Tutorial: Create a WPF application with C#
In this tutorial, you become familiar with many of the tools, dialog boxes, and designers that you can use when you develop applications with Visual Studio. You create a "Hello, World" application, design the user interface, add code, and debug errors. At the same time, learn about working in the Visual Studio integrated development environment (IDE).
- Configure the IDE
- Create a project
- Design the user interface
- Debug and test the application
Prerequisites
- If you don't have Visual Studio, go to Visual Studio downloads to install it for free.
- Make sure the .NET desktop development workload is installed. You can verify this configuration in Visual Studio Installer.
- You can use either .NET Framework or .NET Core for this tutorial. .NET Core is the newer, more modern framework. .NET Core requires Visual Studio 2019 version 16.3 or later.
What is Windows Presentation Foundation?
Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) is a user interface (UI) framework that creates desktop client applications. The WPF development platform supports a broad set of application development features, including an application model, resources, controls, graphics, layout, data binding, documents, and security.
WPF is part of .NET. If you previously built applications with .NET using ASP.NET or Windows Forms, the programming experience should be familiar. WPF uses the Extensible Application Markup Language (XAML) to provide a declarative model for application programming. For more information, see Desktop Guide (WPF .NET).
Configure the IDE
When you launch Visual Studio, the start window opens. Select Continue without code to open the development environment. You see tool windows, the menus and toolbars, and the main window space. Tool windows are docked on the sides of the application window. The search box, menu bar, and the standard toolbar are located at the top. When you load a solution or project, editors and designers appear in the central space of the application window. When you develop an application, you spend most of your time in this central area.
Create the project
When you create an application in Visual Studio, you first create a project and a solution. For this example, you create a Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) project.
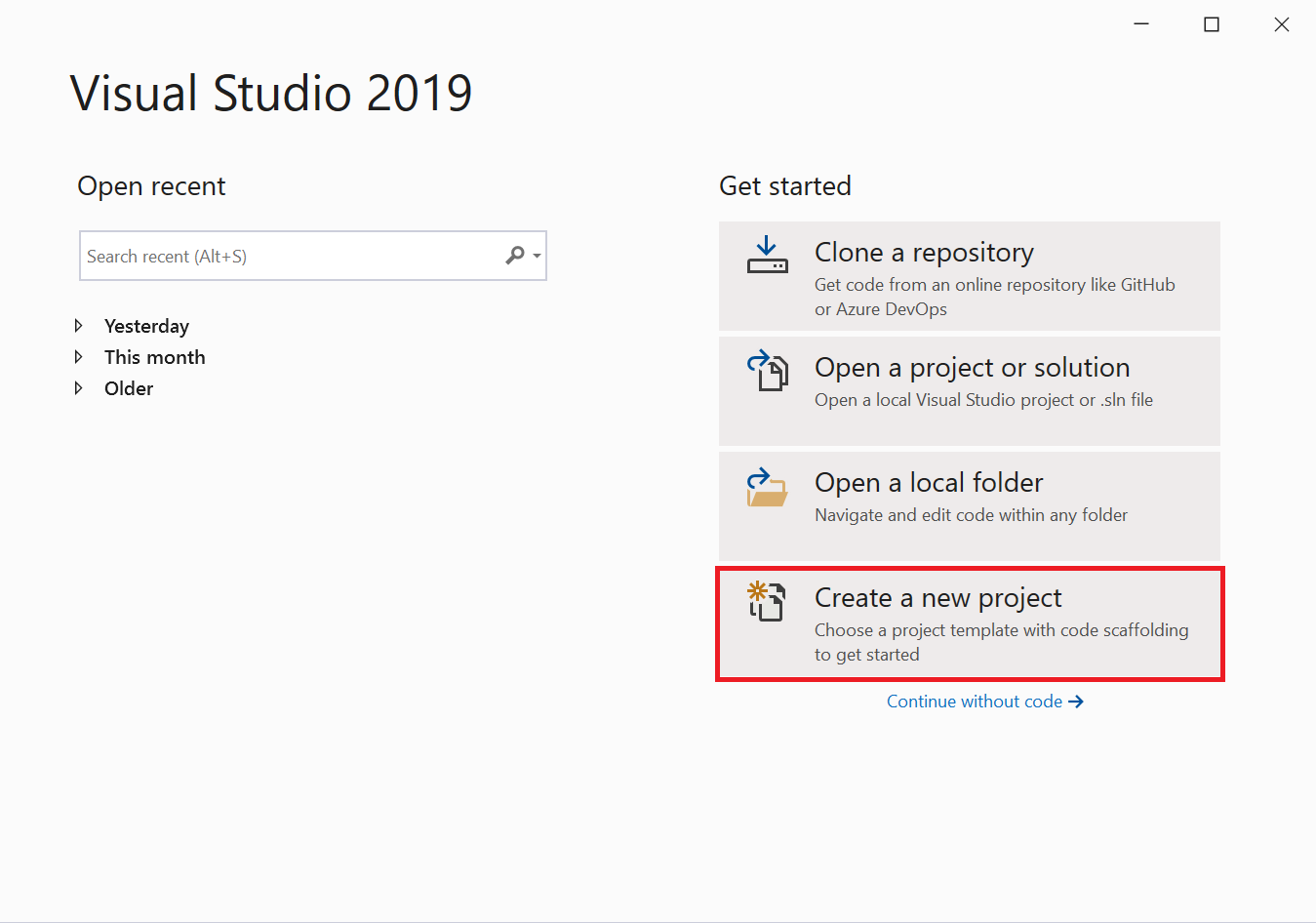
Open Visual Studio.
On the start window, choose Create a new project.
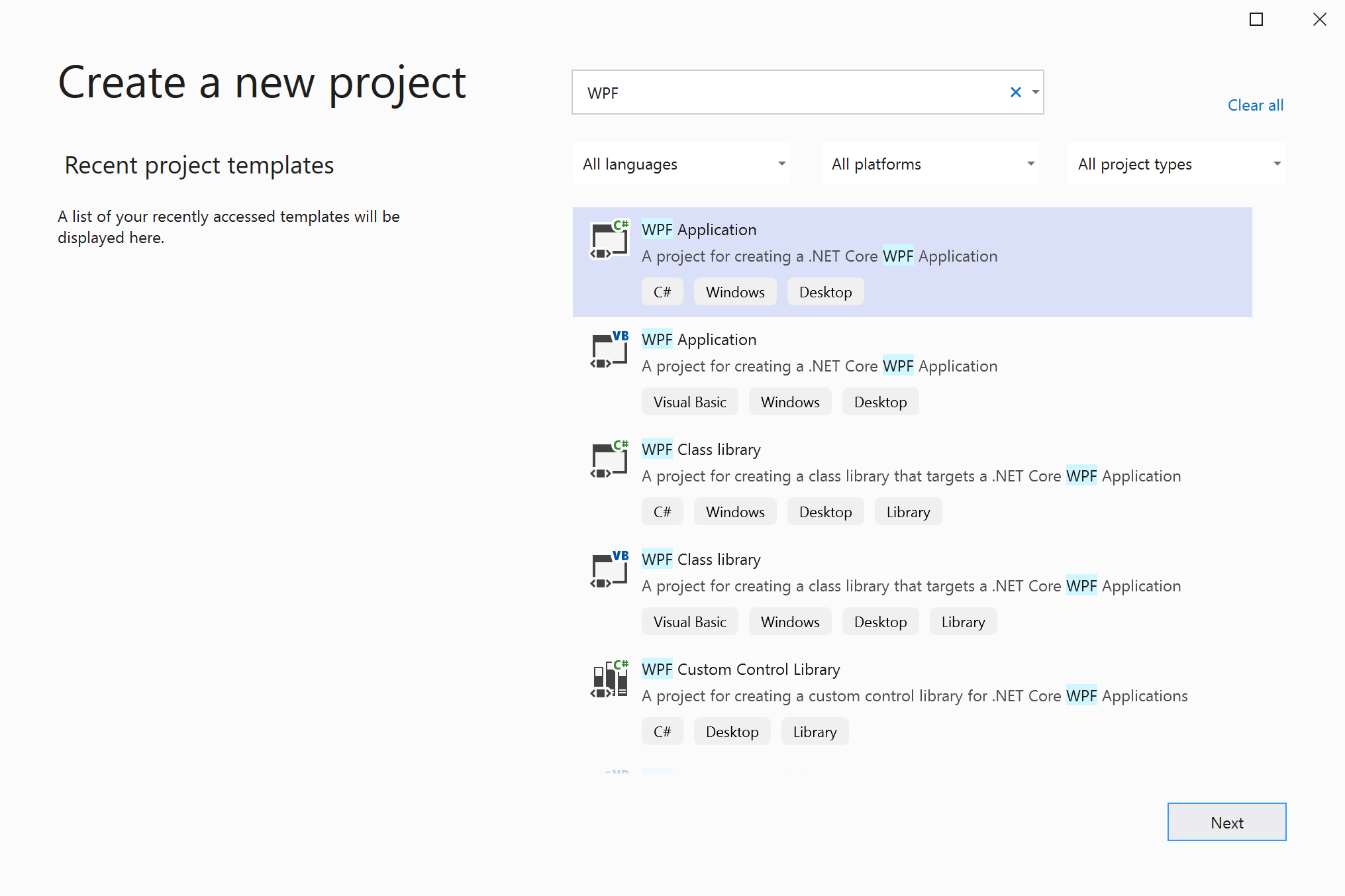
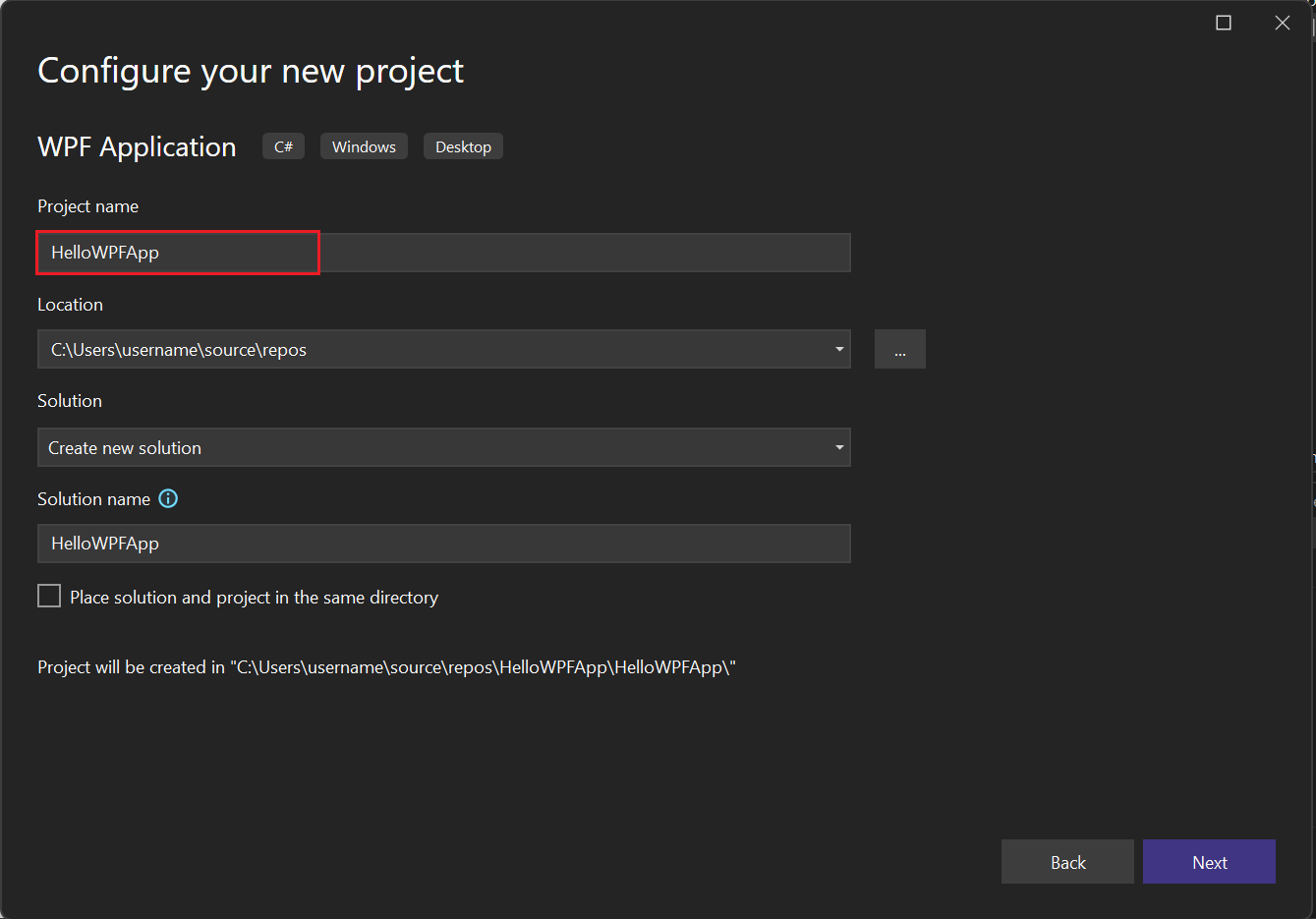
On the Create a new project screen, search for WPF. Choose WPF Application, and then choose Next.
At the next screen, give the project a name, HelloWPFApp, and choose Next.
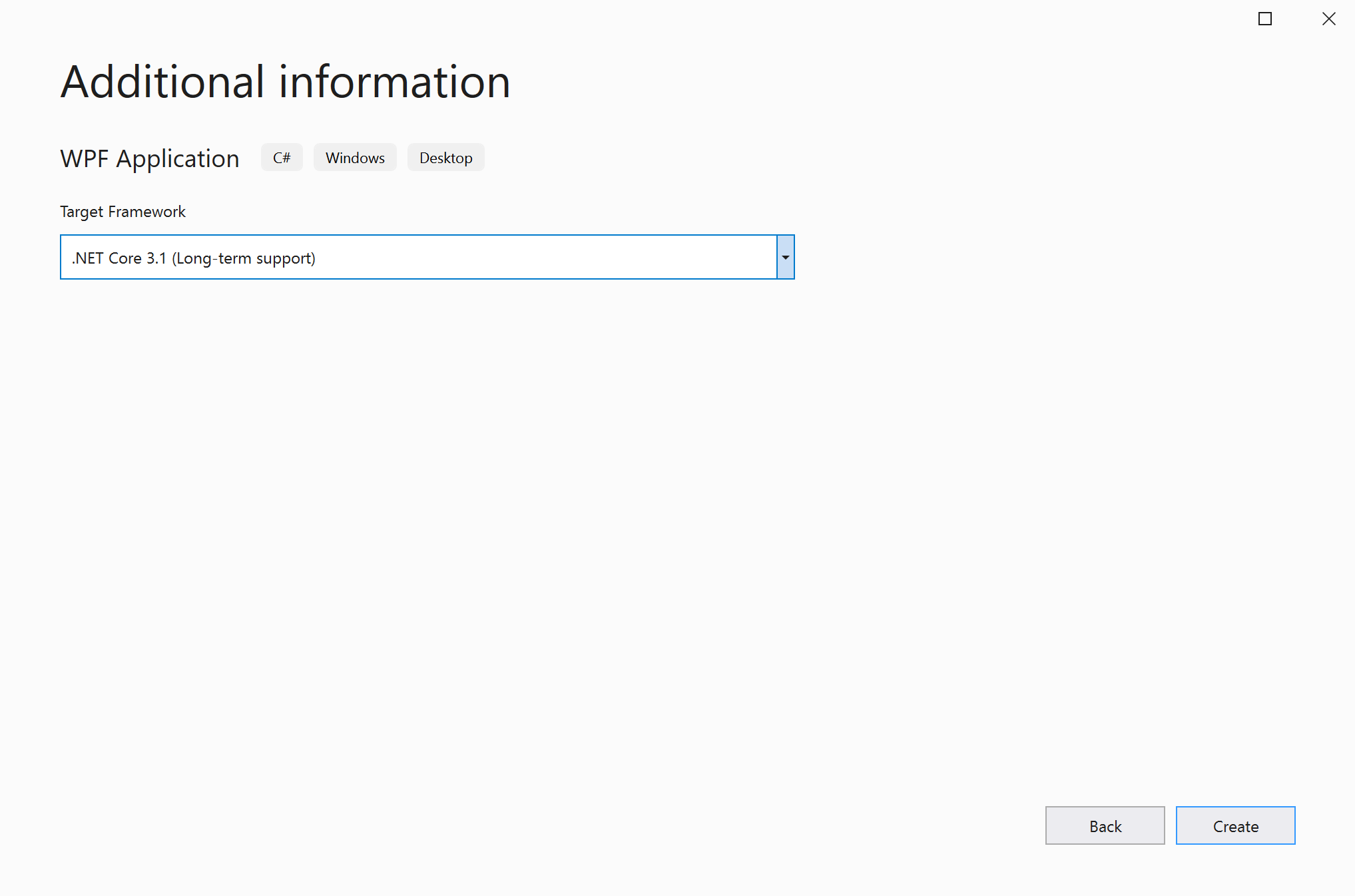
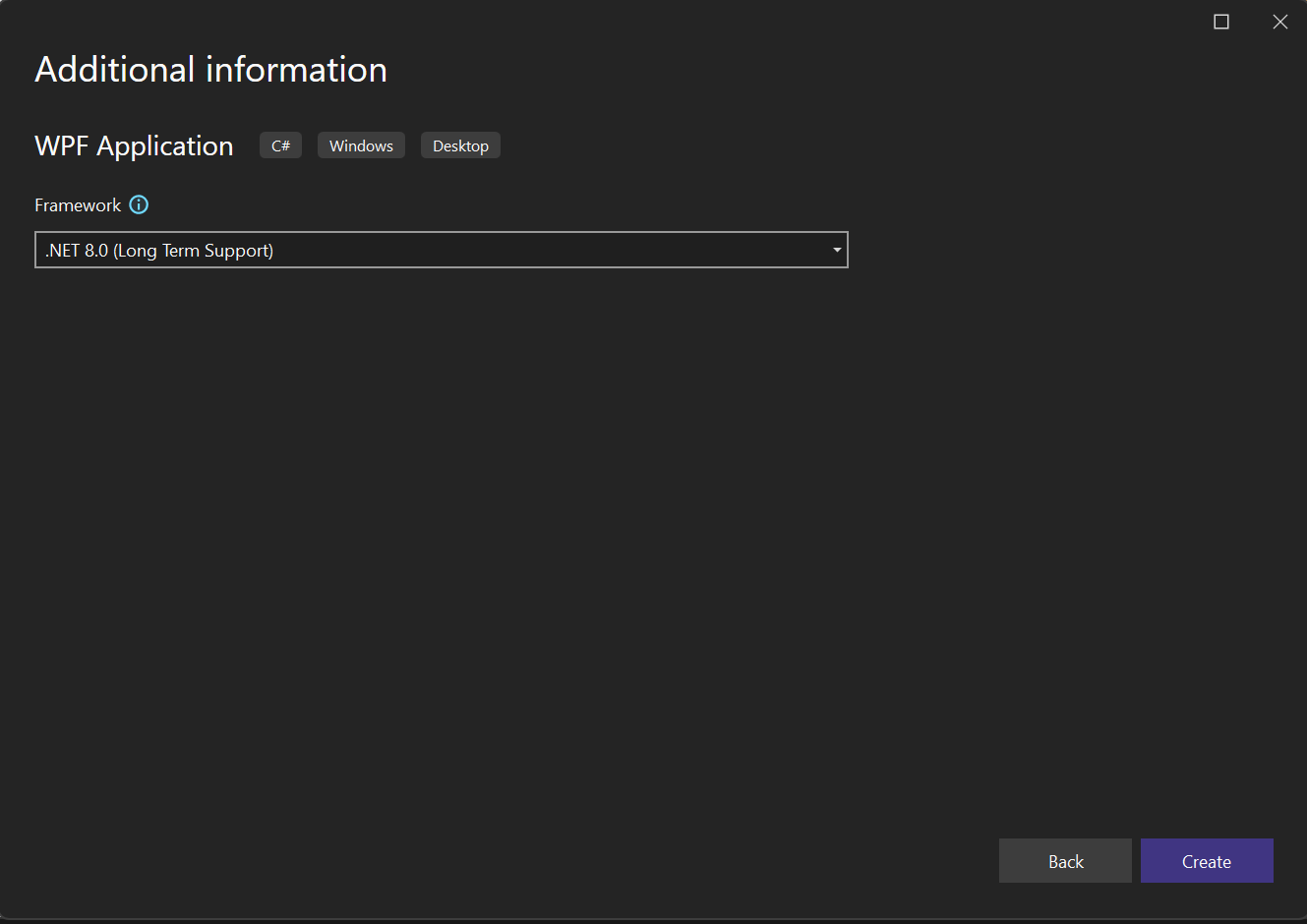
In the Additional information window, .NET Core 3.1 should already be selected for your target framework. If not, select .NET Core 3.1. Then, choose Create.
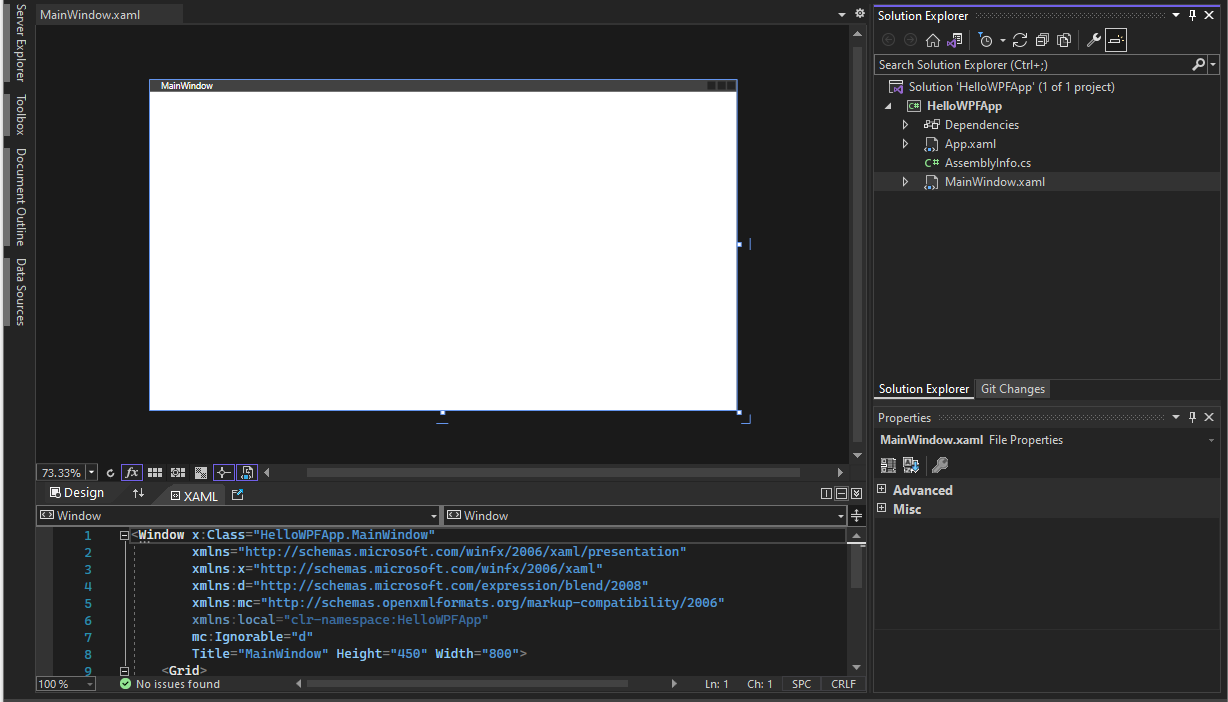
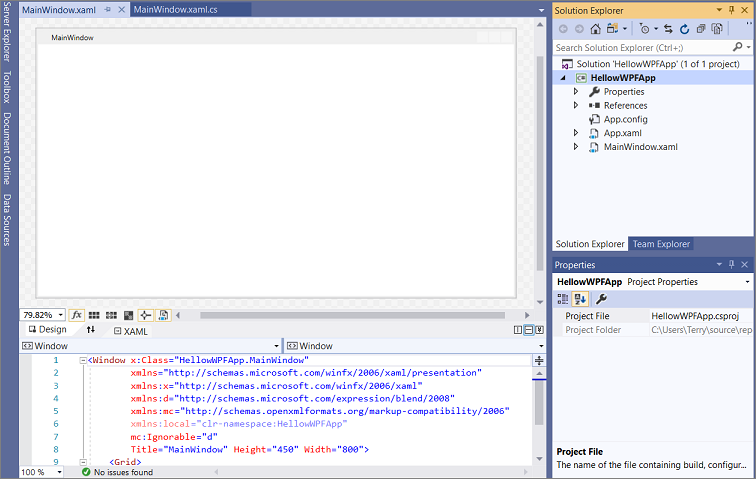
Visual Studio creates the HelloWPFApp project and solution. Solution Explorer shows the various files. The WPF Designer shows a design view and a XAML view of MainWindow.xaml in a split view. You can slide the splitter to show more or less of either view. You can choose to see only the visual view or only the XAML view.
Note
For more information about XAML, see the XAML overview for WPF page.
After you create the project, you can customize it. To do so, choose Properties Window from the View menu, or press F4. You can display and change options for project items, controls, and other items in an application.
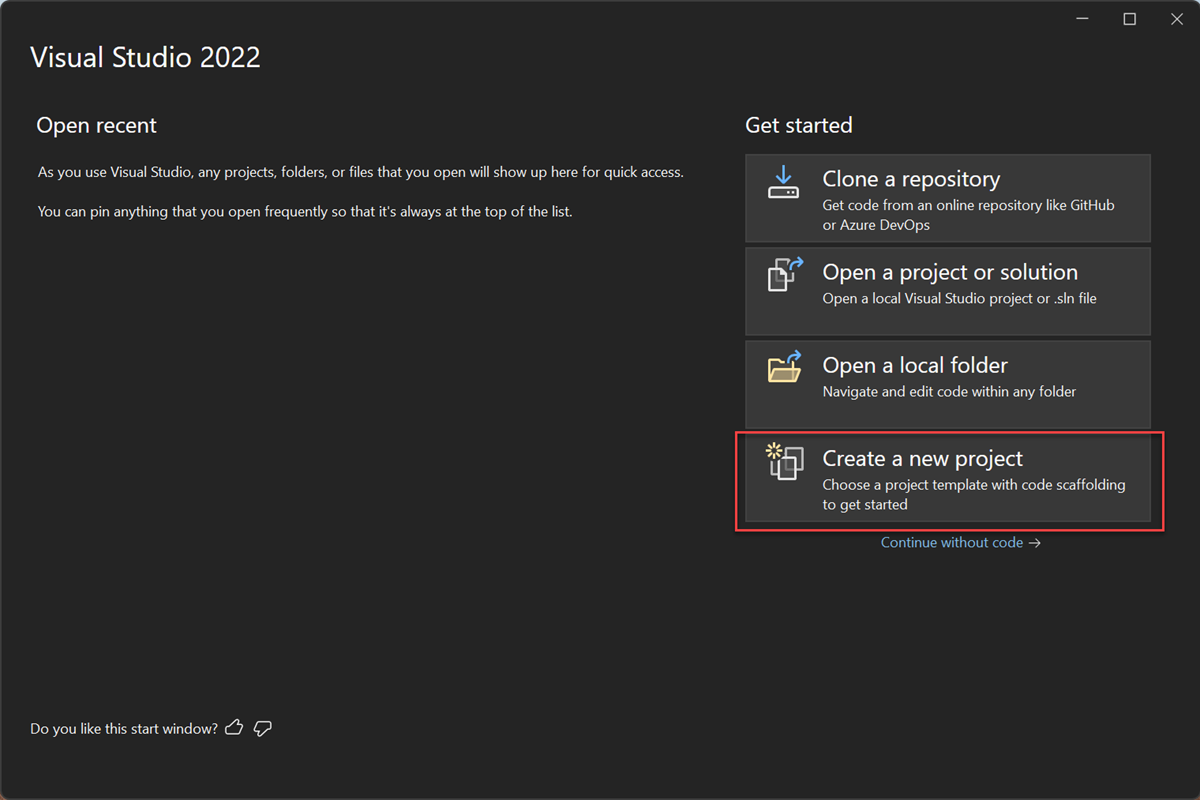
Open Visual Studio.
On the start window, choose Create a new project.
On the Create a new project screen, search for WPF. Choose WPF Application, and then choose Next.
At the next screen, give the project a name, HelloWPFApp, and choose Next.
In the Additional information window, verify that .NET 8.0 is selected for your target framework. Then, choose Create.
Visual Studio creates the HelloWPFApp project and solution. Solution Explorer shows the various files. The WPF Designer shows a design view and a XAML view of MainWindow.xaml in a split view. You can slide the splitter to show more or less of either view. You can choose to see only the visual view or only the XAML view.
Note
For more information the Extensible Application Markup Language (XAML)), see XAML overview for WPF.
After you create the project, you can customize it. To do so, choose Properties Window from the View menu, or press F4. Then, you can display and change options for project items, controls, and other items in an application.
Design the user interface
If the designer isn't open, select MainWindow.xaml and select Shift+F7 to open the designer.
In this tutorial, you add three types of controls to this application: a TextBlock control, two RadioButton controls, and a Button control.
Add a TextBlock control
Follow these steps to add a TextBlock.
Select Ctrl+Q to activate the search box and type Toolbox. Choose View > Toolbox from the results list.
In the Toolbox, expand the Common WPF Controls node to see the TextBlock control.
Add a TextBlock control to the design surface. Choose the TextBlock item and drag it to the window on the design surface. Center the control near the top of the window. In Visual Studio 2019 and later, you can use the guidelines to center the control.
Your window should resemble this illustration:

The XAML markup should look like this example:
<Grid> <TextBlock HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="387,60,0,0" TextWrapping="Wrap" Text="TextBlock" VerticalAlignment="Top"/> </Grid>
Select Ctrl+Q to activate the search box and type Toolbox. Choose View > Toolbox from the results list.
In the Toolbox, expand the Common WPF Controls node to see the TextBlock control.
Add a TextBlock control to the design surface. Choose the TextBlock item and drag it to the window on the design surface. Center the control near the top of the window. You can use the guidelines to center the control.
Your window should resemble this image:
The XAML markup should look like this example:
<Grid> <TextBlock HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="387,60,0,0" TextWrapping="Wrap" Text="TextBlock" VerticalAlignment="Top"/> </Grid>
Customize the text in the text block
You can change what text the TextBlock displays.
In the XAML view, locate the markup for TextBlock and change the Text attribute from
TextBlocktoSelect a message option and then choose the Display button.The XAML markup should look like this example:
<Grid> <TextBlock HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="387,60,0,0" TextWrapping="Wrap" Text="Select a message option and then choose the Display button." VerticalAlignment="Top"/> </Grid>Center the TextBlock again, and then save your changes by selecting Ctrl+S or using the File menu item.
Add radio buttons
Next, add two RadioButton controls to the form.
In the Toolbox, find the RadioButton control.
Add two RadioButton controls to the design surface. Choose the RadioButton item and drag it to the window on the design surface. Move the buttons by selecting them and using the arrow keys. Arrange them so that the buttons appear side by side under the TextBlock control. Use the guidelines to align the controls.
Your window should look like this:

In the Properties window for the left RadioButton control, at the top, change the Name property to
HelloButton.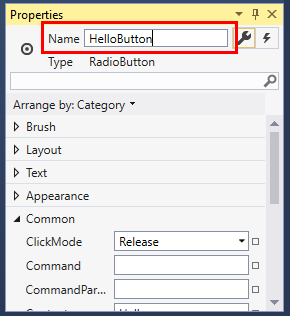
In the Properties window for the right RadioButton control, change the Name property to
GoodbyeButton, and then save your changes.
In the Toolbox, find the RadioButton control.
Add two RadioButton controls to the design surface. Choose the RadioButton item and drag it to the window on the design surface. Move the buttons by selecting them and using the arrow keys. Arrange them so that the buttons appear side by side under the TextBlock control. You can use the guidelines to align the controls.
Your window should look like this:

In the Properties window for the left RadioButton control, at the top, change the Name property to
HelloButton.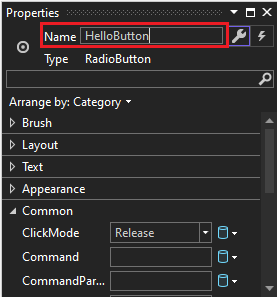
In the Properties window for the right RadioButton control, change the Name property to
GoodbyeButton, and then save your changes.
Add display text for each radio button
Next, add display text for each RadioButton control. The following procedure updates the Content property for a RadioButton control.
Update the Content attribute for the two radio buttons
HelloButtonandGoodbyeButtonto"Hello"and"Goodbye"in the XAML. The XAML markup should now look similar to this example:<Grid> <TextBlock HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="252,47,0,0" TextWrapping="Wrap" Text="Select a message option and then choose the Display button." VerticalAlignment="Top"/> <RadioButton x:Name="HelloButton" Content="Hello" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="297,161,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Top"/> <RadioButton x:Name="GoodbyeButton" Content="Goodbye" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="488,161,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Top"/> </Grid>
Set a radio button to be checked by default
In this step, set HelloButton to be checked by default so that one of the two radio buttons is always selected.
In the XAML view, locate the markup for HelloButton.
Add an IsChecked attribute and set it to True. Specifically, add
IsChecked="True".The XAML markup should now look similar to this example:
<Grid> <TextBlock HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="252,47,0,0" TextWrapping="Wrap" Text="Select a message option and then choose the Display button." VerticalAlignment="Top"/> <RadioButton x:Name="HelloButton" Content="Hello" IsChecked="True" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="297,161,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Top"/> <RadioButton x:Name="GoodbyeButton" Content="Goodbye" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="488,161,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Top"/> </Grid>
Add the button control
The final UI element that you add is a Button control.
In the Toolbox, find the Button control. Add it to the design surface under the RadioButton controls by dragging it to the form in the design view. A guideline helps you center the control.
In the XAML view, change the value of Content for the Button control from
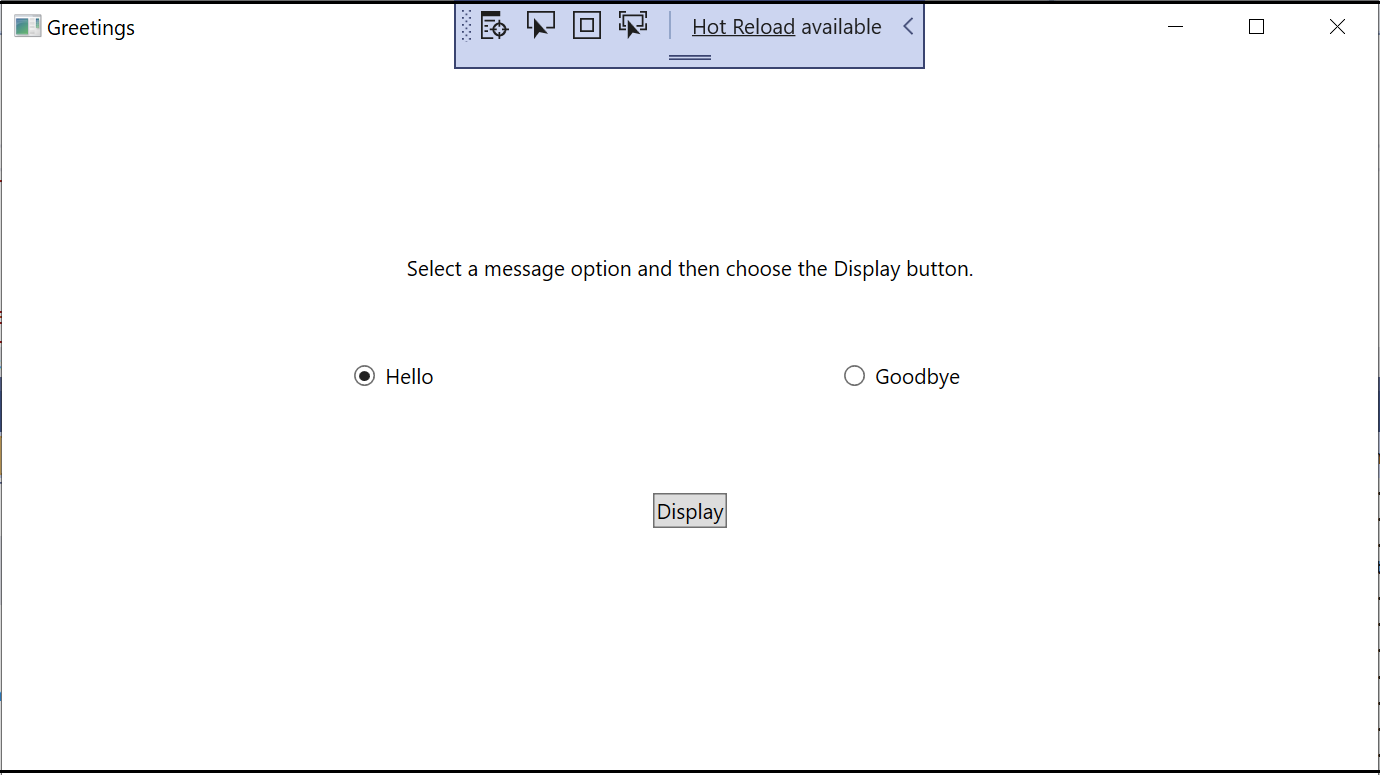
Content="Button"toContent="Display", and then save the changes.Your window should resemble this illustration.
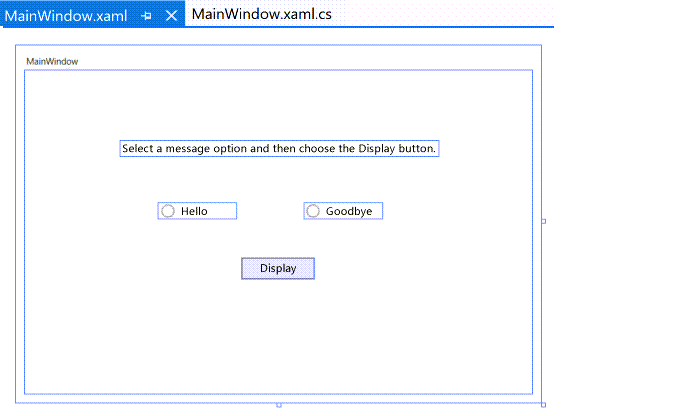
The XAML markup should now look similar to this example:
<Grid> <TextBlock HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="252,47,0,0" TextWrapping="Wrap" Text="Select a message option and then choose the Display button." VerticalAlignment="Top"/> <RadioButton x:Name="HelloButton" Content="Hello" IsChecked="True" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="297,161,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Top"/> <RadioButton x:Name="GoodbyeButton" Content="Goodbye" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="488,161,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Top"/> <Button Content="Display" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="377,270,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Top" Width="75"/> </Grid>
In the Toolbox, find the Button control. Add it to the design surface under the RadioButton controls by dragging it to the form in the design view. The guidelines can help you center the control.
In the XAML view, change the value of Content for the Button control from
Content="Button"toContent="Display", and then save the changes.Your window should resemble this screenshot:
The XAML markup should now look similar to this example:
<Grid> <TextBlock HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="252,47,0,0" TextWrapping="Wrap" Text="Select a message option and then choose the Display button." VerticalAlignment="Top"/> <RadioButton x:Name="HelloButton" Content="Hello" IsChecked="True" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="297,161,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Top"/> <RadioButton x:Name="GoodbyeButton" Content="Goodbye" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="488,161,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Top"/> <Button Content="Display" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="377,270,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Top" Width="75"/> </Grid>
Add code to the display button
When this application runs, a message box appears after a user chooses a radio button and then chooses the Display button. One message box appears for Hello, and another appears for Goodbye. To create this behavior, you add code to the Button_Click event in MainWindow.xaml.cs.
On the design surface, double-click the Display button.
MainWindow.xaml.cs opens, with the cursor in the
Button_Clickevent.private void Button_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { }Inside the braces, add the following code:
if (HelloButton.IsChecked == true) { MessageBox.Show("Hello."); } else if (GoodbyeButton.IsChecked == true) { MessageBox.Show("Goodbye."); }Save the application.
When this application runs, a message box appears after a user chooses a radio button and then chooses the Display button. One message box appears for Hello, and another appears for Goodbye. To create this behavior, you add code to the Button_Click event in MainWindow.xaml.cs.
On the design surface, double-click the Display button.
MainWindow.xaml.cs opens, with the cursor in the
Button_Clickevent.private void Button_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { }When you double-click the Display button,
Click="Button_Click"is added to the XAML.The XAML markup should now look similar to this example:
<Grid> <TextBlock HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="252,47,0,0" TextWrapping="Wrap" Text="Select a message option and then choose the Display button." VerticalAlignment="Top"/> <RadioButton x:Name="HelloButton" Content="Hello" IsChecked="True" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="297,161,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Top"/> <RadioButton x:Name="GoodbyeButton" Content="Goodbye" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="488,161,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Top"/> <Button Content="Display" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Margin="377,270,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Top" Width="75" Click="Button_Click"/> </Grid>Inside the
Button_Clickbraces, add the following code:if (HelloButton.IsChecked == true) { MessageBox.Show("Hello."); } else if (GoodbyeButton.IsChecked == true) { MessageBox.Show("Goodbye."); }Save the application.
Debug and test the application
Next, debug the application to look for errors and test that both message boxes appear correctly. The following instructions tell you how to build and launch the debugger. For more information, see Build a WPF application (WPF) and Debug WPF.
Change the name of MainWindow.xaml
Give MainWindow a more specific name. In Solution Explorer, right-click MainWindow.xaml and choose Rename. Rename the file to Greetings.xaml. In this example, this change creates an error used later to demonstrate debugging.
Find and fix errors
In this step, you find the error that was caused earlier by changing the name of the MainWindow.xaml file.
Start debugging and find the error
Start the debugger by selecting F5 or selecting Debug, then Start Debugging.
A Break Mode window appears. The Output window indicates that an IOException occurred: Cannot locate resource mainwindow.xaml.
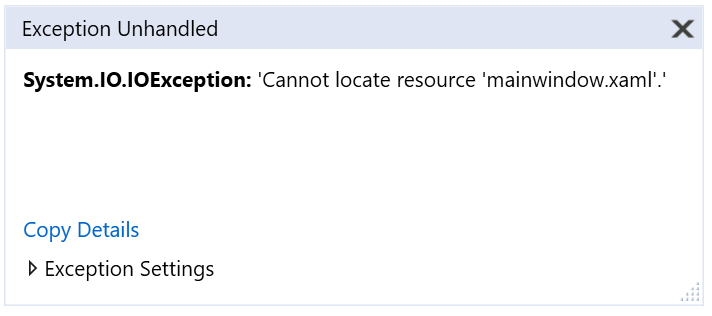
Stop the debugger by choosing Debug > Stop Debugging.
You renamed MainWindow.xaml to Greetings.xaml, but the code still refers to MainWindow.xaml as the startup URI for the application, so the project can't start.
Start the debugger by selecting F5 or selecting Debug, then Start Debugging.
A Break Mode window appears, and the Output window indicates that an IOException occurred: Cannot locate resource mainwindow.xaml.

Stop the debugger by choosing Debug > Stop Debugging.
You renamed MainWindow.xaml to Greetings.xaml, but the code still refers to MainWindow.xaml as the startup URI for the application, so the project can't start.
Specify Greetings.xaml as the startup URI
In Solution Explorer, open the
App.xamlfile.Change
StartupUri="MainWindow.xaml"toStartupUri="Greetings.xaml", and save the changes.
As an optional step, it avoids confusion to change the title of your application window to match this new name.
In Solution Explorer, open the
Greetings.xamlfile that you just renamed.Change the value of the Window.Title property from
Title="MainWindow"toTitle="Greetings", and save the changes.
Start the debugger again (press F5). You should now see the Greetings window of your application.

To stop debugging, close the application window
Debug with breakpoints
You can test the code during debugging by adding some breakpoints. You can add breakpoints by choosing Debug > Toggle Breakpoint, by clicking in the left margin of the editor next to the line of code where you want the break to occur, or by pressing F9.
Add breakpoints
Open Greetings.xaml.cs, and select this line:
MessageBox.Show("Hello.")Add a breakpoint from the menu by selecting Debug, then Toggle Breakpoint.
A red circle appears next to the line of code in the far left margin of the editor window.
Select this line:
MessageBox.Show("Goodbye.").Press the F9 key to add a breakpoint, and then select F5 to start debugging.
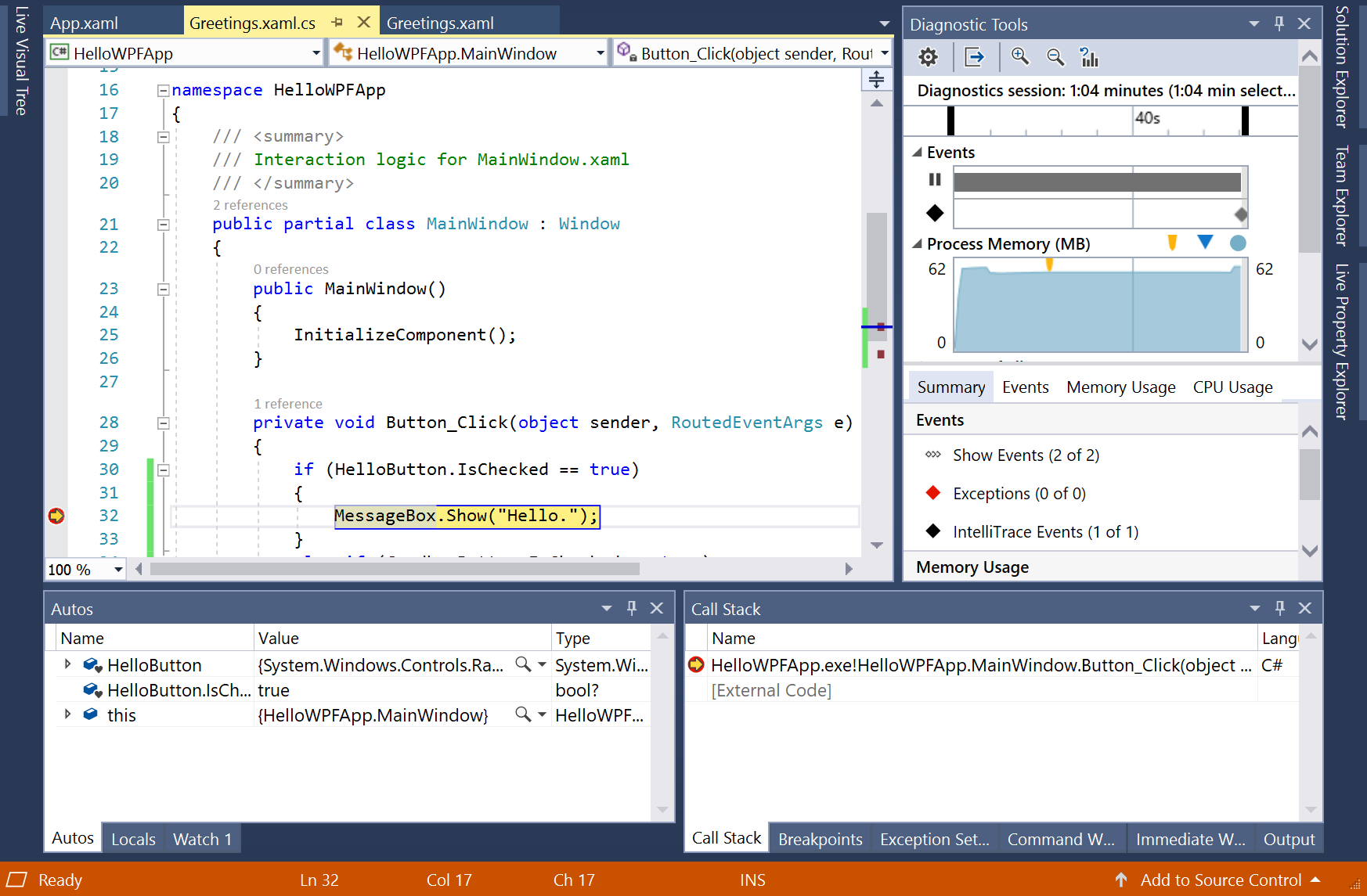
In the Greetings window, choose the Hello radio button, and then choose the Display button.
The line
MessageBox.Show("Hello.")is highlighted in yellow. At the bottom of the IDE, the Autos, Locals, and Watch windows are docked together on the left side. The Call Stack, Breakpoints, Exception Settings, Command, Immediate, and Output windows are docked together on the right side.On the menu bar, choose Debug > Step Out.
The application resumes execution, and a message box with the word "Hello" appears.
Choose OK on the message box to close it.
In the Greetings window, choose the Goodbye radio button, and then choose the Display button.
The line
MessageBox.Show("Goodbye.")is highlighted in yellow.Choose the F5 key to continue debugging. When the message box appears, choose OK on the message box to close it.
To stop debugging, close the application window.
On the menu bar, choose Debug > Disable All Breakpoints.
Open Greetings.xaml.cs, and select this line:
MessageBox.Show("Hello.")Add a breakpoint from the menu by selecting Debug, then Toggle Breakpoint.
A red circle appears next to the line of code in the far left margin of the editor window.
Select this line:
MessageBox.Show("Goodbye.").Press the F9 key to add a breakpoint, and then select F5 to start debugging.
In the Greetings window, choose the Hello radio button, and then choose the Display button.
The line
MessageBox.Show("Hello.")is highlighted in yellow. At the bottom of the IDE, the Autos, Locals, and Watch windows are docked together on the left side. The Call Stack, Breakpoints, Exception Settings, Command, Immediate, and Output windows are docked together on the right side.On the menu bar, choose Debug > Step Out.
The application resumes execution, and a message box with the word "Hello" appears.
Choose OK on the message box to close it.
In the Greetings window, choose the Goodbye radio button, and then choose the Display button.
The line
MessageBox.Show("Goodbye.")is highlighted in yellow.Choose the F5 key to continue debugging. When the message box appears, choose OK on the message box to close it.
To stop debugging, close the application window.
On the menu bar, choose Debug > Disable All Breakpoints.
View a representation of the UI elements
In the running app, you should see a widget that appears at the top of your window. The widget is a runtime helper that provides quick access to some helpful debugging features. Select the first button, Go to Live Visual Tree. You should see a window with a tree that contains all the visual elements of your page. Expand the nodes to find the buttons you added.
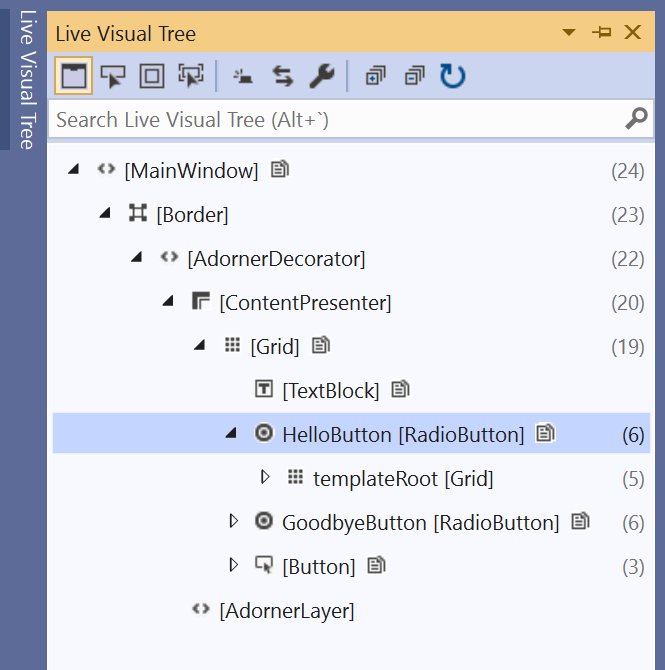
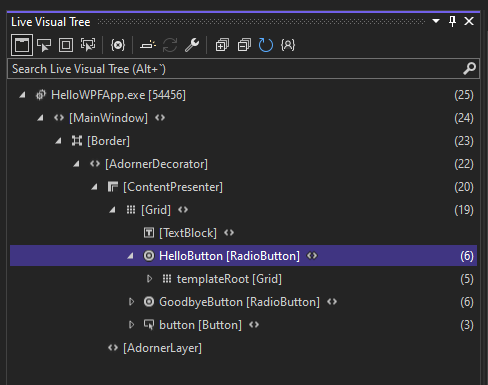
Build a release version of the application
After you verify that everything works, you can prepare a release build of the application.
On the main menu, select Build > Clean solution to delete intermediate files and output files that were created during previous builds. This step isn't required, but it cleans up the debug build outputs.
Change the build configuration for HelloWPFApp from Debug to Release by using the dropdown control on the toolbar. It says Debug currently.
Build the solution by choosing Build > Build Solution.
Congratulations on completing this tutorial! You can find the .exe you built under your solution and project directory (...\HelloWPFApp\HelloWPFApp\bin\Release).
Related content
Next step
Congratulations on completing this tutorial! To learn even more, continue with the following tutorials.