What is Azure Integration Environments? (Preview)
Note
This capability is in preview and is subject to the Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews.
As a developer who works on solutions that integrate services and systems in the cloud, on premises, or both, you often have multiple or different Azure resources to implement your solutions. If you have many Azure resources across various solutions, you might struggle to find and manage these resources across the Azure portal and to keep these resources organized per solution.
Azure Integration Environments simplifies this complexity by providing a central area in the Azure portal where you can create integration environments to help you organize and manage your deployed Azure resources. Within an integration environment, you create application groups to further arrange resources into smaller collections.
For example, your integration environments might be based on your organization's business units, such as Operations, Customer Service, or Finance. Or, your environments might be based on your infrastructure landscapes for development, test, staging, and production. Your application groups might be based on a specific business or customer scenario, such as employee onboarding, order processing, bank reconciliation, shipping notifications, and so on.
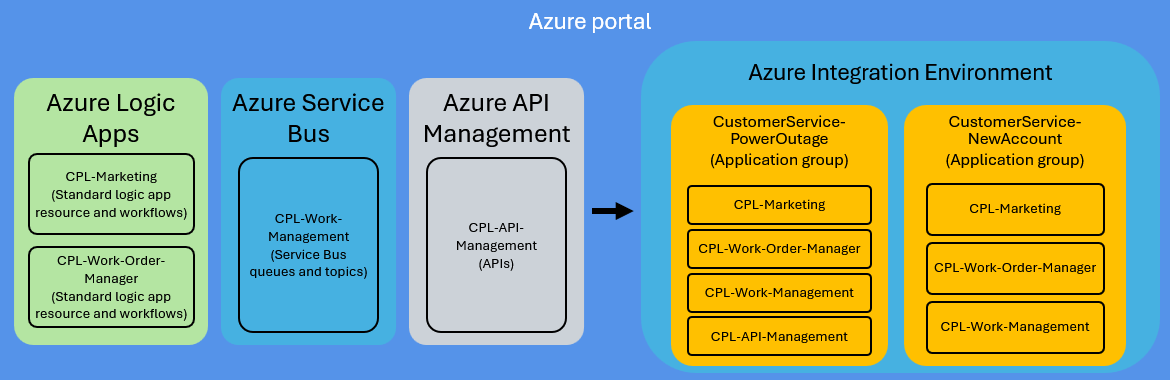
The following diagram shows how you can organize Azure resources from various Azure services into one or more application groups, based on business or customer scenarios:
For more information about the currently supported Azure resources that you can organize, see Supported Azure resources.
Central organization and management
In Azure, an integration environment gives you a centralized way to organize the Azure resources used by your development team to build solutions that integrate the services and systems used by your organization. At the next level in your integration environment, application groups provide a way to sort resources into smaller collections based on specific business scenarios. For example, an integration environment can have many application groups where each group serves a specific purpose such as payroll, order processing, employee onboarding, bank reconciliation, shipping notifications, and so on.
This architecture offers the flexibility for you to create and use integration environments based on your organization's conventions, standards, and principles. For example, you can have integration environments that are based on business units or teams such as Operations, Customer Service, Marketing, Finance, HR, Corporate Services, and so on. Or, you might have integration environments based on infrastructure landscapes such as development, test, staging, user acceptance testing, and production. Regardless how your organization structures itself, integration environments provide the flexibility to meet your organization's needs.
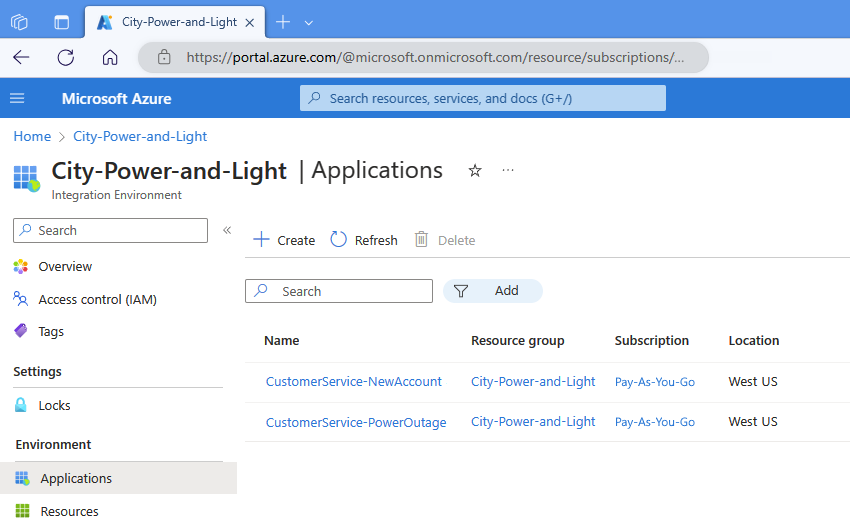
Suppose you're a developer who works on solutions that integrate various services and systems used at a power company. You create an integration environment that contains application groups for the Azure resources that implement the following business scenarios:
| Business scenario | Application group |
|---|---|
| Open a new customer account. | CustomerService-NewAccount |
| Resolve a customer ticket for a power outage. | CustomerService-PowerOutage |
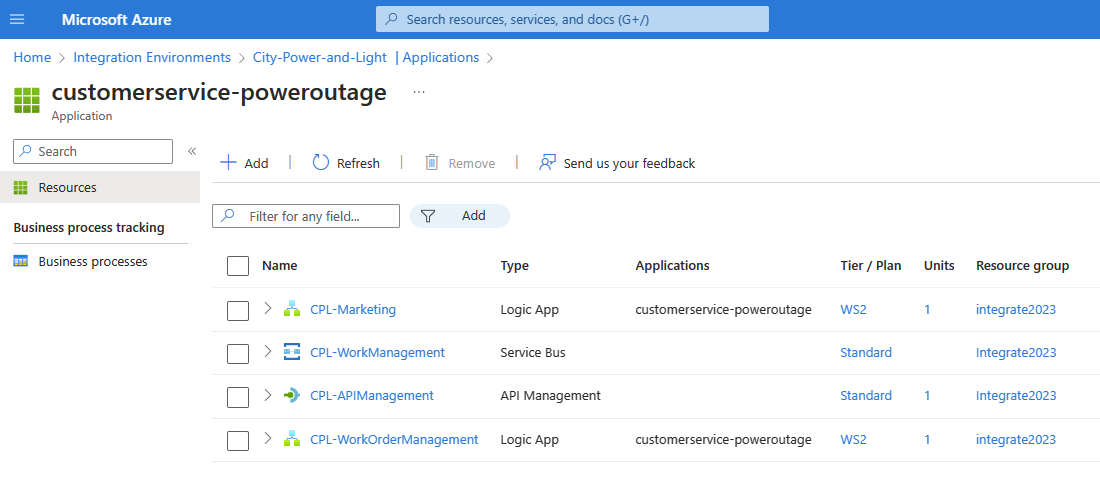
The CustomerService-PowerOutage application group includes following Azure resources:
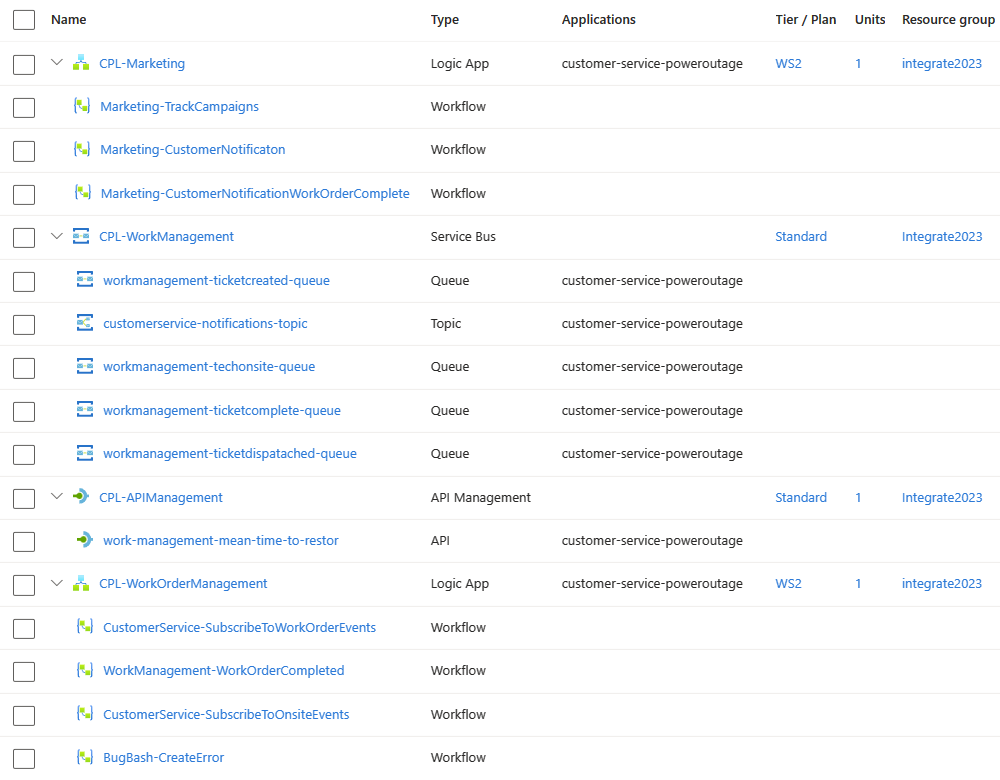
Each expanded Azure resource includes the following components:
To get started, see Create an integration environment.
Business process tracking
To help provide business scenario traceability for the Azure resources in your integration solution, you can optionally and separately use Azure Business Tracking to create business processes that you link to your application group. In Azure Business Process Tracking, a business process is a series of stages that represent the tasks that flow through a real-world business scenario. That way, you add business context about the resources in an application group that visually describe the relationships between your solution's business logic and implementation. To get started, see Create a business process and What is Business Process Tracking?
Supported Azure resources
The following table lists the currently supported Azure resources that you can include in an application group during this release:
| Azure service | Resources |
|---|---|
| Azure Logic Apps | Standard logic apps |
| Azure Service Bus | Queues and topics |
| Azure API Management | APIs |
| Business Process Tracking | Business processes |
For more information about other Azure resource types planned for support, see the Azure Integration Environments preview announcement.
Pricing information
Azure Integration Environments doesn't incur charges during preview. However, when you create an application group, you're required to provide information for an existing or new Azure Data Explorer cluster and database. Your application group uses this database to store specific business property values that you want to capture and track for business process tracking scenarios.
Azure Data Explorer incurs charges, based on the selected pricing option. For more information, see Azure Data Explorer pricing.
Limitations and known issues
- This preview release currently doesn't include application monitoring.