Adding Manipulation Support in Unmanaged Code
This section explains how to add manipulation support to unmanaged code by implementing an event sink for the _IManipulationEvents interface.
The following image outlines the manipulation architecture.
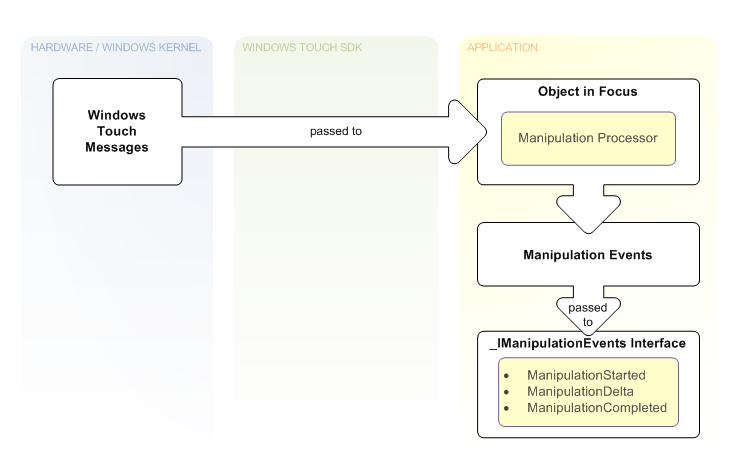
Touch data that is received from WM_TOUCH messages is passed to the IManipulationProcessor together with the contact ID from the touch message. Based on the message sequence, the IManipulationProcessor interface will calculate what kind of transformation is being performed and what the values associated with this transformation are. The IManipulationProcessor will then generate _IManipulationEvents which are handled by an event sink. The event sink can then use these values to perform custom operations on the object being transformed.
To add manipulation support to your application, you must follow these steps:
- Implement an event sink for the _IManipulationEvents interface.
- Create an instance of an IManipulationProcessor interface.
- Create an instance of your event sink and set up touch events.
- Send touch event data to the manipulation processor.
This section explains the steps that you must follow to add manipulation support to your application. Code is provided at each step to get you started.
Note
You cannot use manipulations and gestures at the same time because gesture and touch messages are mutually exclusive.
Implement an Event Sink for _IManipualtionEvents Interface
Before you can create an instance of your event sink, you must create a class that implements the _IManipulationEvents interface for eventing. This is your event sink. Events generated by the IManipulationProcessor interface are handled by your event sink. The following code shows an example header for a class that inherits the _IManipulationEvents interface.
// Manipulation Header Files
#include <comdef.h>
#include <manipulations.h>
#include <ocidl.h>
class CManipulationEventSink : _IManipulationEvents
{
public:
CManipulationEventSink(IManipulationProcessor *manip, HWND hWnd);
int GetStartedEventCount();
int GetDeltaEventCount();
int GetCompletedEventCount();
double CManipulationEventSink::GetX();
double CManipulationEventSink::GetY();
~CManipulationEventSink();
//////////////////////////////
// IManipulationEvents methods
//////////////////////////////
virtual HRESULT STDMETHODCALLTYPE ManipulationStarted(
/* [in] */ FLOAT x,
/* [in] */ FLOAT y);
virtual HRESULT STDMETHODCALLTYPE ManipulationDelta(
/* [in] */ FLOAT x,
/* [in] */ FLOAT y,
/* [in] */ FLOAT translationDeltaX,
/* [in] */ FLOAT translationDeltaY,
/* [in] */ FLOAT scaleDelta,
/* [in] */ FLOAT expansionDelta,
/* [in] */ FLOAT rotationDelta,
/* [in] */ FLOAT cumulativeTranslationX,
/* [in] */ FLOAT cumulativeTranslationY,
/* [in] */ FLOAT cumulativeScale,
/* [in] */ FLOAT cumulativeExpansion,
/* [in] */ FLOAT cumulativeRotation);
virtual HRESULT STDMETHODCALLTYPE ManipulationCompleted(
/* [in] */ FLOAT x,
/* [in] */ FLOAT y,
/* [in] */ FLOAT cumulativeTranslationX,
/* [in] */ FLOAT cumulativeTranslationY,
/* [in] */ FLOAT cumulativeScale,
/* [in] */ FLOAT cumulativeExpansion,
/* [in] */ FLOAT cumulativeRotation);
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// IUnknown methods
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
STDMETHOD_(ULONG, AddRef)(void);
STDMETHOD_(ULONG, Release)(void);
STDMETHOD(QueryInterface)(REFIID riid, LPVOID *ppvObj);
private:
double m_fX;
double m_fY;
int m_cRefCount;
int m_cStartedEventCount;
int m_cDeltaEventCount;
int m_cCompletedEventCount;
IManipulationProcessor* m_pManip;
IConnectionPointContainer* m_pConPointContainer;
IConnectionPoint* m_pConnPoint;
HWND m_hWnd;
};
Given the header, you must create an implementation of the events interface so that your class performs the actions that you want the manipulation processor to perform. The following code is a template that implements the minimum functionality of an event sink for the _IManipulationEvents interface.
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "cmanipulationeventsink.h"
CManipulationEventSink::CManipulationEventSink(IManipulationProcessor *manip, HWND hWnd)
{
m_hWnd = hWnd;
//Set initial ref count to 1.
m_cRefCount = 1;
m_pManip = manip;
m_pManip->put_PivotRadius(-1);
m_cStartedEventCount = 0;
m_cDeltaEventCount = 0;
m_cCompletedEventCount = 0;
HRESULT hr = S_OK;
//Get the container with the connection points.
IConnectionPointContainer* spConnectionContainer;
hr = manip->QueryInterface(
IID_IConnectionPointContainer,
(LPVOID*) &spConnectionContainer
);
//hr = manip->QueryInterface(&spConnectionContainer);
if (spConnectionContainer == NULL){
// something went wrong, try to gracefully quit
}
//Get a connection point.
hr = spConnectionContainer->FindConnectionPoint(__uuidof(_IManipulationEvents), &m_pConnPoint);
if (m_pConnPoint == NULL){
// something went wrong, try to gracefully quit
}
DWORD dwCookie;
//Advise.
hr = m_pConnPoint->Advise(this, &dwCookie);
}
int CManipulationEventSink::GetStartedEventCount()
{
return m_cStartedEventCount;
}
int CManipulationEventSink::GetDeltaEventCount()
{
return m_cDeltaEventCount;
}
int CManipulationEventSink::GetCompletedEventCount()
{
return m_cCompletedEventCount;
}
double CManipulationEventSink::GetX()
{
return m_fX;
}
double CManipulationEventSink::GetY()
{
return m_fY;
}
CManipulationEventSink::~CManipulationEventSink()
{
//Cleanup.
}
///////////////////////////////////
//Implement IManipulationEvents
///////////////////////////////////
HRESULT STDMETHODCALLTYPE CManipulationEventSink::ManipulationStarted(
/* [in] */ FLOAT x,
/* [in] */ FLOAT y)
{
m_cStartedEventCount ++;
return S_OK;
}
HRESULT STDMETHODCALLTYPE CManipulationEventSink::ManipulationDelta(
/* [in] */ FLOAT x,
/* [in] */ FLOAT y,
/* [in] */ FLOAT translationDeltaX,
/* [in] */ FLOAT translationDeltaY,
/* [in] */ FLOAT scaleDelta,
/* [in] */ FLOAT expansionDelta,
/* [in] */ FLOAT rotationDelta,
/* [in] */ FLOAT cumulativeTranslationX,
/* [in] */ FLOAT cumulativeTranslationY,
/* [in] */ FLOAT cumulativeScale,
/* [in] */ FLOAT cumulativeExpansion,
/* [in] */ FLOAT cumulativeRotation)
{
m_cDeltaEventCount ++;
RECT rect;
GetWindowRect(m_hWnd, &rect);
int oldWidth = rect.right-rect.left;
int oldHeight = rect.bottom-rect.top;
// scale and translate the window size / position
MoveWindow(m_hWnd, // the window to move
static_cast<int>(rect.left + (translationDeltaX / 100.0f)), // the x position
static_cast<int>(rect.top + (translationDeltaY/100.0f)), // the y position
static_cast<int>(oldWidth * scaleDelta), // width
static_cast<int>(oldHeight * scaleDelta), // height
TRUE); // redraw
return S_OK;
}
HRESULT STDMETHODCALLTYPE CManipulationEventSink::ManipulationCompleted(
/* [in] */ FLOAT x,
/* [in] */ FLOAT y,
/* [in] */ FLOAT cumulativeTranslationX,
/* [in] */ FLOAT cumulativeTranslationY,
/* [in] */ FLOAT cumulativeScale,
/* [in] */ FLOAT cumulativeExpansion,
/* [in] */ FLOAT cumulativeRotation)
{
m_cCompletedEventCount ++;
m_fX = x;
m_fY = y;
// place your code handler here to do any operations based on the manipulation
return S_OK;
}
/////////////////////////////////
//Implement IUnknown
/////////////////////////////////
ULONG CManipulationEventSink::AddRef(void)
{
return ++m_cRefCount;
}
ULONG CManipulationEventSink::Release(void)
{
m_cRefCount --;
if(0 == m_cRefCount) {
delete this;
return 0;
}
return m_cRefCount;
}
HRESULT CManipulationEventSink::QueryInterface(REFIID riid, LPVOID *ppvObj)
{
if (IID__IManipulationEvents == riid) {
*ppvObj = (_IManipulationEvents *)(this); AddRef(); return S_OK;
} else if (IID_IUnknown == riid) {
*ppvObj = (IUnknown *)(this); AddRef(); return S_OK;
} else {
return E_NOINTERFACE;
}
}
Pay extra attention to implementations of ManipulationStarted, ManipulationDelta, and ManipulationCompleted methods in the class. These are the most likely methods in the interface that will require you to perform operations based on the manipulation information that is passed around in the event. Note also that the second parameter in the constructor is the object that is used in the event manipulations. In the code used for producing the sample, the hWnd for the application is sent to the constructor so that it can be repositioned and resized.
Create an instance of an IManipulationProcessor Interface
In the code where you will use manipulations, you must create an instance of an IManipulationProcessor interface. First you must add support for the manipulations class. The following code shows how you can do this in your class.
//Include windows.h for touch events
#include "windows.h"
// Manipulation implementation file
#include <manipulations_i.c>
// Smart Pointer to a global reference of a manipulation processor, event sink
IManipulationProcessor* g_pIManipProc;
After you have your variable for the manipulation processor and you have included the headers for manipulations, you have to create an instance of the IManipulationProcessor interface. This is a COM object. Therefore, you must call CoCreateInstance, and then create an instance of your reference to the IManipulationProcessor. The following code shows how you can create an instance of this interface.
HRESULT hr = CoInitialize(0);
hr = CoCreateInstance(CLSID_ManipulationProcessor,
NULL,
CLSCTX_INPROC_SERVER,
IID_IUnknown,
(VOID**)(&g_pIManipProc)
);
Create an instance of your Event Sink and set up Touch Events
Include the definition for your event sink class to your code and then add a variable for the manipulation event sink class. The following code example includes the header for the class implementation and sets up a global variable to store the event sink.
//Include your definition of the event sink, CManipulationEventSink.h in this case
#include "CManipulationEventSink.h"
// Set up a variable to point to the manipulation event sink implementation class
CManipulationEventSink* g_pManipulationEventSink;
After you have the variable and have included your definition for the new event sink class, you can construct the class by using the manipulation processor that you have set up in the previous step. The following code shows how an instance of this class would be created from OnInitDialog.
g_pManipulationEventSink = new CManipulationEventSink(g_pIManipProc, hWnd);
RegisterTouchWindow(hWnd, 0);
Note
The way that you create an instance of your event sink depends on what you are doing with the manipulation data. In most cases, you will create a manipulation processor event sink that does not have the same constructor as this example.
Send Touch Event Data to the Manipulation Processor
Now that you have your manipulation processor and event sink set up, you must feed touch data to the manipulation processor to trigger manipulation events.
Note
This is the same procedure as discussed in Getting Started with Windows Touch Messages.
First, you will create some code to decode the WM_TOUCH messages and send them to the IManipulationProcessor interface to raise events. The following code shows an example implementation that is called from the WndProc method and return an LRESULT for messaging.
LRESULT OnTouch(HWND hWnd, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam )
{
UINT cInputs = LOWORD(wParam);
PTOUCHINPUT pInputs = new TOUCHINPUT[cInputs];
BOOL bHandled = FALSE;
if (NULL != pInputs) {
if (GetTouchInputInfo((HTOUCHINPUT)lParam,
cInputs,
pInputs,
sizeof(TOUCHINPUT))) {
for (UINT i=0; i<cInputs; i++){
if (pInputs[i].dwFlags & TOUCHEVENTF_DOWN){
g_pIManipProc->ProcessDown(pInputs[i].dwID, static_cast<FLOAT>(pInputs[i].x), static_cast<FLOAT>(pInputs[i].y));
bHandled = TRUE;
}
if (pInputs[i].dwFlags & TOUCHEVENTF_UP){
g_pIManipProc->ProcessUp(pInputs[i].dwID, static_cast<FLOAT>(pInputs[i].x), static_cast<FLOAT>(pInputs[i].y));
bHandled = TRUE;
}
if (pInputs[i].dwFlags & TOUCHEVENTF_MOVE){
g_pIManipProc->ProcessMove(pInputs[i].dwID, static_cast<FLOAT>(pInputs[i].x), static_cast<FLOAT>(pInputs[i].y));
bHandled = TRUE;
}
}
} else {
// GetLastError() and error handling
}
delete [] pInputs;
} else {
// error handling, presumably out of memory
}
if (bHandled){
// if you don't want to pass to DefWindowProc, close the touch input handle
if (!CloseTouchInputHandle((HTOUCHINPUT)lParam)) {
// error handling
}
return 0;
}else{
return DefWindowProc(hWnd, WM_TOUCH, wParam, lParam);
}
}
Now that you have a utility method for decoding the WM_TOUCH message, you must pass the WM_TOUCH messages to the utility function from your WndProc method. The following code shows how you can do this.
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND hWnd, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
int wmId, wmEvent;
PAINTSTRUCT ps;
HDC hdc;
switch (message)
{
case WM_COMMAND:
wmId = LOWORD(wParam);
wmEvent = HIWORD(wParam);
// Parse the menu selections:
switch (wmId)
{
case IDM_ABOUT:
DialogBox(hInst, MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDD_ABOUTBOX), hWnd, About);
break;
case IDM_EXIT:
DestroyWindow(hWnd);
break;
default:
return DefWindowProc(hWnd, message, wParam, lParam);
}
break;
case WM_TOUCH:
return OnTouch(hWnd, wParam, lParam);
case WM_PAINT:
hdc = BeginPaint(hWnd, &ps);
// TODO: Add any drawing code here...
EndPaint(hWnd, &ps);
break;
case WM_DESTROY:
PostQuitMessage(0);
break;
default:
return DefWindowProc(hWnd, message, wParam, lParam);
}
return 0;
}
The custom methods that you have implemented in your event sink should now work. In this example, touching the window will move it.
Related topics