Microsoft Intune securely manages identities, manages apps, and manages devices
As organizations support hybrid and remote workforces, they're challenged with managing the different devices that access organization resources. Employees and students need to collaborate, work from anywhere, and securely access and connect to these resources. Admins need to protect organization data, manage end user access, and support users from wherever they work.
✅ To help with these challenges and tasks, use Microsoft Intune.
Microsoft Intune is a cloud-based endpoint management solution. It manages user access to organizational resources and simplifies app and device management across your many devices, including mobile devices, desktop computers, and virtual endpoints.
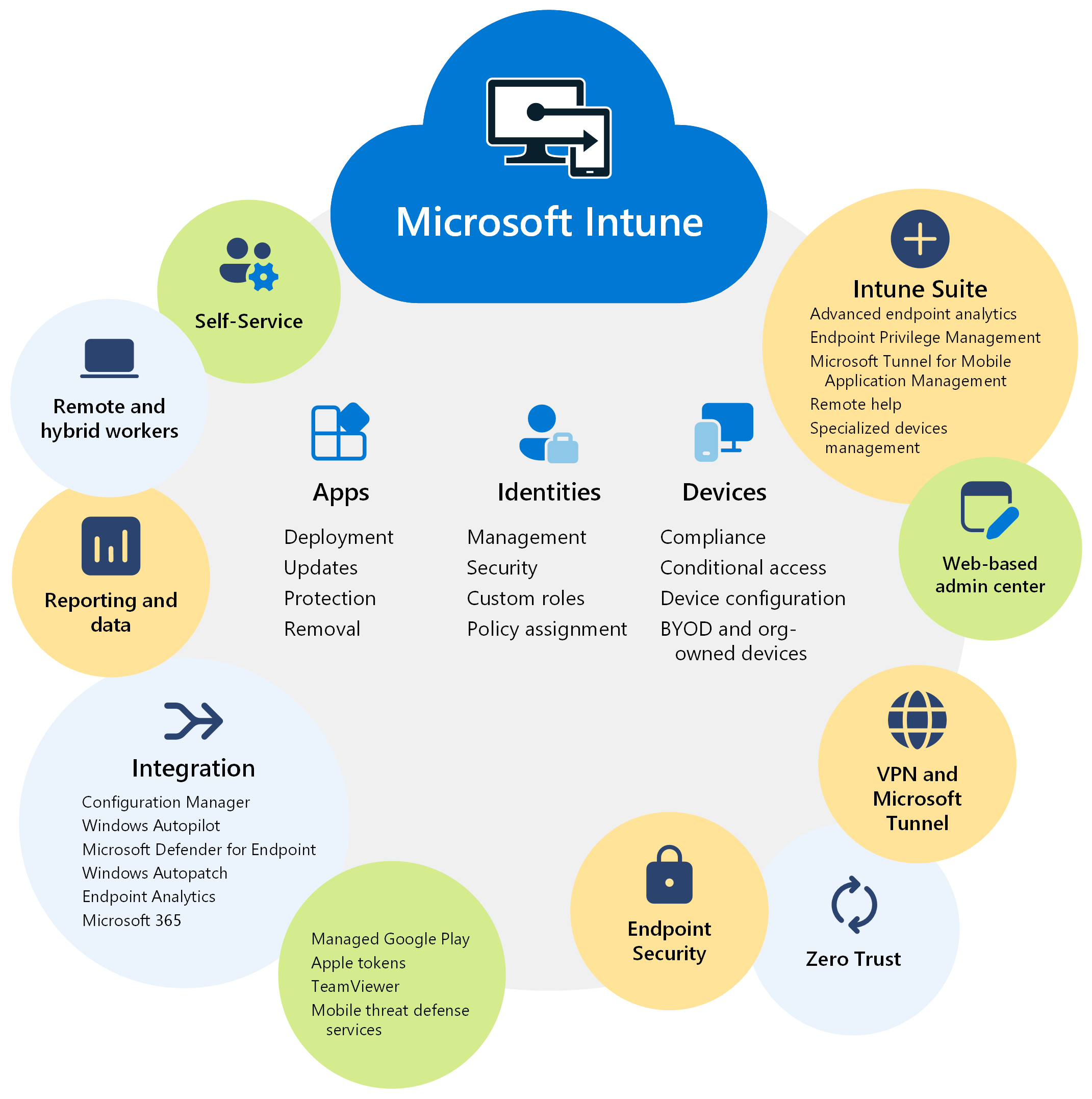
You can protect access and data on organization-owned and users personal devices. And, Intune has compliance and reporting features that support the Zero Trust security model.
This article lists some features and benefits of Microsoft Intune.
Tip
- To get Intune, go to Licenses available for Microsoft Intune and Intune 30-day trial.
- For more information on the Intune licensing plans, go to Microsoft Intune capabilities and plans.
- For information on what it means to be cloud-native, go to Learn more about cloud-native endpoints.
Key features and benefits
Some key features and benefits of Intune include:
✅ Manage users and devices
With Intune, you can manage devices owned by your organization and devices owned by your end users. Microsoft Intune supports Android, Android Open Source Project (AOSP), iOS/iPadOS, Linux Ubuntu Desktop, macOS, and Windows client devices. With Intune, you can use these devices to securely access organization resources with policies you create.
For more information, go to:
- Manage identities using Microsoft Intune
- Manage devices using Microsoft Intune
- Supported operating systems in Microsoft Intune
Note
If you manage on-premises Windows Server, you can use Configuration Manager.
✅ Simplify app management
Intune has a built-in app experience, including app deployment, updates, and removal. You can:
- Connect to and distribute apps from your private app stores.
- Enable Microsoft 365 apps, including Microsoft Teams.
- Deploy Win32 and line-of-business (LOB) apps.
- Create app protection policies that protect data within an app.
- Manage access to apps & their data.
For more information, go to Manage apps using Microsoft Intune.
✅ Automate policy deployment
You can create policies for apps, security, device configuration, compliance, Conditional Access, and more. When the policies are ready, you can deploy these policies to your user groups and device groups. To receive these policies, the devices only need internet access.
For more information, go to Assign policies in Microsoft Intune.
✅ Use the self-service features
Employees and students can use the Company Portal app and website to reset a PIN/password, install apps, join groups, and more. You can customize the Company Portal to help reduce support calls.
For more information, go to Configure the Intune Company Portal apps, Company Portal website, and Intune app.
✅ Integrate with mobile threat defense
Intune integrates with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint and third party partner services. With these services, the focus is on endpoint security. You can create policies that respond to threats, do real-time risk analysis, and automate remediation.
For more information, go to Mobile Threat Defense integration with Intune.
✅ Use a web-based admin center
The Intune admin center focuses on endpoint management, including data-driven reporting. Admins can sign into the admin center from any device that has internet access.
For more information, go to Walkthrough the Intune admin center. To sign in to the admin center, go to Microsoft Intune admin center.
This admin center uses Microsoft Graph REST APIs to programmatically access the Intune service. Every action in the admin center is a Microsoft Graph call. If you're not familiar with Graph, and want to learn more, go to Graph integrates with Microsoft Intune.
✅ Advanced endpoint management and security
The Microsoft Intune Suite offers different features, like Remote Help, Endpoint Privilege Management, Microsoft Tunnel for MAM, and more.
For more information, go to Intune Suite add-on features.
Tip
Step through a training module to learn how you can benefit from modern endpoint management with Microsoft Intune.
✅ Use Microsoft Copilot in Intune for AI-generated analysis
Copilot in Intune is available and has capabilities that are powered by Security Copilot.
Copilot can summarize existing policies, give you more setting information, including recommended values and potential conflicts. You can also get device details and troubleshoot a device.
For more information, go to Microsoft Copilot in Intune.
Integrates with other Microsoft services and apps
Microsoft Intune integrates with other Microsoft products and services that focus on endpoint management, including:
Configuration Manager for on-premises endpoint management and Windows Server, including deploying software updates and managing data centers
You can use Intune and Configuration Manager together in a co-management scenario, use tenant attach, or use both. With these options, you get the benefits of the web-based admin center and can use other cloud-based features available in Intune.
For more specific information, go to:
Windows Autopilot for modern OS deployment and provisioning
With Windows Autopilot, you can provision new devices and send these devices directly to users from an OEM or device provider. For existing devices, you can reimage these devices to use Windows Autopilot and deploy the latest Windows version.
For more specific information, go to:
Endpoint analytics for visibility and reporting on end user experiences, including device performance and reliability
You can use Endpoint analytics to help identify policies or hardware issues that slow down devices. It also provides guidance that can help you proactively improve end user experiences and reduce help desk tickets.
For more specific information, go to:
Microsoft 365 for end user productivity Office apps, including Outlook, Teams, Sharepoint, OneDrive, and more
Using Intune, you can deploy Microsoft 365 apps to users and devices in your organization. You can also deploy these apps when users sign in for the first time.
For more specific information, go to:
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to help enterprises prevent, detect, investigate, and respond to threats
In Intune, you can create a service-to-service connection between Intune and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. When they're connected, you can create policies that scan files, detect threats, and report threat levels to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. You can also create compliance policies that set an allowable level of risk. When combined with Conditional Access, you can block access to organization resources for devices that are noncompliant.
For more specific information, go to:
Windows Autopatch for automatic patching of Windows, Microsoft 365 apps for enterprise, Microsoft Edge, and Microsoft Teams
Windows Autopatch is a cloud based service. It keeps software current, gives users the latest productivity tools, minimizes on-premises infrastructure, and helps free up your IT admins to focus on other projects. Windows Autopatch uses Microsoft Intune to manage patching for Intune-enrolled devices or devices using co-management (Intune + Configuration Manager).
For more specific information, go to:
Integrates with third party partner devices and apps
The Intune admin center makes it easy to connect to different partner services, including:
Managed Google Play for Android apps: When you connect to your Managed Google Play account, admins can access your organization's private store for Android apps, and deploy these apps to your devices.
For more information, go to Add Managed Google Play apps to Android Enterprise devices with Intune.
Apple tokens and certificates for enrollment and apps: When they're added, your iOS/iPadOS and macOS devices can enroll in Intune and receive policies from Intune. Admins can access your volume purchased iOS/iPad and macOS app licenses, and deploy these apps to your devices.
For more information, go to:
TeamViewer for remote assist: When you connect to your TeamViewer account, you can use TeamViewer to remotely assist devices.
For more information, go to Use TeamViewer to remotely administer Intune devices.
With these services, Intune:
- Gives admins simplified access to third party partner app services.
- Can manage hundreds of third party partner apps.
- Supports public retail store apps, line of business (LOB) apps, private apps not available in the public store, custom apps, and more.
For more platform-specific requirements to enroll third party partner devices in Intune, go to:
- Deployment guide: Enroll Android devices in Microsoft Intune
- Deployment guide: Enroll iOS and iPadOS devices in Microsoft Intune
- Deployment guide: Enroll Linux devices in Microsoft Intune
- Deployment guide: Enroll macOS devices in Microsoft Intune
Enroll in device management, application management, or both
✅ Organization-owned devices are enrolled in Intune for mobile device management (MDM). MDM is device centric, so device features are configured based on who needs them. For example, you can configure a device to allow access to Wi-Fi, but only if the signed-in user is an organization account.
In Intune, you create policies that configure features & settings and provide security & protection. Your admin team fully manages the devices, including the user identities that sign in, the apps that are installed, and the data that's accessed.
When devices enroll, you can deploy your policies during the enrollment process. When enrollment completes, the device is ready to use.
✅ For personal devices in bring-your-own-device (BYOD) scenarios, you can use Intune for mobile application management (MAM). MAM is user centric, so the app data is protected regardless of the device used to access this data. There's a focus on apps, including securely accessing apps and protecting data within the apps.
With MAM, you can:
- Publish mobile apps to users.
- Configure apps and automatically update apps.
- View data reports that focus on app inventory and app usage.
✅ You can also use MDM and MAM together. If your devices are enrolled and there are apps that need extra security, then you can also use MAM app protection policies.
For more information, go to:
Protect data on any device
With Intune, you can protect data on managed devices (enrolled in Intune) and protect data on unmanaged devices (not enrolled in Intune). Intune can isolate organization data from personal data. The idea is to protect your company information using policies that you configure and deploy.
For organization-owned devices, you want full control over the devices, especially security. When devices enroll, they receive your security rules and settings.
On devices enrolled in Intune, you can:
- Create and deploy policies that configure security settings, set password requirements, deploy certificates, and more.
- Use mobile threat defense services to scan devices, detect threats, and remediate threats.
- View data and reports that measure compliance with your security settings and rules.
- Use Conditional Access to only allow managed and compliant devices access to organization resources, apps, and data.
- Remove organization data if a device is lost or stolen.
For personal devices, users might not want their IT admins to have full control. To support a hybrid work environment, give users options. For example, users enroll their devices if they want full access to your organization's resources. Or, if these users only want access to Outlook or Microsoft Teams, then use app protection policies that require multifactor authentication (MFA).
On devices using application management, you can:
- Use mobile threat defense services to protect app data. The service can scan devices, detect threats, and assess risk.
- Prevent organization data from being copied and pasted into personal apps.
- Use app protection policies on apps and on unmanaged devices enrolled in a third party or partner MDM.
- Use Conditional Access to restrict the apps that can access organization email and files.
- Remove organization data within apps.
For more information, go to:
Simplify access
Intune helps organizations support employees who can work from anywhere. There are features you can configure that allow users to connect to an organization, wherever they might be.
This section includes some common features that you can configure in Intune.
Use Windows Hello for Business instead of passwords
Windows Hello for Business helps protect against phishing attacks and other security threats. It also helps users sign in to their devices and apps more quickly and easily.
Windows Hello for Business replaces passwords with a PIN or biometric, such as fingerprint or facial recognition. This biometric information is stored locally on the devices and is never sent to external devices or servers.
For more information, go to:
- Get an overview Windows Hello for Business
- Manage Windows Hello for Business on devices when they enroll in Intune
- Manage identities using Microsoft Intune
Create a VPN connection for remote users
VPN policies give users secure remote access to your organization network.
Using common VPN connection partners, including Check Point, Cisco, Microsoft Tunnel, NetMotion, Pulse Secure, and more, you can create a VPN policy with your network settings. When the policy is ready, you deploy this policy to your users and devices that need to connect to your network remotely.
In the VPN policy, you can use certificates to authenticate the VPN connection. When you use certificates, your end users don't need to enter usernames and passwords.
For more information, go to:
- Create VPN profiles to connect to VPN servers in Intune
- Use certificates for authentication in Intune
- Learn more about Microsoft Tunnel for Intune
- Use Microsoft Tunnel for MAM
Create a Wi-Fi connection for on-premises users
For users who need to connect to your organization network on-premises, you can create a Wi-Fi policy with your network settings. You can connect to a specific SSID, select an authentication method, use a proxy, and more. You can also configure the policy to automatically connect to Wi-Fi when the device is in range.
In the Wi-Fi policy, you can use certificates to authenticate the Wi-Fi connection. When you use certificates, your end users don't need to enter usernames and passwords.
When the policy is ready, you deploy this policy to your on-premises users and devices that need to connect to your on-premises network.
For more information, go to:
- Create Wi-Fi policy to connect to Wi-Fi networks in Intune
- Use certificates for authentication in Microsoft Intune
Enable single sign-on (SSO) to your apps and services
When you enable SSO, users can automatically sign in to apps and services using their Microsoft Entra organization account, including some mobile threat defense partner apps.
Specifically:
On Windows devices, SSO is automatically built in and used to sign in to apps and websites that use Microsoft Entra ID for authentication, including Microsoft 365 apps. You can also enable SSO on VPN and Wi-Fi policies.
On iOS/iPadOS and macOS devices, you can use the Microsoft Enterprise SSO plug-in to automatically sign in to apps and websites that use Microsoft Entra ID for authentication, including Microsoft 365 apps.
For more information, go to Single sign-on (SSO) overview and options for Apple devices in Microsoft Intune.
On Android devices, you can use the Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL) to enable SSO to Android apps.
For more information, go to: