Email non-delivery reports and SMTP errors in Exchange Online
If an email message that you send can't be delivered to the intended recipient, Microsoft 365 or Office 365 typically generates an error code and sends a delivery status notification (DSN) to you. This notice is also known as a "bounce message" or "bounce-back message." The most common type of DSN is a non-delivery report (NDR) that informs you that the message wasn't delivered. The cause can be something as simple as a typo in an email address. NDRs also include an error code that indicates why your message wasn't delivered, solutions to help you get your email delivered, a link to more help on the web, and technical details for administrators. To learn more, see What's included in an NDR?
Find your error code and get help to deliver your email
The following table contains the error codes (also known as enhanced status codes) for the most common bounce messages and errors that you might encounter in Exchange Online.
| Error code | Description | Possible cause | Additional information |
|---|---|---|---|
| 432 4.3.2 | STOREDRV.Deliver; recipient thread limit exceeded |
The ability of the recipient mailbox to accept messages is throttled because it's receiving too many messages too quickly. This is done so that a single recipient's mail processing doesn't unfairly affect other recipients who are sharing the mailbox database. | For more information about this by-design throttling, see Store Driver Fault Isolation Improvements in Exchange 2010 SP1. |
| 4.4.7 | Message expired |
The message in the queue has expired. The sending server tried to relay or deliver the message, but the action wasn't completed before the message expiration time. This message can also indicate that a message header limit was reached on a remote server, or some other protocol time-out occurred during server communication. | This message usually indicates an issue on the receiving server. Check the validity of the recipient address, and determine whether the receiving server is configured correctly to receive messages. You might have to reduce the number of recipients in the message header for the host about which you're receiving this error. If you send the message again, the mesage is placed in the queue again. If the receiving server is available, the message is delivered. For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 4.4.7 in Exchange Online. |
| 4.4.8 | MX hosts of <domain> failed MTA-STS validation |
The destination MX host is not the expected host per the domain's STS policy. | This error usually indicates that the destination domain's MTA-STS policy doesn't contain the MX host. For more information, see Enhancing mail flow with MTA-STS. |
| 4.4.316 | Connection refused [Message=Socket error code 10061] |
Microsoft 365 or Office 365 is trying to send a message to an email server outside Microsoft 365 or Office 365, but all attempts to connect are failing because of a network connection issue at the external server's location. | This error almost always indicates an issue that affects the receiving server or network outside of Microsoft 365 or Office 365. The error should also include the IP address of the server or service that's generating the error. You can use this address to identify the party that's responsible for fixing this issue. |
| 450 4.4.317 | Cannot connect to remote server [Message=UntrustedRoot] |
During the TLS handshake, Exchange Online can't verify the authenticity of a leaf certificate that's sent without the full certificate chain by a remote email server. | For more information, see Fix NDR error code 450 4.4.317 "Cannot connect to remote server [Message=UntrustedRoot]". |
| 4.5.3 | Too many recipients |
The message has more than 200 SMTP envelope recipients from the same domain. | An envelope recipient is the original, unexpanded recipient that's used in the RCPT TO command to transmit the message between SMTP servers. When this error is returned by Microsoft 365 or Office 365, the sending server must break up the number of envelope recipients into smaller chunks (chunking) and resend the message. |
| 4.7.5 | Remote certificate failed MTA-STS validation. Reason: <validityStatus> |
The destination mail server's certificate must chain to a trusted root Certificate Authority and the Common Name or Subject Alternative Name must contain an entry for the host name in the STS policy. | This error usually indicates an issue with the destination mail server's certificate. For more information, see Enhancing mail flow with MTA-STS. |
| 4.7.26 | Access denied, a message sent over IPv6 [2a01:111:f200:2004::240] must pass either SPF or DKIM validation, this message is not signed |
The sending message sent over IPv6 must pass either SPF or DKIM. | For more information, see Support for anonymous inbound email messages over IPv6. |
| 4.7.321 | starttls-not-supported: Destination mail server must support TLS to receive mail. |
|
This message usually indicates an issue on the destination email server. Check the validity of the recipient address. Determine whether the destination server is configured correctly to receive the messages. |
| 4.7.322 | certificate-expired: Destination mail server's certificate is expired. |
DNSSEC checks have passed, yet upon establishing the connection, the destination mail server provides a certificate that's expired. | A valid X.509 certificate that isn't expired must be presented. X.509 certificates must be renewed after their expiration, most commonly on an annual basis. |
| 4.7.323 | tlsa-invalid: The domain failed DANE validation. |
Records are DNSSEC authentic, but one or multiple of these scenarios occurred:
|
This message usually indicates an issue on the destination email server. Check the validity of the recipient address and determine whether the destination server is configured correctly to receive messages. For more information, see DANE protocol: updates and operational guidance. |
| 4.7.324 | dnssec-invalid: Destination domain returned invalid DNSSEC records |
The destination domain indicated that it was DNSSEC-authentic, but Exchange Online wasn't able to verify it as DNSSEC-authentic. | For more information, see Overview of DNSSEC. |
| 4.7.325 | certificate-host-mismatch: Remote certificate MUST have a common name or subject alternative name that matches the hostname (DANE) |
This occurs if the presented certificate identities (CN and SAN) of a destination SMTP target host don't match any of the domains or MX host. | This message usually indicates an issue on the destination email server. Check the validity of the recipient address and determine whether the destination server is configured correctly to receive messages. For more information, see How SMTP DNS-based Authentication of Named Entities (DANE) works to secure email communications. |
| 4.7.500-699 | Access denied, please try again later |
Suspicious activity was detected and sending was temporarily restricted for further evaluation. | If this activity is valid, this restriction will be lifted shortly. |
| 4.7.850-899 | Access denied, please try again later |
Suspicious activity was detected on the IP in question, and it is temporarily restricted while being further evaluated. | If this activity is valid, this restriction will be lifted shortly. |
| 5.0.350 | Generic error, x-dg-ref header is too long, or Requested action not taken: policy violation detected (AS345) |
5.0.350 is a generic catch-all error code for a wide variety of nonspecific errors from the recipient's email organization. The specific x-dg-ref header is too long message is related to Rich Text-formatted messages. The specific Requested action not taken: policy violation detected (AS345) message is related to nested attachments. |
For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 550 5.0.350 in Exchange Online. |
| 5.1.0 | Sender denied |
A common cause of this NDR is when you use Microsoft Outlook to save an email message as a file, and then someone opened the message offline and replied to it. The message property preserves only the legacyExchangeDN attribute when Outlook delivers the message. Therefore, the lookup could fail. | Either the recipient address is incorrectly formatted or the recipient couldn't be correctly resolved. The first step in resolving this error is to check the recipient address and send the message again. For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 5.1.0 in Exchange Online. |
| 5.1.1 | Bad destination mailbox address |
This failure might be caused by the following conditions:
|
This error typically occurs if the sender of the message enters an incorrect email address of the recipient. The sender should check the recipient's email address and send again. This error can also occur if the recipient email address was correct in the past but has changed or been removed from the destination email system. If the sender of the message is in the same organization as the recipient, and the recipient's mailbox still exists, determine whether the recipient's mailbox was relocated to a new email server. If so, Outlook might not have updated the recipient cache correctly. Instruct the sender to remove the recipient's address from sender's Outlook recipient cache, and then create a new message. Resending the original message will cause the same failure. For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 5.1.1 through 5.1.20 in Exchange Online. |
| 5.1.8 | Access denied, bad outbound sender |
The account was blocked for sending too much spam. Typically, this problem occurs because the account was compromised (hacked) by phishing or malware. | For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 5.1.8 in Exchange Online. |
| 5.1.10 | Recipient not found |
The recipient's <SMTP Address> wasn't found by SMTP address lookup. |
For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 550 5.1.10 in Exchange Online. |
| 550 5.1.20 | Multiple From addresses are not allowed without Sender address |
An email message has multiple email addresses in the From field, but no email address in the Sender field. | For more information, see Fix NDR error code 550 5.1.20 "Multiple From addresses are not allowed without Sender address". |
| 5.1.90 | Your message can't be sent because you've reached your daily limit for message recipients |
The sender has exceeded the recipient rate limit, as described in Sending limits. | This could indicate that the account was compromised and is being used to send spam. For more information, see Responding to a compromised account. |
| 5.2.2 | Submission quota exceeded |
The sender has exceeded the recipient rate limit or the message rate limit as described in Sending limits. | This could indicate the account was compromised and is being used to send spam. For more information, see Responding to a compromised account. |
| 5.2.121 | Recipient's per hour message receive limit from specific sender exceeded |
The sender has exceeded the maximum number of messages that they're allowed to send per hour to a specific recipient in Exchange Online. | The automated mailer or sender should try again later, and reduce the number of messages that they send per hour to a specific recipient. This limit helps protect Microsoft 365 or Office 365 users from rapidly filling their Inboxes with many messages from errant automated notification systems or other single-sender mail storms. |
| 5.2.122 | Recipient's per hour message receive limit exceeded |
The Microsoft 365 or Office 365 recipient has exceeded the number of messages that they can receive per hour from all senders. | The automated mailer or sender should try again later, and reduce the number of messages that they send per hour to a specific recipient. This limit helps protect Microsoft 365 and Office 365 users from rapidly filling their Inboxes with many messages from errant automated notification systems or other mail storms. |
| 5.3.190 | Journaling on-premises messages to Microsoft 365 or Office 365 not supported when Journaling Archive is disabled |
Journaling on-premises messages to Microsoft 365 or Office 365 isn't supported for this organization because the organization hasn't turned on Journaling Archive in its settings. | A journaling rule is configured in the organization's on-premises environment to journal on-premises messages to Microsoft 365 or Office 365, but Journaling Archive is disabled. For this scenario to work, the organization's Office 365 administrator should either enable Journaling Archive or change the journaling rule to journal messages to a different location. |
| 5.4.1 | Relay Access Denied |
The mail server that's generating the error doesn't accept mail for the recipient's domain. This error is caused by mail server or DNS misconfiguration. | For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 5.4.1 in Exchange Online. |
| 5.4.1 | Recipient address rejected: Access denied |
The recipient's address doesn't exist. | For more information, see Use Directory Based Edge Blocking to reject messages sent to invalid recipients. |
| 5.4.6 or 5.4.14 | Routing loop detected |
A configuration error has caused an email loop. 5.4.6 is generated by on-premises Exchange server (you'll see this code in hybrid environments). 5.4.14 is generated by Exchange Online. By default, after 20 iterations of an email loop, Exchange interrupts the loop and generates an NDR to the sender of the message. |
This error occurs if the delivery of a message generates another message in response. That message then generates a third message, and the process is repeated, creating a loop. To help protect against exhausting system resources, Exchange interrupts the mail loop after 20 iterations. Mail loops are typically created because of a configuration error on the sending mail server, the receiving mail server, or both. Check the sender's and recipient's mailbox rules configuration to determine whether automatic message forwarding is enabled. For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 5.4.6 or 5.4.14 in Exchange Online. |
| 5.4.8 | MX hosts of <domain> failed MTA-STS validation |
The destination MX host was not the host expected per the domain's STS policy. | This error usually indicates that the destination domain's MTA-STS policy doesn't contain the MX host. For more information, see Enhancing mail flow with MTA-STS. |
| 5.4.300 | Message expired |
The email took too long to be successfully delivered, either because the destination server never responded or the sent message generated an error but an NDR couldn't be delivered to the original sender. | |
| 5.5.0 | 550 5.5.0 Requested action not taken: mailbox unavailable |
The recipient's <SMTP Address> domain is @hotmail.com or @outlook.com and it wasn't found by SMTP address lookup. |
Similar to 550 5.1.10. For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 550 5.1.10 in Exchange Online. |
| 5.6.11 | Invalid characters |
Your email program added invalid characters (bare line feed characters) to a message that you sent. | For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 5.6.11 in Exchange Online. |
| 5.7.1 | Delivery not authorized |
The sender of the message isn't allowed to send messages to the recipient. | This error occurs if the sender tries to send a message to a recipient but the sender isn't authorized to do this. This error frequently occurs when a sender tries to send messages to a distribution group that was configured to accept messages only from members of that distribution group or other authorized senders. The sender must request permission to send messages to the recipient. This error can also occur if an Exchange transport rule rejects a message because the message matched conditions that are configured on the transport rule. For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 5.7.1 in Exchange Online. |
| 5.7.1 | Unable to relay |
The sending email system isn't allowed to send a message to an email system that isn't the final destination of the message. | This error occurs if the sending email system tries to send an anonymous message to a receiving email system, and the receiving email system doesn't accept messages for the domain or domains that are specified in one or more of the recipients. The following are the most common cause of this error:
|
| 5.7.1 | Client was not authenticated |
The sending email system didn't authenticate with the receiving email system. The receiving email system requires authentication before message submission. | This error occurs if the receiving server must be authenticated before message submission, and the sending email system hasn't authenticated with the receiving email system. The sending email system administrator must configure the sending email system to authenticate with the receiving email system for delivery to be successful. For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 5.7.1 in Exchange Online. |
| 5.7.5 | Remote certificate failed MTA-STS validation. Reason: <validityStatus> |
The destination mail server's certificate must chain to a trusted root Certificate Authority and the Common Name or Subject Alternative Name must contain an entry for the host name in the STS policy. | This error usually indicates an issue with the destination mail server's certificate. For more information, see Enhancing mail flow with MTA-STS. |
| 5.7.12 | Sender was not authenticated by organization |
The sender's message is rejected because the recipient address is set up to reject messages sent from outside its organization. Only an email administrator for the recipient's organization can change this. | For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 5.7.12 in Exchange Online. |
| 5.7.23 | The message was rejected because of Sender Policy Framework violation |
The destination email system uses SPF to validate inbound mail, and an issue affects your SPF configuration. | For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 5.7.23 in Exchange Online. |
| 5.7.25 | Access denied, the sending IPv6 address [2a01:111:f200:2004::240] must have a reverse DNS record |
The sending IPv6 address must have a reverse DNS record to send email over IPv6. | For more information, see Support for anonymous inbound email messages over IPv6. |
| 5.7.57 | Client was not authenticated to send anonymous mail during MAIL FROM |
You configured an application or device to send (relay) email messages in Microsoft 365 or Office 365 using the smtp.office365.com endpoint, and an issue affects the configuration of the application or device. | For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 5.7.57 in Exchange Online. |
| 5.7.64 | TenantAttribution; Relay Access Denied |
You use an inbound connector to receive messages from your on-premises email environment, and something changed in your on-premises environment that makes the inbound connector's configuration incorrect. | For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 5.7.64 in Exchange Online. |
| 5.7.124 | Sender not in allowed-senders list |
The sender doesn't have permission to send to the distribution group because the sender isn't in the group's allowed-senders list. Depending how the group is set up, even the group's owner might have to be added to the allowed sender list in order to send messages to the group. | For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 5.7.124 in Exchange Online. |
| 5.7.133 | Sender not authenticated for group |
The recipient address is a group distribution list that is set up to reject messages sent from outside its organization. Only an email administrator for the recipient's organization or the group owner can change this. | For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 5.7.133 in Exchange Online. |
| 5.7.134 | Sender was not authenticated for mailbox |
The recipient address is a mailbox that is set up to reject messages sent from outside its organization. Only an email administrator for the recipient's organization can change this. | For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 5.7.134 in Exchange Online. |
| 5.7.13 or 135 | Sender was not authenticated for public folder |
The recipient address is a public folder that is set up to reject messages sent from outside its organization. Only an email administrator for the recipient's organization can change this. | For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 5.7.13 or 5.7.135 in Exchange Online. |
| 5.7.136 | Sender was not authenticated |
The recipient address is a mail user that is set up to reject messages sent from outside its organization. Only an email administrator for the recipient's organization can change this. | For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 5.7.136 in Exchange Online. |
| 5.7.232 | Your message can't be sent because your trial tenant has exceeded its daily limit for sending email to external recipients (tenant external recipient rate limit) |
The number of external recipients emailed in a 24-hour period exceeds the external recipient rate limit in Exchange Online. The limit applies per trial tenant. | The external recipient rate limit is tracked over a 24-hour rolling window. When the count for the most recent 24-hour period falls below the limit, users in the trial tenant can resume sending messages to external recipients. The limit helps prevent the distribution of unsolicited bulk messages. |
| 5.7.233 | Your message can't be sent because your tenant exceeded its daily limit for sending email to external recipients (tenant external recipient rate limit) |
The number of external recipients emailed in a 24-hour period exceeds the external recipient rate limit in Exchange Online. The limit applies per tenant. | The external recipient rate limit is tracked over a 24-hour rolling window. When the count for the most recent 24-hour period falls below the limit, users in the tenant can resume sending messages to external recipients. The limit helps prevent the distribution of unsolicited bulk messages. |
| 5.7.321 | starttls-not-supported: Destination mail server must support TLS to receive mail. |
|
This message usually indicates an issue on the destination mail server. Check the validity of the recipient address and determine if the destination server is configured correctly to receive messages. |
| 5.7.322 | certificate-expired: Destination mail server's certificate is expired. |
DNSSEC checks have passed, yet, upon establishing the connection, the destination mail server provides a certificate that is expired. | A valid X.509 certificate that isn't expired must be presented. X.509 certificates must be renewed after their expiration, most commonly on an annual basis. |
| 5.7.323 | tlsa-invalid: The domain failed DANE validation. |
Records are DNSSEC authentic but one or more of the following things occurred:
|
This message usually indicates an issue exists on the destination mail server. Check the validity of the recipient address and determine if the destination server is configured correctly to receive messages. For more information about DANE, see https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc7671. |
| 5.7.324 | dnssec-invalid: Destination domain returned invalid DNSSEC records |
The destination domain indicated it was DNSSEC authentic but Exchange Online wasn't able to verify it as DNSSEC authentic. | For more information about DNSSEC, see Overview of DNSSEC. |
| 5.7.325 | certificate-host-mismatch: Remote certificate MUST have a common name or subject alternative name matching the hostname (DANE) |
This error occurs if the presented certificate identities (CN and SAN) of a destination SMTP target host don't match any of the domains or MX host. | This message usually indicates an issue on the destination email server. Check the validity of recipient address and determine whether the destination server is configured correctly to receive messages. For more information, see How SMTP DNS-based Authentication of Named Entities (DANE) works to secure email communications. |
| 5.7.501 | Access denied, spam abuse detected |
The sending account was banned because of detected spam activity. | For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error code 451 5.7.500-699 (ASxxx) in Exchange Online. Verify that account issues have been resolved, and reset the account credentials. To restore this account's ability to send mail, contact Microsoft Support through your regular channel. |
| 5.7.502 | Access denied, banned sender |
The sending account was banned because of detected spam activity. | Verify that account issues have been resolved, and reset its credentials. To restore this account's ability to send mail, please contact support through your regular channel. |
| 5.7.503 | Access denied, banned sender |
The sending account was banned because of detected spam activity. | Verify that account issues have been resolved, and reset its credentials. To restore this account's ability to send mail, please contact support through your regular channel. |
| 5.7.504 | [email@contoso.com]: Recipient address rejected: Access denied |
The recipient address that you're trying to contact isn't valid. | Verify the recipient's email address, and try again. |
| 5.7.505 | Access denied, banned recipient |
The recipient that you're trying to contact isn't valid. | If you feel this is an error, contact support. |
| 5.7.506 | Access Denied, Bad HELO |
Your server is trying to introduce itself (HELO according to RFC 821) as the server it's trying to connect to, rather than its own fully qualified domain name. | This isn't allowed, and it's characteristic of typical spambot behavior. |
| 5.7.507 | Access denied, rejected by recipient |
The IP that you're trying to send from was blocked by the recipient's organization. | Contact the recipient to resolve this issue. |
| 5.7.508 | Access denied, [$SenderIPAddress] has exceeded permitted limits within $range range |
The sender's IPv6 range tried to send too many messages in too short a time period. | Not applicable |
| 5.7.509 | Access denied, sending domain [$SenderDomain] does not pass DMARC verification and has a DMARC policy of reject. |
The sender's domain in the 5322.From address doesn't pass DMARC. | For information about why this error occurred, see Why does DMARC fail?. A user too receives this bounce message because it failed DMARC and the DMARC policy is set to reject all failures. The user should contact their email administrator for additional help. |
| 5.7.510 | Access denied, [contoso.com] does not accept email over IPv6 |
The sender is trying to transmit a message to the recipient over IPv6, but the recipient doesn't accept email messages over IPv6. | Not applicable |
| 5.7.511 | Access denied, banned sender |
The IP that you're trying to send from was banned. | To delist the address, email delist@microsoft.com and provide the full NDR code and IP address. For more information, see Use the delist portal to remove yourself from the blocked senders list. |
| 5.7.512 | Access denied, message must be RFC 5322 section 3.6.2 compliant |
Message was sent without a valid "From" email address. | Office 365 only. Each message must contain a valid email address in the "From" header field. Proper formatting of this address includes angle brackets around the email address. For example: <security@contoso.com>. Without an address in this format, Microsoft 365 or Office 365 will reject the message. |
| 5.7.513 | Service unavailable, Client host [$ConnectingIP] blocked by $recipientDomain using Customer Block list (AS16012607) |
The recipient domain added your sending IP address to its custom blocklist. | The domain that received the email message blocked your sender's IP address. If you believe that your IP address was added to the recipient domain's custom blocklist by error, contact the recipient directly and ask them to remove it. |
| 5.7.606-649 | Access denied, banned sending IP [IP1.IP2.IP3.IP4] |
The IP that you're trying to send from was banned. | Verify that you're following the best practices for email deliverability, and make sure that your IP's reputations aren't degraded because of compromise or malicious traffic. If you believe that you're receiving this message in error, you can use the self-service portal to request that your IP address be removed from this list. For more information, see Use the delist portal to remove yourself from the blocked senders list. |
| 5.7.703 | Your message can't be delivered because messages to XXX, YYY are blocked by your organization using Tenant Allow Block List. |
Someone in your organization sent mail to an email address or domain that's blocked in the Tenant Allow/Block List. The whole message is blocked for all internal and external recipients of the message, even if only one recipient email address or domain is defined in a block entry. | |
| 5.7.705 5.7.708 |
5.7.705 Access denied, tenant has exceeded threshold, 5.7.708 Access denied, traffic not accepted from this IP |
Most of the traffic from this tenant is detected as suspicious. Therefore, a ban is put on the sending ability of the tenant. | Make sure that any compromises or open relays were resolved, and then contact support through your regular channel. For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error codes 5.7.700 through 5.7.750 in Exchange Online. |
| 5.7.750 | Service unavailable. Client blocked from sending from unregistered domains |
A suspicious number of messages from unprovisioned domains is coming from this tenant. | Add and validate any or all domains that you use to send email from Microsoft 365 or Office 365. For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error codes 5.7.700 through 5.7.750 in Exchange Online. |
| 5.7.800 | Access denied, banned sender |
The EHLO, P1, or P2 sender domain of this message was banned because of detected spam activity. | To restore this domain's ability to send mail, contact Microsoft support. |
| n/a | The message can't be submitted because the sender's submission quota was exceeded |
The user account exceeded the recipient rate limit (10,000 recipients per day). | The account was likely compromised. For more information, see Fix email delivery issues for error 'the sender's submission quota was exceeded' in Exchange Online. |
Run non-delivery report diagnostics
Note
This feature requires a Microsoft 365 administrator account. This feature isn't available for Microsoft 365 Government, Microsoft 365 operated by 21Vianet, or Microsoft 365 Germany.
To learn more about the NDR, the possible cause, and a solution, you can run an automated diagnostic. Make sure that you get the NDR code or status code from the NDR.
To run the diagnostic, select the following button:
A flyout page opens in the Microsoft 365 admin center. Paste the NDR code or error message, and then select Run Tests.
What's included in an NDR?
Exchange NDRs are designed to be easy to be read and understood by email users and administrators. NDRs have several different formats. The latest-style NDR contains an issue description in everyday language together with steps to fix the issue. The following figure shows the format for this type of NDR.
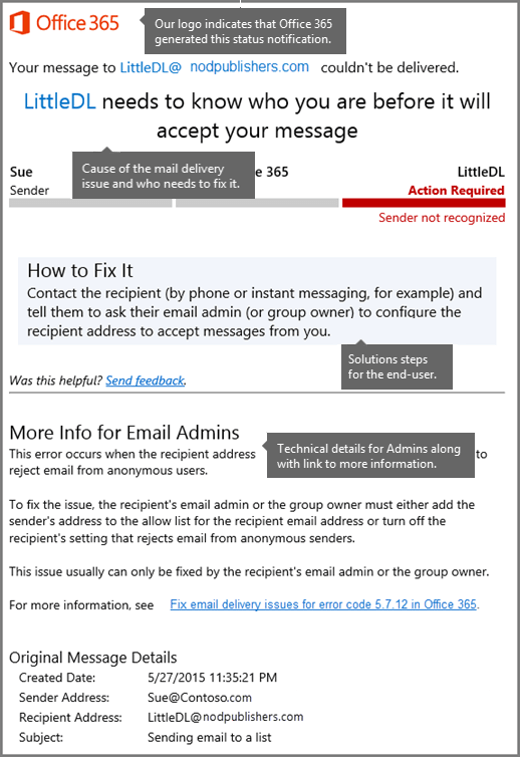
Information that's provided in the latest-style NDRs is designed to help the typical email users solve their issue immediately. If a quick solution isn't possible, the NDR provides details for administrators and also a link to more help on the web. The fields that appear in the latest Office 365 NDRs are described in the following table.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Office 365 logo | This section indicates that Microsoft 365 or Office 365 generated the NDR, and also which messaging endpoints or services are involved in the email transaction. This isn't always clear in older style NDRs. The logo doesn't mean that Microsoft 365 or Office 365 was necessarily responsible for the error. |
| Cause | This section provides the reason that the message wasn't delivered. |
| Fix-it owner indicator | This section provides an at-a-glance view of the issue and who has to fix it. The image shows the three basic parties in a Microsoft 365 or Office 365 email transaction: The sender, Microsoft 365 or Office 365, and the recipient. The area that's marked in red is where the issue usually must be fixed. |
| How to fix it | This section is designed for the user or email sender who receives the NDR. It explains how to fix the issue. |
| More info for email admins | This section provides a detailed explanation of the issue and its solution together with technical details and a link to a web-based article that has detailed reference information. |
| Message hops | This section contains times and system references for the message. These enable an administrator to follow the message hops or server-to-server path. By using this information, an administrator might quickly spot problems between message hops. |
For NDRs that don't have the latest format, the information might be separated into two sections: User information and Diagnostic information for administrators. The following figure shows the format for one type of Exchange Online NDR.
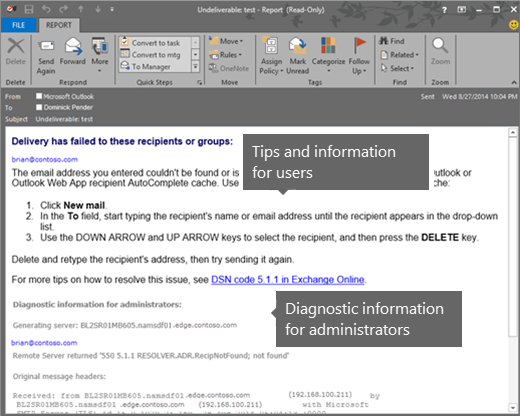
User information
The User information section appears first in some NDRs, and the main purpose is to provide a summary about what went wrong. The text is designed to help the message sender determine why the message was rejected and, if possible, how to resend the message successfully. The email address of each recipient is listed, and the reason for the failure is included in the space below the recipient's email address. The name of the mail server that rejected the message might also be included in this section.
Diagnostic information for administrators
The Diagnostic information for administrators section provides deeper technical information to help administrators troubleshoot the message delivery problem. It contains detailed information about the specific error that occurred during delivery of the message, the server that generated the NDR, and the server that rejected the message. This section uses the following format:
Diagnostic information for administrators
Generating server:
<server name>
<rejected recipient>
<remote server>
<enhanced status code>
<SMTP response>
Original message headers
<message header fields>
Note: The <SMTP response> and message header fields will be in English and aren't customizable.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Generating server | This field indicates the name of the SMTP mail server that created the NDR. If no remote server is listed beneath the sender's email address, the generating server is also the server that rejected the original email message. When the remote mail server acknowledges and accepts the message, but later rejects the message because of content restrictions, for example, the remote server generates the NDR. If the remote mail server never acknowledges and never accepts the message, the sending server in Exchange Online generates the NDR. |
| <Rejected recipient> | This value is the email address of the recipient. If delivery fails to more than one recipient, the email address of each recipient is listed. The following information is also included for each failed recipient:
|
| <Remote server> | This value is the name of the mail server that rejected the message. If the original message is successfully acknowledged by the receiving server, but is later rejected, the remote server value isn't populated. |
| <Enhanced status code> | This value is assigned by the mail server that rejected the original message. It indicates why the message was rejected. These codes are defined in RFC 3463, and use the format abc x.y.z, where the placeholder values are integers. For example, a 5.x.x code indicates a permanent error, and a 4.x.x code indicates a temporary error. Although the enhanced status code is often generated by an external mail server, Exchange Online uses the enhanced status code value to determine the text to display in the User information section. |
| <SMTP response> | This value is returned by the mail server that rejected the original message. This text provides an explanation for the enhanced status code value. The text is always presented in US-ASCII format. |
| Original message headers | This section contains the message header fields of the rejected message. These header fields can provide useful diagnostic information, such as the path that the message took before it was rejected, and whether the To field value matches the rejected recipient value. |
How to interpret an Exchange NDR
Here's an example scenario in which you receive an Exchange NDR that contains the following information:
Delivery has failed to these recipients or groups:
ronald@contoso.com
Your message wasn't delivered due to a permission or security issue. It might have been rejected by a moderator, the address might only accept email from certain senders, or another restriction might be preventing delivery. The following organization rejected your message: mail.contoso.com.
Diagnostic information for administrators:
Generating server: alpineskihouse.com
ronald@contoso.com
mail.contoso.com #<exchange.contoso.com #5.7.1 smtp;530 5.7.1 Client was not authenticated> #SMTP#
Original message headers:
...
From the User information section, you can determine that the recipient is Ronald Slattery, that the message was rejected by the mail server mail.contoso.com, and that server isn't an Exchange Online or Exchange Online Protection mail server.
From the Diagnostic information for administrators section, you can see that alpineskihouse.com tried to connect to the server, mail.contoso.com, to deliver the message to the recipient ronald@contoso.com. However, mail.contoso.com responded with the error 530 5.7.1 Client was not authenticated. Even though bigfish.com generated the NDR, mail.contoso.com actually rejected the message, so the administrators at contoso.com are responsible for understanding and fixing the problem. This particular error indicates that the server, mail.contoso.com, is configured not to accept anonymous email from the Internet.
Although the Original message headers are omitted from this example because of their length and complexity, you can typically extract useful information from the following header fields:
To: This field might be helpful if the email address was mistyped.
Received: These fields show the message path and the last hop that generated the DSN. This is useful if the
Generating servervalue in the NDR isn't clear.Received-SPF: If this value is anything other than
pass, check the Sender Policy Framework (SPF) DNS record for your domain. For more information, see Add or edit custom DNS records.
Still need help to resolve SMTP errors, NDRs, or other status notifications?
Additional email help
Why does DMARC fail?
- Missing or incorrect DMARC/DNS records: Alignment issues, missing SPF, and policy issues
- Missing DKIM or DKIM records: Missing DKIM DNS record (public key) or the message isn't DKIM-signed at the time of sending (private key)
- Forwarding emails: Message forwarding that breaks SPF or DKIM
How do I fix this error?
- If you're using or paying a DMARC service to read your reports, ask the service about what's occurring.
- Read the NDR message to trace information that provides the reasons for the DMARC failure.
- Add, correct, or align, based on the ascertained reasons for the DMARC failure.
How can I see the message headers?
Microsoft includes the headers in the NDR email message that was returned to the original sender of the message that failed DMARC.
Header information
- SPF/DKIM Failures:
Transport; Wed, 22 Mar 2023 21:14:22 +0000
Authentication-Results: spf=none (sender IP is 40.95.88.73)
smtp.mailfrom=o365e083.onmicrosoft.com; dkim=none (message not signed)
header.d=none;dmarc=fail action=oreject
header.from=o365e.onmicrosoft.com;compauth=fail reason=000
Received-SPF: None (protection.outlook.com: o365e.onmicrosoft.com does
not designate permitted sender hosts)
Authentication-Results-Original: dkim=none (message not signed)
header.d=none; dmarc=none action=none
header.from=o365e.onmicrosoft.com;
X-Test-Message-Executed-by: daiq_debug
Message-ID: <991e8244-85@A.MB3331.outlook.com>
From: admin@o365e.onmicrosoft.com
Subject: Consumer dmarc reject test
MIME-Version: 1.0
Content-Type: text/plain
Sender: "admin@o365e.onmicrosoft.com"
<admin@o365e.onmicrosoft.com>
- Alignment P1 and P2 Domains don't align (match)
Message-ID: <1430c613-58@A.MB3outlook.com>
From: admin@o365e083.onmicrosoft.com
Subject: Consumer auto forward test
MIME-Version: 1.0
Content-Type: text/plain
Sender: "admin@o365e039.onmicrosoft.com"
<admin@o365e039.onmicrosoft.com>
X-MS-PublicTrafficType: Email
X-MS-TrafficTypeDiagnostic: AMB3284:EE_|DU0PRMB172:EE
To: Undisclosed recipients:;
Return-Path: admin@o365e039.onmicrosoft.com
Date: Tue, 11 Apr 2023 16:20:03 +0000
Still need help tp resolve DMARC issues?
DNS
Microsoft DNS articles
Header Readers