Agents are apps for Microsoft 365
When you build an agent, you're also building an app for Microsoft 365. Apps for Microsoft 365 share a common manifest schema and packaging format, and unified distribution and management processes and tools. The end result is that your apps and agents reach the widest possible audience and appear contextually within the workflow of your users.
This article describes the key parts of the Microsoft 365 app model that apply to agent development.
Important
- API plugins are currently only supported as actions within declarative agents. They aren't enabled in Microsoft 365 Copilot. For an example that shows how to add an API plugin to a declarative agent, see Add a plugin.
- The capability is enabled by default in all Microsoft 365 Copilot-licensed tenants. Admins can disable this functionality on a user and group basis and control how individual plugins are approved for use, and which plugins are enabled. For more information, see Manage Agents in Integrated Apps.
App package
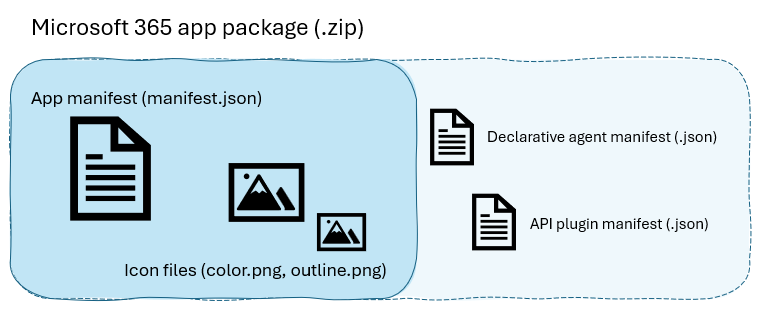
The app package for Microsoft 365, including agents, is a zip file that contains one or more configuration (manifest) files and your app icons. Your app logic and data storage are hosted elsewhere and accessed by the Microsoft 365 host application via HTTPS. You'll submit the app package to your admin to publish to your organization or to Partner Center to publish to Microsoft AppSource.
At minimum, an app package contains:
- The app manifest (
manifest.json), which describes app configuration, capabilities, required resources, and important attributes - A large color icon (
color.png), a full-color 92x92 icon to display your agent in the Microsoft Copilot UI and store - A small outline icon (
outline.png), a 32x32 icon with transparent background (not currently used in Copilot, but required to pass validation)
The app package can also contain declarative agent and API plugin definitions, as well as localization files for other supported languages.
App icons
Your app package must include both a color and outline version of your app icon, as .png files. These icons have specific size requirements in order to pass store validation.
Note
Currently only the color icon is used to represent agents to users (both as its store listing and within the Microsoft 365 Copilot UI), but an outline icon is still required when you submit the app package to Microsoft AppSource.
For design guidance for color and outline icons for the Microsoft 365 app package, see App icons for Teams Store and app bar.
Color icon
The color icon represents your agent within the Microsoft Copilot UI and in-product (Teams, Outlook, Microsoft 365) app stores.
![]()
Your color icon:
- Can be any color
- Must be 192 x 192 pixels in size
- Should contain a symbol of 96 x 96 pixels (to allow 48 pixels of padding for host scenarios where it is cropped)
- Must sit atop a fully solid or fully transparent square background
Outline icon
The outline icon is used to represent pinned and/or active apps on the Teams app bar. It's not currently used for agents, but still required in order for the app package to pass validation.
![]()
Your outline icon:
- Must be 32 x 32 pixels
- Must be either white with a transparent background, or transparent with a white background
- Must not contain additional padding around the symbol
App manifest
The app manifest for Microsoft 365 is a JSON file that describes the functionality and characteristics of your app. At its core, the app manifest for Microsoft 365 is the schema for building Teams apps; however, starting with version 1.13, it supports apps that run across Microsoft 365 hosts, in addition to Teams.
If you're using Copilot Studio to build a declarative agent, the app manifest is generated for you based on the information you provide during the creation process.
Every app manifest must include the following fields.
| Manifest field | Description |
|---|---|
| version | The version number of the app, in the format of MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH (semver standard). |
| id | The unique generated identifier for this app from Microsoft Application Registration Portal (apps.dev.microsoft.com), in GUID form. |
| developer | Information about the developer, including name, website, and links to privacy policy and terms of use. For apps submitted to AppSource, values must match the value provided in the Partner Center app submission form. |
| name | The name of your app, as displayed to end-users within the application host. |
| description | Short and long descriptions of your app for users. For apps submitted to AppSource, these values must match the information in your AppSource entry. |
| icons | Relative paths to color and outline icon files. |
| accentColor | A color to use with and as a background for your outline icons, in RGB hex value, for example #4464ee. |
| Definitions for specific app capabilities | A definition for each app capability, such as personal tabs (staticTabs), message extensions (composeExtensions), or bots. Declarative agents and API plugins are defined under the copilotAgents node. |
The following example shows an app manifest with placeholder sections at the end for message extension and declarative agent app capabilities.
{
"$schema": "https://developer.microsoft.com/en-us/json-schemas/teams/v1.18/MicrosoftTeams.schema.json",
"manifestVersion": "1.18",
"version": "1.0.0",
"id": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000",
"developer": {
"name": "Northwind Traders",
"websiteUrl": "https://www.example.com",
"privacyUrl": "https://www.example.com/termofuse",
"termsOfUseUrl": "https://www.example.com/privacy"
},
"icons": {
"color": "Northwind-Logo-196.png",
"outline": "Northwind-Logo-32.png"
},
"name": {
"short": "Northwind Inventory",
"full": "Northwind Inventory App"
},
"description": {
"short": "App allows you to find and update product inventory information",
"full": "Northwind Inventory is the ultimate tool for managing your product inventory. With its intuitive interface and powerful features, you'll be able to easily find your products by name, category, inventory status, and supplier city. You can also update inventory information with the app."
},
"accentColor": "#3690E9",
"composeExtensions": {
...
},
"copilotAgents": {
...
}
}
To learn more, see the Microsoft 365 app manifest reference.
copilotAgents definitions
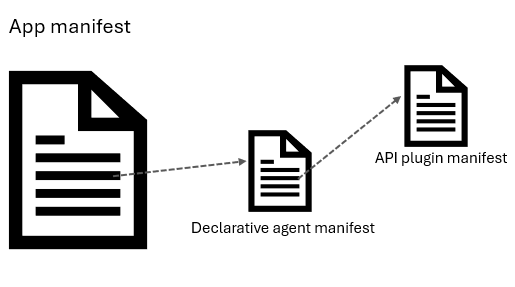
Declarative agents and API plugins each have their own definition schemas. The definition file for a declarative agent is referenced from the copilotAgents object of the app manifest.
The following example shows how to reference a declarative agent:
"copilotAgents": {
"declarativeAgents": [
{
"id": "agent1",
"file": "declarativeAgent1.json"
}
]
},
The definition of an API plugin is referenced (under actions) from the declarative agent definition.
Note the following:
Currently only one declarative agent definition is supported per app manifest.
When you use Copilot Studio to build agents, a unique
idis generated for each, as part of the overall app manifest generation. When building agents with Teams Toolkit or your own IDE, you assign theidyourself, according to your own conventions or friendly name.
Declarative agent manifest
The declarative agent manifest includes instructions for Copilot responses, conversation starter sample prompts, data sources used for grounding, and a list of actions (API plugin skills) the agent is able to perform.
To learn more, see Declarative agent manifest schema for Microsoft 365 Copilot.
API plugin manifest
The API plugin manifest describes the plugin's capabilities, including the APIs it supports and the operations it can perform. It also includes metadata such as name, description, version, and a reference to the OpenAPI definition of the REST APIs with which it interacts. API plugins can be referenced from a declarative agent manifest to be used within the declarative agent experience.
To learn more, see API plugin manifest schema for Microsoft 365 Copilot.