Upgrade cluster runtime from Azure CLI
This how-to guide explains the steps for installing the required Azure CLI and extensions required to interact with Operator Nexus.
Prerequisites
- The Install Azure CLI must be installed.
- The
networkcloudCLI extension is required. If thenetworkcloudextension isn't installed, it can be installed following the steps listed here. - Access to the Azure portal for the target cluster to be upgraded.
- You must be logged in to the same subscription as your target cluster via
az login - Target cluster must be in a running state, with all control plane nodes healthy and 80+% of compute nodes in a running and healthy state.
Checking current runtime version
Verify current cluster runtime version before upgrade: How to check current cluster runtime version.
Finding available runtime versions
Via Azure portal
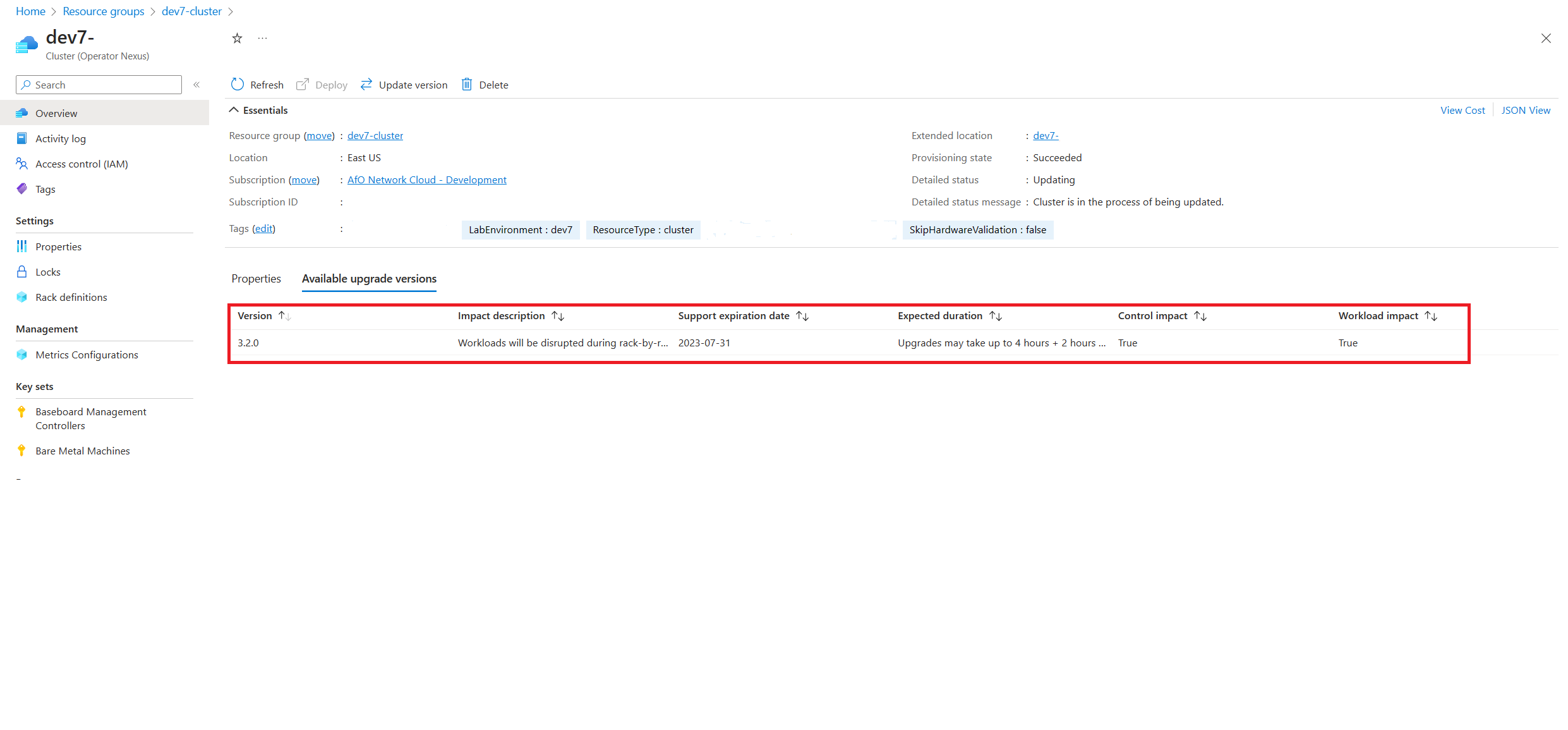
To find available upgradeable runtime versions, navigate to the target cluster in the Azure portal. In the cluster's overview pane, navigate to the Available upgrade versions tab.
From the available upgrade versions tab, we're able to see the different cluster versions that are currently available to upgrade. The operator can select from the listed the target runtime versions. Once selected, proceed to upgrade the cluster.
Via Azure CLI
Available upgrades are retrievable via the Azure CLI:
az networkcloud cluster show --name "<clusterName>" /
--resource-group "<resourceGroup>" /
--subscription <subscriptionID>
In the output, you can find the availableUpgradeVersions property and look at the targetClusterVersion field:
"availableUpgradeVersions": [
{
"controlImpact": "True",
"expectedDuration": "Upgrades may take up to 4 hours + 2 hours per rack",
"impactDescription": "Workloads will be disrupted during rack-by-rack upgrade",
"supportExpiryDate": "2023-07-31",
"targetClusterVersion": "3.3.0",
"workloadImpact": "True"
}
],
If there are no available cluster upgrades, the list is empty.
Configure compute threshold parameters for runtime upgrade using cluster updateStrategy
The following Azure CLI command is used to configure the compute threshold parameters for a runtime upgrade:
az networkcloud cluster update /
--name "<clusterName>" /
--resource-group "<resourceGroup>" /
--update-strategy strategy-type="Rack" threshold-type="PercentSuccess" /
threshold-value="<thresholdValue>" max-unavailable=<maxNodesOffline> /
wait-time-minutes=<waitTimeBetweenRacks> /
--subscription <subscriptionID>
Required parameters:
- strategy-type: Defines the update strategy. This can be
"Rack"(Rack by Rack) OR"PauseAfterRack"(Upgrade one rack at a time and then wait for confirmation before proceeding to the next rack. The default value isRack. To carry out a Cluster runtime upgrade using the "PauseRack" strategy follow the steps outlined in Upgrading cluster runtime with a pause rack strategy - threshold-type: Determines how the threshold should be evaluated, applied in the units defined by the strategy. This can be
"PercentSuccess"OR"CountSuccess". The default value isPercentSuccess. - threshold-value: The numeric threshold value used to evaluate an update. The default value is
80.
Optional parameters:
- max-unavailable: The maximum number of worker nodes that can be offline, that is, upgraded rack at a time. The default value is
32767. - wait-time-minutes: The delay or waiting period before updating a rack. The default value is
15.
The following example is for a customer using Rack by Rack strategy with a Percent Success of 60% and a 1-minute pause.
az networkcloud cluster update --name "<clusterName>" /
--resource-group "<resourceGroup>" /
--update-strategy strategy-type="Rack" threshold-type="PercentSuccess" /
threshold-value=60 wait-time-minutes=1 /
--subscription <subscriptionID>
Verify update:
az networkcloud cluster show --resource-group "<resourceGroup>" /
--name "<clusterName>" /
--subscription <subscriptionID>| grep -a5 updateStrategy
"strategyType": "Rack",
"thresholdType": "PercentSuccess",
"thresholdValue": 60,
"waitTimeMinutes": 1
In this example, if less than 60% of the compute nodes being provisioned in a rack fail to provision (on a Rack by Rack basis), the cluster deployment fails. If 60% or more of the compute nodes are successfully provisioned, cluster deployment moves on to the next rack of compute nodes.
The following example is for a customer using Rack by Rack strategy with a threshold type CountSuccess of 10 nodes per rack and a 1-minute pause.
az networkcloud cluster update --name "<clusterName>" /
--resource-group "<resourceGroup>" /
--update-strategy strategy-type="Rack" threshold-type="CountSuccess" /
threshold-value=10 wait-time-minutes=1 /
--subscription <subscriptionID>
Verify update:
az networkcloud cluster show --resource-group "<resourceGroup>" /
--name "<clusterName>" /
--subscription <subscriptionID>| grep -a5 updateStrategy
"strategyType": "Rack",
"thresholdType": "CountSuccess",
"thresholdValue": 10,
"waitTimeMinutes": 1
In this example, if less than 10 compute nodes being provisioned in a rack fail to provision (on a Rack by Rack basis), the cluster deployment fails. If 10 or more of the compute nodes are successfully provisioned, cluster deployment moves on to the next rack of compute nodes.
Note
update-strategy cannot be changed after the cluster runtime upgrade has started.
When a threshold value below 100% is set, it’s possible that any unhealthy nodes might not be upgraded, yet the “Cluster” status could still indicate that upgrade was successful. For troubleshooting issues with bare metal machines, please refer to Troubleshoot Azure Operator Nexus server problems
Upgrade cluster runtime using CLI
To perform an upgrade of the runtime, use the following Azure CLI command:
az networkcloud cluster update-version --cluster-name "<clusterName>" /
--target-cluster-version "<versionNumber>" /
--resource-group "<resourceGroupName>" /
--subscription <subscriptionID>
The runtime upgrade is a long process. The upgrade first upgrades the management nodes and then sequentially Rack by Rack for the worker nodes. The upgrade is considered to be finished when 80% of worker nodes per rack and 100% of management nodes are successfully upgraded. Workloads might be impacted while the worker nodes in a rack are in the process of being upgraded, however workloads in all other racks are not impacted. Consideration of workload placement in light of this implementation design is encouraged.
Upgrading all the nodes takes multiple hours, depending upon how many racks exist for the Cluster. Due to the length of the upgrade process, the Cluster's detail status should be checked periodically for the current state of the upgrade. To check on the status of the upgrade observe the detailed status of the Cluster. This check can be done via the portal or az CLI.
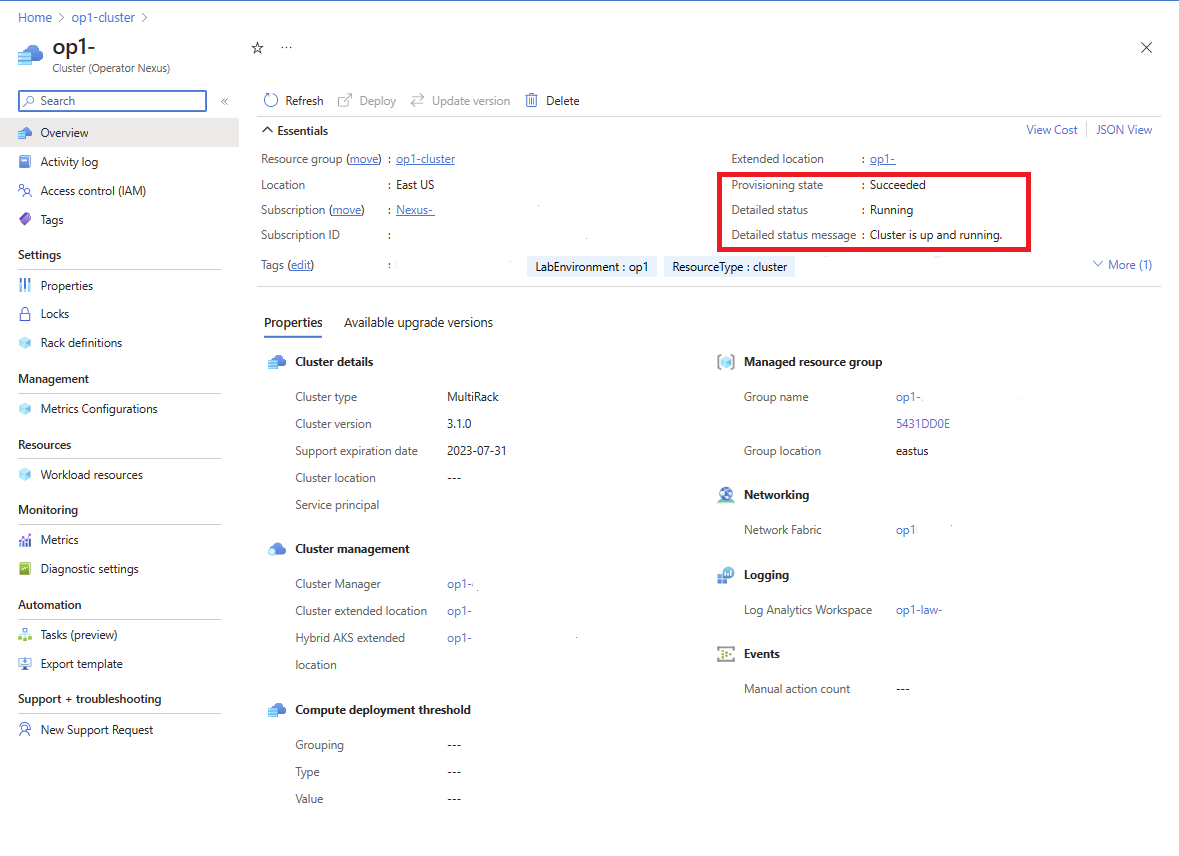
To view the upgrade status through the Azure portal, navigate to the targeted cluster resource. In the cluster's Overview screen, the detailed status is provided along with a detailed status message.
The Cluster upgrade is in-progress when detailedStatus is set to Updating and detailedStatusMessage shows the progress of upgrade. Some examples of upgrade progress shown in detailedStatusMessage are Waiting for control plane upgrade to complete..., Waiting for nodepool "<rack-id>" to finish upgrading..., etc.
The Cluster upgrade is complete when detailedStatus is set to Running and detailedStatusMessage shows message Cluster is up and running
To view the upgrade status through the Azure CLI, use az networkcloud cluster show.
az networkcloud cluster show --cluster-name "<clusterName>" /
--resource-group "<resourceGroupName>" /
--subscription <subscriptionID>
The output should be the target cluster's information and the cluster's detailed status and detail status message should be present. For more detailed insights on the upgrade progress, the individual node in each Rack can be checked for status. An example of checking the status is provided in the reference section under BareMetal Machine roles.
Frequently Asked Questions
Identifying Cluster Upgrade Stalled/Stuck
During a runtime upgrade, it's possible that the upgrade fails to move forward but the detail status reflects that the upgrade is still ongoing. Because the runtime upgrade can take a very long time to successfully finish, there's no set timeout length currently specified. Hence, it's advisable to also check periodically on your cluster's detail status and logs to determine if your upgrade is indefinitely attempting to upgrade.
We can identify an indefinitely attempting to upgrade situation by looking at the Cluster's logs, detailed message, and detailed status message. If a timeout occurs, we would observe that the Cluster is continuously reconciling over the same indefinitely and not moving forward. From here, we recommend checking Cluster logs or configured LAW, to see if there's a failure, or a specific upgrade that is causing the lack of progress.
Hardware Failure doesn't require Upgrade re-execution
If a hardware failure during an upgrade occurs, the runtime upgrade continues as long as the set thresholds are met for the compute and management/control nodes. Once the machine is fixed or replaced, it gets provisioned with the current platform runtime's OS, which contains the targeted version of the runtime.
If a hardware failure occurs, and the runtime upgrade fails because thresholds weren't met for compute and control nodes, re-execution of the runtime upgrade might be needed. Depending on when the failure occurred and the state of the individual servers in a rack. If a rack was updated before a failure, then the upgraded runtime version would be used when the nodes are reprovisioned. If the rack's spec wasn't updated to the upgraded runtime version before the hardware failure, the machine would be provisioned with the previous runtime version. To upgrade to the new runtime version, submit a new cluster upgrade request. Only the nodes with the previous runtime version are upgraded. Hosts that were successful in the previous upgrade action won't.
After a runtime upgrade, the cluster shows "Failed" Provisioning State
During a runtime upgrade, the cluster enters a state of Upgrading. If the runtime upgrade fails, the cluster goes into a Failed provisioning state. Infrastructure components (e.g the Storage Appliance) may cause failures during the upgrade. In some scenarios, it may be necessary to diagnose the failure with Microsoft support.