C# 식
.NET Framework 4.5부터 Windows WF(Workflow Foundation)에서 C# 식이 지원됩니다. Visual Studio 2012에서 .NET Framework 4.5를 대상으로 만들어진 새 C# 워크플로 프로젝트에서는 C# 식을 사용하고, Visual Basic 워크플로 프로젝트에서는 Visual Basic 식을 사용합니다. Visual Basic 식을 사용하는 기존 .NET Framework 4 워크플로 프로젝트는 프로젝트 언어에 관계없이 .NET Framework 4.6.1으로 마이그레이션할 수 있으며 지원됩니다. 이 항목에서는 WF의 C# 식에 대해 간략하게 설명합니다.
워크플로에서 C# 식 사용
워크플로 디자이너에서 C# 식 사용
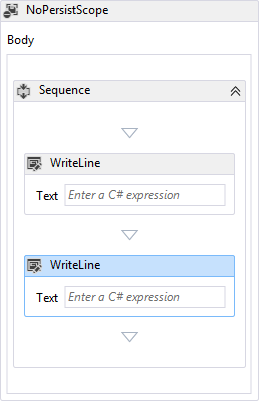
.NET Framework 4.5부터 Windows WF(Workflow Foundation)에서 C# 식이 지원됩니다. Visual Studio 2012에서 .NET Framework 4.5를 대상으로 만들어진 C# 워크플로 프로젝트에서는 C# 식을 사용하지만, Visual Basic 워크플로 프로젝트에서는 Visual Basic 식을 사용합니다. 원하는 C# 식을 지정하려면 C# 식 입력이라는 상자에 해당 식을 입력합니다. 이 레이블은 디자이너에서 활동이 선택된 경우 속성 창에 표시되거나 워크플로 디자이너의 활동에 표시됩니다. 다음 예제에서는 WriteLine의 Sequence 내에 두 개의 NoPersistScope 활동이 포함되어 있습니다.
참고 항목
C# 식은 Visual Studio에서만 지원되며 재호스트된 워크플로 디자이너에서는 지원되지 않습니다. 재호스트된 디자이너에서 지원되는 새로운 WF45 기능에 대한 자세한 내용은 재호스트된 워크플로 디자이너에서 새 Workflow Foundation 4.5 기능에 대한 지원을 참조하세요.
이전 버전과의 호환성
.NET Framework 4.6.1로 마이그레이션된 기존 .NET Framework 4 C# 워크플로 프로젝트의 Visual Basic 식이 지원됩니다. Visual Basic 식이 워크플로 디자이너에 표시될 때 Visual Basic 식이 유효한 C# 구문이 아니면 기존 Visual Basic 식의 텍스트는 값이 XAML로 설정되었습니다.로 대체됩니다. Visual Basic 식이 유효한 C# 구문인 경우에는 해당 식이 표시됩니다. Visual Basic 식을 C#으로 업데이트하려면 워크플로 디자이너에서 식을 편집하고 해당하는 C#식을 지정하면 됩니다. Visual Basic 식을 반드시 C#으로 업데이트할 필요는 없지만, Workflow Designer에서 식을 업데이트한 후에는 식이 C#으로 변환되며 이를 Visual Basic으로 되돌릴 수는 없습니다.
코드 워크플로에서 C# 식 사용
.NET Framework 4.6.1 코드 기반 워크플로에서는 C# 식이 지원되지만 워크플로를 호출하려면 먼저 TextExpressionCompiler.Compile을 사용하여 C# 식을 컴파일해야 합니다. 워크플로 작성자는 CSharpValue를 사용하여 식의 r-value를 나타내고 CSharpReference를 사용하여 식의 l-value를 나타냅니다. 다음 예제에서는 Assign 활동에 포함된 WriteLine 활동과 Sequence 활동으로 워크플로를 만듭니다. CSharpReference의 To 인수에는 Assign가 지정되어 식의 l-value를 나타냅니다. CSharpValue의 Value 인수와 Assign의 Text 인수에는 WriteLine가 지정되어 이 두 식의 r-value를 나타냅니다.
Variable<int> n = new Variable<int>
{
Name = "n"
};
Activity wf = new Sequence
{
Variables = { n },
Activities =
{
new Assign<int>
{
To = new CSharpReference<int>("n"),
Value = new CSharpValue<int>("new Random().Next(1, 101)")
},
new WriteLine
{
Text = new CSharpValue<string>("\"The number is \" + n")
}
}
};
CompileExpressions(wf);
WorkflowInvoker.Invoke(wf);
워크플로가 생성된 후에는 CompileExpressions 도우미 메서드를 호출하여 C# 식을 컴파일한 다음 워크플로를 호출합니다. 다음 예제는 CompileExpressions 메서드입니다.
static void CompileExpressions(Activity activity)
{
// activityName is the Namespace.Type of the activity that contains the
// C# expressions.
string activityName = activity.GetType().ToString();
// Split activityName into Namespace and Type.Append _CompiledExpressionRoot to the type name
// to represent the new type that represents the compiled expressions.
// Take everything after the last . for the type name.
string activityType = activityName.Split('.').Last() + "_CompiledExpressionRoot";
// Take everything before the last . for the namespace.
string activityNamespace = string.Join(".", activityName.Split('.').Reverse().Skip(1).Reverse());
// Create a TextExpressionCompilerSettings.
TextExpressionCompilerSettings settings = new TextExpressionCompilerSettings
{
Activity = activity,
Language = "C#",
ActivityName = activityType,
ActivityNamespace = activityNamespace,
RootNamespace = null,
GenerateAsPartialClass = false,
AlwaysGenerateSource = true,
ForImplementation = false
};
// Compile the C# expression.
TextExpressionCompilerResults results =
new TextExpressionCompiler(settings).Compile();
// Any compilation errors are contained in the CompilerMessages.
if (results.HasErrors)
{
throw new Exception("Compilation failed.");
}
// Create an instance of the new compiled expression type.
ICompiledExpressionRoot compiledExpressionRoot =
Activator.CreateInstance(results.ResultType,
new object[] { activity }) as ICompiledExpressionRoot;
// Attach it to the activity.
CompiledExpressionInvoker.SetCompiledExpressionRoot(
activity, compiledExpressionRoot);
}
참고 항목
C# 식이 컴파일되지 않은 경우 워크플로가 호출되면 다음과 유사한 메시지와 함께 NotSupportedException이 throw됩니다. Expression Activity type 'CSharpValue1'에 실행하기 위해 컴파일이 필요합니다. 워크플로가 컴파일되었는지 확인하세요.'
사용자 지정 코드 기반 워크플로에서 DynamicActivity를 사용하는 경우에는 다음 코드 예제와 같이 CompileExpressions 메서드를 일부 변경해야 합니다.
static void CompileExpressions(DynamicActivity dynamicActivity)
{
// activityName is the Namespace.Type of the activity that contains the
// C# expressions. For Dynamic Activities this can be retrieved using the
// name property , which must be in the form Namespace.Type.
string activityName = dynamicActivity.Name;
// Split activityName into Namespace and Type.Append _CompiledExpressionRoot to the type name
// to represent the new type that represents the compiled expressions.
// Take everything after the last . for the type name.
string activityType = activityName.Split('.').Last() + "_CompiledExpressionRoot";
// Take everything before the last . for the namespace.
string activityNamespace = string.Join(".", activityName.Split('.').Reverse().Skip(1).Reverse());
// Create a TextExpressionCompilerSettings.
TextExpressionCompilerSettings settings = new TextExpressionCompilerSettings
{
Activity = dynamicActivity,
Language = "C#",
ActivityName = activityType,
ActivityNamespace = activityNamespace,
RootNamespace = null,
GenerateAsPartialClass = false,
AlwaysGenerateSource = true,
ForImplementation = true
};
// Compile the C# expression.
TextExpressionCompilerResults results =
new TextExpressionCompiler(settings).Compile();
// Any compilation errors are contained in the CompilerMessages.
if (results.HasErrors)
{
throw new Exception("Compilation failed.");
}
// Create an instance of the new compiled expression type.
ICompiledExpressionRoot compiledExpressionRoot =
Activator.CreateInstance(results.ResultType,
new object[] { dynamicActivity }) as ICompiledExpressionRoot;
// Attach it to the activity.
CompiledExpressionInvoker.SetCompiledExpressionRootForImplementation(
dynamicActivity, compiledExpressionRoot);
}
동적 활동에서 C# 식을 컴파일하는 CompileExpressions 오버로드에는 몇 가지 차이점이 있습니다.
CompileExpressions에 대한 매개 변수는DynamicActivity입니다.형식 이름 및 네임스페이스는
DynamicActivity.Name속성을 사용하여 검색됩니다.TextExpressionCompilerSettings.ForImplementation이true로 설정됩니다.CompiledExpressionInvoker.SetCompiledExpressionRootForImplementation대신CompiledExpressionInvoker.SetCompiledExpressionRoot이 호출됩니다.
코드에서 식을 사용하는 방법에 대한 자세한 내용은 명령 코드를 사용하여 워크플로, 활동 및 식 작성을 참조하세요.
XAML 워크플로에서 C# 식 사용
XAML 워크플로에서는 C# 식이 지원됩니다. 컴파일된 XAML 워크플로는 형식으로 컴파일되고, 느슨한 XAML 워크플로는 런타임에 의해 로드된 후 워크플로가 실행될 때 활동 트리로 컴파일됩니다.
컴파일된 XAML
.NET Framework 4.6.1을 대상으로 하는 C# 워크플로 프로젝트의 일부로서 형식으로 컴파일되는 컴파일된 XAML 워크플로에서는 C# 식이 지원됩니다. 컴파일된 XAML은 Visual Studio에서 워크플로 작성의 기본 형식이며, .NET Framework 4.6.1을 대상으로 Visual Studio에서 만들어진 C# 워크플로 프로젝트는 C# 식을 사용합니다.
느슨한 XAML
느슨한 XAML 워크플로에서는 C# 식이 지원됩니다. 느슨한 XAML 워크플로를 로드 및 호출하는 워크플로 호스트 프로그램은 .NET Framework 4.6.1을 대상으로 하며, CompileExpressions는 true로 설정되어야 합니다(기본값 false). CompileExpressions를 true로 설정하려면 ActivityXamlServicesSettings 속성을 CompileExpressions로 설정하여 true 인스턴스를 만든 후 이를 ActivityXamlServices.Load에 매개 변수로 전달합니다. CompileExpressions가 true로 설정되어 있지 않으면 다음과 유사한 메시지와 함께 NotSupportedException이 throw됩니다. Expression Activity type 'CSharpValue1'에는 실행하기 위해 컴파일이 필요합니다. 워크플로가 컴파일되었는지 확인하세요.'
ActivityXamlServicesSettings settings = new ActivityXamlServicesSettings
{
CompileExpressions = true
};
DynamicActivity<int> wf = ActivityXamlServices.Load(new StringReader(serializedAB), settings) as DynamicActivity<int>;
XAML 워크플로를 사용하는 방법에 대한 자세한 내용은 XAML 간에 워크플로 및 활동 직렬화를 참조하세요.
XAMLX 워크플로 서비스에서 C# 식 사용
XAMLX 워크플로 서비스에서는 C# 식이 지원됩니다. 워크플로 서비스가 IIS 또는 WAS에서 호스트되는 경우에는 추가 단계가 필요하지 않지만, XAML 워크플로 서비스가 자체 호스트되는 경우 C# 식을 컴파일해야 합니다. 자체 호스트된 XAMLX 워크플로 서비스에서 C# 식을 컴파일하려면 먼저 XAMLX 파일을 WorkflowService에 로드한 다음, WorkflowService의 Body를 앞의 코드 워크플로에서 C# 식 사용 섹션에서 설명한 CompileExpressions 메서드에 전달합니다. 다음 예제에서는 XAMLX 워크플로 서비스를 로드하고 C# 식을 컴파일한 다음 워크플로 서비스를 열고 요청을 기다립니다.
// Load the XAMLX workflow service.
WorkflowService workflow1 =
(WorkflowService)XamlServices.Load(xamlxPath);
// Compile the C# expressions in the workflow by passing the Body to CompileExpressions.
CompileExpressions(workflow1.Body);
// Initialize the WorkflowServiceHost.
var host = new WorkflowServiceHost(workflow1, new Uri("http://localhost:8293/Service1.xamlx"));
// Enable Metadata publishing/
ServiceMetadataBehavior smb = new ServiceMetadataBehavior();
smb.HttpGetEnabled = true;
smb.MetadataExporter.PolicyVersion = PolicyVersion.Policy15;
host.Description.Behaviors.Add(smb);
// Open the WorkflowServiceHost and wait for requests.
host.Open();
Console.WriteLine("Press enter to quit");
Console.ReadLine();
C# 식이 컴파일되지 않은 경우 Open 작업이 성공하지만 워크플로 호출에는 실패합니다. 다음 CompileExpressions 메서드는 앞의 코드 워크플로에서 C# 식 사용 섹션에 나온 메서드와 동일합니다.
static void CompileExpressions(Activity activity)
{
// activityName is the Namespace.Type of the activity that contains the
// C# expressions.
string activityName = activity.GetType().ToString();
// Split activityName into Namespace and Type.Append _CompiledExpressionRoot to the type name
// to represent the new type that represents the compiled expressions.
// Take everything after the last . for the type name.
string activityType = activityName.Split('.').Last() + "_CompiledExpressionRoot";
// Take everything before the last . for the namespace.
string activityNamespace = string.Join(".", activityName.Split('.').Reverse().Skip(1).Reverse());
// Create a TextExpressionCompilerSettings.
TextExpressionCompilerSettings settings = new TextExpressionCompilerSettings
{
Activity = activity,
Language = "C#",
ActivityName = activityType,
ActivityNamespace = activityNamespace,
RootNamespace = null,
GenerateAsPartialClass = false,
AlwaysGenerateSource = true,
ForImplementation = false
};
// Compile the C# expression.
TextExpressionCompilerResults results =
new TextExpressionCompiler(settings).Compile();
// Any compilation errors are contained in the CompilerMessages.
if (results.HasErrors)
{
throw new Exception("Compilation failed.");
}
// Create an instance of the new compiled expression type.
ICompiledExpressionRoot compiledExpressionRoot =
Activator.CreateInstance(results.ResultType,
new object[] { activity }) as ICompiledExpressionRoot;
// Attach it to the activity.
CompiledExpressionInvoker.SetCompiledExpressionRoot(
activity, compiledExpressionRoot);
}
.NET
