Compilare un'app LUIS a livello di codice con Node.js
Importante
LUIS verrà ritirato il 1 ottobre 2025 e a partire dal 1 aprile 2023 non è più possibile creare nuove risorse LUIS. Si consiglia di eseguire la migrazione delle applicazioni LUIS a comprensione del linguaggio di conversazione per sfruttare appieno il supporto continuativo per i prodotti e le funzionalità multilingue.
LUIS fornisce un'API a livello di codice che esegue le stesse operazioni del sito Web LUIS. In questo modo è possibile risparmiare tempo quando si dispone di dati preesistenti e sarebbe più veloce creare un'app LUIS a livello di codice anziché immettere manualmente le informazioni.
Attenzione
Questo documento non è stato aggiornato con il testo e gli screenshot dell'ultima versione del portale LUIS.
Prerequisiti
- Accedere al sito Web LUIS e individuare la chiave di creazione in Impostazioni account. Questa chiave viene usata per chiamare l'API di creazione.
- Se non si ha una sottoscrizione di Azure, creare un account gratuito prima di iniziare.
- Questo articolo inizia con un CSV per un file di log di richieste degli utenti di un'ipotetica azienda. Scaricarla qui.
- Installare la versione di Node.js più recente. Scaricarla qui.
- [Consigliato] Visual Studio Code per IntelliSense e debug. Scaricarlo qui gratuitamente.
Tutto il codice di questo articolo è disponibile nel repository GitHub Azure-Samples Language Understanding.
Eseguire il mapping dei dati preesistenti a finalità ed entità
Anche se si dispone di un sistema che non è stato creato considerando LUIS, se contiene dati testuali mappati a cose diverse che gli utenti intendono realizzare, è possibile che si riesca a eseguire il mapping delle categorie di input utente esistenti alle finalità in LUIS. Se è possibile identificare parole o frasi importanti in ciò che gli utenti hanno detto, è possibile eseguire il mapping di queste parole a delle entità.
Apri il file IoT.csv. Questo file contiene un log di richieste degli utenti poste a un ipotetico servizio di domotica e include una suddivisione in categorie, ciò che l'utente ha detto e alcune colonne con informazioni utili estratte da quanto richiesto.
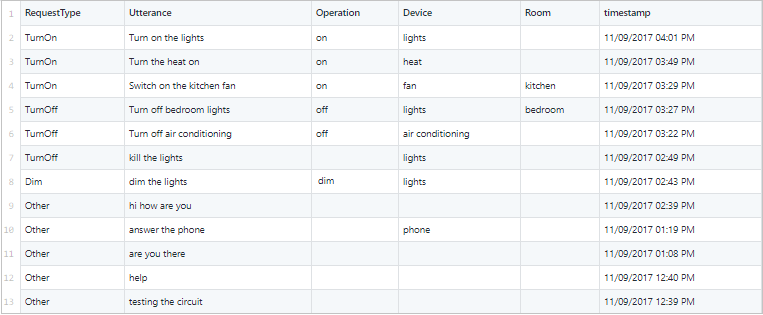
Si noti che il contenuto della colonna RequestType potrebbe rappresentare le finalità e che la colonna Request riporta espressioni di esempio. Gli altri campi potrebbero costituire delle entità, se si presentano nell'espressione. Poiché sono presenti finalità, entità ed espressioni di esempio, ci sono tutti i requisiti per una semplice app di esempio.
Procedura per generate un'app LUIS da dati non LUIS
Per generare un'app LUIS dal file CSV:
- Analizzare i dati dal file CSV:
- Eseguire la conversione in un formato che sia possibile caricare in LUIS usando l'API di creazione.
- Dai dati analizzati raccogliere informazioni su finalità ed entità.
- Eseguire chiamate API di creazione a:
- Creare l'app.
- Aggiungere le finalità e le entità raccolte dai dati analizzati.
- Dopo aver creato l'app LUIS, è possibile aggiungere le espressioni di esempio ottenute dai dati analizzati.
È possibile osservare questo flusso di programmi nell'ultima parte del file index.js. Copiare o scaricare questo codice e salvarlo in index.js.
Importante
Al termine, ricordarsi di rimuovere la chiave dal codice e non renderlo mai pubblico. Per un ambiente di produzione usare un metodo sicuro per l'archiviazione e l'accesso alle proprie credenziali, ad esempio Azure Key Vault. Per altre informazioni, vedere l'articolo sulla sicurezza del Servizi di Azure AI.
var path = require('path');
const parse = require('./_parse');
const createApp = require('./_create');
const addEntities = require('./_entities');
const addIntents = require('./_intents');
const upload = require('./_upload');
// Change these values
const LUIS_authoringKey = "YOUR_AUTHORING_KEY";
const LUIS_appName = "Sample App - build from IoT csv file";
const LUIS_appCulture = "en-us";
const LUIS_versionId = "0.1";
// NOTE: final output of add-utterances api named utterances.upload.json
const downloadFile = "./IoT.csv";
const uploadFile = "./utterances.json"
// The app ID is returned from LUIS when your app is created
var LUIS_appId = ""; // default app ID
var intents = [];
var entities = [];
/* add utterances parameters */
var configAddUtterances = {
LUIS_subscriptionKey: LUIS_authoringKey,
LUIS_appId: LUIS_appId,
LUIS_versionId: LUIS_versionId,
inFile: path.join(__dirname, uploadFile),
batchSize: 100,
uri: "https://westus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/luis/api/v2.0/apps/{appId}/versions/{versionId}/examples"
};
/* create app parameters */
var configCreateApp = {
LUIS_subscriptionKey: LUIS_authoringKey,
LUIS_versionId: LUIS_versionId,
appName: LUIS_appName,
culture: LUIS_appCulture,
uri: "https://westus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/luis/api/v2.0/apps/"
};
/* add intents parameters */
var configAddIntents = {
LUIS_subscriptionKey: LUIS_authoringKey,
LUIS_appId: LUIS_appId,
LUIS_versionId: LUIS_versionId,
intentList: intents,
uri: "https://westus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/luis/api/v2.0/apps/{appId}/versions/{versionId}/intents"
};
/* add entities parameters */
var configAddEntities = {
LUIS_subscriptionKey: LUIS_authoringKey,
LUIS_appId: LUIS_appId,
LUIS_versionId: LUIS_versionId,
entityList: entities,
uri: "https://westus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/luis/api/v2.0/apps/{appId}/versions/{versionId}/entities"
};
/* input and output files for parsing CSV */
var configParse = {
inFile: path.join(__dirname, downloadFile),
outFile: path.join(__dirname, uploadFile)
};
// Parse CSV
parse(configParse)
.then((model) => {
// Save intent and entity names from parse
intents = model.intents;
entities = model.entities;
// Create the LUIS app
return createApp(configCreateApp);
}).then((appId) => {
// Add intents
LUIS_appId = appId;
configAddIntents.LUIS_appId = appId;
configAddIntents.intentList = intents;
return addIntents(configAddIntents);
}).then(() => {
// Add entities
configAddEntities.LUIS_appId = LUIS_appId;
configAddEntities.entityList = entities;
return addEntities(configAddEntities);
}).then(() => {
// Add example utterances to the intents in the app
configAddUtterances.LUIS_appId = LUIS_appId;
return upload(configAddUtterances);
}).catch(err => {
console.log(err.message);
});
Analizzare il file CSV
Le voci di colonna che contengono le espressioni nel file CSV devono essere analizzate in un formato JSON che LUIS è in grado di comprendere. Questo formato JSON deve contenere un campo intentName che identifica la finalità dell'espressione. Deve anche contenere un campo entityLabels, che può essere vuoto nel caso in cui non siano presenti entità nell'espressione.
Ad esempio, la voce relativa a "Turn on the lights" esegue il mapping a questo codice JSON:
{
"text": "Turn on the lights",
"intentName": "TurnOn",
"entityLabels": [
{
"entityName": "Operation",
"startCharIndex": 5,
"endCharIndex": 6
},
{
"entityName": "Device",
"startCharIndex": 12,
"endCharIndex": 17
}
]
}
In questo esempio intentName deriva dalla richiesta dell'utente sotto l'intestazione di colonna Request nel file CSV, mentre entityName deriva dalle altre colonne con informazioni chiave. Ad esempio, se è presente una voce per Operation o Device e tale stringa è presente anche nella richiesta effettiva, può essere etichettata come entità. Il codice seguente illustra questo processo di analisi. È possibile copiarlo oppure scaricarlo e salvarlo in _parse.js.
// node 7.x
// built with streams for larger files
const fse = require('fs-extra');
const path = require('path');
const lineReader = require('line-reader');
const babyparse = require('babyparse');
const Promise = require('bluebird');
const intent_column = 0;
const utterance_column = 1;
var entityNames = [];
var eachLine = Promise.promisify(lineReader.eachLine);
function listOfIntents(intents) {
return intents.reduce(function (a, d) {
if (a.indexOf(d.intentName) === -1) {
a.push(d.intentName);
}
return a;
}, []);
}
function listOfEntities(utterances) {
return utterances.reduce(function (a, d) {
d.entityLabels.forEach(function(entityLabel) {
if (a.indexOf(entityLabel.entityName) === -1) {
a.push(entityLabel.entityName);
}
}, this);
return a;
}, []);
}
var utterance = function (rowAsString) {
let json = {
"text": "",
"intentName": "",
"entityLabels": [],
};
if (!rowAsString) return json;
let dataRow = babyparse.parse(rowAsString);
// Get intent name and utterance text
json.intentName = dataRow.data[0][intent_column];
json.text = dataRow.data[0][utterance_column];
// For each column heading that may be an entity, search for the element in this column in the utterance.
entityNames.forEach(function (entityName) {
entityToFind = dataRow.data[0][entityName.column];
if (entityToFind != "") {
strInd = json.text.indexOf(entityToFind);
if (strInd > -1) {
let entityLabel = {
"entityName": entityName.name,
"startCharIndex": strInd,
"endCharIndex": strInd + entityToFind.length - 1
}
json.entityLabels.push(entityLabel);
}
}
}, this);
return json;
};
const convert = async (config) => {
try {
var i = 0;
// get inFile stream
inFileStream = await fse.createReadStream(config.inFile, 'utf-8')
// create out file
var myOutFile = await fse.createWriteStream(config.outFile, 'utf-8');
var utterances = [];
// read 1 line at a time
return eachLine(inFileStream, (line) => {
// skip first line with headers
if (i++ == 0) {
// csv to baby parser object
let dataRow = babyparse.parse(line);
// populate entityType list
var index = 0;
dataRow.data[0].forEach(function (element) {
if ((index != intent_column) && (index != utterance_column)) {
entityNames.push({ name: element, column: index });
}
index++;
}, this);
return;
}
// transform utterance from csv to json
utterances.push(utterance(line));
}).then(() => {
console.log("intents: " + JSON.stringify(listOfIntents(utterances)));
console.log("entities: " + JSON.stringify(listOfEntities(utterances)));
myOutFile.write(JSON.stringify({ "converted_date": new Date().toLocaleString(), "utterances": utterances }));
myOutFile.end();
console.log("parse done");
console.log("JSON file should contain utterances. Next step is to create an app with the intents and entities it found.");
var model =
{
intents: listOfIntents(utterances),
entities: listOfEntities(utterances)
}
return model;
});
} catch (err) {
throw err;
}
}
module.exports = convert;
Creare l'app LUIS
Dopo aver analizzato i dati in JSON, aggiungerli a un'app LUIS. Il codice seguente crea l'app LUIS. Copiarlo oppure scaricarlo e salvarlo in _create.js.
// node 7.x
// uses async/await - promises
var rp = require('request-promise');
var fse = require('fs-extra');
var path = require('path');
// main function to call
// Call Apps_Create
var createApp = async (config) => {
try {
// JSON for the request body
// { "name": MyAppName, "culture": "en-us"}
var jsonBody = {
"name": config.appName,
"culture": config.culture
};
// Create a LUIS app
var createAppPromise = callCreateApp({
uri: config.uri,
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key': config.LUIS_subscriptionKey
},
json: true,
body: jsonBody
});
let results = await createAppPromise;
// Create app returns an app ID
let appId = results.response;
console.log(`Called createApp, created app with ID ${appId}`);
return appId;
} catch (err) {
console.log(`Error creating app: ${err.message} `);
throw err;
}
}
// Send JSON as the body of the POST request to the API
var callCreateApp = async (options) => {
try {
var response;
if (options.method === 'POST') {
response = await rp.post(options);
} else if (options.method === 'GET') { // TODO: There's no GET for create app
response = await rp.get(options);
}
// response from successful create should be the new app ID
return { response };
} catch (err) {
throw err;
}
}
module.exports = createApp;
Aggiungere tipi
Dopo aver creato un'app, è necessario aggiungervi le finalità. Il codice seguente crea l'app LUIS. Copiarlo oppure scaricarlo e salvarlo in _intents.js.
var rp = require('request-promise');
var fse = require('fs-extra');
var path = require('path');
var request = require('requestretry');
// time delay between requests
const delayMS = 1000;
// retry recount
const maxRetry = 5;
// retry request if error or 429 received
var retryStrategy = function (err, response, body) {
let shouldRetry = err || (response.statusCode === 429);
if (shouldRetry) console.log("retrying add intent...");
return shouldRetry;
}
// Call add-intents
var addIntents = async (config) => {
var intentPromises = [];
config.uri = config.uri.replace("{appId}", config.LUIS_appId).replace("{versionId}", config.LUIS_versionId);
config.intentList.forEach(function (intent) {
config.intentName = intent;
try {
// JSON for the request body
var jsonBody = {
"name": config.intentName,
};
// Create an intent
var addIntentPromise = callAddIntent({
// uri: config.uri,
url: config.uri,
fullResponse: false,
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key': config.LUIS_subscriptionKey
},
json: true,
body: jsonBody,
maxAttempts: maxRetry,
retryDelay: delayMS,
retryStrategy: retryStrategy
});
intentPromises.push(addIntentPromise);
console.log(`Called addIntents for intent named ${intent}.`);
} catch (err) {
console.log(`Error in addIntents: ${err.message} `);
}
}, this);
let results = await Promise.all(intentPromises);
console.log(`Results of all promises = ${JSON.stringify(results)}`);
let response = results;
}
// Send JSON as the body of the POST request to the API
var callAddIntent = async (options) => {
try {
var response;
response = await request(options);
return { response: response };
} catch (err) {
console.log(`Error in callAddIntent: ${err.message} `);
}
}
module.exports = addIntents;
Aggiungere entità
Il codice seguente aggiunge le entità all'app LUIS. Copiarlo oppure scaricarlo e salvarlo in _entities.js.
// node 7.x
// uses async/await - promises
const request = require("requestretry");
var rp = require('request-promise');
var fse = require('fs-extra');
var path = require('path');
// time delay between requests
const delayMS = 1000;
// retry recount
const maxRetry = 5;
// retry request if error or 429 received
var retryStrategy = function (err, response, body) {
let shouldRetry = err || (response.statusCode === 429);
if (shouldRetry) console.log("retrying add entity...");
return shouldRetry;
}
// main function to call
// Call add-entities
var addEntities = async (config) => {
var entityPromises = [];
config.uri = config.uri.replace("{appId}", config.LUIS_appId).replace("{versionId}", config.LUIS_versionId);
config.entityList.forEach(function (entity) {
try {
config.entityName = entity;
// JSON for the request body
// { "name": MyEntityName}
var jsonBody = {
"name": config.entityName,
};
// Create an app
var addEntityPromise = callAddEntity({
url: config.uri,
fullResponse: false,
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key': config.LUIS_subscriptionKey
},
json: true,
body: jsonBody,
maxAttempts: maxRetry,
retryDelay: delayMS,
retryStrategy: retryStrategy
});
entityPromises.push(addEntityPromise);
console.log(`called addEntity for entity named ${entity}.`);
} catch (err) {
console.log(`Error in addEntities: ${err.message} `);
//throw err;
}
}, this);
let results = await Promise.all(entityPromises);
console.log(`Results of all promises = ${JSON.stringify(results)}`);
let response = results;// await fse.writeJson(createResults.json, results);
}
// Send JSON as the body of the POST request to the API
var callAddEntity = async (options) => {
try {
var response;
response = await request(options);
return { response: response };
} catch (err) {
console.log(`error in callAddEntity: ${err.message}`);
}
}
module.exports = addEntities;
Aggiungere espressioni
Dopo aver definito le entità e le finalità nell'app LUIS, è possibile aggiungere le espressioni. Il codice seguente usa l'API Utterances_AddBatch, che consente di aggiungere fino a 100 espressioni alla volta. Copiarlo oppure scaricarlo e salvarlo in _upload.js.
// node 7.x
// uses async/await - promises
var rp = require('request-promise');
var fse = require('fs-extra');
var path = require('path');
var request = require('requestretry');
// time delay between requests
const delayMS = 500;
// retry recount
const maxRetry = 5;
// retry request if error or 429 received
var retryStrategy = function (err, response, body) {
let shouldRetry = err || (response.statusCode === 429);
if (shouldRetry) console.log("retrying add examples...");
return shouldRetry;
}
// main function to call
var upload = async (config) => {
try{
// read in utterances
var entireBatch = await fse.readJson(config.inFile);
// break items into pages to fit max batch size
var pages = getPagesForBatch(entireBatch.utterances, config.batchSize);
var uploadPromises = [];
// load up promise array
pages.forEach(page => {
config.uri = "https://westus.api.cognitive.microsoft.com/luis/api/v2.0/apps/{appId}/versions/{versionId}/examples".replace("{appId}", config.LUIS_appId).replace("{versionId}", config.LUIS_versionId)
var pagePromise = sendBatchToApi({
url: config.uri,
fullResponse: false,
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Ocp-Apim-Subscription-Key': config.LUIS_subscriptionKey
},
json: true,
body: page,
maxAttempts: maxRetry,
retryDelay: delayMS,
retryStrategy: retryStrategy
});
uploadPromises.push(pagePromise);
})
//execute promise array
let results = await Promise.all(uploadPromises)
console.log(`\n\nResults of all promises = ${JSON.stringify(results)}`);
let response = await fse.writeJson(config.inFile.replace('.json','.upload.json'),results);
console.log("upload done");
} catch(err){
throw err;
}
}
// turn whole batch into pages batch
// because API can only deal with N items in batch
var getPagesForBatch = (batch, maxItems) => {
try{
var pages = [];
var currentPage = 0;
var pageCount = (batch.length % maxItems == 0) ? Math.round(batch.length / maxItems) : Math.round((batch.length / maxItems) + 1);
for (let i = 0;i<pageCount;i++){
var currentStart = currentPage * maxItems;
var currentEnd = currentStart + maxItems;
var pagedBatch = batch.slice(currentStart,currentEnd);
var j = 0;
pagedBatch.forEach(item=>{
item.ExampleId = j++;
});
pages.push(pagedBatch);
currentPage++;
}
return pages;
}catch(err){
throw(err);
}
}
// send json batch as post.body to API
var sendBatchToApi = async (options) => {
try {
var response = await request(options);
//return {page: options.body, response:response};
return {response:response};
}catch(err){
throw err;
}
}
module.exports = upload;
Eseguire il codice
Installare le dipendenze di Node.js
Installare le dipendenze di Node.js nel terminale/riga di comando.
> npm install
Modificare le impostazioni di configurazione
Per usare questa applicazione, è necessario modificare i valori del file index.js con la propria chiave endpoint e specificare il nome che si desidera assegnare all'app. È anche possibile definire la lingua dell'app o modificare il numero di versione.
Aprire il file index.js e modificare questi valori nella parte superiore del file.
// Change these values
const LUIS_programmaticKey = "YOUR_AUTHORING_KEY";
const LUIS_appName = "Sample App";
const LUIS_appCulture = "en-us";
const LUIS_versionId = "0.1";
Eseguire lo script
Eseguire lo script da un terminale/riga di comando con Node.js.
> node index.js
O
> npm start
Avanzamento della richiesta
Mentre l'applicazione è in esecuzione, la riga di comando mostra lo stato di avanzamento. L'output della riga di comando include il formato delle risposte di LUIS.
> node index.js
intents: ["TurnOn","TurnOff","Dim","Other"]
entities: ["Operation","Device","Room"]
parse done
JSON file should contain utterances. Next step is to create an app with the intents and entities it found.
Called createApp, created app with ID 314b306c-0033-4e09-92ab-94fe5ed158a2
Called addIntents for intent named TurnOn.
Called addIntents for intent named TurnOff.
Called addIntents for intent named Dim.
Called addIntents for intent named Other.
Results of all calls to addIntent = [{"response":"e7eaf224-8c61-44ed-a6b0-2ab4dc56f1d0"},{"response":"a8a17efd-f01c-488d-ad44-a31a818cf7d7"},{"response":"bc7c32fc-14a0-4b72-bad4-d345d807f965"},{"response":"727a8d73-cd3b-4096-bc8d-d7cfba12eb44"}]
called addEntity for entity named Operation.
called addEntity for entity named Device.
called addEntity for entity named Room.
Results of all calls to addEntity= [{"response":"6a7e914f-911d-4c6c-a5bc-377afdce4390"},{"response":"56c35237-593d-47f6-9d01-2912fa488760"},{"response":"f1dd440c-2ce3-4a20-a817-a57273f169f3"}]
retrying add examples...
Results of add utterances = [{"response":[{"value":{"UtteranceText":"turn on the lights","ExampleId":-67649},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"turn the heat on","ExampleId":-69067},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"switch on the kitchen fan","ExampleId":-3395901},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"turn off bedroom lights","ExampleId":-85402},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"turn off air conditioning","ExampleId":-8991572},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"kill the lights","ExampleId":-70124},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"dim the lights","ExampleId":-174358},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"hi how are you","ExampleId":-143722},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"answer the phone","ExampleId":-69939},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"are you there","ExampleId":-149588},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"help","ExampleId":-81949},"hasError":false},{"value":{"UtteranceText":"testing the circuit","ExampleId":-11548708},"hasError":false}]}]
upload done
Aprire l'app LUIS
Al termine dello script, è possibile accedere a LUIS e visualizzare l'app LUIS appena creata in App personali. Le espressioni aggiunte dovrebbero apparire sotto le finalitàTurnOn, TurnOff e None.
Passaggi successivi
Test e training dell'app sul sito Web LUIS.
Risorse aggiuntive
Questa applicazione di esempio usa le API LUIS seguenti: