Step 1: Publish the SAP Artifacts as a WCF Service

Time to complete: 10 minutes
Objective: You can use the WCF Adapter Service Development Wizard to generate a WCF service that can be hosted in a hosting environment such as Internet Information Services (IIS) or Windows Process Activation Service (WAS). This topic demonstrates how to use the wizard to generate a WCF service file.
Prerequisites
Before running the wizard, install the following:
Microsoft Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) Line of Business (LOB) Adapter SDK either with the Complete option or the Custom option (and choosing Tools within this option). This installs the Visual Studio template for the WCF Adapter Service Development Wizard.
Microsoft BizTalk Adapter for mySAP Business Suite from the BizTalk Adapter Pack.
The required SAP client libraries.
For more information about these prerequisites, see the BizTalk Adapter Pack installation guide. The installation guide is typically installed at <installation drive>:\Program Files\Microsoft BizTalk Adapter Pack\Documents.
To publish the SAP artifacts as a WCF service
Start Visual Studio, and then create a project.
In the New Project dialog box, from the Project types pane, select Visual C#. From the Templates pane, select WCF Adapter Service.
Alternatively, from the Project types pane, expand Visual C#, and then select Web. From the Templates pane, select WCF Adapter Service.
Note
If you installed Visual Studio 2013 with the Web Development component, the WCF Adapter Service template is also available from the New Website option.
Specify a name and location for the solution, and then click OK. The WCF Adapter Service Development Wizard starts.
On the Welcome page, click Next.
On the Choose Operations page, specify a connection string to connect to the SAP system. To do so:
In the Select a binding list, click sapBinding, and then click Configure.
In the Configure Adapter dialog box, click the Security tab.
In the Client credential type list, select Username, and then specify a valid SAP user name and password to connect to the SAP system.
Click the URI Properties tab, and then specify values for the connection parameters. For more information about the connection URI for the SAP adapter, see Create the SAP system connection URI.
Note
If the connection parameters contain any reserved characters (such as XML special characters), you must specify them as-is in the URI Properties tab, that is, without using any escape characters. However, if you specify the URI directly in the Configure a URI box and the connection parameters contain reserved characters, you must specify the connection parameters using proper escape characters.
Click the Binding Properties tab, and then specify values for the binding properties, if any, required for the operations you want to target. In this tutorial, the BAPI_SALESORDER_GETLIST RFC is invoked to get the list of sales orders for a specific customer. The sales order information might also contain date columns. When retrieving values for the date column, we recommend that you set the EnableSafeTyping binding property to True when generating the metadata. If this property is set, the SAP DATS data type is surfaced as strings.
For more information about how the SAP data types are mapped to equivalent .NET types, see Basic SAP Data Types.
For more information about binding properties, see Read about BizTalk Adapter for mySAP Business Suite binding properties.
Click OK, and then click Connect. After the connection is established, the connection status is shown as Connected.
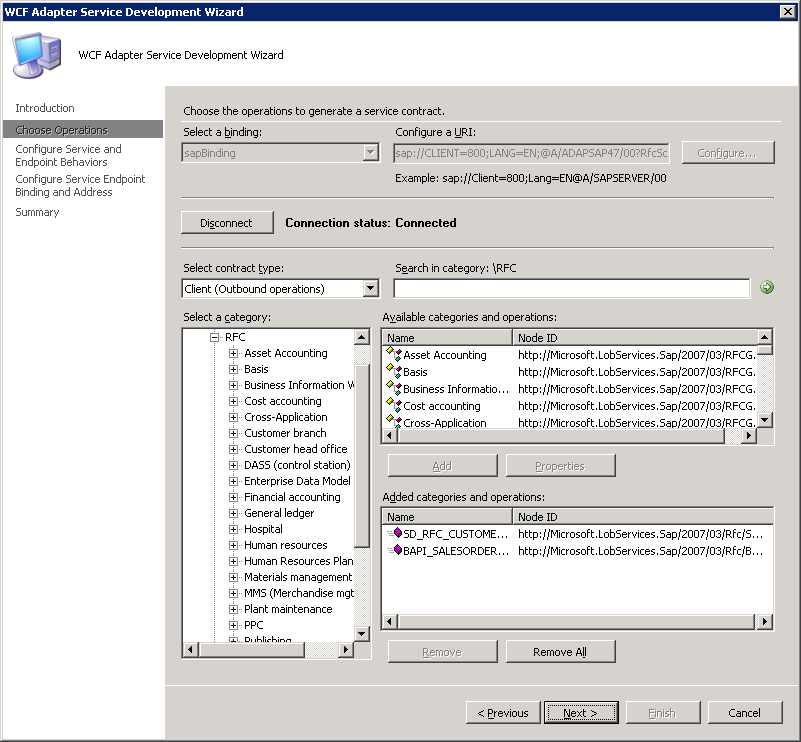
On the Choose Operations page, in the Select contract type list, click Client (Outbound operations).
In the Select a category box, expand an SAP artifact type. For example, expand the RFC node to see the functional group containing the RFC for which you want to generate a WCF service.
In the Available categories and operations box, select the operations for which you want to generate a WCF service, and then click Add. The selected operations are listed in the Added categories and operations box.
Note
You can add more than one operation for each artifact. You can also add operations for different SAP artifacts. For example, you can add one operation for RFC and another for IDOC. In addition, you can search for specific operations by specifying wildcard characters in search expressions. For more information about the supported special characters and the node levels at which you can search for the operations, see Connecting to SAP in Visual Studio Using Add Adapter Metadata Wizard
For this example, the SD_RFC_CUSTOMER_GET and BAPI_SALESORDER_GETLIST RFCs are added.
Note
Some versions of the SAP system expose an RFC_CUSTOMER_GET RFC instead of SD_RFC_CUSTOMER_GET.
On the Choose Operations page, click Next.
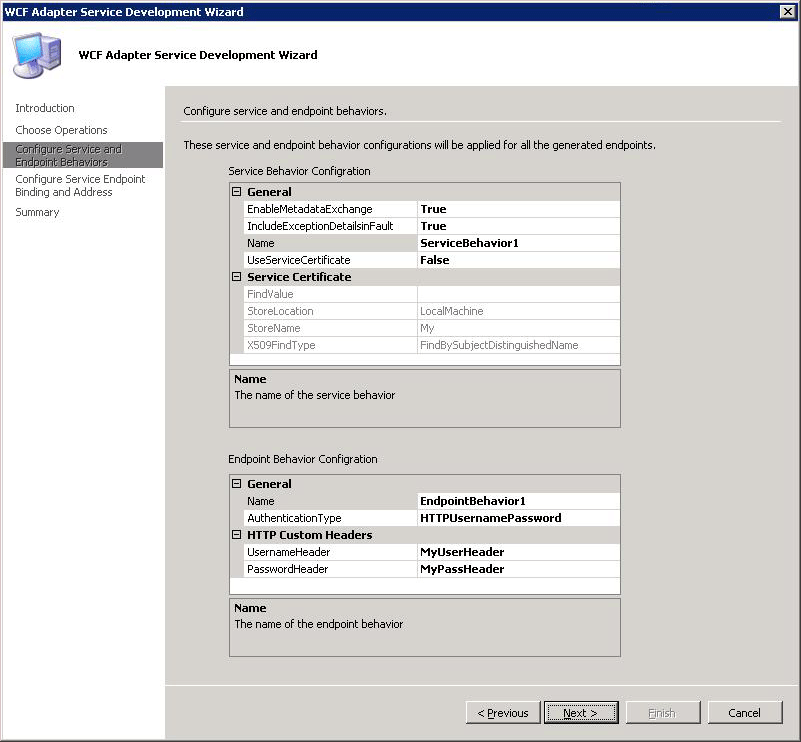
On the Configure Service and Endpoint Behaviors page, specify values to configure the service and endpoint behavior.
In the Service Behavior Configuration box, specify values for the following:
For the property Specify the value EnableMetadataExchange Set this to True to create a metadata exchange endpoint. By setting this to True, you make the service metadata available using standardized protocols, such as WS-Metadata Exchange (MEX) and HTTP/GET requests.
Default is False.IncludeExceptionDetailsinFault Set this to True to include managed exception information in detail of SOAP faults returned to the client for debugging purposes. Default is False. Name Name for the service behavior configuration. UseServiceCertificate Specifies whether you want to use the message level security mode of WCF. Default is True.
For this tutorial, you must set this to False.FindValue A string that specifies the value to search for in the X.509 certificate store.
Note: Specify a value for this property only if UseServiceCertificate is set to True.StoreLocation A value that specifies the location of the certificate store that the service can use to validate the client's certificate.
Note: Specify a value for this property only if UseServiceCertificate is set to True.StoreName Name of the X.509 certificate store to open.
Note: Specify a value for this property only if UseServiceCertificate is set to True.X509FindType The type of X.509 search to be executed.
Note: Specify a value for this property only if UseServiceCertificate is set to True.Note
For more information about the certificates and the associated properties, see "X509ClientCertificateCredentialsElement Properties" at https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=103771.
In the Endpoint Behavior Configuration box, specify values for the following:
For the property Specify the value Authentication Type - Set this to ClientCredentialUserNamePassword to enable the clients to specify the user name and password when consuming the WCF service.
- Set this to HTTPUserNamePassword to enable clients to specify user name and password as part of the HTTP header.
- Set this to Auto to first enable clients to specify credentials through the ClientCredential interface. If this fails, clients can pass credentials as part of the HTTP header.
Default is Auto. For Microsoft Office SharePoint Server to consume the WCF service, you should set this as HTTPUserNamePassword.Name Specify a name for the endpoint behavior configuration. UsernameHeader Name for the user name header. For this example, specify MyUserHeader. For more information about HTTP headers, see "Support for Custom HTTP and SOAP Headers" at https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=106692.
Note: You must specify a value for this property if the Authentication Type is set to HTTPUserNamePassword. If Authentication Type is set to Auto, this property is optional.PasswordHeader Name for the password header. For this example, specify MyPassHeader. For more information about HTTP headers, see "Support for Custom HTTP and SOAP Headers" at https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=106692.
Note: You must specify a value for this property if the Authentication Type is set to HTTPUserNamePassword. If Authentication Type is set to Auto, this property is optional.The following figure shows the Configure Service and Endpoint Behaviors page with the specified values.
On the Configure Service and Endpoint Behaviors page, click Next.
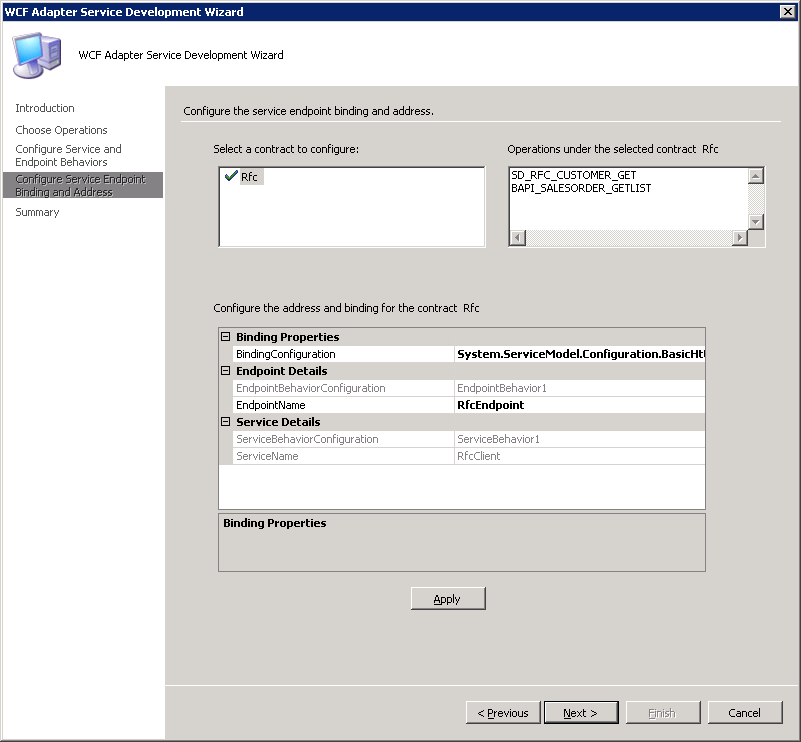
On the Configure Service Endpoint Binding and Address page, the Select a contract to configure box lists the SAP artifacts for which you selected the operations on the Choose Operations page.
For example, if you selected artifacts under RFC and IDOC, the Select a Contract to configure lists both RFC and IDOC. If you selected only an RFC, the box will only list RFC.
The Operations under the selected contract box displays the operations you selected for each artifact on the Choose Operations page.
In the Configure the address and binding for the contract box, specify values for the following:
For the property Specify the value Binding Configuration The wizard only supports basic HTTP binding. So, the binding configuration field is automatically populated to System.ServiceModel.Configuration.BasicHttpBindingElement.
Click the ellipsis button (…) to change the properties for HTTP binding. To use a secure communication channel, you must always set the Mode property to Transport. The wizard sets the default value for the Mode property as Transport.
For more information about the other bindings exposed, see "BasicHttpBindingElement Members" at https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=103773.Endpoint Name Specify an endpoint name for the contract. The other fields on this page are automatically populated based on the values you specified in the earlier pages.
Click Apply. Perform this step for all the contracts displayed under the Select a contract to configure box.
Note
If you do not specify any values on this page, the default values are accepted for all the contracts.
The following figure shows the Configure Service Endpoint Binding and Address page with the specified values.
On the Configure Service Endpoint Binding and Address page, click Next. The Summary page lists a tree structure of the SAP artifacts and, under that, the operations selected for each artifact.
Review the summary, and then click Finish.
The wizard creates a WCF service and adds the following files to the Visual Studio project:
.svc file. This is the WCF service file. The wizard generates one file for each contract.
Web.config file.
Service code (.cs file)
Publish the WCF service.
Make sure SSL is enabled for Internet Information Services (IIS). For instructions on how to enable SSL for IIS, see https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=197170.
Right-click the project in Solution Explorer, and then click Publish.
In the Publish Web dialog box, specify a URL for the WCF service. For example:
https://<computer_name>/Customer_Order/From the Copy box, click All project files.
Click Publish.
Verify that the WCF service is published successfully.
Start the IIS Microsoft Management Console. Click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
Navigate to the node where you published the service. For the Customer_Order service, navigate to Internet Information Services > <Computer Name> > Web Sites > Default Web Site > Customer_Order.
On the right pane, right-click the Rfc.svc file, and then click Browse.
The Web page shows up with the URL for retrieving the WSDL. You may want to test metadata retrieval using the svcutil command. For example, the command to retrieve metadata for the Customer_Order service is:
svcutil.exe https://<computer_name>/Customer_Order/Rfc.svc?wsdl
Next Step
To create an application definition file for the SAP artifacts, use the Business Data Catalog Definition Editor. See Step 2: Create an Application Definition File for the SAP Artifacts for instructions. The application definition file identifies where the LOB data is stored and the format in which it is stored.
See Also
Tutorial 1: Presenting Data from an SAP System on a SharePoint Site