Create and manage container leases with JavaScript or TypeScript
This article shows how to create and manage container leases using the Azure Storage client library for JavaScript. You can use the client library to acquire, renew, release, and break container leases.
Prerequisites
- The examples in this article assume you already have a project set up to work with the Azure Blob Storage client library for JavaScript. To learn about setting up your project, including package installation, importing modules, and creating an authorized client object to work with data resources, see Get started with Azure Blob Storage and JavaScript.
- The authorization mechanism must have permissions to work with a container lease. To learn more, see the authorization guidance for the following REST API operation:
About container leases
A lease establishes and manages a lock on a container for delete operations. The lock duration can be 15 to 60 seconds, or can be infinite. A lease on a container provides exclusive delete access to the container. A container lease only controls the ability to delete the container using the Delete Container REST API operation. To delete a container with an active lease, a client must include the active lease ID with the delete request. All other container operations succeed on a leased container without the lease ID. If you've enabled container soft delete, you can restore deleted containers.
To learn more about lease states and when you can perform a given action on a lease, see Lease states and actions.
Lease operations are handled by the BlobLeaseClient class, which provides a client containing all lease operations for blobs and containers. To learn more about blob leases using the client library, see Create and manage blob leases with JavaScript.
Acquire a lease
When you acquire a container lease, you obtain a lease ID that your code can use to operate on the container. If the container already has an active lease, you can only request a new lease by using the active lease ID. However, you can specify a new lease duration.
To acquire a lease, create an instance of the BlobLeaseClient class, and then use one of the following methods:
The following example acquires a 30-second lease for a container:
async function acquireContainerLeaseAsync(blobContainerClient) {
const leaseClient = blobContainerClient.getBlobLeaseClient();
await leaseClient.acquireLease(30);
return leaseClient;
}
Renew a lease
You can renew a container lease if the lease ID specified on the request matches the lease ID associated with the container. The lease can be renewed even if it expires, as long as the container hasn't been leased again since the expiration of that lease. When you renew a lease, the duration of the lease resets.
To renew a lease, use one of the following methods on a BlobLeaseClient instance:
The following example renews a container lease:
async function renewContainerLeaseAsync(blobContainerClient, leaseID) {
const leaseClient = blobContainerClient.getBlobLeaseClient(leaseID);
await leaseClient.renewLease();
}
Release a lease
You can release a container lease if the lease ID specified on the request matches the lease ID associated with the container. Releasing a lease allows another client to acquire a lease for the container immediately after the release is complete.
You can release a lease using one of the following methods on a BlobLeaseClient instance:
The following example releases a lease on a container:
async function releaseContainerLeaseAsync(blobContainerClient, leaseID) {
const leaseClient = blobContainerClient.getBlobLeaseClient(leaseID);
await leaseClient.releaseLease();
}
Break a lease
You can break a container lease if the container has an active lease. Any authorized request can break the lease; the request isn't required to specify a matching lease ID. A lease can't be renewed after it's broken, and breaking a lease prevents a new lease from being acquired until the original lease expires or is released.
You can break a lease using one of the following methods on a BlobLeaseClient instance:
The following example breaks a lease on a container:
async function breakContainerLeaseAsync(blobContainerClient) {
const leaseClient = blobContainerClient.getBlobLeaseClient();
await leaseClient.breakLease();
}
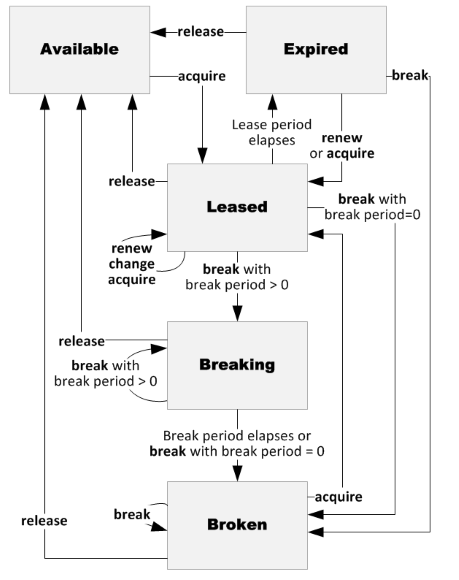
Lease states and actions
The following diagram shows the five states of a lease, and the commands or events that cause lease state changes.
The following table lists the five lease states, gives a brief description of each, and lists the lease actions allowed in a given state. These lease actions cause state transitions, as shown in the diagram.
| Lease state | Description | Lease actions allowed |
|---|---|---|
| Available | The lease is unlocked and can be acquired. | acquire |
| Leased | The lease is locked. | acquire (same lease ID only), renew, change, release, and break |
| Expired | The lease duration has expired. | acquire, renew, release, and break |
| Breaking | The lease has been broken, but the lease will continue to be locked until the break period has expired. | release and break |
| Broken | The lease has been broken, and the break period has expired. | acquire, release, and break |
When a lease expires, the lease ID is maintained by the Blob service until the container is modified or leased again. A client may attempt to renew or release the lease using the expired lease ID. If the request fails, the client knows that the container was leased again, or the container was deleted since the lease was last active.
If a lease expires rather than being explicitly released, a client may need to wait up to one minute before a new lease can be acquired for the container. However, the client can renew the lease with the expired lease ID immediately.
Resources
To learn more about managing container leases using the Azure Blob Storage client library for JavaScript, see the following resources.
Code samples
- View JavaScript and TypeScript code samples from this article (GitHub)
REST API operations
The Azure SDK for JavaScript contains libraries that build on top of the Azure REST API, allowing you to interact with REST API operations through familiar JavaScript paradigms. The client library methods for managing container leases use the following REST API operation:
Client library resources
See also
Related content
- This article is part of the Blob Storage developer guide for JavaScript/TypeScript. To learn more, see the full list of developer guide articles at Build your JavaScript/TypeScript app.