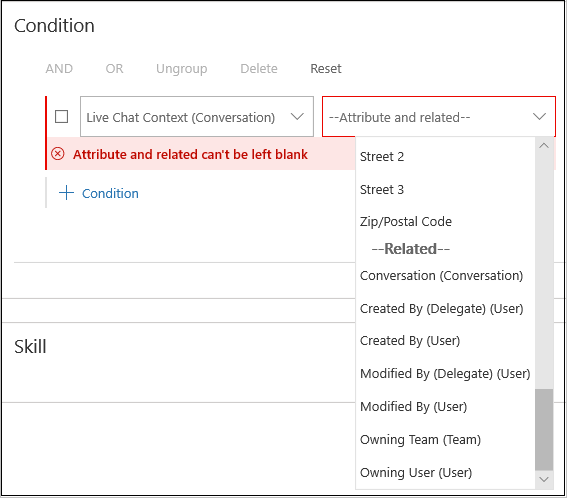
- In the Condition section, provide the conditions for the rule. Based on the conditions defined, the conversations are routed to the correct queues. You can define the conditions based on the following:
- Entity
- Attribute or related entity
- Attribute
- Operator
- Value
For an entity, you can define rules based on related level 1 attributes.
- In the General information section of the General tab, provide the following information:
Select Save.