System requirements for Skype for Business Server 2019
Summary: Prepare to install Skype for Business Server 2019 with the help of this article. Hardware, OS, software, databases, certificates, Active Directory, DNS, and fileshares are covered here. All the system requirements and recommendations are here to help ensure a successful installation and deployment of your server farm.
As you might expect, there are some preparations to make before you begin to deploy Skype for Business Server 2019. This article walks you through planning for:
Hardware for Skype for Business Server 2019
After you have your topology established (and if you don't, you can check out the Topology Basics for Skype for Business Server 2019 article), it's time to think about servers. Skype for Business Server 2019 server requires 64-bit hardware. Our recommendations for hardware are listed in the following tables. These aren't requirements, but they reflect the requirements necessary for optimal performance. We have capacity planning documentation that helps you determine whether you need more than these requirements, depending on your circumstances.
Recommended hardware for Standard Edition servers
| Hardware component | Recommended |
|---|---|
| CPU | Intel Xeon E5-2673 v3 dual processor, 6-core, 2.4 gigahertz (GHz) or greater. Intel Itanium processors aren't supported for Skype for Business Server 2019 roles. |
| Memory | 32 gigabytes (GB). |
| Disk | EITHER: OR |
| Network | One dual-port network adapter, 1 Gbps or greater (two network adapters can be used, but they have to be teamed with a single MAC address and a single IP address). Dual or multi-homed configurations are not supported for Front End Servers, Back End Servers, and Standard Edition servers. You can have out-of-band management systems, such as DRAC or ILO, as long as they aren't exposed to the operating system and are used to monitor and manage server hardware. This scenario doesn't constitute a multi-homed server, and it's supported. |
Recommended hardware for Front End and Back End Servers
| Hardware component | Recommended |
|---|---|
| CPU | Intel Xeon E5-2673 v3 dual processor, 6-core, 2.4 gigahertz (GHz) or greater. Intel Itanium processors aren't supported for Skype for Business Server 2019 roles. |
| Memory | 64 gigabytes (GB). |
| Disk | EITHER: OR |
| Network | One dual-port network adapter, 1 Gbps or greater (two network adapters can be used, but they have to be teamed with a single MAC address and a single IP address). Dual or multi-homed configurations are not supported for Front End Servers, Back End Servers, and Standard Edition servers. You can have out-of-band management systems, such as DRAC or ILO, as long as they aren't exposed to the operating system and are used to monitor and manage server hardware. This scenario doesn't constitute a multi-homed server, and it's supported. |
Recommended hardware for Edge Servers, standalone Mediation Servers, and Directors
| Hardware component | Recommended |
|---|---|
| CPU | Intel Xeon E5-2673 v3 dual processor, 6-core, 2.4 gigahertz (GHz) or greater. Intel Itanium processors aren't supported for Skype for Business Server 2019 roles. |
| Memory | 32 gigabytes. |
| Disk | EITHER: OR |
| Network | One dual-port network adapter, 1 Gbps or greater (two network adapters can be used, but they have to be teamed with a single MAC address and a single IP address). Dual or multi-homed configurations are not supported for Video Interop Servers and Directors. Microsoft Edge servers require two network interfaces that are dual-port network adapters, 1 Gbps or greater (or two paired network adapters, for a total of four, each pair that is teamed with a single MAC address and a single IP address, for a total of two pairs). On standalone Mediation Servers, the installation of additional network interface cards (NICs) to allow the configuration of a specific PSTN IP address is supported. |
Note
Regardless of the server role, we also recommend the following hardware settings for Skype for Business Server 2019 (the settings might vary depending on the brand of hardware you purchase, so refer to manufacturer documentation for specifics):
- BIOS config - should be set to FLAT from NUMA.
- Enable Hyperthreading.
- The RSS queue setting should be set to 8 queue.
Operating systems for Skype for Business Server 2019
After you have the hardware set, you have to install the operating system (OS) that enables you to install and successfully use Skype for Business Server 2019:
- Windows Server 2022
- Windows Server 2019
- Windows Server 2016
Anything other than the operating systems that are listed here won't work correctly. Don't try to use anything else for installations of Skype for Business Server 2019. For example, Server Core option isn't listed. Therefore, it's not supported.
Note
Windows Server 2022 qualifies only with Skype for Business Server 2019 for Cumulative Update 7 and later versions (minimum Build Number 2046.524).
An in-place upgrade of the OS isn't supported. You must deploy a separate pool that's running a different OS, and then migrate users to the new pool. All servers within a pool must have the same OS version.
If you're installing Windows Admin Center 2019 on your Windows Server 2019 computer, the program prompts you for a port to listen on. There's a likelihood that you might choose port 443. However, if that computer has Skype for Business Server 2019 installed, or will have Skype for Business Server 2019 installed, then you must choose a different port number.
Why? If Windows Admin Center 2019 is running on port 443, you can't connect to the server by using the Skype for Business Control Panel, nor will you be able to connect to any internal web service that's running on the server (Address Book Web Service, Autodiscover Service, WebTicket Service, and so on). In fact, you can't connect to any Internal Web Service URL. When you might need or want to put Windows Admin Center 2019 on a server that has Skype for Business Server 2019, choose a different port.
Software that should be installed before a Skype for Business Server 2019 deployment
Note
As a prerequisite to installing the Skype for Business Server 2019, while using Windows Server 2022, you must run the compatibility script for Windows Server 2022.
There are some things that you must install or configure for any server that's running Skype for Business Server 2019. These things are listed in the following tables, followed by additional requirements for specific server roles.
Important
Skype For Business 2019 supports .NET Framework 4.8. and .NET Framework 4.8.1
Skype for Business Server 2019 requires Visual C++ redistributable package for Visual Studio 2012 and Visual C++ redistributable package for Visual Studio 2013, which are automatically installed as part of the Skype for Business Server 2019 installation.
The system requirements for the Visual C++ redistributable package for Visual Studio 2012 and Visual C++ redistributable package for Visual Studio 2013 don't mention support for Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2019, or Windows Server 2022, but the redistributable package is safe to install on these versions of Windows.
All servers
| Software/role | Details |
|---|---|
| Windows PowerShell 3.0 | All Skype for Business Server servers must have Windows PowerShell 3.0 installed. |
| Microsoft .NET Framework | WCF services are a Feature that's installed as a Windows feature, under Server Manager. Initially, no downloads are needed. 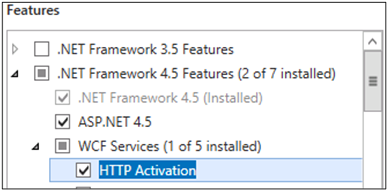 Don't worry if you get another pop-up window that states that some other things have to be installed in order for HTTP Activation to be installed. That's normal. Select OK and continue. If you don't get this pop-up window, you can assume that those things are already installed. Microsoft .NET Framework is installed when Windows Server 2016 is installed. Skype for Business Server requires Microsoft .NET Framework 4.7, 4.8 or 4.8.1 though, so you'd probably have to update it. You can find the update here |
| Media Foundation | For Windows Server 2016, the Windows Media Format Runtime installs with Microsoft Media Foundation. All Front End Servers and Standard Edition servers used for conferencing require Windows Media Format Runtime to run the Windows Media Audio (.wma) files that the Call Park, Announcement, and Response Group applications play for announcements and music. |
| Windows Identity Foundation | We need Windows Identity Foundation 3.5 to support server-to-server authentication scenarios for Skype for Business Server 2019. |
| Remote Server Administration Tools | Role Administration Tools: AD DS and AD LDS tools |
Front End Servers and Standard Edition server
| Software/role | Details |
|---|---|
| Internet Information Services (IIS) | IIS is needed on all Front End Servers and all Standard Edition servers, with the following modules selected: Anonymous Access is also needed, but you get that when you install IIS, so you don't have a place to select it on the list. |
| Windows Media Format Runtime | For Windows Server 2016, you have to install the Media Foundation feature in Server Manager. You actually can start your Skype for Business Server 2019 installation without this feature. However, you're prompted to install it, and then restart the server before the Skype for Business Server 2019 installation can continue. It's better to do it ahead of time. |
| Silverlight | You can install the latest version of Silverlight here. |
| For users in China region | Run PowerShell script after you update the server to the minimum build number Skype for Business Server 2019 Cumulative Update 7 Hotfix 1 (2046.524). |
To help you out, here's a sample PowerShell script that you can run to automate this process:
Add-WindowsFeature RSAT-ADDS, Web-Server, Web-Static-Content, Web-Default-Doc, Web-Http-Errors, Web-Asp-Net, Web-Net-Ext, Web-ISAPI-Ext, Web-ISAPI-Filter, Web-Http-Logging, Web-Log-Libraries, Web-Request-Monitor, Web-Http-Tracing, Web-Basic-Auth, Web-Windows-Auth, Web-Client-Auth, Web-Filtering, Web-Stat-Compression, Web-Dyn-Compression, NET-WCF-HTTP-Activation45, Web-Asp-Net45, Web-Mgmt-Tools, Web-Scripting-Tools, Web-Mgmt-Compat, Windows-Identity-Foundation, Server-Media-Foundation, Telnet-Client, BITS, ManagementOData, Web-Mgmt-Console, Web-Metabase, Web-Lgcy-Mgmt-Console, Web-Lgcy-Scripting, Web-WMI, Web-Scripting-Tools, Web-Mgmt-Service
Directors also need:
IIS, with the following modules selected:
Common HTTP Features
Default Document
HTTP Errors
Static Content
Health and Diagnostics
HTTP Logging
Logging Tools
Tracing
Performance
- Static Content Compression
Security
Request Filtering
Client Certificate Mapping Authentication
Windows Authentication
Application Development
.NET Extensibility 3.5
.NET Extensibility 4.5
ASP.NET 3.5
ASP.NET 4.5
ISAPI Extension
ISAPI Filters
(In case you're wondering, it's the same module set as the Front End Servers and Standard Edition servers, not including the Dynamic Content Compression and Management Tools.)
And we also have some PowerShell code for this process:
Add-WindowsFeature RSAT-ADDS, Web-Server, Web-Static-Content, Web-Default-Doc, Web-Http-Errors, Web-Asp-Net, Web-Net-Ext, Web-ISAPI-Ext, Web-ISAPI-Filter, Web-Http-Logging, Web-Log-Libraries, Web-Request-Monitor, Web-Http-Tracing, Web-Basic-Auth, Web-Windows-Auth, Web-Client-Auth, Web-Filtering, Web-Stat-Compression, NET-WCF-HTTP-Activation45, Web-Asp-Net45, Web-Scripting-Tools, Web-Mgmt-Compat, Server-Media-Foundation, Telnet-Client
Installation of compatibility script for Windows Server 2022
When you set up the Skype for Business Server for Windows Server 2022, you must run the following script to ensure compatibility with Windows Server 2022:
$providerName = "AesProvider"
$keyContainerName = "iisCustomConfigurationKey"
$exe = Get-ChildItem -Path "$env:SystemRoot\Microsoft.NET\Framework64" -Filter "aspnet_regiis.exe" -Recurse -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Select-Object -First 1
if ($exe -eq $null) {
Write-Error "aspnet_regiis.exe not found. Exiting";
Exit
}
$existingProvider = Get-WebConfiguration -PSPath 'MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST' -Filter "configProtectedData/providers/add[@name='$providerName']"
if ($null -ne $existingProvider) { # Provider already exists
Write-Host "Script has already run. $providerName already exists. Exiting"
Exit 0
}
& $exe.FullName -pc $keyContainerName -exp
& $exe.FullName -pa $keyContainerName "BUILTIN\IIS_IUSRS"
& $exe.FullName -pa $keyContainerName "NT SERVICE\WMSVC"
Add-WebConfigurationProperty -PSPath 'MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST' -Filter "configProtectedData/providers" -Name "." -Value @{name="$providerName";type='System.Configuration.RsaProtectedConfigurationProvider,System.Configuration, Version=4.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=b03f5f7f11d50a3a'}
$applicationHostConfigPath = "$env:SystemRoot\System32\inetsrv\config\applicationHost.config"
[xml] $applicationHostConfigFile = Get-Content $applicationHostConfigPath
foreach ($ele in $applicationHostConfigFile.configuration.configProtectedData.providers.add) {
if ($ele.name -eq $providerName) {
$ele.SetAttribute("keyContainerName", $keyContainerName)
$ele.SetAttribute("useMachineContainer", "true")
$ele.SetAttribute("useOAEP", "false")
$ele.SetAttribute("useFIPS", "true")
}
}
$applicationHostConfigFile.Save($applicationHostConfigPath)
Write-Host "Script ran successfully. Key container $keyContainerName created. Provider $providerName added."
Back-end databases that work with Skype for Business Server 2019
When you install Skype for Business Server 2019 Standard Edition, SQL Server 2016 Express (64-bit edition) is also installed. Starting with Skype for Business 2019 CU8, Standard Edition also supports SQL Server 2022 Express (64-bit edition). This is achieved by running an in place upgrade of SQL Express on existing installation of Skype for Business 2019 CU8 (or later) Standard Edition.
Starting with Skype for Business 2019 CU8, Skype for Business Server 2019 Enterprise Edition also supports SQL Server 2022 Express (64-bit edition) for local SQL express instances. This can also be updated by an in place upgrade of SQL Express.
Skype for Business Server 2019 Enterprise Edition requires the full version of SQL Server, as indicated here (only 64-bit edition; don't use 32-bit editions):
- Microsoft SQL Server 2022 (64-bit edition) - must be run together with the latest updates, starting with Skype for Business Server 2019 CU8
- Microsoft SQL Server 2019 (64-bit edition) - must be run together with the latest updates
- Microsoft SQL Server 2017 (64-bit edition) - must be run together with the latest updates
- Microsoft SQL Server 2016 (64-bit edition) - must be run together with the latest updates
If you don't see the SQL Server edition that you want to use listed here, you can't use it.
Note
You must also install SQL Server Reporting Services for the Monitoring Server role.
SQL Clustering and SQL Always On
SQL Clustering with Skype for Business Server 2019 is supported. If you want to set up SQL Clustering, that's done in SQL Server.
Make sure that you have an active/passive configuration for SQL Clustering, which is supported. Don't share the passive node with any other SQL instance.
For failover clustering, you can have:
Two-node:
- Microsoft SQL Server 2022 Standard (64-bit edition), and we recommend running with the latest service pack, starting with Skype for Business Server 2019 CU8.
- Microsoft SQL Server 2019 Standard (64-bit edition), and we recommend running with the latest service pack.
- Microsoft SQL Server 2017 Standard (64-bit edition), and we recommend running with the latest service pack.
- Microsoft SQL Server 2016 Standard (64-bit edition), and we recommend running with the latest service pack.
Sixteen-node:
- Microsoft SQL Server 2022 Enterprise (64-bit edition), and we recommend running with the latest service pack, starting with Skype for Business Server 2019 CU8.
- Microsoft SQL Server 2019 Enterprise (64-bit edition), and we recommend running with the latest service pack.
- Microsoft SQL Server 2017 Enterprise (64-bit edition), and we recommend running with the latest service pack.
- Microsoft SQL Server 2016 Enterprise (64-bit edition), and we recommend running with the latest service pack.
SQL Always On is supported, and you can read more about it in Back End Server high availability in Skype for Business Server 2019.
Additional server installation recommendations
Don't install any Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration (ISA) Server client software, or any other Winsock Layered Service Providers (LSP) software (any third-party firewalls or anti-virus network inspection software would be included here) on any of your front end servers or standalone mediation servers. Poor media traffic performance has been seen when that software is installed.
Active Directory
Although much of the configuration data for servers and services is stored in the Skype for Business Server 2019 Central Management store, some things are still stored in Active Directory.
| Active Directory objects | Object types |
|---|---|
| Schema extensions | User object extensions |
| Extensions for Skype for Business Server 2015 and Lync Server 2013, to maintain backward compatibility with the previous supported versions | |
| Data | User SIP URI and other user settings |
| Contact objects for applications (like the Response Group application and the Conferencing Attendant application) | |
| Data published for backward compatibility | |
| A service control point (SCP) for the Central Management store | |
| Kerberos Authentication Account (an optional computer object) |
OS for Domain Controllers
The following Domain Controller operating systems can be used:
- Windows Server 2022
- Windows Server 2019
- Windows Server 2016
- Windows Server 2012 R2
- Windows Server 2012
The domain functional level of any domain that you deploy Skype for Business Server 2019 into, and the forest functional level of any forest that you deploy Skype for Business Server 2019 into, must be one of the following:
- Windows Server 2016
- Windows Server 2012 R2
- Windows Server 2012
Can you have read-only domain controllers in these environments? Yes, you can — as long as writable domain controllers are also available.
It's important to know that Skype for Business Server 2019 doesn't support single-labeled domains. What are these? If you have a root domain that's labeled "contoso.local," that will work. If you have a root domain that's named "local," that won't work, and it's not supported. For more information, see Deployment and operation of Active Directory domains that are configured by using single-label DNS names.
Skype for Business Server 2019 also doesn't support renaming domains. If you must rename your domain, you have to uninstall Skype for Business Server 2019, do the domain rename, and then reinstall Skype for Business Server 2019.
Finally, you may be dealing with a domain that has a locked-down AD DS environment, and that's acceptable. We have more information about how to deploy Skype for Business Server 2019 into a locked-down AD DS environment in the Deployment documentation.
AD Topologies
Supported topologies in Skype for Business Server 2019 are as follows:
Single forest with single domain
Single forest with a single tree and multiple domains
Single forest with multiple trees and disjoint namespaces
Multiple forests in a central forest topology
Multiple forests in a resource forest topology
Multiple forests in a Skype for Business resource forest topology with Exchange Online
Multiple forests in a resource forest topology with Skype for Business Online and Microsoft Entra Connect
We have diagrams and descriptions to help you determine what topology you have in your environment, or what you may have to set up prior to installing Skype for Business Server 2019. To keep it simple, we're also including a key:
Single forest with single domain
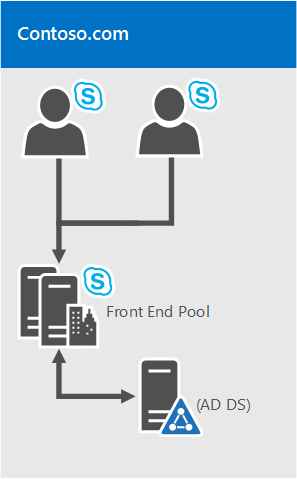
It doesn't get easier than this. It's a single domain forest, a common topology.
Single forest with a single tree and multiple domains
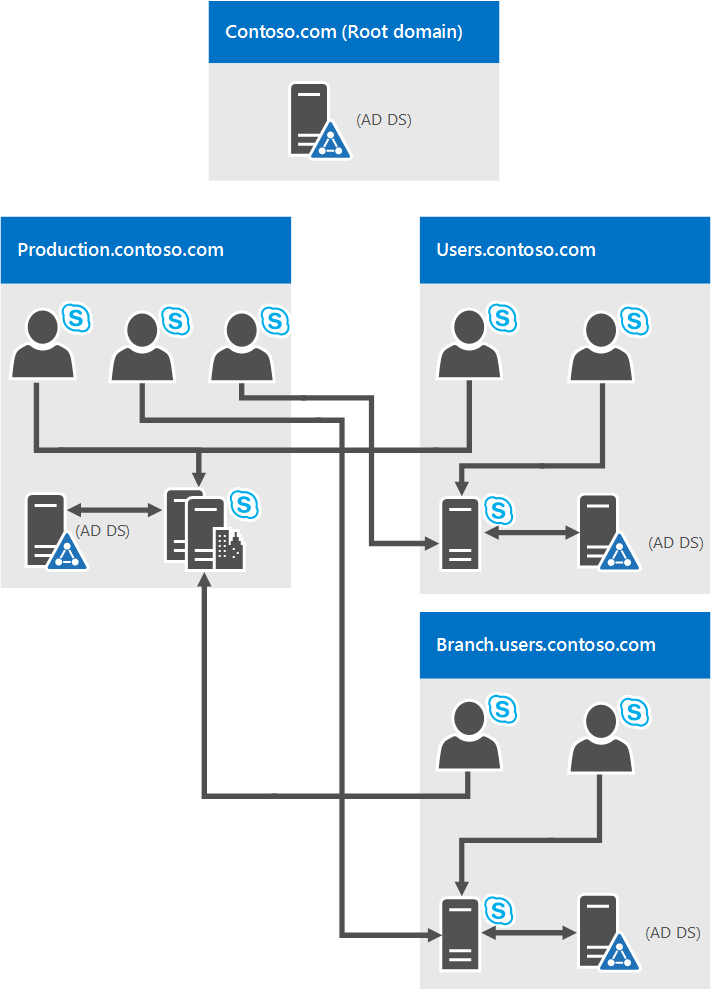
This diagram shows a single forest, again, but it has one or more child domains also (there are three in this specific example). So the domain the users are created in might be different from the domain Skype for Business Server 2019 is deployed to. Why worry about this situation? It's important to remember that when you deploy a Skype for Business Server Front End pool, all the servers in that pool need to be in a single domain. You can have cross-domain administration via Skype for Business Server support of Windows universal administrator groups.
In the previous diagram, you can see that users from one domain are able to access Skype for Business Server pools from the same domain or from different domains, even if those users are in a child domain.
Single forest with multiple trees and disjoint namespaces
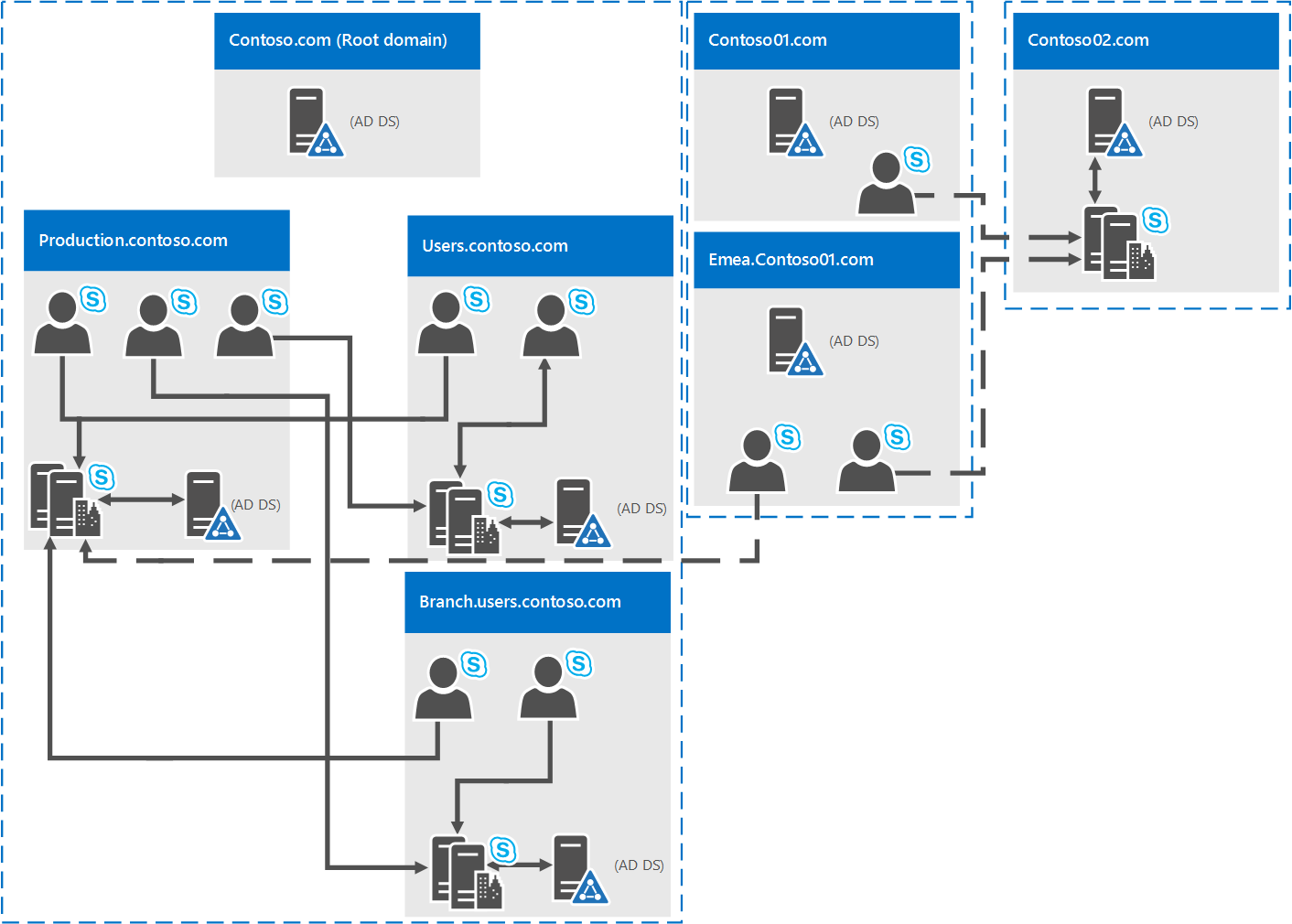
You may have a topology similar to this diagram, where you have one forest, but within that forest are multiple domains, with separate AD namespaces. In this case, this diagram is a good illustration, because it includes users in three different domains accessing Skype for Business Server 2019. Solid lines indicate they're accessing a Skype for Business Server pool in their own domain, whereas a dashed line indicates they're going to a pool in a different tree altogether.
As you can see, users in the same domain, the same tree, or even a different tree can access pools successfully.
Multiple forests in a central forest topology
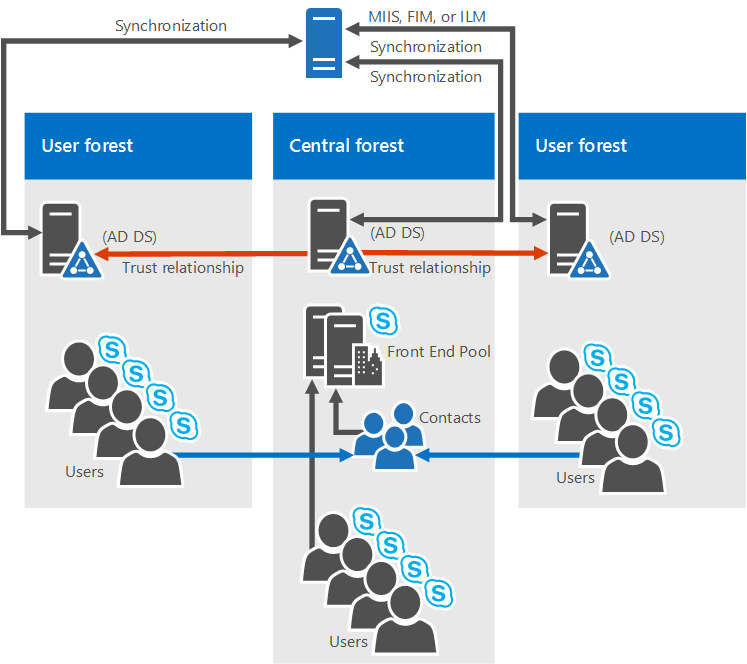
Skype for Business Server 2019 does support multiple forests configured in a central forest topology. If you're not sure that's what you have, the central forest in the topology uses objects in it to represent users in the other forests, and hosts user accounts for any users in the forest.
How does this work? A directory synchronization product (such as Forefront Identity Manager, or FIM) manages your organization's user accounts throughout their existence. When an account is created or deleted from a forest, that change is synched up to the corresponding contact in the central forest.
Clearly, if your AD infrastructure is in place, moving to this topology might not be easy, but if you're already there, or still planning out your forest infrastructure, this can be a good choice. You can centralize your Skype for Business Server 2019 deployment within a single forest, while users can search, communicate, and view the presence of other users in any forest. All user contact updates are handled automatically with synchronization software.
Multiple forests in a Skype for Business resource forest topology
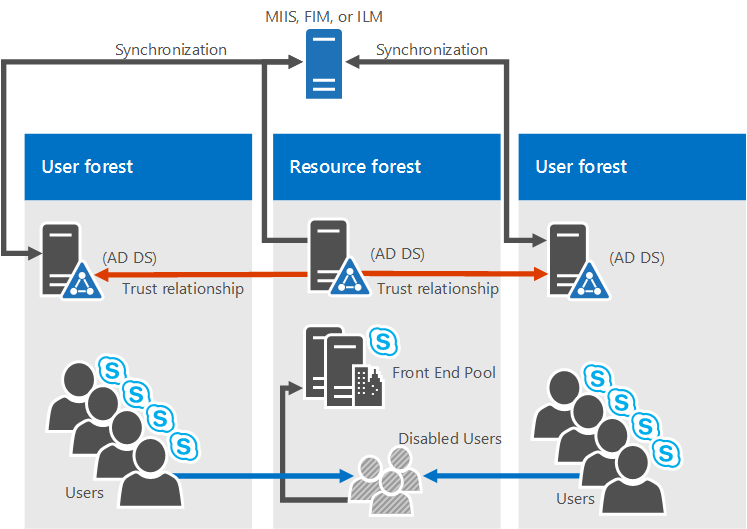
A resource forest topology is also supported; it's where a forest is dedicated to running your server applications, like Microsoft Exchange Server and Skype for Business Server 2019. This resource forests also hosts a synchronized representation of active user objects, but no logon-enabled user accounts. So the resource forest is a shared services environment for other forests in which user objects reside, and they have a forest-level trust relationship with the resource forest.
Exchange Server can be deployed in the same resource forest as Skype for Business Server or in a different forest.
To deploy Skype for Business Server 2019 in this type of topology, you would create one user who has disabilities object in the resource forest for each user account in the user forests (if Microsoft Exchange Server is already in the environment, this action might be done for you). Then you need a directory synchronization tool (like Forefront Identity Manager, or FIM) to manage user accounts through their life cycle.
Multiple forests in a Skype for Business resource forest topology with Exchange Online
This topology is similar to the topology described in Multiple forests in a Skype for Business resource forest topology.
In this topology, there are one or more user forests, and Skype for Business Server is deployed in a dedicated resource forest. Exchange Server can be deployed on-premises in the same resource forest or a different forest and configured for hybrid with Exchange Online, or email services may be provided exclusively by Exchange Online for the on-premises accounts. There is no diagram available for this topology.
Multiple forests in a resource forest topology with Skype for Business Online and Microsoft Entra Connect
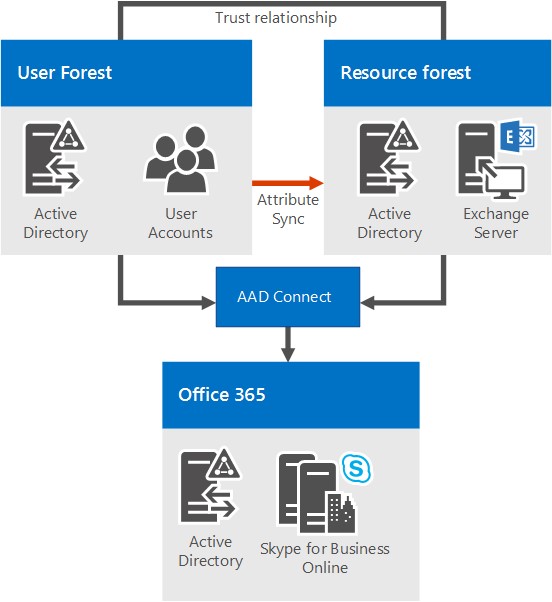
With this scenario, there are multiple forests on-premises, with a resource forest topology. There is a full trust relationship between the Active Directory forests. The Microsoft Entra Connect tool is used to synchronize accounts between the on-premises user forests and Microsoft 365 or Office 365.
The organization also has Microsoft 365 or Office 365, and uses Microsoft Entra Connect to synchronize their on-premises accounts with Microsoft 365 or Office 365. Users who are enabled for Skype for Business are enabled via Microsoft 365 or Office 365 and Skype for Business Online. Skype for Business Server isn't deployed on-premises.
Single sign-on authentication is provided by an Active Directory Federation Services farm located in the user forest.
In this scenario, it is supported to deploy Exchange on-premises, Exchange Online, a hybrid Exchange solution, or to not have Exchange deployed at all. (The diagram shows only Exchange on-premises, but the other Exchange solutions are also fully supported.)
Multiple forests in a resource forest topology with hybrid Skype for Business
In this scenario, there are one or more on-premises user forests, and Skype for Business is deployed in a dedicated resource forest and is configured for hybrid mode with Skype for Business Online. Exchange Server can be deployed on-premises in the same resource forest or a different forest and may be configured for hybrid with Exchange Online. Alternatively, email services may be provided exclusively by Exchange Online for the on-premises accounts.
For more information, see Configure a multi-forest environment for hybrid Skype for Business.
Domain Name System (DNS)
Skype for Business Server 2019 requires DNS for the following reasons:
DNS enables Skype for Business Server 2019 to discover internal servers or pools, allowing for server-to-server communications.
DNS allows client computers to discover the Front End pool or Standard Edition server that is used for SIP transactions.
It associates simple URLs for conferences with the servers hosting those conferences.
DNS allows external users and client computers to connect to your Edge Servers, or the HTTP reverse proxy, for instant messaging (IM) or conferencing.
It lets unified communications (UC) devices that aren't logged in discover the Front End pool or Standard Edition server that's running the Device Update web service to get updates and send logs.
Using DNS allows mobile clients to automatically discover web services resources without requiring users to manually enter URLs in their device settings.
It's used in DNS load balancing.
It's important to note that Skype for Business Server 2019 doesn't support internationalized domain names (IDNs).
And it's extremely important to remember that any name in DNS be identical to the computer name configured on any server that is used by Skype for Business Server 2019. Specifically, we can't have any short-names in the environment, and must have FQDNs for Topology Builder.
This seems like it would be logical for any computer already joined to a domain. But if you have an Edge Server that's not joined to your domain, by default, it may have a short name without a domain suffix. Make sure that this isn't the case, either in DNS or on the Edge Server, or any Skype for Business Server 2019 server or pool.
Definitely don't use Unicode characters or underscores in domain names. Standard characters (which are A-Z, a-z, 0-9, and hyphens) are supported by external DNS and public Certificate Authorities (you have to assign FQDNs to the SN in the certificate, it's important to remember). Therefore, you'll spare yourself a lot of trouble if you keep this rule in mind from the start.
For more information about DNS requirements for Networking, check out the Networking section of our Planning documentation.
Certificates
One of the most important things you can do before deploying is to make sure that you have your certificates in order. Skype for Business Server 2019 needs a public key infrastructure (PKI) for transport layer security (TLS) and mutual transport layer security (MTLS) connections. Basically, to communicate securely in a standardized way, Skype for Business Server uses certificates that are issued by Certificate Authorities (CAs).
These are some of the things that Skype for Business Server 2019 uses certificates for:
TLS connections between clients and servers
MTLS connections between servers
Federation using automatic DNS discovery of partners
Remote user access for instant messaging (IM)
External user access to audio/video (AV) sessions, application sharing, and conferencing
Talking to web applications and Outlook Web Access (OWA)
So certificate planning is a must. Now, let's look at a list of some of the things you need to keep in mind when requesting certificates:
All server certificates must support server authorization (Server EKU).
All server certificates must contain a CRL Distribution Point (CDP).
All certificates must be signed using a signing algorithm supported by the operating system. Skype for Business Server 2019 supports the SHA-1 and SHA-2 suite of digest sizes (224-bit, 256-bit, 384-bit and 512-bit), and meets or exceeds the operating system requirements.
Auto-enrollment is supported for internal servers running Skype for Business Server 2019.
Auto-enrollment isn't supported for Skype for Business Server 2019 Edge Servers.
Note
Using the RSASSA-PSS signature algorithm is unsupported and may cause errors on login and call forwarding issues, among other problems.
Encryption key lengths of 1024, 2048, and 4096 are supported. Key lengths of 2048 and greater are recommended.
The default digest, or hash signing, algorithm is RSA. The ECDH_P256, ECDH_P384, and ECDH_P521 algorithms are also supported.
That's a lot to think about, and there are various comfort levels for requesting certificates from a CA. We'll give you some further guidance in the following sections to make your planning as painless as possible.
Certificates for your internal servers
You need certificates for most of your internal servers, and most likely, you'll get them from an internal CA (that's a CA located in your domain). If you want, you can request these certificates from an external CA (one located on the Internet). If you're wondering which public CA you should go to, you can check out the Unified Communications certificate partners list.
You'll also need certificates when Skype for Business Server 2019 communicates with other applications and servers, such as Microsoft Exchange Server. This will, obviously, have to be a certificate that these other apps and servers can use in a supported way. Skype for Business Server 2019 and other Microsoft products support the Open Authorization (OAuth) protocol for server-to-server authentication and authorization. If you're interested, we have an additional planning article for OAuth and Skype for Business Server 2019.
Skype for Business Server 2019 also includes support for (without requiring) certificates signed using the SHA-256 cryptographic hash function. To support external access using SHA-256, the external certificate needs to be issued by a public CA using SHA-256.
To keep things straightforward, we've put the certificate requirements for Standard Edition servers, Front End pools, and other roles into the following tables, and we used the fictional contoso.com for examples (you'll probably be using something else for your environment). These are all standard web server certificates, with private keys that are non-exportable. Some additional things to note:
Server enhanced key usage (EKU) is automatically configured when you use the certificate wizard to request certificates.
Each certificate friendly name has to be unique in the computer store.
As per the following sample names, if you've configured sipinternal.contoso.com, or sipexternal.contoso.com in your DNS, they have to be added to the certificate's Subject Alternative Name (SAN).
Certificates for Standard Edition servers
| Certificate | Subject name/common name | Subject alternative name | Example | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default | FQDN of the pool | FQDN of the pool and FQDN of the server If you have multiple SIP domains and have enabled automatic client configuration, the certificate wizard detects and adds each supported SIP domain FQDNs. If this pool is the auto-logon server for clients and strict Domain Name System (DNS) matching is required in group policy, you also need entries for sip.sipdomain (for each SIP domain that you have). |
SN=se01.contoso.com; SAN=se01.contoso.com If this pool is the auto-logon server for clients and strict DNS matching is required in group policy, you also need SAN=sip.contoso.com; SAN=sip.fabrikam.com |
On Standard Edition servers, the server FQDN is the same as the pool FQDN. The wizard detects any SIP domains you specified during setup and automatically adds them to the subject alternative name. You can also use this certificate for Server-to-Server Authentication. |
| Web internal | FQDN of the server | Each of the following: AND OR |
SN=se01.contoso.com; SAN=se01.contoso.com; SAN=meet.contoso.com; SAN=meet.fabrikam.com; SAN=dialin.contoso.com; SAN=admin.contoso.com Using a wildcard certificate: SN=se01.contoso.com; SAN=se01.contoso.com; SAN=*.contoso.com |
You can't override the Internal web FQDN in Topology Builder. If you have multiple Meet simple URLs, you must include all of them as SANs. Wildcard entries are supported for the simple URL entries. |
| Web external | FQDN of the server | Each of the following: AND OR |
SN=se01.contoso.com; SAN=webcon01.contoso.com; SAN=meet.contoso.com; SAN=meet.fabrikam.com; SAN=dialin.contoso.com Using a wildcard certificate: SN=se01.contoso.com; SAN=webcon01.contoso.com; SAN=*.contoso.com |
If you have multiple Meet simple URLs, you must include all of them as subject alternative names. Wildcard entries are supported for the simple URL entries. |
Certificates for Front End Servers in a Front End pool
| Certificate | Subject name/common name | Subject alternative name | Example | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default | FQDN of the pool | FQDN of the pool and FQDN of the server If you have multiple SIP domains and have enabled automatic client configuration, the certificate wizard detects and adds each supported SIP domain FQDNs. If this pool is the auto-logon server for clients and strict Domain Name System (DNS) matching is required in group policy, you also need entries for sip.sipdomain (for each SIP domain that you have). |
SN=eepool.contoso.com; SAN=eepool.contoso.com; SAN=ee01.contoso.com If this pool is the auto-logon server for clients and strict DNS matching is required in group policy, you also need SAN=sip.contoso.com; SAN=sip.fabrikam.com |
The wizard detects any SIP domains you specified during setup and automatically adds them to the subject alternative name. You can also use this certificate for Server-to-Server Authentication. |
| Web internal | FQDN of the pool | Each of the following: AND OR |
SN=ee01.contoso.com; SAN=ee01.contoso.com; SAN=meet.contoso.com; SAN=meet.fabrikam.com; SAN=dialin.contoso.com; SAN=admin.contoso.com Using a wildcard certificate: SN=ee01.contoso.com; SAN=ee01.contoso.com; SAN=*.contoso.com |
If you have multiple Meet simple URLs, you must include all of them as subject alternative names. Wildcard entries are supported for the simple URL entries. |
| Web external | FQDN of the pool | Each of the following: AND OR |
SN=ee01.contoso.com; SAN=webcon01.contoso.com; SAN=meet.contoso.com; SAN=meet.fabrikam.com; SAN=dialin.contoso.com Using a wildcard certificate: SN=ee01.contoso.com; SAN=webcon01.contoso.com; SAN=*.contoso.com |
If you have multiple Meet simple URLs, you must include all of them as subject alternative names. Wildcard entries are supported for the simple URL entries. |
Certificates for the Director
| Certificate | Subject name/common name | Subject alternative name | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Default | Director pool | FQDN of the Director, FQDN of the Director pool. If this pool is the auto-logon server for clients and strict DNS matching is required in group policy, you'll also need entries for sip.sipdomain (for each SIP domain that you have). |
pool.contoso.com; SAN=dir01.contoso.com If this Director pool is the auto-logon server for clients and strict DNS matching is required in group policy, you also need SAN=sip.contoso.com; SAN=sip.fabrikam.com |
| Web internal | FQDN of the server | Each of the following: AND OR |
SN=dir01.contoso.com; SAN=dir01.contoso.com; SAN=meet.contoso.com; SAN=meet.fabrikam.com; SAN=dialin.contoso.com; SAN=admin.contoso.com Using a wildcard certificate: SN=dir01.contoso.com; SAN=dir01.contoso.com SAN=*.contoso.com |
| Web external | FQDN of the server | Each of the following: AND OR |
The Director external web FQDN must be different from the Front End pool or Front End Server. SN=dir01.contoso.com; SAN=directorwebcon01.contoso.com SAN=meet.contoso.com; SAN=meet.fabrikam.com; SAN=dialin.contoso.com Using a wildcard certificate: SN=dir01.contoso.com; SAN=directorwebcon01.contoso.com SAN=*.contoso.com |
Certificates for Stand-alone Mediation Server
| Certificate | Subject name/common name | Subject alternative name | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Default | FQDN of the pool | FQDN of the pool FQDN of the pool member server |
SN=medsvr-pool.contoso.net; SAN=medsvr-pool.contoso.net; SAN=medsvr01.contoso.net |
Certificates for Survivable Branch Appliance (Specifically, Survivable Branch Appliance 2015 for Skype for Business Server 2019)
| Certificate | Subject name/common name | Subject alternative name | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Default | FQDN of the appliance | SIP.<sipdomain> (you need only one entry per SIP domain) | SN=sba01.contoso.net; SAN=sip.contoso.com; SAN=sip.fabrikam.com |
Certificates for external user access (Edge)
Skype for Business Server 2019 supports the use of a single public certificate for access and web conferencing Edge external interfaces, plus the A/V Authentication service, which is all provided via the Edge Server(s). Your Edge internal interface uses a private certificate issued by your internal CA, but if you'd prefer, you can use a public certificate for this also, if it's from a trusted CA.
Your reverse proxy (RP) will also use a public certificate, and it encrypts the communication from your RP to clients, and the RP to internal servers by using HTTP (or more precisely, TLS over HTTP).
Certificates for mobility
If you're deploying mobility and you're supporting automatic discovery for mobile clients, you will have to include some additional subject alternate name entries on your certificates to support the secure connections from the mobile clients.
You need SAN names for automatic discovery on the following certificates:
Director pool
Front End pool
Reverse Proxy
The specifics are listed in the tables that follow.
This is where a little pre-planning is good. But sometimes, you've deployed Skype for Business Server 2019 without intending to deploy mobility, and that comes up later when you already have certificates in your environment. Reissuing the certificates through an internal CA is typically pretty easy. But for public certificates from a public CA, that can be a little more pricey.
If that's the situation that you're looking at, and if you have lots of SIP domains (which would make adding SANS more expensive), you can configure your reverse proxy to use HTTP for the initial Autodiscover Service request instead of using HTTPS (the default configuration). For more information, see Plan for Mobility.
Director pool and Front End pool certificate requirements
| Description | SAN entry |
|---|---|
| Internal Autodiscover service URL | SAN=lyncdiscoverinternal.<sipdomain> |
| External Autodiscover service URL | SAN=lyncdiscover.<sipdomain> |
You can, alternatively, use SAN=*.<sipdomain>
Reverse Proxy (Public CA) certificate requirements
| Description | SAN entry |
|---|---|
| External Autodiscover service URL | SAN=lyncdiscover.<sipdomain> |
This SAN must be assigned to the certificate that's assigned to the SSL Listener on your reverse proxy.
Note
Your reverse proxy listener will have SANs for your external Web Services URL(s). Some examples would be SAN=skypewebextpool01.contoso.com and dirwebexternal.contoso.com, if you've deployed the Director (optional).
File share
Skype for Business Server 2019 can use the same file share for all file storage. You should keep the following in mind:
A file share has to be on either direct attached storage (DAS) or a storage area network (SAN). This requirement includes the Distributed File System (DFS) and also a redundant array of independent disks (RAID) for file stores. For more information about DFS for Windows Server 2012, see DFS Namespaces and DFS Replication Overview.
We recommend that you use a shared cluster for the file share. If you're already using one, you should cluster Windows Server 2012 or later versions.
Note
Why the latest Windows? Earlier versions may not have the right permissions to enable all features. You can use Cluster Administrator to create the file shares. For more information, see How to create file shares on a cluster.
Caution
You should know that using network attached storage (NAS) as a file share isn't supported. Therefore, use one of the options that are listed here. This support limitation is caused by the variable design of NAS devices that have to provide file system adaptability to the Windows Server-based computer that accesses the devices' shared file system.