Variations overview in SharePoint Server
APPLIES TO:  2013
2013  2016
2016  2019
2019  Subscription Edition
Subscription Edition  SharePoint in Microsoft 365
SharePoint in Microsoft 365
The variations feature in SharePoint Server and SharePoint in Microsoft 365 syncs content from a source variation site to each target variation site to make the content available to specific audiences on different sites. When users visit the root site, they're redirected to the appropriate variation site, based on the language setting of their web browser. Content on a target variation site can be translated into other languages before it's published. You can use variations only on sites that are created by using one of the Publishing site templates, or on sites for which the SharePoint Server Publishing Infrastructure feature was activated.
This article contains an overview of the variations feature. It describes the elements of the variations feature; provides an overview of site, list, and page creation for variation sites; lists some limitations of variations; and describes scenarios for using variations in SharePoint Server. This article doesn't describe the tasks that are involved in planning a solution that uses variations. For info about how to plan to use variations in your solution, see Plan for variations in SharePoint Server. This article also doesn't describe how to create variation labels and hierarchies. For info about how to create a variation site, see Create a multi-language website.
Important
- The variations will remain supported but deprecated for the SharePoint Server 2019 release. For more info, see What's deprecated or removed from SharePoint Server 2019.
- The Machine Translation Services for the variations feature will no longer be supported as of the end of July 2022. All existing instances of variations using the Machine Translation Server APIs will no longer display multilingual functionality in your Microsoft 365 environment.
- If you're using modern communication sites in SharePoint, we recommend that you use the modern multilingual sites and pages feature instead of the variations feature.
Use and benefits of variations
Many organizations have a global reach. However, even in domestic markets, organizations have to reach a diverse user base speaking many languages or having specific information based on regional differences. These types of organizations need websites that deliver customized content to suit different cultures, different markets, and different geographic regions. Producing and maintaining different versions of a site can be difficult and time-consuming. By using the variations feature as part of a SharePoint Server 2013 solution, site architects and site administrators can simplify the process of producing and maintaining these sites. The variations feature automates the creation, management, synchronization, and translation of sites, lists, and pages, thereby eliminating the need to manually create a site and all associated lists and pages for each instance of a needed variation.
Scenarios for using variations
You can use variations to create sites, lists, and page content for specific languages. In this scenario, most of the content is authored in the language of the source variation site and synced to some or all of the target variation sites for translation into different languages. For example, the content might be authored in English and be synced to target variation sites for translation into German, French, and Spanish.
You can also use variations to create content for specific locales. For example, a company based in North America might have target variation sites for the following locales: English (United States), English (Canada), French (Canada), and Spanish (Mexico). Most of the content is authored in English (United States), and the variation feature syncs that content to the target variation sites. Content on the French (Canada) and Spanish (Mexico) site is translated into French and Spanish, whereas content for English (Canada) is edited to account for regional differences in United States and Canadian English. Other content that is unique to a specific locale is created on the target variation sites for which it's needed.
In SharePoint Server 2010, you could use variations to create sites for different mobile devices, or that used different branding. In SharePoint Server 2016, variations are used only for multilingual sites. To create sites for different mobile devices, use Device Channels. To create sites that use different branding, use cross-site publishing. Plan for cross-site publishing in SharePoint Server.
Elements of variations
The variations feature consists of the following elements:
Variation root site The variation root site provides the URL for all source and target variation sites and contains the landing page that redirects users to the correct variation site. This site isn't the same as the root site of a site collection, although you can specify the root site of a site collection to also be the root site of the variations hierarchy.
Variation labels A variation label is an identifier that names a new variation site. Variations of a site are defined by creating variation labels, one for each planned variation.
Note
SharePoint Server supports up to 209 variation labels. SharePoint in Microsoft 365 supports up to 50 variation labels.
Variation sites Variation sites are the sites that are created based on the defined variation labels. There are two types of variation sites:
Source variation site The source variation site is the site where shared content is authored and published, and it's the site from which the shared content is synced with target variation sites. There can be only one source variation site in a single site collection. After a source variation site is selected, it can't be changed.
Target variation sites The target variation sites receive most of their content from the source variation site. New content can be created on a target variation site. However, that content isn't synced with other sites and is unique to the site on which it was created.
Variations hierarchy The variations hierarchy is the complete set of sites in all variation labels.
Variation lists Variation lists are lists for which you specify target variation labels to receive list items.
Variation pages Variation pages are the publishing pages that are stored in the Pages library of the source variation site and the target variation sites.
Important
We recommend that you do not add nonpublishing pages to the Pages library of a site that uses variations. If you do, the Variations Create Hierarchies Job Definition timer job might fail.
Understanding variations
The variations feature creates sites and syncs content and supported list items from a source variation site to one or more target variation sites. By default, the variations feature syncs publishing pages from the Pages library of the source variation site, and any lists that are configured to be synced to specific target variation sites.
By default, when users visit the root site, they're redirected to the appropriate variation site, based on the language setting of their web browser. For example, if a user's default browser language is French, SharePoint Server redirects that user to the French variation site. You can customize this behavior by replacing the default redirection page, VariationRoot.aspx, with a different page. This new page can implement logic that identifies the user's preferred language. For info about how to customize variation sites redirection, see How to: Customize the Variation Root Landing Logic.
Variation labels
A variation label is an identifier that names a variation site. You select one variation label as the source, which represents the source variation site. The remaining variation labels are the target labels, representing the target variation sites to which content is synced. You create variation sites from variation labels by using the Create Hierarchies command on the Variation Labels page.
Only one set of variation labels, the variation hierarchy, can be defined for a site collection. The corresponding variation sites can be created anywhere within the site collection hierarchy. The source variation site and the target variation sites are always created as subsites of the variation root site. Users who visit the variation root site are redirected to the appropriate variation site.
The following illustration provides an example of a variation site hierarchy, and shows how publishing content is synced to target variation sites.
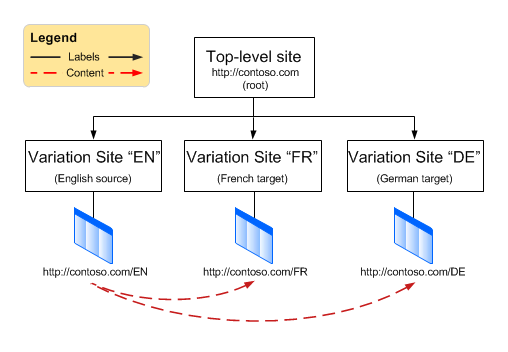
Three variation labels, "EN," "FR," and "DE," are created on the root site https://contoso.com. When the variations hierarchy is created, the corresponding variation sites, labeled "EN," "FR," and "DE," are created one level below the variation root site. Because site "https://contoso.com/EN" is specified as the source variation site, lists and pages that are authored and published on site "https://contoso.com/EN" are synced to the target variation sites, "https://contoso.com/FR" and "https://contoso.com/DE."
When you create a variation label, you select a locale for it to use. The locale setting assists with browser redirection and regional settings such as sort order and calendar. It doesn't affect the language of the user interface. If language packs were installed on the front-end web server, you can also select a language for the variation site. The language setting in SharePoint Server determines the language of the user interface on the variation site. If no language packs were installed, the option to select a language isn't available, and the variation site uses the default language of the SharePoint Server installation on the server, regardless of the locale that is selected for the variation label. For example, if SharePoint Server was installed by using the English version, and no language packs were installed, when a new variation label is created for the Japanese locale, the user interface for the new variation target site is in English, not Japanese. If you want the user interface of a target variation site to be displayed using a specific language, you should install the language pack for each language before you create the variation sites. If a language pack isn't available when a target variation site is created, the target variation site can still be created, and users can change the alternate language for a site by using the multilingual user interface. For information about the multilingual user interface, see Plan for multilingual sites in SharePoint Server. For info about how to install language packs, see Install or uninstall language packs for SharePoint Server 2016.
When you create a variations hierarchy, a navigation term set is created for each variation label. By default, the term set for the source variation label is named Variations Navigation. The term set for a target variation label is named Variations Navigation ( LabelName). For example, if you have a target label named en-ca, the term set for that label will be named Variations Navigation (en-ca). By default, when the variations feature creates a target page for the first time, a corresponding navigation term is also created on the target variation site. When you export a page for translation, its associated navigation term is also exported.
Variation settings
The Variations Settings page contains the following options:
Site, List, and Page Creation Behavior Determines whether sites, lists, and pages on the source variation site are created automatically on the target variation sites. By default, Create Everywhere is enabled. If you enable Create Selectively, the first time that you sync sites, lists, and pages from the source variation site to target variation sites, you must do so manually. Subsequent updates to items on the source variation site will be synced based on the target label sync preferences.
Recreate Deleted Target Page Determines whether a page should be re-created on a target variation site if the page was deleted from the target variation site, and the page on the source variation site was republished. By default, this option is enabled. If you disable this option, deleted pages aren't re-created on target variation sites. For example, consider the case in which a content author creates a page on the source variation site that isn't relevant to a target variation site. However, because Create Everywhere is enabled, the page is created automatically on the target variation site, and the target label content owner later deletes the unwanted target page. The next time that the content author updates the source page, the page won't be re-created on the target variation site.
Update Target Page Web Parts Determines whether changes that were made to Web Parts on pages on a source variation site are also made on pages on target variation sites. By default, this option is enabled.
Notification Sends an email message to the contact of the target label of a target variation site when a new page or site is created or to the contact person of the specified page when a page is updated with revisions from the source variation site. If the label doesn't have a contact, then the email message is sent to the contact of the welcome page of a target variation site. By default, this option is enabled.
For info about how to specify variations settings, see Create a multi-language website.
Variations timer jobs
The variations feature uses timer jobs to perform tasks such as creating and propagating sites and pages. A timer job runs inside OWSTIMER, a Windows service for SharePoint Server. Each timer job has its own default schedule for when the job runs. You can change the frequency with which each job runs on the Job Definitions page on the Central Administration website. The variations feature uses the following timer jobs:
Variations Create Hierarchies Job Definition Creates a complete variations hierarchy by creating all variation sites, lists, and pages from the source variation site, based on the variation labels. By default, this timer job runs hourly.
Variations Propagate List Items Job Definition Creates and updates list items on target variation sites after a list is configured to send items to specific target variation labels. By default, this timer job runs every 15 minutes.
Variations Propagate Page Job Definition Creates and updates pages on target variation sites after a page on the source variation site is approved or after it's manually submitted by a user. By default, this timer job runs every 15 minutes.
Variations Propagate Sites and Lists Job Definition Creates variation sites and lists when the Create Everywhere option is enabled. By default, this timer job runs every 30 minutes.
Note
Timer jobs aren't configurable in SharePoint in Microsoft 365.
For information about timer jobs, see View timer job status in SharePoint Server 2016.
Understanding source variation and target variation site creation
Source variation and target variation sites are always created one level below the variation root site. Each variation site is created by using the same site template that's used to create the variation root site. This same-template usage means that by default, each variation site will use the same master page as the variation root site. However, each variation site can use separate master pages, page layouts, and CSS files. This provision is useful when you want to have separate layouts for different locales. For example, you can use a right-to-left layout for one language and a left-to-right layout for another language. For info, see Overview of the SharePoint 2013 page model.
When the variations hierarchy is first created, only sites that are based on the list of defined variation labels are created. If the variation root site has sites below it in a hierarchical site structure, and you want to include those sites in the hierarchical site structure of each variation site, you must manually create the hierarchical structure of those sites below the source variation site after you create the variation hierarchy. By default, the next time that the Variations Create Hierarchies Job Definition timer job runs, the sites are synced only to any new target variation sites that are created at that time. For info about how sites below the source variation site are created on existing target variation sites, see Understanding site, list, and page creation later in this article.
After the variations hierarchy is first created, when you add a new label to the variations hierarchy, on the Variation Labels page, select Create Hierarchies, and a new target variation site is created for each new label. By default, if the source variation site has content in the Pages library, a list that is configured to send list items to specific target variation labels, or contains sites below it in the site hierarchy, those pages, lists, and sites are created on all new target variation sites only.
Understanding site, list, and page creation
By default, the following components are synced automatically to the target variation sites:
- Sites that are created below the source variation site
- Lists and pages that are published on the source variation site or on any sites below it in the site hierarchy
The following list types (or lists that inherit from these types) are supported:
- 100 - Generic list
- 101 - Document library
- 104 - Announcements list
- 109 - Picture library
If Create Selectively is enabled, you must manually create any sites, lists, and pages on the selected target variation sites.
This section describes the ways in which sites, lists, and pages are created on target variation sites.
Site creation
When the Variations Create Hierarchies Job Definition timer job runs for the first time and creates the variations hierarchy from the list of variation labels, only the source variation and target variation sites are created. After the source variation site is created, you can create sites below it in the site hierarchy, and those sites are then created on the existing target variation sites the next time that the Variations Propagate Sites and Lists Job Definition timer job runs. If Create Selectively is enabled, use the Site Variation Settings page on any site that is below the source variation site to manually create a target variation of the current site on one or more target variation sites. The new site is created on the specified target variation site when the next Variations Propagate Sites and Lists Job Definition timer job runs. You can create a target variation of the current site anytime after Create Selectively is enabled.
Note
When source variation and target variation sites are created, they're created by using the default site definition provided by the template selected when the source label was created. No custom site configurations or settings are synced to the new sites. If you want the source variation and target variation sites to have custom site configurations or settings, such as navigation customizations, you must make those changes on each site after you create the variations hierarchy.
List and page creation
List items sync with variation target sites only when the list on the source variation site is configured to specify the target variation sites to which they should be synced. By default, list syncs with specific target variation sites only after it's configured so, and when the next Variations Propagate Sites and Lists Job Definition timer job runs. If a new item is added to a list that has already been synced to target variation sites, it's synced when the next Variations Propagate List Items Job Definition timer job runs. If a new target variation label is added after the variations hierarchy is created, the list will be created on the new target variation site. By default, content approval is enabled on target lists. When a new item is synced to a target list, it must be approved before it will appear in a Content Query Web Part on the target variation site.
Note
Although you can specify individual pages that you want to sync to specific target labels, you can't sync individual list items. You can only specify a complete list to sync to specific target labels.
If the Publishing Site template was selected when the source variation site was created, pages on the source variation site or on any site below it in the site hierarchy must be published before they're eligible to be synced to target variation sites. If the Publishing Site with Workflow template was selected, pages must be approved for publication by using the publishing workflow before they're eligible to be synced to target variation sites. By default, after a new page is published or approved for publication, if it uses workflows, it's synced to all target variation sites when the next Variations Propagate Page Job Definition timer job runs. If the page was published previously and is changed and republished on the source variation site, and the Automatically update target variation pages setting is selected for the target labels, the page is synced to all target variation sites when the next Variations Propagate Page Job Definition timer job runs.
Note
On target variation sites, a page that is synced from the source variation site is always assigned a minor version number. If the page is new to the target site, it's assigned version 0.1. If the page already exists on the target variation site, the synced page is assigned the next available minor version number. For example, if a target variation site has version 2.1 of a page and a new variation of that page is synced to the target site, the page becomes version 2.2. Pages and additional resources, such as images that are approved for publishing on the source variation site, are synced to the target variation site together with their Approval status set to Draft, and they must be approved before they can be viewed by readers of the site.
If Create Selectively is enabled, a user must create the page for a specific variation label by using the Create new targets command in the Variations group on the Publish tab of the page on the source variation site. The new page is synced to one or more target variation sites when the next Variations Propagate Page Job Definition timer job runs. If the page was published previously and is changed and republished on the source variation site, it's synced only to the specified target variation site when the next Variations Propagate Page Job Definition timer job runs. For info about how to enable Create Selectively for variation pages, see Create a multi-language website.
By default, when a page that was synced from the source variation site is deleted from a target variation site, that page is re-created on the target variation site the next time it's published on the source variation site and the next time that the Variations Propagate Page Job Definition timer job runs. If Recreate Deleted Target Page is disabled, deleted pages aren't re-created on the target variation sites.
For info about how to create variation source pages and how to work with content on variation target pages, see Create a multi-language website.
Limitations of variations
The following list contains info about the limitations of the variations feature in SharePoint Server:
Variations feature is a single-tier hierarchy. The source and target variation sites exist at the same level within the site hierarchy, one level down from the variations root site. However, you can have only one source variation site per site collection. A site can't be both a source and a target site. You can sync content from a source variation site to one or more target variation sites, but you can't sync content from one target variation site to another target variation site. For example, if you have a source variation site in English (United States), and a target variation site in French (France), which has a French (Canada) site below it, the variations feature will only sync content from the English (United States) source variation site to the French (France) target variation site. The variations feature can't also sync content from the French target variation site to the French (Canada) site below it.
You can use variations together with cross-site publishing to reuse content from one variation site in the context of another variation site. For example, you could reuse content from the French (France) site on the French (Canada) site.
For more info, see Plan the logical architecture for cross-site publishing in SharePoint Server.
Content syncing is unidirectional. The variations feature syncs content from a source variation site to one or more target variation sites. You can't use the variations feature to sync content from a target variation site back to a source variation site. Also, target variation sites can't sync content to other target variation sites.