Manage your apps and app data in Microsoft Intune
Managing and protecting apps and their data is a significant part of any endpoint management strategy and solution. In most environments, users can install public retail apps and possibly access organization data from these apps. Many organizations also have their own private apps and line-of-business apps that need to be deployed & managed. They must make sure this app data stays within the organization.
App management can be challenging and Intune can help. Microsoft Intune is a cloud-based service that can manage many apps types. Using Intune, admins can deploy, configure, protect, and update apps that access your organization resources. For more information on Intune and its benefits, go to What is Microsoft Intune?.
Microsoft Intune can manage apps on Android, iOS/iPadOS, macOS, and Windows client devices. So, you can use Intune's app management features across your many devices.
From a service perspective, Intune uses Microsoft Entra ID for identity management. To use some apps, these Microsoft Entra user identities must have licenses assigned to them. The Microsoft Intune admin center can also help you manage licensing.
This article discusses concepts and features you should consider when managing and securing apps.
Deploy apps your organization uses
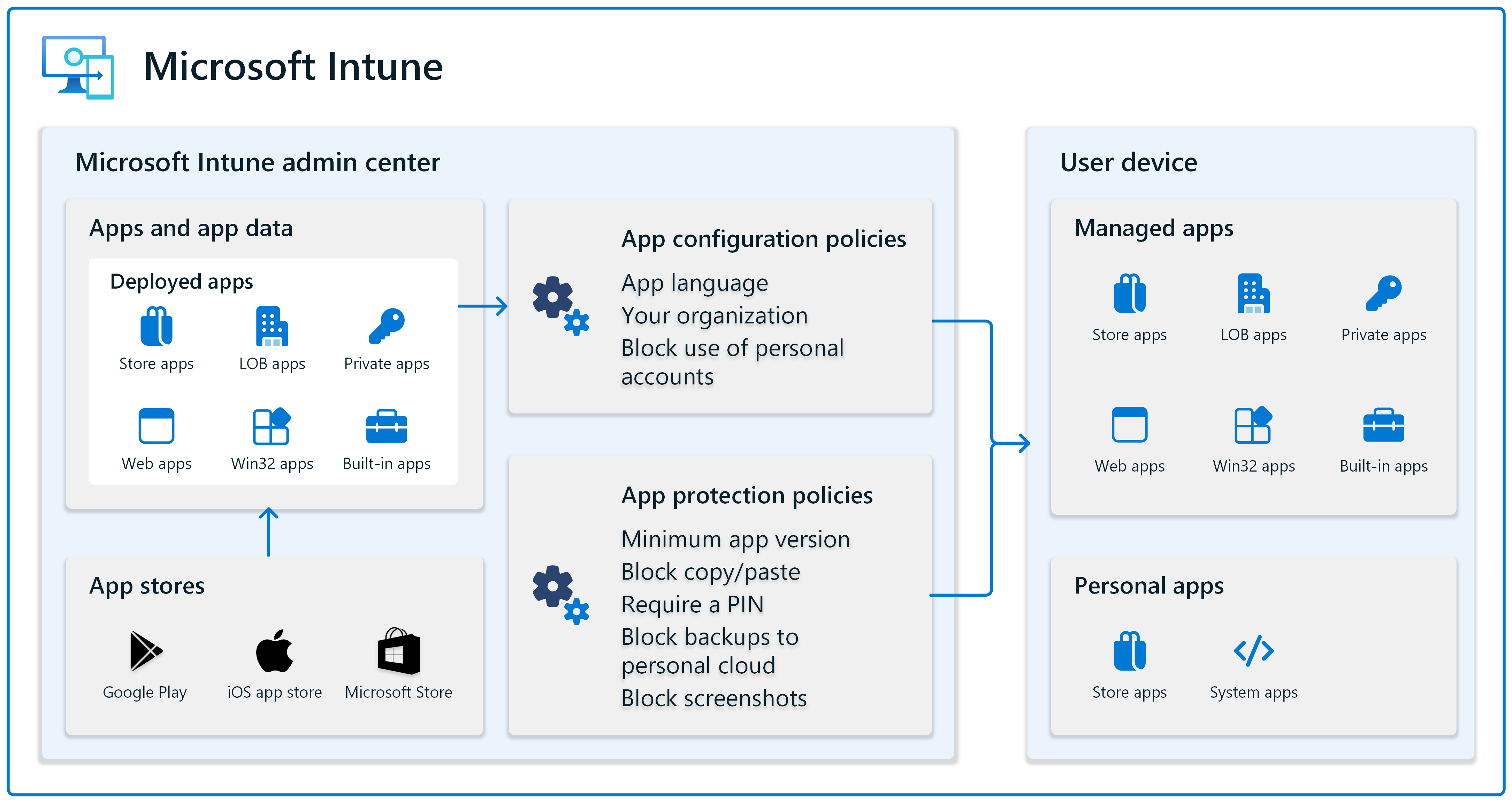
Organizations use many different types of apps, including store apps, line-of-business (LOB) apps, web apps, and more. You can add apps to Intune and then use its app policy management to deploy these apps to your devices.
The app features in the Intune admin center make it easier to deploy these different kinds of apps.
For Android devices, the Intune admin center automatically connects to the public Play Store and gives you the ability to search for apps. You can also sync with your Managed Google Play account to access your Android Enterprise apps, including private apps.
On Android devices, you can deploy:
- Public and retail apps from the public Play Store
- Managed Google Play apps to Android Enterprise devices
- Web links to web apps
- Built-in apps, which are apps automatically included and available in the Intune admin center
- Custom line-of-business apps your organization creates
- Android Enterprise system apps, which are apps typically included on Android devices
If you use Google Mobile Services (GMS) (opens Android's web site), you can purchase licenses to GMS, which typically happens when you purchase Android devices. GMS gives users access to the public Play Store and its public apps.
If your organization doesn't use Google Mobile Services (GMS) (opens Android's web site), then Intune can also manage devices using the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) platform.
For more specific information, go to:
For iOS/iPadOS devices, the Intune admin center automatically connects to the public App Store and gives you the ability to search for apps. You can also sync with your Apple Business Manager or Apple School Manager account to access your volume-licensed apps. When you sync, the apps you purchase (your licensed apps) are automatically shown in the admin center.
On iOS/iPadOS devices, you can deploy:
- Public and retail apps from the public App Store
- Volume-licensed apps using Apple Business Manager or Apple School Manager
- Web clips, which are shortcuts to web site links that you can add to the home screen
- Web links to web apps
- Built-in apps, which are apps automatically included and available in the Intune admin center
- Custom line-of-business apps your organization creates
For more specific information, go to:
For macOS devices, the Intune admin center has built-in features that include apps commonly deployed to macOS, including Microsoft Edge and Microsoft 365 apps. You can also sync with your Apple Business Manager or Apple School Manager account to access your volume-licensed apps. When you sync, the apps you purchase (your licensed apps) are automatically shown in the admin center.
On macOS devices, you can deploy:
- Volume-licensed apps using Apple Business Manager or Apple School Manager
- Microsoft 365 apps, which include Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook, OneNote, Teams, and OneDrive
- Microsoft Edge version 77 and newer, which is the modern chromium version
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, which is a cloud service that detects malicious intent and can help remediate security threats
- Web links to web apps
- Custom line-of-business apps your organization creates
- Apple disk image (DMG) apps, which is a file that includes one or more apps to deploy
For more specific information, go to:
For Windows devices, the Intune admin center automatically connects to the public Microsoft Store and gives you the ability to search for apps. You can also sync with your Microsoft Store for Business account to access your volume-licensed apps. When you sync, the apps you purchase (your licensed apps) are automatically shown in the admin center.
On Windows devices, you can deploy:
- Volume-licensed apps using Microsoft Store for Business
- Public and retail apps from the Microsoft Store
- Microsoft 365 apps, which include Word, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook, OneNote, Teams, and OneDrive
- Microsoft Edge version 77 and newer, which is the modern chromium version
- Web links to web apps
- Custom line-of-business apps your organization creates
- Win32 apps
For more specific information, go to:
Note
Microsoft Store for Business is being retired. Starting with Windows 11, you have a new option for your private volume-licensed apps. For more information, go to Private app repository in Windows 11 and Update to Microsoft Intune integration with the Microsoft Store on Windows.
Configure apps before they're installed
When an app is deployed to your users and devices, your users can be prompted for configuration information. Users might not know what to enter or you might have organization settings you want configured a certain way.
App configuration policies give you these features. You can create app configuration policies that automatically configure apps. Depending on your policy settings, users might not need to enter any configuration information when they open the app.
For example, in an app configuration policy, you can enter the app language, add your organization's logo, block apps from using personal accounts, and more.
Your app configuration policies can be deployed at any time. If you want to configure apps before users open them the first time, then include the app configuration policy when users enroll their devices. During enrollment, your app configuration policies are automatically deployed and the apps include your configuration settings.
For more specific information, go to App configuration policies in Intune.
Protect apps on organization owned and personal devices
App protection policies are a key part to protecting data in apps that access organization data. If user-owned personal devices are accessing your organization data, then you need app protection policies. Use these policies to protect email, protect shared files, protect access to meetings, and more.
You can use Intune to create, configure, and deploy app protection policies to your users and your devices, including personally owned devices and devices managed by another MDM provider. Typically, organization owned devices are managed by your organization. If there are apps on these managed devices that require extra security, then you can also use app protection policies on these devices.
App protection policies also help separate personal data from organization data. For example, you can create policies that block copy-and-paste between apps, require a PIN when opening an app, block backups to personal cloud services, and more.
For more specific information, go to:
Update apps to the latest version
Apps are often updated to include bug fixes, feature improvements, security updates, and more. When apps are deployed using Intune, most apps are automatically updated when there's an app update available. So, it's recommended to use Intune to deploy apps used by your organization.
You can also use Windows Autopatch for automatic patching of Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise, Microsoft Edge, and Microsoft Teams.
If users install apps themselves, including from a public app store, then these apps need updated manually. In this situation, you can use app protection policies to enforce a minimum app version, and even wipe organization data on devices that don't meet your standards.
For more information, go to:
- Add and update apps
- Windows Autopatch overview
- Wipe corporate data from Intune-managed apps
- Selectively wipe data using app protection policy conditional launch actions