JavaScript SDK for Azure Web PubSub
Azure Web PubSub service is an Azure-managed service that helps developers easily build web applications with real-time features and publish-subscribe pattern. Any scenario that requires real-time publish-subscribe messaging between server and clients or among clients can use Azure Web PubSub service. Traditional real-time features that often require polling from server or submitting HTTP requests can also use Azure Web PubSub service.
There are two libraries offered for JavaScript: the service client library and express middleware. The following sections contain more information about these libraries.
Azure Web PubSub service client library for JavaScript
You can use this library in your app server side to manage the WebSocket client connections, as shown in below diagram:
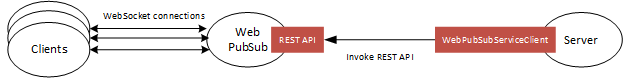
- Send messages to hubs and groups.
- Send messages to particular users and connections.
- Organize users and connections into groups.
- Close connections
- Grant, revoke, and check permissions for an existing connection
Source code | Package (NPM) | API reference documentation | Product documentation | Samples
Getting started
Currently supported environments
Prerequisites
- An Azure subscription.
- An existing Azure Web PubSub service instance.
1. Install the @azure/web-pubsub package
npm install @azure/web-pubsub
2. Create and authenticate a WebPubSubServiceClient
const { WebPubSubServiceClient } = require("@azure/web-pubsub");
const serviceClient = new WebPubSubServiceClient(
"<ConnectionString>",
"<hubName>"
);
You can also authenticate the WebPubSubServiceClient using an endpoint and an AzureKeyCredential:
const {
WebPubSubServiceClient,
AzureKeyCredential,
} = require("@azure/web-pubsub");
const key = new AzureKeyCredential("<Key>");
const serviceClient = new WebPubSubServiceClient(
"<Endpoint>",
key,
"<hubName>"
);
Or authenticate the WebPubSubServiceClient using Microsoft Entra ID
- Install the
@azure/identitydependency
npm install @azure/identity
- Update the source code to use
DefaultAzureCredential:
const {
WebPubSubServiceClient,
AzureKeyCredential,
} = require("@azure/web-pubsub");
const key = new DefaultAzureCredential();
const serviceClient = new WebPubSubServiceClient(
"<Endpoint>",
key,
"<hubName>"
);
Examples
Get the access token for a client to start the WebSocket connection
const { WebPubSubServiceClient } = require("@azure/web-pubsub");
const serviceClient = new WebPubSubServiceClient(
"<ConnectionString>",
"<hubName>"
);
// Get the access token for the WebSocket client connection to use
let token = await serviceClient.getClientAccessToken();
// Or get the access token and assign the client a userId
token = await serviceClient.getClientAccessToken({ userId: "user1" });
// return the token to the WebSocket client
Broadcast messages to all connections in a hub
const { WebPubSubServiceClient } = require("@azure/web-pubsub");
const serviceClient = new WebPubSubServiceClient(
"<ConnectionString>",
"<hubName>"
);
// Send a JSON message
await serviceClient.sendToAll({ message: "Hello world!" });
// Send a plain text message
await serviceClient.sendToAll("Hi there!", { contentType: "text/plain" });
// Send a binary message
const payload = new Uint8Array(10);
await serviceClient.sendToAll(payload.buffer);
Send messages to all connections in a group
const { WebPubSubServiceClient } = require("@azure/web-pubsub");
const serviceClient = new WebPubSubServiceClient(
"<ConnectionString>",
"<hubName>"
);
const groupClient = serviceClient.group("<groupName>");
// Add user to the group
await groupClient.addUser("user1");
// Send a JSON message
await groupClient.sendToAll({ message: "Hello world!" });
// Send a plain text message
await groupClient.sendToAll("Hi there!", { contentType: "text/plain" });
// Send a binary message
const payload = new Uint8Array(10);
await groupClient.sendToAll(payload.buffer);
Send messages to all connections for a user
const { WebPubSubServiceClient } = require("@azure/web-pubsub");
const serviceClient = new WebPubSubServiceClient(
"<ConnectionString>",
"<hubName>"
);
// Send a JSON message
await serviceClient.sendToUser("user1", { message: "Hello world!" });
// Send a plain text message
await serviceClient.sendToUser("user1", "Hi there!", {
contentType: "text/plain",
});
// Send a binary message
const payload = new Uint8Array(10);
await serviceClient.sendToUser("user1", payload.buffer);
Check if the group has any connection
const { WebPubSubServiceClient } = require("@azure/web-pubsub");
const WebSocket = require("ws");
const serviceClient = new WebPubSubServiceClient(
"<ConnectionString>",
"<hubName>"
);
const groupClient = serviceClient.group("<groupName>");
// close all the connections in the group
await groupClient.closeAllConnections({ reason: "<closeReason>" });
// check if the group has any connections
const hasConnections = await serviceClient.groupExists("<groupName>");
Access the raw HTTP response for an operation
const { WebPubSubServiceClient } = require("@azure/web-pubsub");
function onResponse(rawResponse: FullOperationResponse): void {
console.log(rawResponse);
}
const serviceClient = new WebPubSubServiceClient(
"<ConnectionString>",
"<hubName>"
);
await serviceClient.sendToAll({ message: "Hello world!" }, { onResponse });
Service client troubleshooting
Enable logs
You can set the following environment variable to get the debug logs when using this library.
- Getting debug logs from the Azure Web PubSub client library
export AZURE_LOG_LEVEL=verbose
For more detailed instructions on how to enable logs, you can look at the @azure/logger package docs.
Live Trace
Use Live Trace from the Web PubSub service portal to view the live traffic.
Azure Web PubSub CloudEvents handlers for Express
When a WebSocket connection connects, the Web PubSub service transforms the connection lifecycle and messages into events in CloudEvents format. This library provides an express middleware to handle events representing the WebSocket connection's lifecycle and messages, as shown in below diagram:
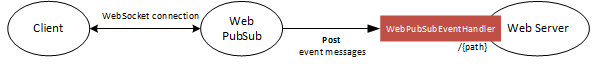
Source code | Package (NPM) | API reference documentation | Product documentation | Samples
Getting started
Currently supported environments
- LTS versions of Node.js
- Express version 4.x.x or higher
Prerequisites
- An Azure subscription.
- An existing Azure Web PubSub endpoint.
1. Install the @azure/web-pubsub-express package
npm install @azure/web-pubsub-express
2. Create a WebPubSubEventHandler
const express = require("express");
const { WebPubSubEventHandler } = require("@azure/web-pubsub-express");
const handler = new WebPubSubEventHandler("chat");
const app = express();
app.use(handler.getMiddleware());
app.listen(3000, () =>
console.log(
`Azure WebPubSub Upstream ready at http://localhost:3000${handler.path}`
)
);
Express examples
Handle the connect request and assign <userId>
const express = require("express");
const { WebPubSubEventHandler } = require("@azure/web-pubsub-express");
const handler = new WebPubSubEventHandler("chat", {
handleConnect: (req, res) => {
// auth the connection and set the userId of the connection
res.success({
userId: "<userId>",
});
},
allowedEndpoints: ["https://<yourAllowedService>.webpubsub.azure.com"],
});
const app = express();
app.use(handler.getMiddleware());
app.listen(3000, () =>
console.log(
`Azure WebPubSub Upstream ready at http://localhost:3000${handler.path}`
)
);
Only allow specified endpoints
const express = require("express");
const { WebPubSubEventHandler } = require("@azure/web-pubsub-express");
const handler = new WebPubSubEventHandler("chat", {
allowedEndpoints: [
"https://<yourAllowedService1>.webpubsub.azure.com",
"https://<yourAllowedService2>.webpubsub.azure.com",
],
});
const app = express();
app.use(handler.getMiddleware());
app.listen(3000, () =>
console.log(
`Azure WebPubSub Upstream ready at http://localhost:3000${handler.path}`
)
);
Set custom event handler path
const express = require("express");
const { WebPubSubEventHandler } = require("@azure/web-pubsub-express");
const handler = new WebPubSubEventHandler("chat", {
path: "/customPath1",
});
const app = express();
app.use(handler.getMiddleware());
app.listen(3000, () =>
// Azure WebPubSub Upstream ready at http://localhost:3000/customPath1
console.log(
`Azure WebPubSub Upstream ready at http://localhost:3000${handler.path}`
)
);
Set and read connection state
const express = require("express");
const { WebPubSubEventHandler } = require("@azure/web-pubsub-express");
const handler = new WebPubSubEventHandler("chat", {
handleConnect(req, res) {
// You can set the state for the connection, it lasts throughout the lifetime of the connection
res.setState("calledTime", 1);
res.success();
},
handleUserEvent(req, res) {
var calledTime = req.context.states.calledTime++;
console.log(calledTime);
// You can also set the state here
res.setState("calledTime", calledTime);
res.success();
},
});
const app = express();
app.use(handler.getMiddleware());
app.listen(3000, () =>
console.log(
`Azure WebPubSub Upstream ready at http://localhost:3000${handler.path}`
)
);
Troubleshooting
Enable logs
You can set the following environment variable to get the debug logs when using this library.
- Getting debug logs from the Azure Web PubSub client library
export AZURE_LOG_LEVEL=verbose
For more detailed instructions on how to enable logs, see @azure/logger package docs.
Live Trace
Use Live Trace from the Web PubSub service portal to view the live traffic.
Next steps
Use these resources to start building your own application: