Configure ExpressRoute and Site-to-Site coexisting connections using the Azure portal
This article helps you configure ExpressRoute and Site-to-Site VPN connections that coexist. Configuring both connections has several advantages, such as providing a secure failover path or connecting to sites not linked through ExpressRoute. This guide applies to the Resource Manager deployment model.
Advantages of Coexisting Connections
- Secure Failover Path: Configure a Site-to-Site VPN as a backup for ExpressRoute.
- Connect to Additional Sites: Use Site-to-Site VPNs to connect to sites not connected through ExpressRoute.
The steps to configure both scenarios are covered in this article. You can configure either gateway first, typically without incurring downtime when adding a new gateway or gateway connection.
Note
- For creating a Site-to-Site VPN over an ExpressRoute connection, see Site-to-site over Microsoft peering.
- If you already have ExpressRoute, you don't need to create a virtual network or gateway subnet as they're prerequisites for creating an ExpressRoute.
- For encrypted ExpressRoute Gateway, MSS (maximum segment size) Clamping is done over Azure VPN Gateway to clamp TCP packet size at 1,250 bytes.
Limits and Limitations
- Only route-based VPN gateway is supported: Use a route-based VPN gateway. You can also use a route-based VPN gateway with a VPN connection configured for 'policy-based traffic selectors' as described in Connect to multiple policy-based VPN devices.
- ExpressRoute-VPN Gateway coexist configurations are not supported on the Basic SKU.
- BGP Communication: Both the ExpressRoute and VPN gateways must communicate via BGP. Ensure that any UDR on the gateway subnet doesn't include a route for the gateway subnet range itself, as doing so interferes with the BGP traffic.
- Transit Routing: For transit routing between ExpressRoute and VPN, the ASN of Azure VPN Gateway must be set to 65515. Azure VPN Gateway supports the BGP routing protocol. To work together, keep the ASN of your Azure VPN gateway at its default value, 65515. If you change the ASN to 65515, reset the VPN gateway for the setting to take effect.
- Gateway Subnet Size: The gateway subnet must be /27 or a shorter prefix (such as /26 or /25), or you receive an error message when adding the ExpressRoute virtual network gateway.
Configuration Designs
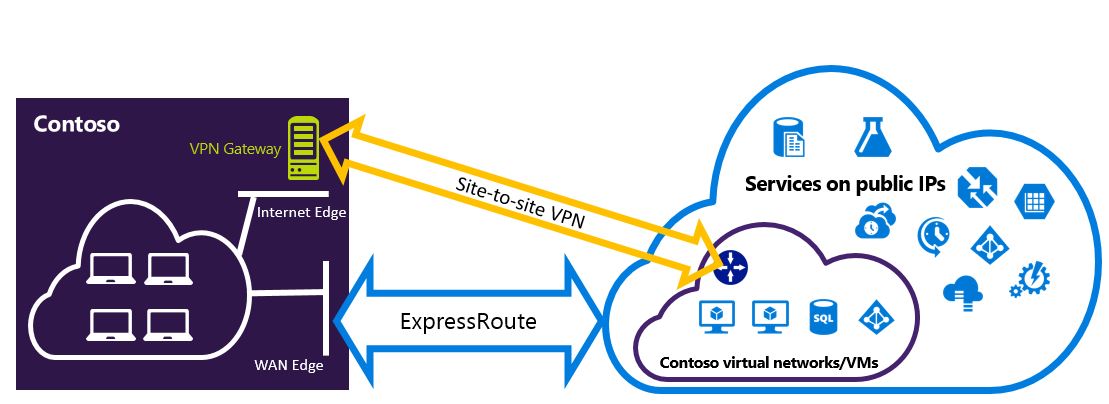
Configure a Site-to-Site VPN as a Failover Path for ExpressRoute
You can set up a Site-to-Site VPN connection as a backup for ExpressRoute. This setup is applicable only to virtual networks linked to the Azure private peering path. There's no VPN-based failover solution for services accessible through Azure Microsoft peering. The ExpressRoute circuit remains the primary link, and data flows through the Site-to-Site VPN path only if the ExpressRoute circuit fails. To avoid asymmetrical routing, configure your local network to prefer the ExpressRoute circuit over the Site-to-Site VPN by setting a higher local preference for the routes received via ExpressRoute.
Note
If you have ExpressRoute Microsoft Peering enabled, you can receive the public IP address of your Azure VPN gateway on the ExpressRoute connection. To set up your Site-to-Site VPN connection as a backup, configure your on-premises network so that the VPN connection is routed to the Internet.
Note
While the ExpressRoute circuit is preferred over Site-to-Site VPN when both routes are the same, Azure will use the longest prefix match to choose the route towards the packet's destination.
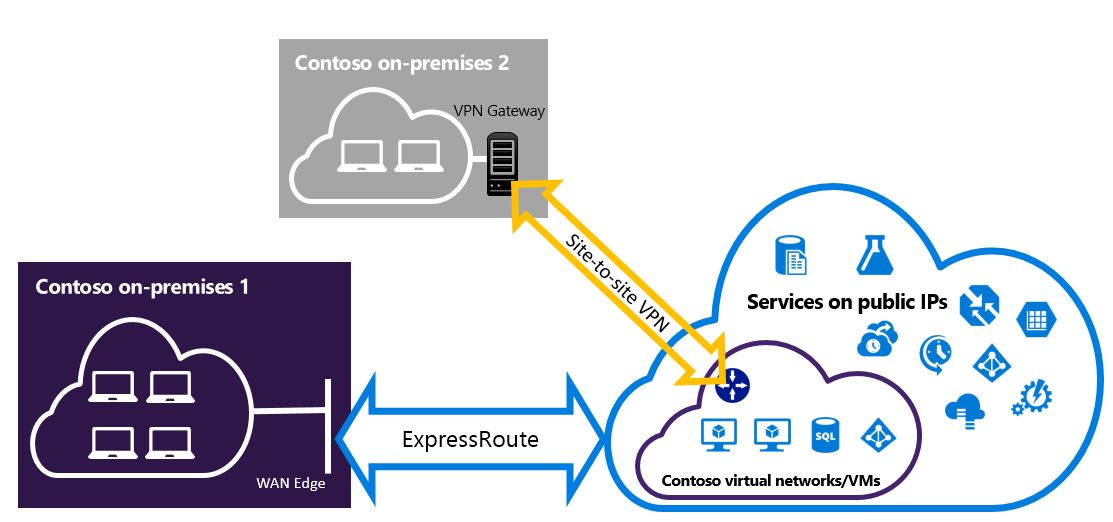
Configure a Site-to-Site VPN to Connect to Sites Not Connected Through ExpressRoute
You can configure your network so that some sites connect directly to Azure over Site-to-Site VPN, while others connect through ExpressRoute.
Selecting the Steps to Use
There are two different sets of procedures to choose from. The configuration procedure you select depends on whether you have an existing virtual network that you want to connect to or if you need to create a new virtual network.
I don't have a VNet and need to create one.
If you don’t already have a virtual network, follow the steps in To create a new virtual network and coexisting connections to create a new virtual network using the Resource Manager deployment model and set up new ExpressRoute and Site-to-Site VPN connections.
I already have a Resource Manager deployment model VNet.
If you already have a virtual network with an existing Site-to-Site VPN connection or ExpressRoute connection, and the gateway subnet prefix is /28 or longer (/29, /30, etc.), you need to delete the existing gateway. Follow the steps in To configure coexisting connections for an already existing virtual network to delete the gateway and create new ExpressRoute and Site-to-Site VPN connections.
Deleting and recreating your gateway will result in downtime for your cross-premises connections. However, your VMs and services can still communicate out through the load balancer during this process if they're configured to do so.
To create a new virtual network and coexisting connections
This procedure guides you through creating a virtual network and configuring coexisting Site-to-Site and ExpressRoute connections.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
On the top left-hand side of the screen, select + Create a resource and search for Virtual network.
Select Create to begin configuring the virtual network.
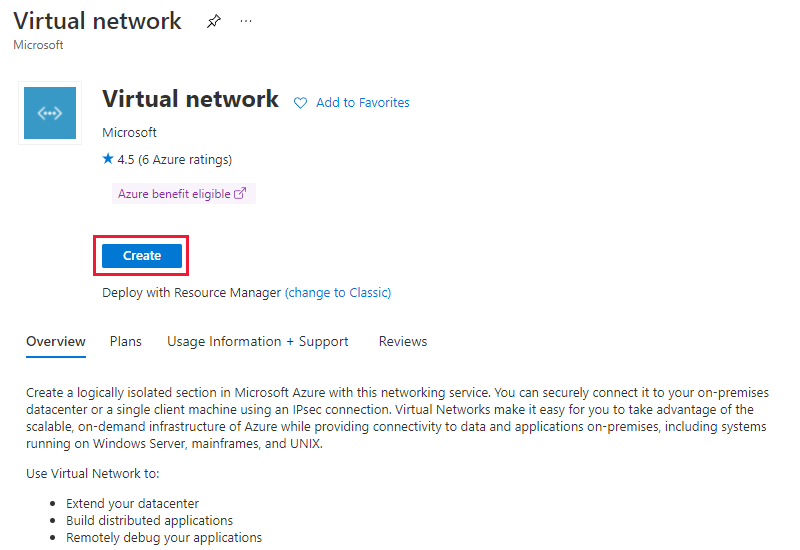
On the Basics tab, select or create a new resource group to store the virtual network. Enter the name and select the region to deploy the virtual network. Select Next: IP Addresses > to configure the address space and subnets.
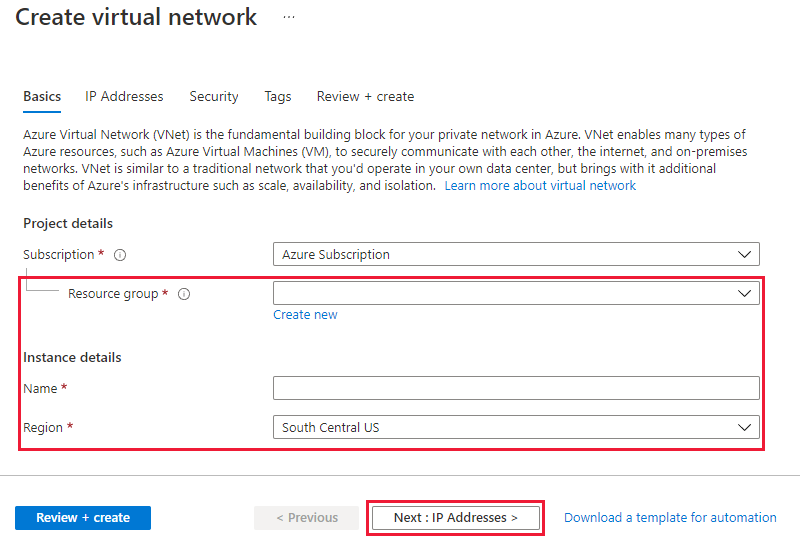
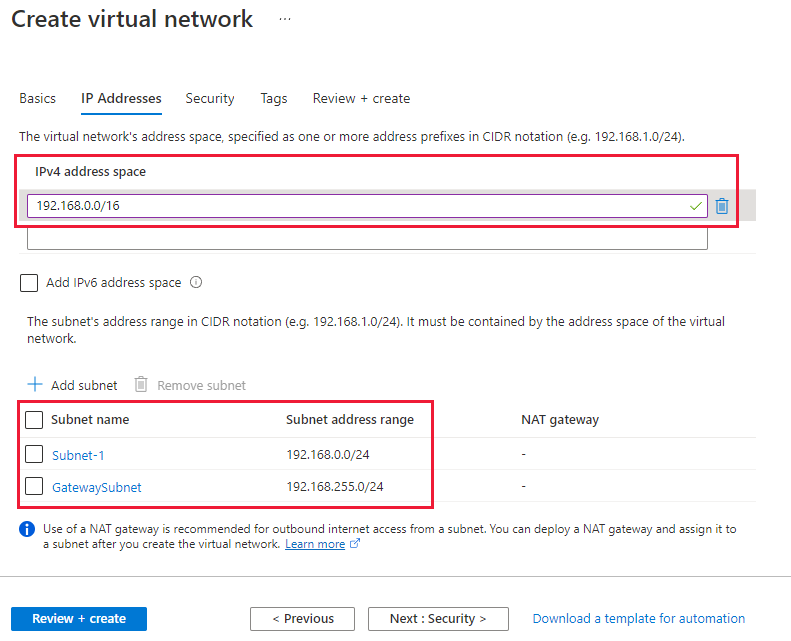
On the IP Addresses tab, configure the virtual network address space. Define the subnets you want to create, including the gateway subnet. Select Review + create, then Create to deploy the virtual network. For more information about creating a virtual network, see Create a virtual network. For more information about creating subnets, see Create a subnet.
Important
The Gateway Subnet must be /27 or a shorter prefix (such as /26 or /25).
Create the Site-to-Site VPN gateway and local network gateway. For more information about the VPN gateway configuration, see Configure a virtual network with a Site-to-Site connection. The GatewaySku is only supported for VpnGw1, VpnGw2, VpnGw3, Standard, and HighPerformance VPN gateways. ExpressRoute-VPN Gateway coexist configurations aren't supported on the Basic SKU. The VpnType must be RouteBased.
Configure your local VPN device to connect to the new Azure VPN gateway. For more information about VPN device configuration, see VPN Device Configuration.
If you're connecting to an existing ExpressRoute circuit, skip steps 8 & 9 and jump to step 10. Configure ExpressRoute circuits. For more information about configuring an ExpressRoute circuit, see Create an ExpressRoute circuit.
Configure Azure private peering over the ExpressRoute circuit. For more information about configuring Azure private peering over the ExpressRoute circuit, see Configure peering.
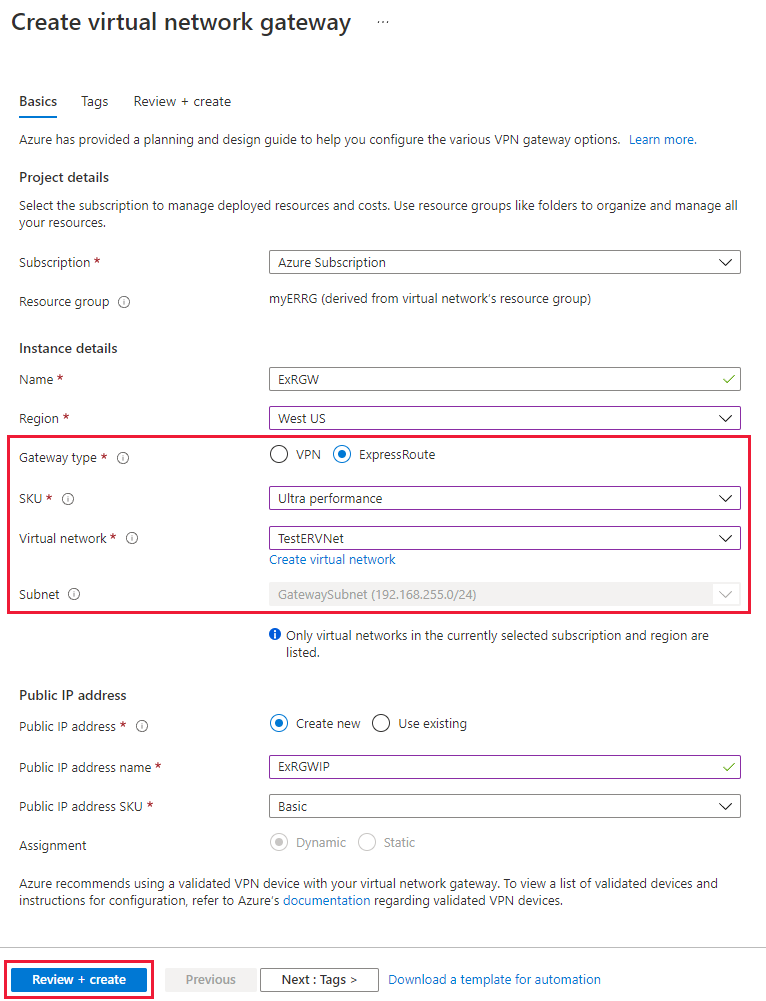
Select + Create a resource and search for Virtual network gateway. Then select Create.
Select the ExpressRoute gateway type, the appropriate SKU, and the virtual network to deploy the gateway to.
Link the ExpressRoute gateway to the ExpressRoute circuit. After this step is completed, the connection between your on-premises network and Azure through ExpressRoute is established. For more information about the link operation, see Link VNets to ExpressRoute.
To configure coexisting connections for an already existing virtual network
If you have a virtual network with only one virtual network gateway (for example, a Site-to-Site VPN gateway) and you want to add another gateway of a different type (for example, ExpressRoute gateway), check the gateway subnet size. If the gateway subnet is /27 or larger, you can skip the following steps and follow the steps in the previous section to add either a Site-to-Site VPN gateway or an ExpressRoute gateway. If the gateway subnet is /28 or /29, you must first delete the virtual network gateway and increase the gateway subnet size. The steps in this section show you how to do that.
Delete the existing ExpressRoute or Site-to-Site VPN gateway.
Delete and recreate the GatewaySubnet with a prefix of /27 or shorter.
Configure a virtual network with a Site-to-Site connection and then Configure the ExpressRoute gateway.
Once the ExpressRoute gateway is deployed, you can link the virtual network to the ExpressRoute circuit.
To add point-to-site configuration to the VPN gateway
You can add a Point-to-Site configuration to your coexisting set by following the instructions in Configuring Point-to-Site VPN connection using Azure certificate authentication.
To enable transit routing between ExpressRoute and Azure VPN
If you want to enable connectivity between one of your local networks connected to ExpressRoute and another local network connected to a Site-to-Site VPN connection, you need to set up Azure Route Server.
Next steps
For more information about ExpressRoute, see the ExpressRoute FAQ.