Hardware offloaded audio driver implementation
When you implement a driver for offloaded audio, you develop a driver that is able to process offloaded audio streams, and to expose that ability to the Windows audio system.
This topic presents the implementation details for an audio driver that is developed for an audio adapter that is capable of processing hardware-offloaded audio streams.
These additional topics in this section discuss the issues that you should be aware of when you develop an audio driver for an audio adapter that implements a hardware audio engine to handle offloaded audio streams.
Portcls Helper Interfaces for Offloaded Audio Processing
Glitch Reporting for Offloaded Audio
Hardware offload - KS filter topology
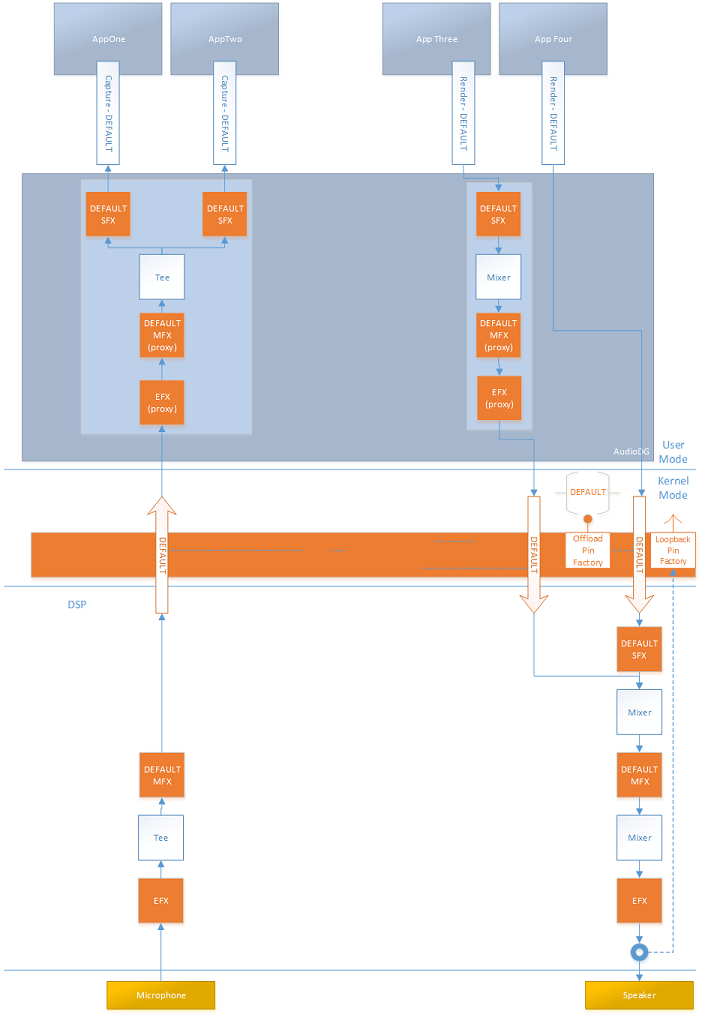
Windows supports the use of an audio adapter that can use an on-board hardware audio engine to process audio streams. When you develop such an audio adapter, the associated audio driver must expose this fact to the user mode audio system in a specific manner, so that the audio system can discover, use and properly expose the features of this adapter and its driver.
The KSNODETYPE_AUDIO_ENGINE GUID for node descriptors
If an audio adapter is capable of processing offloaded audio streams, the adapter’s audio driver exposes this capability by using a node in the KS-filter for the adapter.
If an audio adapter is capable of processing offloaded audio streams, the adapter’s audio driver exposes this capability by using a specific node in the KS-filter for the adapter.
Each node in the path of the audio stream has a node descriptor, for hardware off load, the driver must set the Type GUID to KSNODETYPE_AUDIO_ENGINE.
Here’s an example of how the driver could configure the node descriptor for this node:
typedef struct _KSNODE_DESCRIPTOR {
const KSAUTOMATION_TABLE *AutomationTable; // drv specific
const GUID *Type; // must be set to KSNODETYPE_AUDIO_ENGINE
const GUID *Name; // drv specific (KSNODETYPE_AUDIO_ENGINE?)
} KSNODE_DESCRIPTOR, *PKSNODE_DESCRIPTOR;
If the Name GUID is set to KSNODETYPE_AUDIO_ENGINE, then you must create a default name string for this node. You then add that string to ks.inf, so that during installation of the driver, the string can be used to populate the MediaCategories registry key.
The definition of the GUID for the node type, KSNODETYPE_AUDIO_ENGINE, is as follows:
Code style
#define STATIC_KSNODETYPE_AUDIO_ENGINE\
0x35caf6e4, 0xf3b3, 0x4168, 0xbb, 0x4b, 0x55, 0xe7, 0x7a, 0x46, 0x1c, 0x7e
DEFINE_GUIDSTRUCT("35CAF6E4-F3B3-4168-BB4B-55E77A461C7E", KSNODETYPE_AUDIO_ENGINE);
#define KSNODETYPE_AUDIO_ENGINE DEFINE_GUIDNAMED(KSNODETYPE_AUDIO_ENGINE)
For more information, see the ksmedia.h header file.
And based on the preceding information, a descriptor for a miniport node could look like the following:
PCNODE_DESCRIPTOR MiniportNodes[] =
{
// KSNODE_WAVE_AUDIO_ENGINE
{
0, // Flags
NULL, // AutomationTable
&KSNODETYPE_AUDIO_ENGINE, // Type KSNODETYPE_AUDIO_ENGINE
NULL // Name
}
};
The KSPROPSETID_AudioEngine KS property set for audio engines
The KSPROPSETID_AudioEngine property set is used to support hardware audio engines and hardware-offloaded audio processing. So the driver for an adapter that can process offloaded audio streams must support the properties in this new property set.
The property set, KSPROPSETID_AudioEngine, is defined as follows:
#define STATIC_KSPROPSETID_AudioEngine\
0x3A2F82DCL, 0x886F, 0x4BAA, 0x9E, 0xB4, 0x8, 0x2B, 0x90, 0x25, 0xC5, 0x36
DEFINE_GUIDSTRUCT("3A2F82DC-886F-4BAA-9EB4-082B9025C536", KSPROPSETID_AudioEngine);
#define KSPROPSETID_AudioEngine DEFINE_GUIDNAMED(KSPROPSETID_AudioEngine)
The names of the properties in this property set are defined in the KSPROPERTY_AUDIOENGINE enum, and the driver must support these names.
Here are the properties in the KSPROPSETID_AudioEngine property set:
KSPROPERTY_AUDIOENGINE_BUFFER_SIZE_RANGE
KSPROPERTY_AUDIOENGINE_DESCRIPTOR
KSPROPERTY_AUDIOENGINE_DEVICEFORMAT
KSPROPERTY_AUDIOENGINE_GFXENABLE
KSPROPERTY_AUDIOENGINE_LFXENABLE
KSPROPERTY_AUDIOENGINE_LOOPBACK_PROTECTION
KSPROPERTY_AUDIOENGINE_MIXFORMAT
KSPROPERTY_AUDIOENGINE_SUPPORTEDDEVICEFORMATS
KSPROPERTY_AUDIOENGINE_VOLUMELEVEL
Required properties in the KSPROPSETID_ Audio property set
In addition to supporting the properties in the KSPROPSETID_AudioEngine property set, the driver must also support the following existing properties in the KSPROPSETID_Audio property set:
And to complete the implementation of driver support for hardware-offloaded audio processing, properties are available to the KSPROPSETID_ Audio property set.
KSPROPERTY_AUDIO_LINEAR_BUFFER_POSITION
KSPROPERTY_AUDIO_PRESENTATION_POSITION
KSPROPERTY_AUDIO_WAVERT_CURRENT_WRITE_POSITION
Port-class driver updates and glitch reporting
In addition to the support described in the preceding sections for hardware-offloaded audio processing, the Windows port-class driver provides "helper interfaces" to make it simple to develop a driver that can work with offloaded audio streams. And when such a driver detects glitches, there is a mechanism in place to allow the driver to report the glitch errors. The following topics provide more details about the helper interfaces and glitch reporting:
Portcls Helper Interfaces for Offloaded Audio Processing In addition to the support described in the preceding sections for hardware-offloaded audio processing, the Windows port-class driver has also includes "helper interfaces" to make it simple to develop a driver that can work with offloaded audio streams. And when such a driver detects glitches, there is a mechanism in place to allow the driver to report the glitch errors. The following topics provide more details about the helper interfaces and glitch reporting: