Adición de una capa de polígono al mapa (Android SDK)
En este artículo se muestra cómo representar las áreas de las geometrías de las características Polygon y MultiPolygon en el mapa con una capa de polígono.
Nota:
Retirada de Android SDK de Azure Maps
El SDK nativo de Azure Maps para Android ya está en desuso y se retirará el 31 de marzo de 2025. Para evitar interrupciones del servicio, migre al SDK web de Azure Maps antes del 31 de marzo de 2025. Para obtener más información, consulte Guía de migración de Android SDK de Azure Maps.
Requisitos previos
Asegúrese de completar los pasos descritos en el documento Inicio rápido: Creación de una aplicación de Android. Los bloques de código de este artículo se pueden insertar en el controlador de eventos onReady de mapas.
Uso de una capa de polígono
Cuando una capa de polígono se conecta a un origen de datos y se carga en el mapa, representa el área con las características Polygon y MultiPolygon. Para crear un polígono, agréguelo a un origen de datos y represéntelo con una capa de polígono mediante la clase PolygonLayer.
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
DataSource source = new DataSource();
map.sources.add(source);
//Create a rectangular polygon.
source.add(Polygon.fromLngLats(
Arrays.asList(
Arrays.asList(
Point.fromLngLat(-73.98235, 40.76799),
Point.fromLngLat(-73.95785, 40.80044),
Point.fromLngLat(-73.94928, 40.79680),
Point.fromLngLat(-73.97317, 40.76437),
Point.fromLngLat(-73.98235, 40.76799)
)
)
));
//Create and add a polygon layer to render the polygon on the map, below the label layer.
map.layers.add(new PolygonLayer(source,
fillColor("red"),
fillOpacity(0.7f)
), "labels");
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
val source = DataSource()
map.sources.add(source)
//Create a rectangular polygon.
source.add(
Polygon.fromLngLats(
Arrays.asList(
Arrays.asList(
Point.fromLngLat(-73.98235, 40.76799),
Point.fromLngLat(-73.95785, 40.80044),
Point.fromLngLat(-73.94928, 40.79680),
Point.fromLngLat(-73.97317, 40.76437),
Point.fromLngLat(-73.98235, 40.76799)
)
)
)
)
//Create and add a polygon layer to render the polygon on the map, below the label layer.
map.layers.add(
PolygonLayer(
source,
fillColor("red"),
fillOpacity(0.7f)
), "labels"
)
En la captura de pantalla siguiente se muestra cómo el código anterior representa el área de un polígono mediante una capa de polígono.
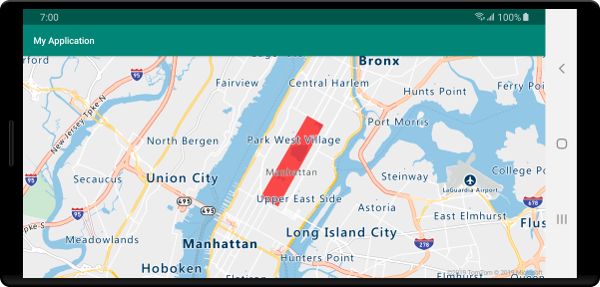
Uso de un polígono y una capa de línea conjuntamente
Una capa de línea se usa para representar el contorno de los polígonos. En el ejemplo de código siguiente se representa un polígono como en el ejemplo anterior, pero ahora se agrega una capa de línea. Esta capa de línea es una segunda capa conectada al origen de datos.
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
DataSource source = new DataSource();
map.sources.add(source);
//Create a rectangular polygon.
source.add(Polygon.fromLngLats(
Arrays.asList(
Arrays.asList(
Point.fromLngLat(-73.98235, 40.76799),
Point.fromLngLat(-73.95785, 40.80044),
Point.fromLngLat(-73.94928, 40.79680),
Point.fromLngLat(-73.97317, 40.76437),
Point.fromLngLat(-73.98235, 40.76799)
)
)
));
//Create and add a polygon layer to render the polygon on the map, below the label layer.
map.layers.add(new PolygonLayer(source,
fillColor("rgba(0, 200, 200, 0.5)")
), "labels");
//Create and add a line layer to render the outline of the polygon.
map.layers.add(new LineLayer(source,
strokeColor("red"),
strokeWidth(2f)
));
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
val source = DataSource()
map.sources.add(source)
//Create a rectangular polygon.
source.add(
Polygon.fromLngLats(
Arrays.asList(
Arrays.asList(
Point.fromLngLat(-73.98235, 40.76799),
Point.fromLngLat(-73.95785, 40.80044),
Point.fromLngLat(-73.94928, 40.79680),
Point.fromLngLat(-73.97317, 40.76437),
Point.fromLngLat(-73.98235, 40.76799)
)
)
)
)
//Create and add a polygon layer to render the polygon on the map, below the label layer.
map.layers.add(
PolygonLayer(
source,
fillColor("rgba(0, 200, 200, 0.5)")
), "labels"
)
//Create and add a line layer to render the outline of the polygon.
map.layers.add(
LineLayer(
source,
strokeColor("red"),
strokeWidth(2f)
)
)
En la siguiente captura de pantalla se muestra cómo el código anterior representa un polígono con su contorno representado mediante una capa de línea.
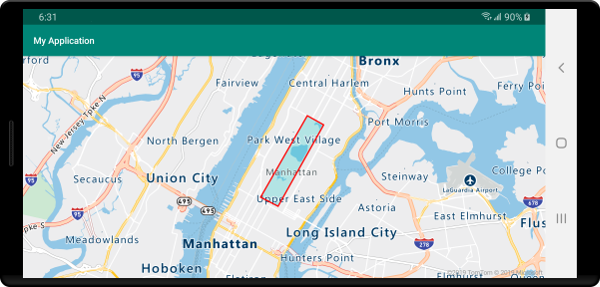
Sugerencia
Cuando cree el contorno de un polígono con una capa de línea, asegúrese de cerrar todos los anillos de los polígonos, de modo que cada matriz de puntos tenga el mismo punto inicial y final. Si no lo hace así, es posible que la capa de línea no conecte el último punto del polígono al primer punto.
Relleno de un polígono con un patrón
Además de rellenar un polígono con un color, puede usar un patrón de imágenes para rellenarlo. Cargue un patrón de imagen en los recursos de sprite de la imagen de los mapas y luego haga referencia a esta imagen con la opción fillPattern de la capa de polígono.
//Load an image pattern into the map image sprite.
map.images.add("fill-checker-red", R.drawable.fill_checker_red);
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
DataSource source = new DataSource();
map.sources.add(source);
//Create a polygon.
source.add(Polygon.fromLngLats(
Arrays.asList(
Arrays.asList(
Point.fromLngLat(-50, -20),
Point.fromLngLat(0, 40),
Point.fromLngLat(50, -20),
Point.fromLngLat(-50, -20)
)
)
));
//Create and add a polygon layer to render the polygon on the map, below the label layer.
map.layers.add(new PolygonLayer(source,
fillPattern("fill-checker-red"),
fillOpacity(0.5f)
), "labels");
//Load an image pattern into the map image sprite.
map.images.add("fill-checker-red", R.drawable.fill_checker_red)
//Create a data source and add it to the map.
val source = DataSource()
map.sources.add(source)
//Create a polygon.
source.add(
Polygon.fromLngLats(
Arrays.asList(
Arrays.asList(
Point.fromLngLat(-50, -20),
Point.fromLngLat(0, 40),
Point.fromLngLat(50, -20),
Point.fromLngLat(-50, -20)
)
)
)
)
//Create and add a polygon layer to render the polygon on the map, below the label layer.
map.layers.add(
PolygonLayer(
source,
fillPattern("fill-checker-red"),
fillOpacity(0.5f)
), "labels"
)
En este ejemplo, la imagen siguiente se ha cargado en la carpeta Drawable de la aplicación.
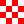 |
|---|
| fill-checker-red.png |
La imagen siguiente es una captura de pantalla del código anterior que representa un polígono con un patrón de relleno en el mapa.
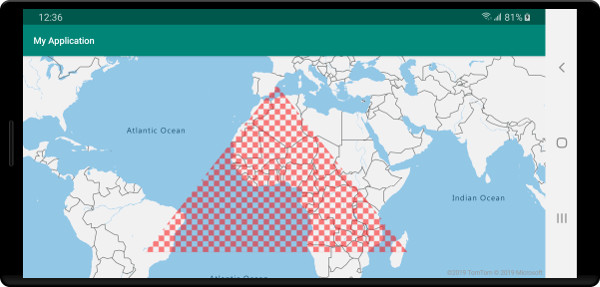
Pasos siguientes
Para obtener más ejemplos de código para agregar a los mapas: