Import from Hive Query
Important
Support for Machine Learning Studio (classic) will end on 31 August 2024. We recommend you transition to Azure Machine Learning by that date.
Beginning 1 December 2021, you will not be able to create new Machine Learning Studio (classic) resources. Through 31 August 2024, you can continue to use the existing Machine Learning Studio (classic) resources.
- See information on moving machine learning projects from ML Studio (classic) to Azure Machine Learning.
- Learn more about Azure Machine Learning.
ML Studio (classic) documentation is being retired and may not be updated in the future.
This article describes how to use the Import Data module in Machine Learning Studio (classic), to get data from Hadoop clusters and HDInsight distributed storage.
Note
Applies to: Machine Learning Studio (classic) only
Similar drag-and-drop modules are available in Azure Machine Learning designer.
Importing data from Hive is particularly useful for loading large datasets, or if you want to pre-process the data using a MapReduce job before loading the data into a machine learning experiment.
Important
As of July 31, 2018, Microsoft Azure HDInsight version 3.3 was the last version of HDInsight on Windows. If you have any HDInsight clusters on Windows 3.3 or earlier, you must migrate to HDInsight on Linux (HDInsight version 3.5 or later). Please see the Retired versions section for more information on retired versions of HDInsight. Machine Learning Studio (classic) will support HDInsight on Linux in certain scenarios.
Support for HDInsight on Linux
Machine Learning Studio (classic) has support for HDInsight on Linux in the following scenarios:
- Hadoop 2.7.3 (HDI 3.6) Blob as default, ADLS secondary
- Spark 2.1.0 (HDI 3.6) Blob as default, ADLS secondary
- Spark 2.2.0 (HDI 3.6) Blob as default, ADLS secondary
- Spark 2.3.0 (HDI 3.6) Blob as default, ADLS secondary
Known Issues
There are several known issues with using the Import Data module for Hive Queries with HDInsight on Linux:
- Enterprise Security Package is not supported
- /tmp/hive not writeable
How to import data from Hive queries
Use the wizard
The module features a new wizard to help you choose a storage option, select from among existing subscriptions and accounts, and quickly configure all options.
Add the Import Data module to your experiment. You can find the module in Studio (classic), in the Data Input and Output category.
Click Launch Import Data Wizard and follow the prompts.
When configuration is complete, to actually copy the data into your experiment, right-click the module, and select Run Selected.
If you need to edit an existing data connection, the wizard loads all previous configuration details so that you don't have to start again from scratch
Manually set import properties
The following steps describe how to manually configure the import source.
Add the Import Data module to your experiment. You can find the module in Studio (classic), in the Data Input and Output category.
For Data source, select Hive Query.
In the Hive database query text box, specify the data you want to read by using HiveQL.
HiveQL is a SQL-like query language that can also be used to aggregate data and perform data filtering before you add the data to Machine Learning Studio (classic). However, the Hive query must return the data in a tabular format.
For example, this statement is a valid Hive query:
SELECT <column list> FROM table WHERE <expression>;Click the HCatalog server URI text box, and then type the fully qualified name of your cluster.
For example, if you created a cluster with the name mycluster001, use this format:
https://mycluster001.azurehdinsight.netClick the Hadoop user account name text box, and paste in the Hadoop user account that you used when you provisioned the cluster.
Click the Hadoop user account password text box, and type the credentials that you used when you provisioned the cluster.
For more information about cluster naming and authentication for Hadoop, see Provision Hadoop clusters in HDInsight.
For Location of output data, select the option that indicates where the data is stored. If the data is in the Hadoop distributed file system (HDFS), it must be accessible via the same account and password that you just entered. If the data is in Azure, provide the location and credentials of the storage account.
HDFS: Type or paste the HDFS server URI. Be sure to use the HDInsight cluster name without the
HTTPS://prefix.Azure: For Azure storage account name, type the name of the Azure account. For example, if the full URL of the storage account is
https://myshared.blob.core.windows.net, you would typemyshared.Azure storage key: Copy and paste the key that is provided for accessing the storage account.
For Azure container name, specify the default container for the cluster. See the Tips section for help figuring out which container to use.
Select the Use cached results options if you don't expect the data to change much, or if you want to avoid reloading the data each time you run the experiment.
When this is selected, if there are no other changes to module parameters, the experiment loads the data the first time the module is run, and thereafter uses a cached version of the dataset.
If you want to re-load the dataset on each iteration of the experiment dataset, deselect the Use cached results option. Results are also re-loaded when there are changes to the parameters of Import Data.
Run the experiment.
Results
When complete, click the output dataset and select Visualize to see if the data was imported successfully.
If you get errors, check your data for missing values, additional empty columns, or incompatible data types.
Examples
For examples of how to configure an HDInsight cluster and use Hive queries in machine learning experiments, see these resources:
This article provides a detailed walkthrough of how to create a cluster, upload data, and call the data from Studio (classic) using Hive: Advanced Analytics Process and Technology in Action: Using HDInsight Hadoop clusters.
This blog by MVP Vesa Tikkanen describes some issues and workarounds when reading very large files (distributed queries) from an HD cluster on Linux: Reading Linux HDInsight Hive from Azure ML
Although Hive offers superior features for many kinds of data clean-up and pre-processing, after import, you might find these tools useful for preparing the data for modeling:
Use the Edit Metadata and other modules to change column names, specify which columns contain labels and features, and specify the column data type. For examples, see Dataset Processing.
Post-process text data using Python, to remove punctuation, flag parts of speech, and much more. For examples, see Text Classification.
Combine multiple tables from different sources into a single table of training data. For examples, see Predictive maintenance.
Technical notes
This section contains implementation details, tips, and answers to frequently asked questions.
How to determine the default container
If you created your cluster by accepting all defaults, a container with the same name as the cluster was created at the same time the cluster was created. That container is the default container for the cluster. However, if you chose the CUSTOM CREATE option when creating a cluster, you are given two options for selecting the default container. The first option is to select an existing container. When you do so, that container becomes the default storage container for the cluster. The second option is Create default container. When you use this option, the default container has the same name as the cluster.
How to call Python scripts from a Hive query
You can use the Import Data module to run Hive queries that call Python UDFs to process records.
For more information, see Use Python with Hive and Pig in HDInsight.
Avoiding out of memory problems when using Hive to pre-process data
When using Hive queries to extract records from big data sources, sometimes the default configuration of the Hadoop cluster is too limited to support running the MapReduce job. For example, in these Release Notes for HDInsight, the default settings are defined as a four-node cluster.
If the requirements of the MapReduce job exceed available capacity, the Hive queries might return an Out of Memory error message, which causes the Import Data operation to fail. If this happens, you can change the default memory allocation for Hive queries in the Import Data module, as shown here:
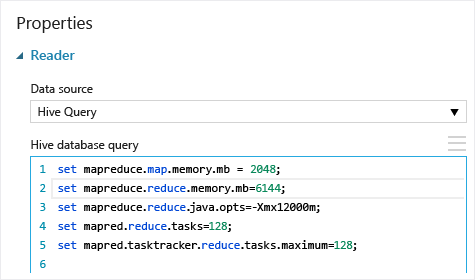
In this example, the commands set mapreduce.map.memory.mb and set mapreduce.reduce.memory.mb are used to increase the amount of memory, to use the maximum allowed in the cluster.
Common questions
How can I avoid re-loading the same data unnecessarily
If your source data changes, you can refresh the dataset and add new data by re-running Import Data. However, if you don't want to re-read from the source each time you run the experiment, select the Use cached results option to TRUE. When this option is set to TRUE, the module will check whether the experiment has run previously using the same source and same input options, and if a previous run is found, the data in the cache is used, instead of re-loading the data from the source.
Can I filter data as it is being read from the source
The Import Data module itself does not support filtering as data is being read.
To filter data before reading it into Machine Learning Studio (classic), use a Hive query or a MapReduce job to aggregate and transform the data.
There are also multiple options for filtering data after it has been loaded into Machine Learning Studio (classic):
- Use a custom R script to get only the data you want.
- Use the Split Data module with a relative expression or a regular expression to isolate the data you want, and then save it as a dataset.
Note
If you find that you have loaded more data than you need, you can overwrite the cached dataset by reading a new dataset, and saving it with the same name as the older, larger data.
Module parameters
| Name | Range | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data source | List | Data Source Or Sink | Azure Blob Storage | Data source can be HTTP, FTP, anonymous HTTPS or FTPS, a file in Azure BLOB storage, an Azure table, an Azure SQL Database, an on-premises SQL Server database, a Hive table, or an OData endpoint. |
| Hive database query | any | StreamReader | HQL query | |
| HCatalog server URI | any | String | Templeton endpoint | |
| Hadoop user account name | any | String | Hadoop HDFS/HDInsight username | |
| Hadoop user account password | any | SecureString | Hadoop HDFS/HDInsight password | |
| Location of output data | any | DataLocation | HDFS | Specify HDFS or Azure for outputDir |
| HDFS server URI | any | String | HDFS rest endpoint | |
| Azure storage account name | any | String | Azure storage account name | |
| Azure storage key | any | SecureString | Azure storage key | |
| Azure container name | any | String | Azure container name | |
| Data content type | List (subset) | Url Contents | OData | Data format type |
| Source URL | any | String | URL for Power Query data source | |
| Use cached results | TRUE/FALSE | Boolean | FALSE | description |
Outputs
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Results dataset | Data Table | Dataset with downloaded data |
Exceptions
| Exception | Description |
|---|---|
| Error 0027 | An exception occurs when two objects have to be the same size, but they are not. |
| Error 0003 | An exception occurs if one or more of inputs are null or empty. |
| Error 0029 | An exception occurs when an invalid URI is passed. |
| Error 0030 | An exception occurs in when it is not possible to download a file. |
| Error 0002 | An exception occurs if one or more parameters could not be parsed or converted from the specified type to the type required by the target method. |
| Error 0009 | An exception occurs if the Azure storage account name or the container name is specified incorrectly. |
| Error 0048 | An exception occurs when it is not possible to open a file. |
| Error 0015 | An exception occurs if the database connection has failed. |
| Error 0046 | An exception occurs when it is not possible to create a directory on specified path. |
| Error 0049 | An exception occurs when it is not possible to parse a file. |
For a list of errors specific to Studio (classic) modules, see Machine Learning Error codes.
For a list of API exceptions, see Machine Learning REST API Error Codes.
See also
Import Data
Export Data
Import from Web URL via HTTP
Import from Azure SQL Database
Import from Azure Table
Import from Azure Blob Storage
Import from Data Feed Providers
Import from On-Premises SQL Server Database