Normalize Data
Important
Support for Machine Learning Studio (classic) will end on 31 August 2024. We recommend you transition to Azure Machine Learning by that date.
Beginning 1 December 2021, you will not be able to create new Machine Learning Studio (classic) resources. Through 31 August 2024, you can continue to use the existing Machine Learning Studio (classic) resources.
- See information on moving machine learning projects from ML Studio (classic) to Azure Machine Learning.
- Learn more about Azure Machine Learning.
ML Studio (classic) documentation is being retired and may not be updated in the future.
Rescales numeric data to constrain dataset values to a standard range
Category: Data Transformation / Scale and Reduce
Note
Applies to: Machine Learning Studio (classic) only
Similar drag-and-drop modules are available in Azure Machine Learning designer.
Module overview
This article describes how to use the Normalize Data module in Machine Learning Studio (classic), to transform a dataset through normalization.
Normalization is a technique often applied as part of data preparation for machine learning. The goal of normalization is to change the values of numeric columns in the dataset to use a common scale, without distorting differences in the ranges of values or losing information. Normalization is also required for some algorithms to model the data correctly.
For example, assume your input dataset contains one column with values ranging from 0 to 1, and another column with values ranging from 10,000 to 100,000. The great difference in the scale of the numbers could cause problems when you attempt to combine the values as features during modeling.
Normalization avoids these problems by creating new values that maintain the general distribution and ratios in the source data, while keeping values within a scale applied across all numeric columns used in the model.
This module offers several options for transforming numeric data:
- You can change all values to a 0-1 scale, or transform the values by representing them as percentile ranks rather than absolute values.
- You can apply normalization to a single column, or to multiple columns in the same dataset.
- If you need to repeat the experiment, or apply the same normalization steps to other data, you can save the steps as a normalization transform, and apply it to other datasets that have the same schema.
Warning
Some algorithms require that data be normalized before training a model. Other algorithms perform their own data scaling or normalization. Therefore, when you choose a machine learning algorithm to use in building a predictive model, be sure to review the data requirements of the algorithm before applying normalization to the training data.
How to configure Normalize Data
You can apply only one normalization method at a time using this module. Therefore, the same normalization method is applied to all columns that you select. To use different normalization methods, use a second instance of Normalize Data.
Add the Normalize Data module to your experiment. You can find the module in Machine Learning Studio (classic), under Data Transformation, in the Scale and Reduce category.
Connect a dataset that contains at least one column of all numbers.
Use the Column Selector to choose the numeric columns to normalize. If you don't choose individual columns, by default all numeric type columns in the input are included, and the same normalization process is applied to all selected columns.
This can lead to strange results if you include numeric columns that shouldn't be normalized! Always check the columns carefully.
If no numeric columns are detected, check the column metadata to verify that the data type of the column is a supported numeric type.
Tip
To ensure that columns of a specific type are provided as input, try using the Select Columns in Dataset module before Normalize Data.
Use 0 for constant columns when checked: Select this option when any numeric column contains a single unchanging value. This ensures that such columns are not used in normalization operations.
From the Transformation method dropdown list, choose a single mathematical functions to apply to all selected columns.
Zscore: Converts all values to a z-score.
The values in the column are transformed using the following formula:
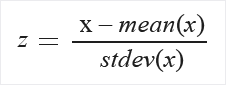
Mean and standard deviation are computed for each column separately. Population standard deviation is used.
MinMax: The min-max normalizer linearly rescales every feature to the [0,1] interval.
Rescaling to the [0,1] interval is done by shifting the values of each feature so that the minimal value is 0, and then dividing by the new maximal value (which is the difference between the original maximal and minimal values).
The values in the column are transformed using the following formula:
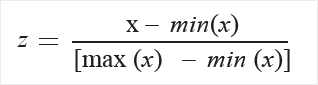
Logistic: The values in the column are transformed using the following formula:
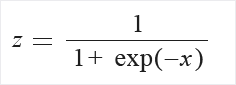
LogNormal: This option converts all values to a lognormal scale.
The values in the column are transformed using the following formula:

Here μ and σ are the parameters of the distribution, computed empirically from the data as maximum likelihood estimates, for each column separately.
TanH: All values are converted to a hyperbolic tangent.
The values in the column are transformed using the following formula:
Run the experiment, or double-click the Normalize Data module and select Run Selected.
Results
The Normalize Data module generates two outputs:
To view the transformed values, right-click the module, select Transformed dataset, and click Visualize.
By default, values are transformed in place. If you want to compare the transformed values to the original values, use the Add Columns module to recombine the datasets and view the columns side-by-side.
To save the transformation so that you can apply the same normalization method to another similar dataset, right-click the module, select Transformation function, and click Save as Transform.
You can then load the saved transformations from the Transforms group of the left navigation pane and apply it to a dataset with the same schema by using Apply Transformation.
Examples
For examples of how normalization is used in machine learning, see the Azure AI Gallery:
- Credit risk prediction: In this sample, normalization is applied to all numeric data except the class column, the credit risk score. This example uses the tanh transformation, which converts all numeric features to values within a range of 0-1.
Technical notes
This module supports only the standard normalization methods listed in the How to section, and does not support matrix normalization or other complex transforms.
If you need to create a custom normalization method, you can use the Execute R Script or Execute Python Script modules to compute and apply the transformation.
Algorithms that apply normalization
Normalizing features so that they use a common scale is a general requirement for many machine learning algorithms.
In linear classification algorithms, instances are viewed as vectors in multi-dimensional space. Since the range of values of raw data varies widely, some objective functions do not work properly without normalization. For example, if one of the features has a broad range of values, the distances between points is governed by this particular feature.
Therefore, numeric features should be normalized so that each feature contributes approximately proportionately to the final distance. This can provide significant speedup and accuracy benefits.
When using the Logistic Regression and Averaged Perceptron algorithms, by default, features are normalized before training.
Further reading and resources
If you are unsure which type of normalization suits your data, see these resources:
Recommend Modules for My Data: This custom module by a member of the Azure ML team evaluates your dataset and recommends steps for cleaning and scaling data.
Feature scaling: This article in Wikipedia explains the basic methods used for normalizing numeric data.
Data Preparation for Data Mining covers many data preparation steps in depth. See Chapter 7 for a discussion of data normalization.
Expected inputs
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Dataset | Data Table | Input dataset |
Module parameters
| Name | Range | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transformation method | any | TransformationMethods | ZScore | Choose the mathematical method used for scaling |
| Columns to transform | any | ColumnSelection | NumericAll | Select all columns to which the selected transformation should be applied |
Outputs
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Transformed dataset | Data Table | Transformed dataset |
| Transformation function | ITransform interface | Definition of the transformation function, which can be applied to other datasets |
Exceptions
| Exception | Description |
|---|---|
| Error 0001 | Exception occurs if one or more specified columns of data set couldn't be found. |
| Error 0003 | Exception occurs if one or more of inputs are null or empty. |
| Error 0017 | Exception occurs if one or more specified columns have type unsupported by current module. |
| Error 0020 | Exception occurs if number of columns in some of the datasets passed to the module is too small. |
| Error 0021 | Exception occurs if number of rows in some of the datasets passed to the module is too small. |
For a list of errors specific to Studio (classic) modules, see Machine Learning Error codes.
For a list of API exceptions, see Machine Learning REST API Error Codes.