Polygon
A Polygon is a two-dimensional surface stored as a sequence of points defining an exterior bounding ring and zero or more interior rings.
Polygon instances
A Polygon instance can be formed from a ring that has at least three distinct points. A Polygon instance can also be empty.
The exterior and any interior rings of a Polygon define its boundary. The space within the rings defines the interior of the Polygon.
The illustration below shows examples of Polygon instances.
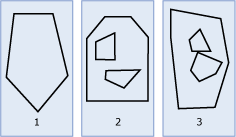
As shown in the illustration:
Figure 1 is a
Polygoninstance whose boundary is defined by an exterior ring.Figure 2 is a
Polygoninstance whose boundary is defined by an exterior ring and two interior rings. The area inside the interior rings is part of the exterior of thePolygoninstance.Figure 3 is a valid
Polygoninstance because its interior rings intersect at a single tangent point.
Accepted instances
Accepted Polygon instances are instances that can be stored in a geometry or geography variable without throwing an exception. The following are accepted Polygon instances:
An Empty
PolygoninstanceA
Polygoninstance that has an acceptable exterior ring and zero or more acceptable interior rings
The following criteria are needed for a ring to be acceptable.
The
LineStringinstance must be accepted.The
LineStringinstance must have at least four points.The starting and ending points of the
LineStringinstance must be the same.
The following example shows accepted Polygon instances.
DECLARE @g1 geometry = 'POLYGON EMPTY';
DECLARE @g2 geometry = 'POLYGON((1 1, 3 3, 3 1, 1 1))';
DECLARE @g3 geometry = 'POLYGON((-5 -5, -5 5, 5 5, 5 -5, -5 -5),(0 0, 3 0, 3 3, 0 3, 0 0))';
DECLARE @g4 geometry = 'POLYGON((-5 -5, -5 5, 5 5, 5 -5, -5 -5),(3 0, 6 0, 6 3, 3 3, 3 0))';
DECLARE @g5 geometry = 'POLYGON((1 1, 1 1, 1 1, 1 1))';
As @g4 and @g5 show an accepted Polygon instance may not be a valid Polygon instance. @g5 also shows that a Polygon instance needs to only contain a ring with any four points to be accepted.
The following examples throw a System.FormatException because the Polygon instances are not accepted.
DECLARE @g1 geometry = 'POLYGON((1 1, 3 3, 1 1))';
DECLARE @g2 geometry = 'POLYGON((1 1, 3 3, 3 1, 1 5))';
@g1 is not accepted because the LineString instance for the exterior ring does not contain enough points. @g2 is not accepted because the starting point of the exterior ring LineString instance is not the same as the ending point. The following example has an acceptable exterior ring, but the interior ring is not acceptable. This also throws a System.FormatException.
DECLARE @g geometry = 'POLYGON((-5 -5, -5 5, 5 5, 5 -5, -5 -5),(0 0, 3 0, 0 0))';
Valid instances
The interior rings of a Polygon can touch both themselves and each other at single tangent points, but if the interior rings of a Polygon cross, the instance is not valid.
The following example shows valid Polygon instances.
DECLARE @g1 geometry = 'POLYGON((-20 -20, -20 20, 20 20, 20 -20, -20 -20))';
DECLARE @g2 geometry = 'POLYGON((-20 -20, -20 20, 20 20, 20 -20, -20 -20), (10 0, 0 10, 0 -10, 10 0))';
DECLARE @g3 geometry = 'POLYGON((-20 -20, -20 20, 20 20, 20 -20, -20 -20), (10 0, 0 10, 0 -10, 10 0), (-10 0, 0 10, -5 -10, -10 0))';
SELECT @g1.STIsValid(), @g2.STIsValid(), @g3.STIsValid();
@g3 is valid because the two interior rings touch at a single point and do not cross each other. The following example shows Polygon instances that are not valid.
DECLARE @g1 geometry = 'POLYGON((-20 -20, -20 20, 20 20, 20 -20, -20 -20), (20 0, 0 10, 0 -20, 20 0))';
DECLARE @g2 geometry = 'POLYGON((-20 -20, -20 20, 20 20, 20 -20, -20 -20), (10 0, 0 10, 0 -10, 10 0), (5 0, 1 5, 1 -5, 5 0))';
DECLARE @g3 geometry = 'POLYGON((-20 -20, -20 20, 20 20, 20 -20, -20 -20), (10 0, 0 10, 0 -10, 10 0), (-10 0, 0 10, 0 -10, -10 0))';
DECLARE @g4 geometry = 'POLYGON((-20 -20, -20 20, 20 20, 20 -20, -20 -20), (10 0, 0 10, 0 -10, 10 0), (-10 0, 1 5, 0 -10, -10 0))';
DECLARE @g5 geometry = 'POLYGON((10 0, 0 10, 0 -10, 10 0), (-20 -20, -20 20, 20 20, 20 -20, -20 -20) )';
DECLARE @g6 geometry = 'POLYGON((1 1, 1 1, 1 1, 1 1))';
SELECT @g1.STIsValid(), @g2.STIsValid(), @g3.STIsValid(), @g4.STIsValid(), @g5.STIsValid(), @g6.STIsValid();
@g1 is not valid because the inner ring touches the exterior ring in two places. @g2 is not valid because the second inner ring in within the interior of the first inner ring. @g3 is not valid because the two inner rings touch at multiple consecutive points. @g4 is not valid because the interiors of the two inner rings overlap. @g5 is not valid because the exterior ring is not the first ring. @g6 is not valid because the ring does not have at least three distinct points.
Examples
The following example creates a simple geometry``Polygon instance with a hole and SRID 10.
DECLARE @g geometry;
SET @g = geometry::STPolyFromText('POLYGON((0 0, 0 3, 3 3, 3 0, 0 0), (1 1, 1 2, 2 1, 1 1))', 10);
Aninstance that is not valid may be entered and converted to a valid geometry instance. In the following example of a Polygon, the interior and exterior rings overlap and the instance is not valid.
DECLARE @g geometry;
SET @g = geometry::Parse('POLYGON((1 0, 0 1, 1 2, 2 1, 1 0), (2 0, 1 1, 2 2, 3 1, 2 0))');
In the following example, the invalid instance is made valid with MakeValid().
SET @g = @g.MakeValid();
SELECT @g.ToString();
The geometry instance returned from the above example is a MultiPolygon.
MULTIPOLYGON (((2 0, 3 1, 2 2, 1.5 1.5, 2 1, 1.5 0.5, 2 0)), ((1 0, 1.5 0.5, 1 1, 1.5 1.5, 1 2, 0 1, 1 0)))
Here is another example of converting an invalid instance to a valid geometry instance. In the following example the Polygon instance has been created using three points that are exactly the same:
DECLARE @g geometry
SET @g = geometry::Parse('POLYGON((1 3, 1 3, 1 3, 1 3))');
SET @g = @g.MakeValid();
SELECT @g.ToString()
The geometry instance returned above is a Point(1 3). If the Polygon given is POLYGON((1 3, 1 5, 1 3, 1 3)) then MakeValid() would return LINESTRING(1 3, 1 5).
See Also
STArea (geometry Data Type) STExteriorRing (geometry Data Type) STNumInteriorRing (geometry Data Type) STInteriorRingN (geometry Data Type) STCentroid (geometry Data Type) STPointOnSurface (geometry Data Type) MultiPolygon Spatial Data (SQL Server) STIsValid (geography Data Type) STIsValid (geometry Data Type)