Connecting to SAP in Visual Studio Using Add Adapter Metadata Wizard
The SAP adapter is also exposed as a BizTalk adapter and hence, you can use the Add Adapter Metadata Wizard to generate schema for the operations you want to perform on an SAP system using the adapter.
Connecting to an SAP System Using Add Adapter Metadata Wizard
Perform the following steps to connect to an SAP system using the Add Adapter Metadata Wizard.
To connect to an SAP system
To connect using the Add Adapter Metadata Wizard in a BizTalk solution:
Create a BizTalk project using Visual Studio.
Right-click the project name in Solution Explorer, point to Add, and then click Add Generated Items.
In the Add Generated Items dialog box, do the following:
Use this To do this Categories Click Add Adapter. Templates Click Add Adapter Metadata. Click Add. The Add Adapter Metadata Wizard opens.
In the Add Adapter Wizard, select WCF-SAP. Select the computer on which BizTalk Server is installed and the name of the BizTalk database.
Important
If you already have a WCF-SAP port configured in BizTalk, select the port from the Port list.
Click Next.
From the Select a binding drop-down list, select sapBinding and click Configure.
In the Configure Adapter dialog box, click the Security tab, and from the Client credential type drop-down list box, select Username and specify the user name and password to connect to the SAP system.
Important
If you are using the SAP Secure Network Connection (SNC) library to connect to an SAP system, do not specify a username and password.
Click the URI Properties tab and specify values for the connection parameters. For more information about the connection URI for the SAP adapter, see Create the SAP system connection URI.
Important
If you are using the SAP SNC library to connect to an SAP system, set the UseSnc connection property to True.
Note
If the connection parameters contain any reserved characters, you must specify them as-is in the URI Properties tab, that is, without using any escape characters. However, if you specify the URI directly in the Configure a URI field and the connection parameters contain reserved characters, you must specify the connection parameters using proper escape characters.
Click the Binding Properties tab, and then specify values for the binding properties, if any, required by the operations you want to target. For example, if you want to target a ReceiveIdoc operation you must set the ReceiveIdocFormat binding property to String. For more information about binding properties, see Read about BizTalk Adapter for mySAP Business Suite binding properties.
Note
If you are generating metadata using Add Adapter Metadata Wizard and you selected an existing WCF-SAP send port, you need not specify the binding properties. The binding properties are picked from the send port configuration. However, you may choose to specify the binding properties that are required at design-time, if any. In such case, the new values for binding properties will be used at design-time while generating the metadata. However, at run-time the values specified for binding properties in the send port configuration will be applicable.
Important
If you are using the SAP SNC library to connect to an SAP system, set the SncLibrary and SncPartnerName to appropriate values.
The SncLibrary binding property takes the path and the filename of the DLLs required for using SNC to connect to an SAP system. These DLLs must be present on the computer with the SAP client and SAP adapter installed. For more information see the BizTalk Adapter Pack installation guide available at <installation guide>:\Program Files\Microsoft BizTalk Adapter Pack\Documents.
The SncPartnerName binding property takes the SNC name of the communication partner.
Click OK.
Click Connect. After the connection is established, the connection status is shown as Connected.
The following figure shows the Consume Adapter Service Add-in immediately after the connection is established. The graphical user interface is same for the Add Adapter Metadata Wizard.
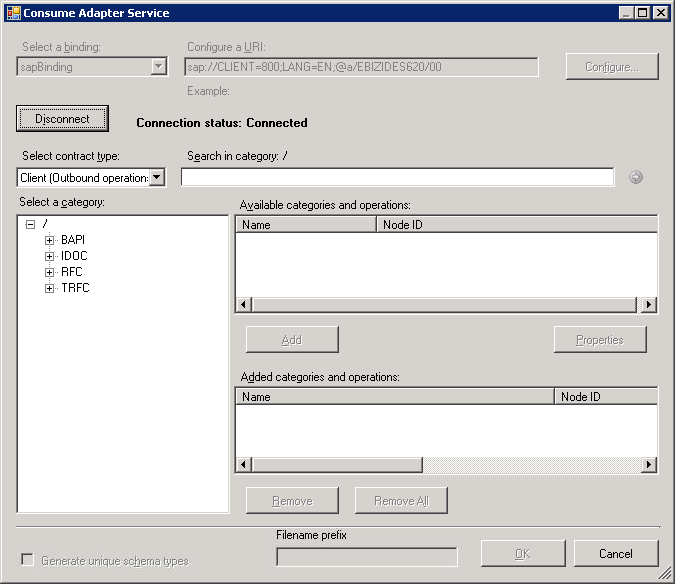
The Consume Adapter Service Add-in displays different nodes containing various artifacts that can be invoked in an SAP system. For example, the RFC node contains all the RFCs available in the SAP system you connected to. For more information about these nodes, see Metadata Node IDs.